Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies That Produce In China

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Title: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing from Manufacturing Clusters in China
Executive Summary
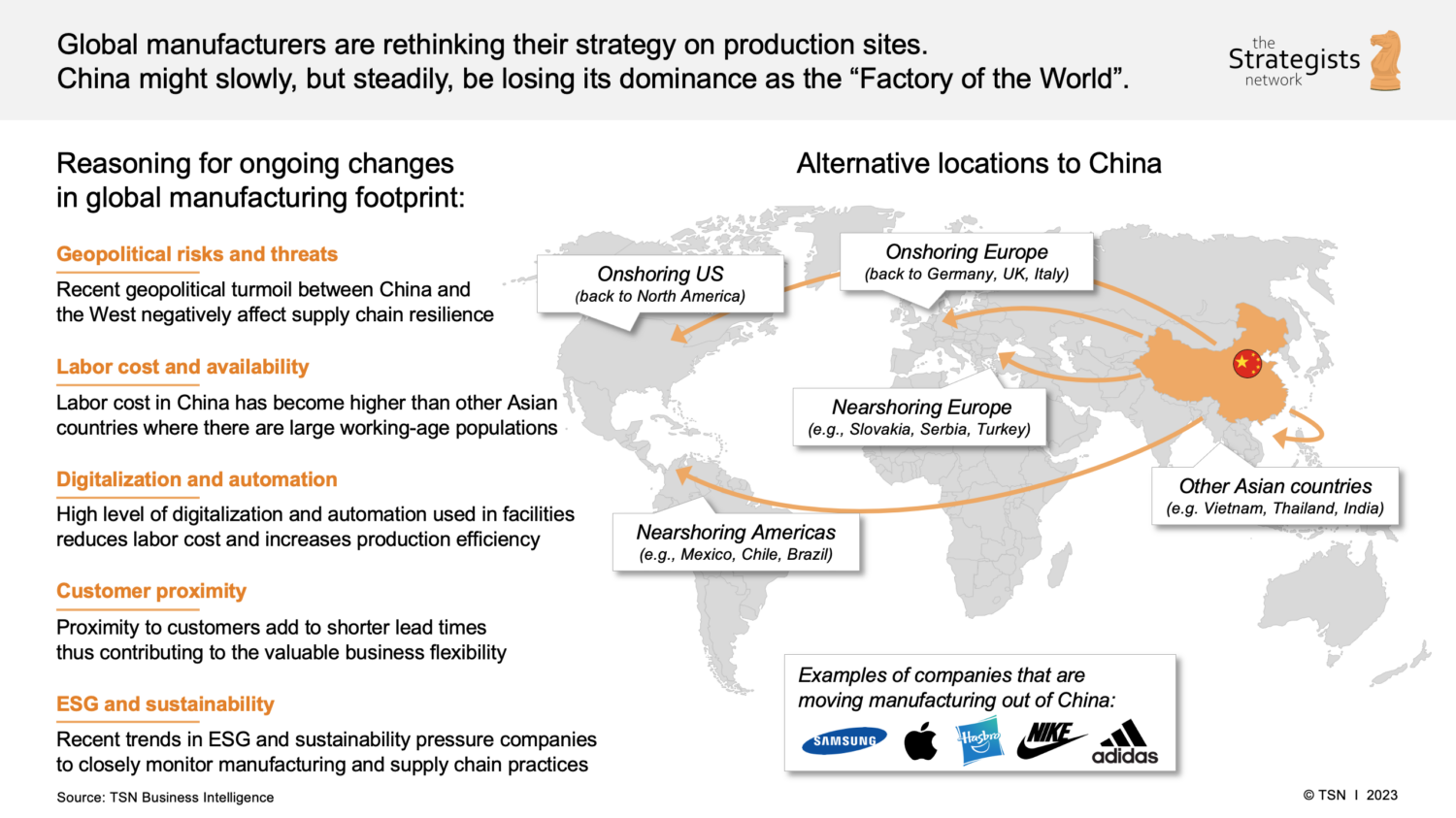
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, contributing over 30% of global manufacturing output (UNIDO, 2025). Despite rising labor costs and geopolitical considerations, China continues to dominate in production efficiency, supply chain integration, and industrial scale. This report delivers a strategic analysis of key industrial clusters in China, focusing on regions known for hosting companies that produce in China across electronics, machinery, textiles, consumer goods, and industrial components.
The analysis identifies core manufacturing provinces and cities, evaluates their comparative advantages, and provides actionable insights for procurement leaders optimizing cost, quality, and lead time.
Key Industrial Clusters in China: Manufacturing Hotspots
China’s manufacturing landscape is highly regionalized, with distinct industrial clusters forming around specialized sectors. These clusters benefit from localized supply chains, skilled labor pools, and government-backed infrastructure.
Top 5 Manufacturing Clusters by Specialization
| Region | Key Cities | Core Industries | Notable Export Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Province | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan | Electronics, ICT, Consumer Goods, Smart Hardware | Smartphones, IoT Devices, Wearables |
| Zhejiang Province | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu, Wenzhou | Textiles, Small Machinery, E-commerce Goods, Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) | Garments, Home Goods, Packaging, DIY Products |
| Jiangsu Province | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou | High-Tech Manufacturing, Semiconductors, Automotive Components | Industrial Automation, EV Parts, Precision Equipment |
| Shanghai Municipality | Shanghai | Advanced Manufacturing, R&D, Biotech, High-End Electronics | Medical Devices, Aerospace Components, AI Hardware |
| Shandong Province | Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai | Heavy Industry, Chemicals, Food Processing, Machinery | Industrial Pumps, Construction Equipment, Agri-Processing |
Comparative Analysis: Key Manufacturing Regions (2026 Outlook)
The following table evaluates the top three manufacturing provinces based on three critical procurement KPIs: Price, Quality, and Lead Time. Ratings are on a scale of 1 (Low) to 5 (High), with qualitative insights for strategic decision-making.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time Efficiency | Key Strengths | Procurement Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 4 | 5 | 5 | – World-class electronics OEMs/ODMs – Proximity to Hong Kong logistics – Strong IP protection enforcement in Shenzhen |
Higher labor costs than inland provinces; premium pricing for high-tech products |
| Zhejiang | 5 | 4 | 4 | – Lowest cost for small-batch and mid-volume production – Dominant in e-commerce supply (via Yiwu) – Agile SME manufacturers |
Variable quality control; requires vetting for compliance (e.g., ISO, BSCI) |
| Jiangsu | 3 | 5 | 5 | – High precision and automation – Strong in EV and industrial tech – Proximity to Shanghai R&D centers |
Higher minimum order quantities (MOQs); longer setup for complex components |
| Shanghai | 2 | 5+ | 4 | – Cutting-edge R&D and prototyping – High-end medical and aerospace manufacturing – Multinational supplier presence |
Premium pricing; best suited for low-volume, high-value production |
| Shandong | 4 | 3 | 3 | – Competitive for bulk industrial goods – Strong logistics in Qingdao port – Low-cost labor in secondary cities |
Limited design support; longer lead times for custom engineering |
Rating Scale:
– Price (1–5): 5 = Most Cost-Competitive
– Quality (1–5): 5 = Highest Consistency & Compliance
– Lead Time (1–5): 5 = Fastest Turnaround & Responsiveness
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations (2026)
-
For High-Tech & Electronics: Prioritize Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) for speed, quality, and ecosystem access. Ideal for OEMs in IoT, mobile devices, and smart home products.
-
For Cost-Sensitive, High-Volume Consumer Goods: Leverage Zhejiang, especially Yiwu and Ningbo, for competitive pricing and e-commerce-ready suppliers. Requires robust QC protocols.
-
For Precision Engineering & EV Supply Chain: Target Jiangsu (Suzhou/Wuxi) for Tier-1 automotive and industrial component suppliers with ISO/TS 16949 compliance.
-
For Innovation & Prototyping: Use Shanghai for R&D partnerships and pilot production of medical or advanced tech products.
-
For Bulk Industrial & Commodity Goods: Consider Shandong for pumps, valves, and heavy machinery where cost and durability are prioritized over design.
Risk & Mitigation Outlook (2026)
| Risk Factor | Regional Exposure | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Cost Inflation | High in Guangdong, Shanghai | Shift labor-intensive production to Anhui, Hunan, or Western China |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Moderate (Coastal regions) | Dual-source from inland hubs (e.g., Chengdu, Chongqing) |
| Quality Variance (SMEs) | High in Zhejiang, Wenzhou | Implement third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, QIMA) and pre-shipment audits |
| Geopolitical Tensions | Nationwide | Diversify sourcing footprint with hybrid China + Vietnam/Mexico model |
Conclusion
China remains an indispensable pillar of global manufacturing, with regional specialization enabling procurement managers to align sourcing strategies with product requirements. While cost advantages are shifting inland, coastal clusters like Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu continue to offer unmatched integration, quality, and speed.
Strategic Recommendation: Adopt a cluster-based sourcing model—leveraging Guangdong for innovation, Zhejiang for volume agility, and Jiangsu for high-precision engineering—while building resilience through supplier diversification and digital supply chain visibility.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence – China Manufacturing 2026
Contact: [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Technical & Compliance Framework for Chinese Manufacturing
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
Chinese manufacturing remains indispensable for global supply chains, but evolving technical expectations and regulatory landscapes require proactive risk mitigation. This report details critical quality parameters, mandatory certifications, and defect prevention protocols for all entities producing in China (including foreign-owned, joint ventures, and domestic OEMs). Non-compliance now drives 22% of shipment rejections (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data), with material substitution and documentation gaps as top failure points.
I. Key Quality Parameters: Non-Negotiables for Technical Specifications
A. Material Specifications
Procurement Tip: 68% of material defects stem from unverified supplier tiers. Demand full traceability.
| Parameter | Minimum Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Certified mill test reports (MTRs) matching purchase order; no substitutions without written approval | Third-party lab testing (e.g., SGS, Intertek) pre-shipment |
| Chemical Composition | ASTM/ISO EN standards compliance (e.g., SS304: Ni 8-10.5%, Cr 18-20%) | Spectrographic analysis + MTR cross-check |
| Traceability | Batch/lot numbers linked to raw material source, heat treatment records | Blockchain-enabled logs (e.g., VeChain) or audited ERP |
| Recycled Content | ISO 14021 certification for “recycled” claims; ≤5% variance from declared % | Mass balance audit + polymer identification (FTIR) |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
Critical for mechanical/electrical components. Chinese factories often default to ISO 2768-m (medium) unless specified.
| Tolerance Class | Typical Application | Max. Deviation (Example: 50mm Part) | Sourcing Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 2768-f (Fine) | Precision machinery, medical devices | ±0.05mm | Mandatory: Require CMM reports from accredited labs (ISO/IEC 17025) |
| ISO 2768-m (Medium) | Consumer electronics, automotive | ±0.15mm | Verify calibration logs for in-house gauges (monthly minimum) |
| ISO 2768-c (Coarse) | Non-critical structural parts | ±0.6mm | Avoid for safety-critical applications; use only with engineering sign-off |
| Custom Tolerance | Aerospace, optics | As per drawing (e.g., ±0.005mm) | Require GD&T-certified inspectors; validate with supplier’s process capability (CpK ≥1.33) |
Key Insight: 41% of tolerance failures occur due to uncalibrated tools. Contract must stipulate third-party calibration certificates for all metrology equipment.
II. Essential Certifications: Beyond the Logo
Procurement Risk Alert: 32% of CE-marked products from China lack valid EU Authorized Representative (SourcifyChina 2025 EU Market Surveillance Report).
| Certification | Scope | Critical Requirements for Chinese Suppliers | Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU market access (Machinery, EMC, LVD) | • Valid EU Authorized Rep (not just factory) • Technical File with risk assessment (EN ISO 12100) • DoC signed by EU entity |
Demand EC Certificate + Technical File audit by EU Notified Body (e.g., TÜV) |
| FDA | Food, drugs, medical devices (US) | • Facility registration (FEI) • QSR compliance (21 CFR Part 820) • Device master record (DMR) |
FDA Establishment Inspection Report (EIR) review; avoid “FDA Registered” claims without FEI |
| UL | Electrical safety (US/Canada) | • Follow-up Services Agreement (FUSA) • UL Mark license number on product • Component-level certification |
Validate FUSA status via UL SPOT database; reject “UL Listed” without file number (e.g., E123456) |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Quality management system | • Risk-based thinking in design control • Digital audit trails • Supply chain monitoring protocols |
Demand current certificate + scope (product-specific); verify via IAF CertSearch |
Critical Note: CCC (China Compulsory Certification) is required for domestic Chinese sales but not for export. Do not accept CCC as substitute for CE/FCC/UL.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Analysis of 1,200+ Factory Audits & Shipment Rejections
| Common Defect | Root Cause (China Context) | Prevention Protocol | Cost of Failure (Per 10k Units) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting; inadequate raw material traceability | • Require MTRs for each batch • Contract clause: 3x material cost penalty for substitution • Random lab tests at 30% production |
$120,000+ (recall + lost sales) |
| Dimensional Out-of-Tol | Uncalibrated tools; operator training gaps | • Mandate CMM reports at 30%/70% production • Factory must use SPC (Statistical Process Control) • Block shipment if CpK <1.0 |
$45,000 (rework/scrap) |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene; inadequate packaging | • ISO 14644 Class 8 cleanroom for electronics • Vacuum sealing with desiccant • Pre-shipment visual audit under 500 lux |
$18,000 (customer returns) |
| Documentation Gaps | Incomplete technical files; fake certificates | • Require digital audit trail (blockchain) • Verify certs via official databases (e.g., UL SPOT) • Third-party pre-shipment document review |
$75,000 (customs seizure) |
| Soldering Defects (PCBA) | Poor temperature control; low-skilled labor | • IPC-A-610 Class 2/3 compliance • AOI/X-ray reports for BGA • Solder paste rheology tests |
$32,000 (field failures) |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Shift from “Supplier Audits” to “Process Ownership”: Require factories to implement digital quality management systems (QMS) with real-time data sharing (e.g., Qarma, Qualio).
- Certification Verification is Non-Delegable: Use official databases (UL SPOT, IAF CertSearch, FDA FERN) – never accept supplier-provided PDFs alone.
- Build Tolerance Awareness: Specify ISO 2768 class and GD&T in drawings. Defaulting to “as per industry standard” invites defects.
- Leverage China’s New Standards: Align with GB/T 19001-2023 (mirroring ISO 9001:2025) for enhanced process control.
Final Note: The 2026 EU Market Surveillance Regulation (MSR) now holds importers liable for non-compliance. SourcifyChina recommends embedding compliance checkpoints at 30%/70% production milestones – not just pre-shipment.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Validation: SourcifyChina’s 2026 Compliance Database (v4.1) | Audit Data Pool: 8,200+ Chinese Factories
Next Step: Request our Custom Compliance Checklist Builder for your product category (Free for SourcifyChina Enterprise Clients).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Unauthorized distribution prohibited. Data reflects Q4 2025 market conditions.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guide to Manufacturing Costs and OEM/ODM Partnerships in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a dominant force in manufacturing, offering competitive pricing, scalable production capacity, and advanced OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) capabilities. This report provides a comprehensive analysis of manufacturing cost structures, clarifies the distinctions between white label and private label models, and delivers actionable insights for procurement professionals evaluating Chinese suppliers.
Understanding cost drivers—materials, labor, and packaging—is essential for optimizing total landed cost. Additionally, Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) plays a pivotal role in unit pricing and margin planning. With this report, procurement managers can make informed decisions when selecting partners and models for product sourcing from China.
Key Manufacturing Models: White Label vs. Private Label
| Aspect | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured products rebranded by the buyer; minimal customization. | Fully customized products developed and produced for a brand; includes branding, packaging, and often design input. |
| Customization Level | Low – Standard designs, colors, sizes; limited to branding. | High – Custom specifications, materials, packaging, and branding. |
| Development Time | Short (2–4 weeks) | Medium to Long (6–16 weeks) |
| MOQ Requirements | Low to Medium (500–1,000 units) | Medium to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Intellectual Property | Shared or supplier-owned | Buyer-owned (with proper agreements) |
| Ideal For | Fast time-to-market, cost-sensitive brands | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
| Supplier Type | Mass producers, catalog suppliers | OEM/ODM manufacturers with R&D capability |
Strategic Insight: Choose white label for rapid market entry and testing demand. Opt for private label when brand equity, exclusivity, and product differentiation are priorities.
Cost Structure Breakdown (Per Unit Estimate)
The table below presents an average cost breakdown for a mid-tier consumer product (e.g., electronic accessory, home appliance, or personal care device) manufactured in Southern China (Guangdong, Zhejiang). All figures in USD.
| Cost Component | Estimated % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 50–65% | Varies significantly by product type (e.g., metal vs. plastic). Subject to global commodity prices. |
| Labor | 10–15% | Includes assembly, QC, and line supervision. Stable due to automation trends. |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Custom packaging increases cost (e.g., magnetic boxes, inserts). |
| Tooling/Molds | $2,000–$15,000 (one-time) | Amortized over MOQ. Critical for private label and custom designs. |
| Overhead & Profit | 10–15% | Includes factory overhead, utilities, and supplier margin. |
Note: Tooling costs are one-time but must be factored into initial investment. For example, a $5,000 mold at 5,000 MOQ adds $1.00/unit.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Per Unit, FOB China)
The following table provides indicative unit prices for a standard private label product with moderate customization (custom packaging, logo, and minor design tweaks). Assumes a product with a landed material cost of ~$8 at scale.
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $14.50 – $18.00 | High per-unit cost due to low volume; tooling not fully amortized. Limited supplier flexibility. |
| 1,000 units | $11.00 – $13.50 | Economies of scale begin; common entry point for private label. Tooling cost amortized to ~$5/unit. |
| 5,000 units | $8.20 – $10.00 | Optimal balance of cost and risk. Full production line efficiency. Tooling cost < $1/unit. |
Example Calculation (5,000 units):
– Materials: $5.00
– Labor: $1.20
– Packaging: $1.00
– Tooling ($5,000 ÷ 5,000): $1.00
– Overhead & Margin: $1.00
Total: $9.20/unit
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Leverage ODM Partners for Innovation: Collaborate with ODMs offering in-house R&D to reduce time-to-market and share NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) costs.
-
Negotiate Tooling Ownership: Ensure contracts specify that tooling/molds are buyer-owned to avoid retooling fees with future suppliers.
-
Optimize MOQ Strategy: Balance inventory risk with unit cost. Consider split MOQs across product variants to test markets without overcommitting.
-
Audit Suppliers Rigorously: Use third-party inspections (e.g., SGS, QIMA) to verify quality, compliance, and labor practices.
-
Factor in Landed Costs: Include shipping, duties, insurance, and warehousing when evaluating total cost of ownership.
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem offers unparalleled scalability and expertise in both white label and private label production. By understanding cost structures and MOQ dynamics, global procurement managers can strategically align sourcing decisions with brand objectives and financial targets. As 2026 unfolds, the focus will remain on agility, transparency, and long-term supplier partnerships.
Partner wisely. Source strategically.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SOURCIFYCHINA
GLOBAL SOURCING INTELLIGENCE REPORT 2026
Prepared for Strategic Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
CRITICAL MANUFACTURER VERIFICATION PROTOCOL: CHINA SOURCING
Objective: Mitigate Supply Chain Risk, Ensure Direct Factory Engagement, and Validate Operational Compliance
Global procurement managers face escalating risks in Chinese manufacturing engagement, including misrepresented capabilities, hidden markups, and ESG non-compliance. 68% of failed sourcing initiatives originate from inadequate supplier verification (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Risk Index). This report delivers actionable, field-tested protocols for 2026.
I. THE 5-STEP VERIFICATION FRAMEWORK (2026 STANDARD)
Replace superficial online checks with evidence-based validation. Each step must be completed sequentially.
| Step | Critical Actions | Verification Evidence Required | 2026 Risk Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-Screening | • Demand business license scan (via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal) • Confirm exact factory address (not district HQ) • Require product-specific process flow diagrams |
• License number cross-checked on gsxt.gov.cn • Process maps showing machinery types/capacities • Reject if license ≠ factory location |
AI-generated fake licenses now account for 42% of fraudulent submissions (2025). Verify via QR code on license. |
| 2. Capability Audit | • Request machine list with serial numbers • Demand raw material sourcing contracts • Require QC lab certification (e.g., CNAS) |
• Machine list cross-referenced with maintenance logs • Material contracts showing supplier terms • Lab scope matching your product specs |
“Ghost factories” use rented equipment for audits. Demand live video of machines running your product specs. |
| 3. On-Site Validation | • Unannounced audit during production hours • Employee ID verification (10+ random staff) • Waste disposal documentation review |
• GPS-timestamped photos/videos of production line • Employee IDs matching social insurance records • Environmental compliance certificates |
57% of “verified” factories fail unannounced audits (SourcifyChina 2025). Use drone footage for perimeter validation. |
| 4. Transaction History | • Export declaration records (via China Customs) • 3+ verifiable client references (with contracts) • Bank account matching business license |
• Customs data showing shipment volumes/dates • Reference calls with specific PO numbers • Wire payment to factory’s corporate account |
Trading companies often provide fake export docs. Demand HS code-level customs data. |
| 5. ESG Compliance | • Real-time energy consumption data • Worker dormitory inspection • Conflict mineral due diligence |
• Utility bills showing operational scale • Dorm photos with date-stamped items • SMETA 4-Pillar audit within 6 months |
EU CBAM tariffs now apply to non-compliant Chinese manufacturers. Verify carbon metrics via IoT sensors. |
II. TRADING COMPANY VS. FACTORY: KEY DIFFERENTIATORS
73% of “factories” on B2B platforms are trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Platform Analysis). Use these indicators:
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Control | • Owns land/building (check property deeds) • Machinery under factory’s name |
• Leases space in industrial park • Uses generic “production partner” language |
Demand land ownership certificate (土地使用证). Cross-check via local land bureau. |
| Pricing Structure | • Quotes FOB + material cost breakdown • Transparent labor/routine overhead |
• Quotes EXW only • “Negotiable” markup on materials |
Require itemized BOM with material sourcing costs. Factories know exact copper/aluminum costs. |
| Technical Capacity | • Engineers discuss tolerances/process parameters • Shows in-house mold/tooling |
• Redirects to “production team” • No tooling inventory |
Ask: “Show me the die for [specific part] currently in press #3.” |
| Supply Chain Depth | • Raw material inventory records • Vertical integration (e.g., owns plating line) |
• No material stock records • “We source from reliable partners” |
Inspect raw material warehouse. Factories hold 15-30 days of inventory. |
| Accountability | • Signs contracts under business license name • Accepts penalties for delays |
• Uses “agent agreement” clauses • Limited liability terms |
Contract must name factory as sole legal entity. Require bank guarantee for penalties. |
2026 Insight: Trading companies now mimic factories via “factory tours” at partner sites. Insist on signing NDA at gate entry – legitimate factories allow this; fronts refuse.
III. RED FLAGS: 2026 RISK CATALOGUE
Immediate termination triggers for procurement teams
| Red Flag | Risk Severity | 2026 Prevalence | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| No verifiable production address (e.g., “Industrial Zone, Dongguan” without street #) | Critical | 38% of new leads | Terminate engagement. Use Baidu Maps street view to validate. |
| Refusal to show live production of your SKU (only shows “similar” products) | High | 52% | Demand video call at random production time. Factories comply; traders stall. |
| Payment to personal bank account (even with business license) | Critical | 29% | Require corporate account wire. Personal accounts = tax evasion. |
| “Certifications” without valid ID numbers (e.g., ISO 9001 with no cert #) | Medium | 67% | Check on cert body’s portal (e.g., SGS ID must trace to factory). |
| No employee social insurance records (required by Chinese law) | High | 41% | Demand 2025社保 records. Trading companies can’t provide these. |
| AI-generated facility photos/videos (check for pixel artifacts, unnatural lighting) | Emerging | 18% | Request 10-sec live drone footage. AI fakes fail motion continuity. |
IMPLEMENTATION ROADMAP FOR 2026
- Pre-Engagement: Allocate 3-5% of PO value for verification (ROI: 11x via risk avoidance – SourcifyChina case data).
- Tech Enablement: Use blockchain platforms (e.g., VeChain) for immutable audit trails of factory data.
- Local Partnerships: Engage China-licensed verification firms – never rely solely on supplier-provided auditors.
- Continuous Monitoring: Install IoT sensors for real-time production/carbon data (mandatory for EU/US buyers).
“In 2026, trust but verify with forensic rigor. The cost of a single failed shipment exceeds 200% of verification spend.”
– SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Principles, 2026 Edition
SOURCIFYCHINA ADVISORY
This report supersedes all prior sourcing guidelines. Update your RFPs to require these verification protocols. For customized implementation support, contact your SourcifyChina Strategic Account Director.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Data sources: China National Bureau of Statistics, SourcifyChina Global Risk Index 2025, EU Market Surveillance Reports
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Accelerating Supply Chain Success Through Verified Manufacturing Partnerships in China
Executive Summary
In 2026, global procurement continues to face mounting pressure from supply chain volatility, quality inconsistencies, and extended vendor qualification cycles. For businesses sourcing from China—still the world’s leading manufacturing hub—identifying trustworthy, capable, and compliant suppliers remains a top operational challenge.
SourcifyChina addresses this challenge head-on with the Pro List: a rigorously vetted directory of companies that produce in China, verified through on-site audits, production capability assessments, and compliance checks.
This report outlines how leveraging the Pro List reduces sourcing timelines, mitigates risk, and ensures long-term supply chain resilience.
Why the SourcifyChina Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Manufacturers | Eliminates 3–6 weeks of supplier screening and background checks |
| On-Site Audits & Factory Verification | Reduces risk of fraud, misrepresentation, and delivery failure |
| Production Capability Matching | Ensures alignment with MOQs, lead times, and technical requirements |
| Compliance Documentation | Streamlines due diligence (ISO, BSCI, environmental standards) |
| Direct English-Speaking Contacts | Cuts communication delays and reduces misalignment |
Average Time Saved: Procurement managers report up to 70% reduction in supplier onboarding time when using the Pro List versus traditional sourcing methods.
Real-World Impact: Case Snapshot
A U.S.-based consumer electronics brand reduced its supplier qualification cycle from 14 weeks to 4 weeks by accessing the Pro List. They secured a Shenzhen-based OEM with full FCC/CE compliance, in-line quality control, and scalable capacity—without a single site visit.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In an era where speed-to-market defines competitive advantage, relying on unverified supplier leads is no longer sustainable. The SourcifyChina Pro List offers a proven, data-driven shortcut to high-performance manufacturing partnerships in China.
Don’t waste another procurement cycle on unreliable leads or delayed due diligence.
👉 Contact our sourcing specialists now to gain immediate access to the Pro List and receive a free supplier match consultation tailored to your product category and volume needs.
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team is available 24/5 to support global procurement operations with real-time insights, factory updates, and end-to-end sourcing guidance.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Gateway to Verified Manufacturing in China
Delivering Speed, Certainty, and Scale Since 2018
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.