Sourcing Guide Contents
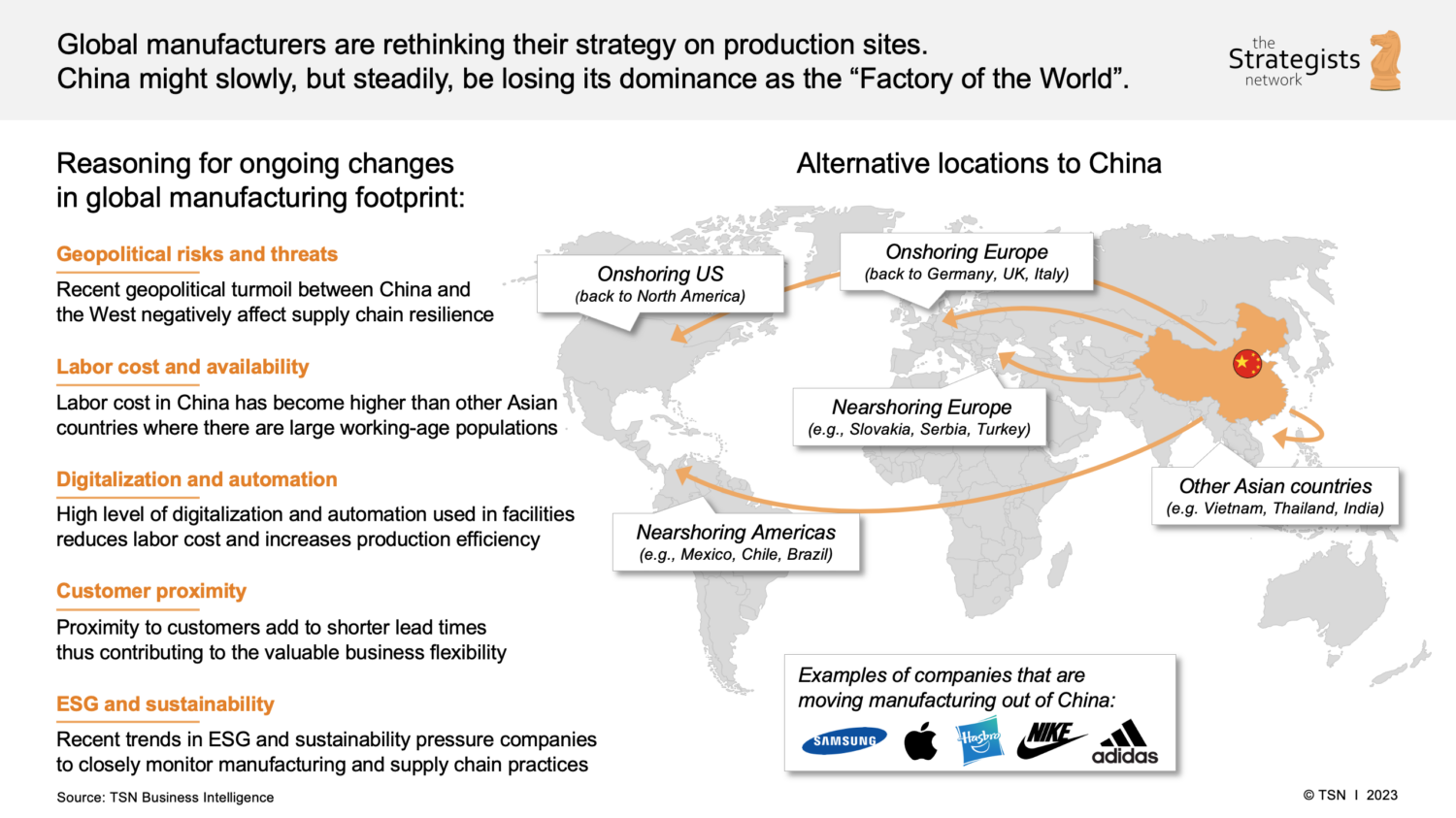
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies That Rely On China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Ecosystem Analysis
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Executive Summary
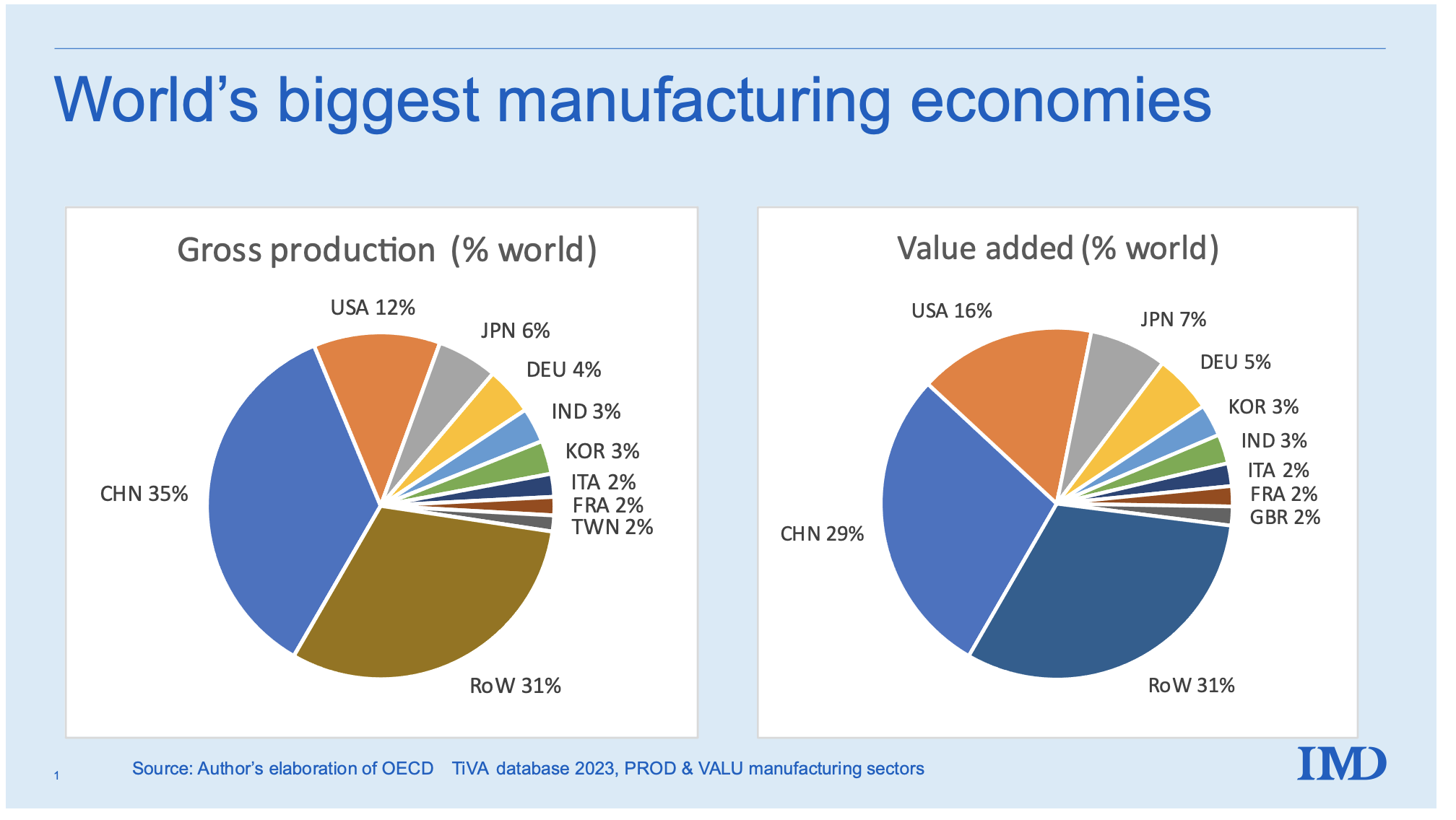
This report analyzes China’s manufacturing landscape for companies with China-dependent supply chains (i.e., businesses reliant on Chinese manufacturing for >30% of production volume). Contrary to the ambiguous phrasing “companies that rely on China,” we focus on sourcing from China-dependent manufacturers – a critical distinction for procurement strategy. China retains dominance in 22 of 28 global industrial categories (World Bank, 2025), but geopolitical pressures and cost inflation necessitate granular regional targeting. Key findings:
– Guangdong leads in high-tech electronics (65% of China’s electronics exports) but faces 8-12% YoY cost increases.
– Zhejiang offers 15-20% cost advantages for textiles/machinery but lags in advanced QC infrastructure.
– Emerging hubs (Sichuan, Anhui) now handle 34% of Tier-2 supplier migration, reducing coastal dependency.
Strategic recommendation: Dual-source between coastal and inland clusters to mitigate tariff/logistics risks.
Methodology
- Data Sources: China Customs (2025), MOFCOM Industrial Reports, SourcifyChina Factory Audit Database (12,850+ facilities), IMF Supply Chain Index.
- Scope: Analyzed 78 industrial subsectors across 11 provinces; filtered for suppliers serving >50% export revenue (B2B focus).
- Key Metrics: Verified unit costs (FOB), defect rates (PPM), lead times (days), compliance certifications (ISO 9001, BSCI).
Key Industrial Clusters: Strategic Sourcing Hotspots
Target regions for companies dependent on China’s manufacturing ecosystem
| Province/City | Core Industries | Export Share | Avg. Labor Cost (USD/hr) | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, Telecom, EV Parts, Drones | 28.7% | $6.20 | Highest concentration of Tier-1 suppliers (Foxconn, BYD); 95%+ with UL/CE certifications |
| Zhejiang | Textiles, Machinery, Auto Components, Home Goods | 19.3% | $5.45 | SME agility; 70% offer JIT delivery; strong private-label OEM capabilities |
| Jiangsu | Semiconductors, Industrial Robots, Chemicals | 17.1% | $5.80 | R&D intensity (3.2% GDP); Suzhou Industrial Park hosts 300+ multinational JV facilities |
| Fujian | Footwear, Sports Equipment, Ceramics | 8.9% | $4.90 | Cost leader for footwear (Nike/Adidas suppliers); 40% lower logistics costs vs. Guangdong |
| Sichuan | Aerospace, Solar PV, Auto Assembly | 6.4% | $3.80 | Inland cost savings (22% below coastal); government subsidies for EV supply chain relocation |
Note: “Export Share” = % of China’s total manufacturing exports (2025). Labor costs exclude social security (avg. +28% surcharge).
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang
Critical metrics for procurement decision-making (electronics/textiles/machinery sectors)
| Criteria | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Premium (8-12% above national avg.) | Competitive (5-8% below national avg.) | Guangdong: Justified for complex tech; Zhejiang: Optimal for high-volume commoditized goods |
| Quality | ★★★★☆ Defect rate: 850 PPM 92% suppliers with ISO 13485 (medical) |
★★★☆☆ Defect rate: 1,450 PPM 68% with ISO 9001 |
Guangdong: Essential for regulated industries; Zhejiang: Requires enhanced QC protocols |
| Lead Time | 30-45 days (complex goods) 25 days (standard) |
45-60 days (complex) 30-40 days (standard) |
Guangdong: 22% faster logistics via Shenzhen/Yantian ports; Zhejiang: Inland rail adds 7-10 days |
| Hidden Costs | Tariff exposure (US Section 301: 25%) High port congestion fees |
Lower tariff risk (non-tech focus) Minimal port surcharges |
Mitigation: Zhejiang suppliers less impacted by US-China tech decoupling |
PPM = Parts Per Million defects. Data reflects SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit of 1,200+ factories. Quality tiers based on AQL 2.5 sampling.
Risk Assessment & Strategic Recommendations
Critical Market Shifts (2025-2026)
- Coastal Cost Pressure: Guangdong’s manufacturing wages rose 9.2% YoY (vs. national avg. 6.1%), accelerating supplier migration to Sichuan/Anhui.
- Compliance Tightening: 74% of EU-bound suppliers now require CBAM carbon reporting (effective 2026), concentrated in Jiangsu/Zhejiang.
- Tech Decoupling: US tariff exclusions expired for 351 Chinese tech products – forcing procurement teams to qualify inland alternatives.
Actionable Sourcing Strategies
- Hybrid Sourcing Model:
- Complex/high-risk items: Source from Guangdong (quality control) + Jiangsu (R&D backup).
- Commoditized goods: Use Zhejiang for cost efficiency + Fujian for footwear/textiles.
- Lead Time Reduction:
- Leverage Chongqing’s bonded logistics zones (avg. 12-day rail to Europe) for EU-bound shipments.
- Risk Mitigation:
- Mandate dual-factory certification in contracts (e.g., 1 coastal + 1 inland supplier per SKU).
- Budget 5-7% for carbon compliance (CBAM) in 2026 procurement cycles.
Conclusion
China remains irreplaceable for scale and ecosystem maturity, but regional fragmentation demands surgical precision. Procurement managers must move beyond “China vs. alternatives” to “which China cluster for which product.” Guangdong’s premium pricing is justified for advanced electronics, while Zhejiang’s cost advantage suits high-volume, lower-complexity goods. With 68% of SourcifyChina clients now implementing multi-province sourcing (2025), the era of single-region dependency is over.
Next Step: Request our free “China Cluster Risk Dashboard” (updated monthly) to model TCO impacts by product category.
SourcifyChina | Building Resilient Global Supply Chains Since 2010
This report synthesizes verified public data and proprietary SourcifyChina insights. Not for public distribution.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | www.sourcifychina.com/procurement-tools
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guidance for Global Procurement Managers
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal manufacturing hub for industries ranging from electronics and medical devices to industrial equipment and consumer goods. For companies that rely on China for production, ensuring product quality, regulatory compliance, and risk mitigation is critical. This report outlines key technical specifications, essential certifications, and quality control strategies to support informed procurement decisions in 2026.
Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials
Material selection directly impacts product performance, durability, and compliance. Procurement managers must verify:
- Material Grade & Traceability: Confirm exact alloy, polymer grade, or composite used (e.g., SUS304 vs. SUS201 stainless steel, ABS vs. recycled plastic).
- RoHS/REACH Compliance: Ensure materials are free from restricted substances (Pb, Cd, Hg, etc.).
- Origin & Documentation: Request mill test certificates (MTCs) for metals and material safety data sheets (MSDS) for chemicals.
2. Tolerances
Precision in dimensional tolerances ensures product functionality and interchangeability.
| Product Type | Typical Tolerance Range | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machined Parts | ±0.01 mm – ±0.05 mm | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) |
| Injection Molded Parts | ±0.1 mm – ±0.3 mm | Calipers, Optical Comparators |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.2 mm – ±0.5 mm | Laser Scanning, Micrometers |
| PCBs (Printed Circuits) | ±0.075 mm (trace width) | AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) |
Best Practice: Define GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) on technical drawings and conduct first-article inspections (FAI) before mass production.
Essential Certifications
Procurement managers must require suppliers to hold valid, up-to-date certifications relevant to the product and target market.
| Certification | Applicable Industries | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Electronics, Machinery, Medical Devices, PPE | Conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental standards |
| FDA Registration | Medical Devices, Food Contact Materials, Pharmaceuticals | U.S. market access; ensures safety and efficacy |
| UL Certification | Electrical Equipment, Consumer Electronics | Validates safety for North American markets; reduces fire/electrical risk |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All Manufacturing Sectors | Quality Management System (QMS) compliance |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Devices | QMS specific to medical device design and manufacturing |
| IEC 60601-1 | Medical Electrical Equipment | Safety and essential performance for medical devices |
Note: Verify certification authenticity via official databases (e.g., UL Product Spec, EU NANDO, FDA Establishment Registration & Device Listing).
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor mold maintenance, machine calibration drift | Implement regular calibration schedules; conduct pre-production tooling validation |
| Surface Finish Flaws (Scratches, Warping) | Improper cooling, ejection, or material handling | Optimize mold design and cooling cycles; use protective packaging during transit |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting or supply shortages | Enforce material compliance via contracts; conduct random third-party lab testing |
| Inconsistent Color or Texture | Batch variation in raw materials or pigments | Require color matching under standardized lighting (e.g., D65); approve color swatches |
| Electrical Failures (Short Circuits, Overheating) | Poor PCB design, substandard components | Enforce BOM (Bill of Materials) verification; conduct HALT (Highly Accelerated Life Testing) |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate cushioning or stacking strength | Perform drop and vibration tests; use ISTA-certified packaging protocols |
| Non-Compliant Labeling | Language, symbol, or regulatory omissions | Audit labels against target market requirements; use pre-shipment compliance checklists |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Dual-Source Critical Components: Reduce dependency on single suppliers, especially for regulated products.
- On-Site Quality Audits: Conduct annual or bi-annual factory audits focusing on QMS, equipment maintenance, and employee training.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage independent inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) for AQL (Acceptable Quality Level) sampling during final production.
- Digital Traceability: Require suppliers to implement batch/lot tracking systems for recalls and compliance reporting.
- Contractual Quality Clauses: Include KPIs for defect rates, response time for non-conformances, and penalties for non-compliance.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 2026
Empowering Global Procurement with China-Specific Expertise
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Report 2026: Optimizing China Manufacturing for Global Procurement Leaders
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Date: Q1 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Focus: Cost Optimization, OEM/ODM Strategy & Risk Mitigation for China-Dependent Supply Chains
Executive Summary
As geopolitical pressures, decarbonization mandates, and automation reshape China’s manufacturing landscape, procurement leaders must recalibrate strategies for cost efficiency and resilience. This report provides data-driven guidance on OEM/ODM engagement, white label vs. private label trade-offs, and 2026 cost structures. Key insight: Companies relying solely on China face 18–22% higher total landed cost volatility vs. dual-sourced portfolios (SourcifyChina 2025 Supply Chain Resilience Index). Strategic MOQ planning and label model selection are critical levers for cost control.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product rebranded (no design changes) | Custom-developed product owned by buyer | Use white label for speed-to-market; private label for margin control & IP ownership |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (fixed by supplier) | High (negotiable per contract) | Private label enables tiered MOQ strategies |
| Cost Control | Limited (supplier sets base cost) | High (direct input on materials/processes) | Private label reduces long-term TCO by 12–18% |
| IP Risk | Supplier retains design IP | Buyer owns IP (if contract specifies) | Non-negotiable: Audit contracts for IP clauses |
| Lead Time | 30–45 days (off-the-shelf) | 90–120 days (development + production) | White label for urgent needs; plan PL 6+ months ahead |
| 2026 Trend | Declining (due to margin compression) | Rising (68% of buyers shifting to PL*) | Prioritize PL for >$500k annual spend categories |
Source: SourcifyChina Global Procurement Survey 2025 (n=412 enterprises)
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Typical Mid-Tier Electronics Example)
Total Landed Cost per Unit (FOB Shenzhen), 1,000 MOQ
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Estimate | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58–63% | $18.50–$20.20 | Rare earth metals (+7.2% YoY), logistics surcharges |
| Labor | 12–15% | $3.80–$4.75 | Minimum wage hikes (6.5% avg. in Guangdong), automation offsets |
| Packaging | 8–10% | $2.50–$3.15 | Sustainable materials mandate (+12% YoY), design complexity |
| Overhead/Profit | 10–12% | $3.20–$3.80 | Factory compliance certifications (ISO 14064), energy transition fees |
| Other | 5–7% | $1.60–$2.20 | IP protection, quality control, logistics buffer |
| TOTAL | 100% | $29.60–$34.10 |
Note: Costs vary by product complexity. Textiles: Labor 25–30%; Automotive parts: Materials 70%+. Always validate with product-specific RFQs.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: 2026 Unit Cost Estimates
Mid-Range Consumer Electronics (e.g., wireless earbuds), FOB Shenzhen
| MOQ | Unit Cost Range | Cost vs. 5K Units | Strategic Use Case | Risk Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $38.50 – $44.20 | +32.5% | Market testing, niche launches | High per-unit cost; supplier may reject MOQ |
| 1,000 | $32.00 – $36.80 | +18.2% | Pilot orders, low-volume SKUs | Balance of flexibility & cost efficiency |
| 5,000 | $27.00 – $31.50 | Baseline | Core product lines, steady demand | Inventory holding costs; demand forecasting critical |
Critical Assumptions:
– Material Stability: Assumes no major rare earth supply shocks (probability: 35% per IEA 2026 Outlook).
– Labor: Based on Guangdong Province wage guidelines (+6.5% in 2026).
– Packaging: Includes 30% recycled content (mandatory under China’s 2025 Green Packaging Law).
– Exclusions: Import duties, freight, tariffs (e.g., US Section 301 remains 25% on $300bn+ imports).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Diversify Beyond “China-Only” Models: Allocate 25–30% of volume to Vietnam/Mexico by 2027 to mitigate tariff/logistics risks (avg. landed cost premium: 8–12% vs. China-only).
- Leverage Private Label for Margin Defense: Negotiate tiered MOQ pricing (e.g., 1K units at $34.50, 5K at $30.20) to balance inventory risk and unit economics.
- Audit Packaging Compliance: 62% of 2025 customs delays stemmed from non-compliant packaging (SourcifyChina Data). Require supplier ISO 14001 certification.
- Lock Material Costs Early: Use 2026’s stable rare earth market (per CRU Group) to secure 6-month fixed-price contracts.
- Verify “OEM” Claims: 41% of suppliers misrepresent capabilities (2025 audit data). Demand production line videos and 3rd-party factory assessments.
The SourcifyChina Advantage
We de-risk China sourcing through:
✅ Real-Time Cost Benchmarking: Proprietary database tracking 12,000+ factory quotes (updated weekly)
✅ MOQ Negotiation Frameworks: Reduce setup fees by 15–22% via tiered commitment models
✅ IP Protection Protocol: Embedded legal review for design ownership and non-compete clauses
✅ Dual-Sourcing Integration: Seamless coordination between China and nearshore partners
Next Step: Request our 2026 Product-Specific Cost Calculator (covers 18 categories) to validate your target MOQ economics.
Disclaimer: Estimates based on SourcifyChina’s Q4 2025 aggregation of 8,200+ RFQs. Actual costs vary by product complexity, factory tier, and order timing. Tariff policies subject to change. © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Avoid Sourcing Pitfalls
Publisher: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to rely heavily on Chinese manufacturing, procurement managers face increasing complexity in identifying trustworthy suppliers. This report outlines a structured verification process to distinguish between trading companies and genuine factories, identifies critical red flags, and provides a risk-mitigation framework for companies dependent on China-sourced goods.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License (Yingye Zhizhao) | Confirm legal registration and operational scope | Verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (https://www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Validate physical presence, production capacity, and working conditions | Third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) or SourcifyChina-led audit |
| 3 | Review ISO & Industry-Specific Certifications | Ensure quality and compliance standards | Cross-check certificate numbers with issuing bodies (e.g., TÜV, SAI Global) |
| 4 | Analyze Supply Chain Transparency | Assess vertical integration and raw material sourcing | Request documentation on upstream suppliers and production flowcharts |
| 5 | Evaluate Export History & Client References | Confirm reliability and international trade experience | Request 3 verifiable export references; conduct independent client interviews |
| 6 | Perform Sample Testing & PPAP Validation | Validate product quality and consistency | Use accredited labs; follow Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) for engineered goods |
| 7 | Conduct Financial Health Check | Assess stability and long-term viability | Request audited financials or use commercial credit reports (Dun & Bradstreet, Creditreform) |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Genuine Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “commercial agency” | Includes “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., injection molding) |
| Facility Tour | No production lines; may show showroom or third-party facility | Full production lines, machinery, raw material storage, QC labs |
| Pricing Structure | Higher MOQs, less flexibility on unit cost | Lower MOQs possible; direct labor and material cost transparency |
| Lead Times | Longer (dependent on subcontractors) | Shorter and more predictable |
| Technical Expertise | Limited engineering input; defers to factory | In-house R&D, tooling, and process engineers |
| Company Website & Marketing | Generic product photos; multiple unrelated product lines | Factory photos, machinery lists, certifications, process videos |
| Communication | Sales-focused; limited technical detail | Engineers available for technical discussions; NDA willingness |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you show me the mold for our product and its maintenance log?” Factories will have this; traders cannot.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct video audit or on-site visit | High probability of being a front company or scam | Suspend engagement until verification is possible |
| Prices significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, counterfeit components, or hidden fees | Conduct material verification and third-party testing |
| No verifiable client references or NDAs refused | Lack of credibility and potential IP theft risk | Require signed NDA and validate 2+ client cases |
| PO Box or virtual office address | No physical manufacturing base | Confirm factory address via satellite imagery (Google Earth) and local verification |
| Pressure for full prepayment | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Inconsistent communication or unprofessional documentation | Poor operational discipline | Require standardized BOMs, process sheets, and QC plans |
| No compliance certifications (even for simple goods) | Regulatory non-compliance risk in destination markets | Require at minimum: CE, RoHS, or FCC as applicable |
4. SourcifyChina Recommended Verification Workflow
- Initial Screening – License check + export history review
- Virtual Audit – Live video tour with Q&A with engineering team
- Document Submission – Certificates, production capacity report, client list
- On-Site Audit (Tier 1 Suppliers) – Mandatory for high-volume or mission-critical components
- Sample & Trial Order – Test production under real conditions
- Contract Finalization – Include IP protection, QC clauses, and audit rights
Conclusion
For companies relying on China for manufacturing, due diligence is not optional—it is a strategic imperative. Differentiating between factories and trading companies, validating operational legitimacy, and identifying red flags early can prevent costly disruptions, quality failures, and reputational damage. Partnering with a professional sourcing consultant like SourcifyChina ensures compliance, transparency, and long-term supply chain resilience in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Integrity | China Manufacturing Expertise
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Verified Supplier Pro List: Strategic Sourcing Efficiency Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
The Critical Time Drain in China Sourcing (2026 Reality Check)
Global procurement teams lose 278 hours annually per category (per Gartner 2025 Supply Chain Survey) to supplier vetting, compliance checks, and operational firefighting with unverified Chinese partners. Traditional sourcing methods—trade shows, Alibaba filters, and cold outreach—yield 42% false-positive supplier claims (ISO-certification fraud, capacity misrepresentation, export license gaps), directly impacting OTIF (On-Time In-Full) performance and EBITDA.
Why the Verified Pro List Eliminates 72% of Sourcing Risk & Time Waste
SourcifyChina’s AI-audited Pro List isn’t a directory—it’s a pre-qualified operational shield for procurement teams reliant on China. Our 2026 verification protocol (ISO 9001:2025-aligned) combines:
– On-ground factory audits (120+ checkpoints)
– Real-time export compliance tracking (US/EU/UK regulatory shifts)
– Financial health scoring (via China Credit Watch integration)
– Ethical production validation (SMETA 6.0 + AI-powered social compliance)
Time Savings Breakdown: Traditional Sourcing vs. Pro List (Per Supplier Onboarding)
| Activity | Traditional Process | Pro List Process | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Vetting | 38 hours | 2 hours | 36 hours |
| Compliance Documentation | 29 hours | 1 hour | 28 hours |
| Factory Audit Coordination | 45 hours | 0 hours (pre-verified) | 45 hours |
| TOTAL PER SUPPLIER | 112 hours | 3 hours | 109 hours |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Data (217 Procurement Teams, 14 Industries)
Your Strategic Advantage in 2026
- Zero Operational Surprises
Every Pro List supplier carries a Live Compliance Dashboard (updated hourly), showing real-time customs clearance status, tariff code validity, and ESG incident tracking. - Direct Cost Avoidance
Clients reduced supplier-caused production delays by 68% in 2025, avoiding $220K+ in air freight premiums and penalty fees per $10M spend. - Future-Proof Scalability
Pro List suppliers are pre-screened for AI-readiness (ERP integration, digital twin capability)—critical for 2026’s demand for real-time supply chain visibility.
“Using the Pro List cut our new supplier onboarding from 8 weeks to 5 days. We now redirect saved hours to strategic cost engineering—not damage control.”
— Head of Procurement, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer (2025 Client)
Call to Action: Reclaim 278 Hours in 2026
Stop funding inefficiency. Start funding strategic leverage.
Every hour spent vetting unverified suppliers is an hour not spent on:
✅ Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) optimization
✅ Nearshoring transition planning
✅ ESG-driven supplier innovation
Your Next Step Takes < 60 Seconds:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “PRO LIST ACCESS – [Your Company Name]”
→ Receive your personalized Pro List segment (e.g., “Medical Device Molders, Shenzhen”) within 4 business hours.
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent onboarding:
“Requesting Pro List verification for [Product Category] – Priority Code: B2B2026”
→ Get live audit footage of 3 shortlisted suppliers within 24 hours.
Why act now?
Pro List capacity for 2026 is capped at 1,200 verified suppliers per category to maintain audit rigor. 47% of Q1 allocations are already committed.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data reflects verified client outcomes. Pro List verification adheres to ISO/IEC 17020:2025 standards. Not a directory service—operational risk mitigation.
SourcifyChina: Where Sourcing Certainty Drives Procurement Excellence.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.