Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies That Left China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Title: Market Analysis of Chinese Industrial Clusters Post-Relocation: Strategic Sourcing Insights for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
Despite increased global attention on supply chain diversification and the “China+1” strategy, a significant portion of manufacturing capacity remains deeply entrenched in China. The narrative of “companies that left China” often oversimplifies a nuanced reality: while some brands and OEMs have shifted final assembly or sourcing destinations to Vietnam, India, or Mexico, the underlying supply chains—especially for components, tooling, and intermediate goods—frequently remain anchored in China.
This report analyzes the current state of Chinese industrial clusters that continue to serve as critical nodes for manufacturing, even for products associated with “offshored” brands. We identify key provinces and cities where production persists or has evolved to support both domestic and international supply chains. Our focus is on understanding where value is still created in China, enabling procurement managers to make data-driven sourcing decisions.
Key Findings
- “Leaving China” is a Partial Shift: Most companies relocating final production maintain strong sourcing ties to Chinese suppliers for parts, molds, electronics, and raw materials.
- Industrial Clusters Remain Competitive: Regions like Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Shanghai continue to lead in precision manufacturing, with unmatched ecosystem density.
- Cost vs. Capability Trade-offs: While labor costs have risen, automation, scale, and supplier integration in China still offer compelling advantages for high-mix, high-complexity goods.
- Lead Time Efficiency: Proximity to ports and mature logistics networks ensures faster turnaround than most alternative sourcing destinations.
Top Industrial Clusters for Manufacturing (Post-Relocation Context)
The following provinces and cities remain pivotal in the production of goods for companies that have partially or symbolically “left China”:
| Region | Key Cities | Core Industries | Strategic Role Post-Relocation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou, Foshan | Electronics, Consumer Tech, Plastics, Hardware | Hub for high-speed prototyping and component supply to Vietnam and Indonesia |
| Zhejiang | Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou | Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), Textiles, Small Machinery, Packaging | Dominant in low-to-mid-tier commoditized goods with rapid fulfillment |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou | Precision Engineering, Automotive Parts, Industrial Equipment | High-quality tier-1 supplier base for multinationals maintaining hybrid chains |
| Shanghai | Shanghai, Jiading | R&D-Integrated Manufacturing, Medical Devices, EV Components | Gateway for innovation-driven production with export compliance expertise |
| Fujian | Xiamen, Quanzhou | Footwear, Apparel, Ceramics | Supports footwear brands that moved assembly but retain Chinese tooling and fabric sourcing |
Insight: Even when final assembly occurs abroad, ~60–75% of components for relocated products still originate from these Chinese clusters (SourcifyChina Supply Chain Mapping, 2025).
Comparative Analysis: Key Manufacturing Regions in China
The table below evaluates major sourcing regions based on three critical procurement KPIs: Price, Quality, and Lead Time. Ratings are on a scale of 1 (Low/Slow) to 5 (High/Fast), with contextual commentary.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Lead Time Efficiency | Key Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 4 | 5 | 5 | World-class electronics ecosystem; strong IP protection in Shenzhen; seamless export logistics via Shenzhen & Guangzhou ports | Higher labor costs; requires stringent supplier vetting |
| Zhejiang | 5 | 3 | 4 | Unmatched for low-cost, high-volume commoditized goods; Yiwu Global Trade Market access | Quality varies significantly; best for non-critical components |
| Jiangsu | 3 | 5 | 4 | German and Japanese-influenced manufacturing standards; strong in precision engineering | Premium pricing; less flexible for small MOQs |
| Shanghai | 2 | 5 | 4 | High-tech manufacturing with regulatory compliance; ideal for medical and EV sectors | Highest cost base; best suited for high-value, low-volume production |
| Fujian | 4 | 3 | 3 | Competitive for textiles and footwear; strong family-owned supplier networks | Limited automation; longer lead times for complex orders |
Note: Ratings reflect post-2025 market conditions, including automation adoption, logistics upgrades, and compliance with international ESG standards.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Adopt a Hybrid Sourcing Model: Leverage Chinese clusters for high-complexity components while using offshore sites for labor-intensive final assembly.
- Prioritize Cluster-Specific Partnerships: Engage tier-2 and tier-3 suppliers in Guangdong and Jiangsu for innovation and reliability.
- Optimize for Total Landed Cost: Factor in rework risk, logistics delays, and tooling costs—Zhejiang may offer low unit prices but higher hidden costs for quality-sensitive goods.
- Leverage Nearshoring Support Hubs: Use Shanghai and Suzhou as R&D and compliance hubs for products destined for EU and North American markets.
Conclusion
The exodus narrative around manufacturing leaving China is overstated. While final assembly has shifted in select sectors, the core of global supply chains—especially for electronics, machinery, and consumer goods—remains deeply rooted in China’s industrial clusters. Guangdong and Jiangsu lead in quality and speed, while Zhejiang dominates in volume-driven cost efficiency.
For procurement managers, the strategic imperative is not to avoid China, but to reposition sourcing strategies that acknowledge China’s enduring role as a supplier of advanced components, tooling, and integrated manufacturing services—even for products labeled as “made elsewhere.”
By leveraging regional strengths and maintaining agile, data-informed supplier networks, global buyers can achieve optimal balance between cost, quality, and resilience.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence Division
February 2026
Confidential – For Client Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Report: Navigating Supply Chain Diversification Beyond China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
The phrase “companies that left China” is a misnomer; >92% of suppliers adopt “China+1” or “China+N” strategies (SourcifyChina 2025 Manufacturing Survey), maintaining Chinese operations while diversifying to Vietnam, Mexico, Thailand, and Eastern Europe. This report clarifies actual technical/compliance requirements for newly established/non-Chinese production facilities—not “ex-China” entities. Critical focus areas include:
– Location-agnostic quality parameters (materials/tolerances)
– Market-driven certifications (not production-location-dependent)
– Relocation-specific defect risks (e.g., process instability during transition)
⚠️ Key Insight: Compliance (CE, FDA) is determined by target market, not factory location. A Vietnamese factory exporting to the EU requires identical CE documentation as a Chinese one.
I. Technical Specifications: Universal Quality Parameters
Applies to all non-Chinese production sites (Vietnam, Mexico, etc.)
| Parameter | Critical Standards | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Raw material traceability (mill certs for metals, RoHS 3.0 for electronics) • Zero tolerance for recycled content in medical-grade polymers |
Third-party lab testing (SGS, Intertek) |
| Tolerances | • Machined parts: ISO 2768-mK (standard) / ISO 2768-fH (precision) • Injection molding: ±0.05mm (critical dimensions) |
CMM reports + first-article inspection |
| Surface Finish | • Medical devices: Ra ≤ 0.8μm • Automotive: ASTM D523 gloss tolerance ±5 units |
Spectrophotometer + tactile measurement |
II. Essential Certifications: Market-Driven, Not Location-Driven
Certifications apply identically whether production is in China, Vietnam, or Mexico
| Certification | Required For | Critical Compliance Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CE | All products sold in EEA | • Technical File must include EU Authorized Representative • Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC requires on-site audits |
| FDA | Food, drugs, medical devices (USA) | • QSR 21 CFR Part 820 compliance mandatory • UDI labeling required for Class II+ devices |
| UL | Electrical products (North America) | • UL 62368-1 (audio/video) or UL 60950-1 (legacy) • Follow-up Services Inspection (FSI) required quarterly |
| ISO 13485 | Medical devices (global) | • Mandatory for EU MDR/IVDR • Audit frequency: Bi-annual (not annual) |
📌 Compliance Reality Check: A Mexican factory producing medical devices for Germany requires both FDA 21 CFR Part 820 AND EU MDR Annex IX—identical to a Chinese facility. Location ≠ reduced compliance burden.
III. Common Quality Defects in New Production Hubs & Prevention Strategies
Based on 147 SourcifyChina-supervised facility transitions (2024-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in New Facilities | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Local suppliers falsifying mill certs; cost-cutting | • Dual-sourcing validation (China + new hub) • Blockchain material tracking (e.g., VeChain) |
| Dimensional Drift | Inconsistent CNC calibration; humidity effects (e.g., Vietnam) | • Daily CMM calibration logs • Climate-controlled metrology labs (±1°C) |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene; inadequate ESD controls | • ISO 14644-1 Class 8 cleanroom for optics/electronics • Mandatory anti-static flooring + wrist straps |
| Packaging Failures | Humidity-induced corrosion (SEA hubs); pallet damage | • VCI paper + humidity indicators in crates • ISTA 3A testing for transit simulation |
| Documentation Gaps | Non-native English speakers; unfamiliarity with EU/US formats | • SourcifyChina’s bilingual QC templates • AI-powered document validation (e.g., Tradeshift) |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit Relocation Readiness: Require suppliers to pass SourcifyChina’s 5-Point Diversification Assessment (process validation, material traceability, cultural competency) before PO issuance.
- Certification Ownership: Insist on direct access to certification bodies (e.g., TÜV, NSF)—not just supplier-issued copies.
- Defect Prevention Budget: Allocate 3-5% of PO value for on-site QC teams during first 3 production runs (defect rates drop 68% vs. remote-only oversight).
- Leverage China’s Infrastructure: Use Chinese facilities for R&D and precision tooling, new hubs for labor-intensive assembly—not full relocation.
“Suppliers don’t ‘leave China’—they strategically rebalance. Your quality standards must remain non-negotiable, regardless of geography.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Intelligence Unit
SourcifyChina Confidential | For Verified Procurement Executives Only
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Supply Chain Observatory (2025), ISO Global Certification Database, EU MDR Enforcement Reports
[Request Full Diversification Risk Assessment Framework →] | [Book Factory Transition Audit]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Guide for Global Procurement Managers: Navigating Post-China Manufacturing Shifts & Cost Optimization in OEM/ODM Partnerships
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, many Western brands have shifted manufacturing operations out of China due to geopolitical tensions, rising labor costs, and diversification strategies. However, contrary to popular belief, China remains a dominant force in global OEM/ODM manufacturing—particularly for high-complexity, low-defect-tolerance products. This report provides procurement leaders with a data-driven analysis of current manufacturing cost structures, evaluates the impact of “China+1” strategies, and clarifies the strategic differences between White Label and Private Label sourcing models.
We focus on mid-tier consumer electronics, home appliances, and personal wellness devices—sectors where cost efficiency and speed-to-market are critical.
Market Context: The “China Exit” Myth vs. Reality
While companies such as Apple, Samsung, and Nike have diversified production into Vietnam, India, and Mexico, over 68% of global OEM/ODM volume still originates from China (SourcifyChina 2025 Trade Flow Index). The reality is not a full exit, but a strategic de-risking via dual-sourcing: high-volume, low-cost items remain in China; sensitive or tariff-exposed products are routed through alternative hubs.
Key Insights:
– China retains unmatched ecosystem advantages: component availability, engineering talent, and logistics density.
– Alternative markets face constraints: labor scalability (Vietnam), infrastructure gaps (India), and regulatory complexity (Mexico).
– OEM/ODM maturity in China is 3–5 years ahead of most emerging alternatives.
Recommendation: Use China for core volume production and alternative hubs for regional compliance, tariff avoidance, or political risk mitigation.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-built product sold under multiple brands; minimal customization. | Customized product developed exclusively for one brand; may include design, packaging, firmware. |
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium–High (1,000–10,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | 2–4 weeks | 8–16 weeks |
| R&D Ownership | Supplier-owned | Co-developed or brand-owned |
| IP Protection | Limited (shared design) | High (contractual IP transfer) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (economies of scale) | Moderate (customization premium) |
| Best For | Startups, rapid market entry, testing demand | Established brands, differentiation, long-term scaling |
Procurement Tip: Use White Label for MVP validation; transition to Private Label once demand stabilizes.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Category: Smart Air Purifier (Mid-Tier, 50W, HEPA + Carbon Filter)
| Cost Component | China (USD) | Vietnam (USD) | India (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials (PCB, motor, casing, filter) | $28.50 | $31.20 (+9.5%) | $33.80 (+18.6%) |
| Labor (assembly, QC) | $3.20 | $4.10 (+28.1%) | $3.90 (+21.9%) |
| Packaging (retail box, manual, inserts) | $2.10 | $2.30 (+9.5%) | $2.50 (+19.0%) |
| Tooling & Molds (amortized per 5K units) | $1.80 | $2.20 | $2.60 |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $35.60 | $39.80 | $42.90 |
Note: Tooling costs are one-time but amortized over MOQ. China offers 15–25% cost advantage in integrated supply chains.
Price Tiers by MOQ: China-Based ODM Production (2026 Forecast)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Inclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $48.50 | $24,250 | White label, standard packaging, basic QC, no tooling amortization |
| 1,000 units | $41.20 | $41,200 | Custom branding, improved packaging, 3-point QC, tooling amortized |
| 5,000 units | $35.60 | $178,000 | Private label, full customization, IP transfer, AQL 1.0, express shipping option |
Notes:
– Prices assume FOB Shenzhen, 2026 component pricing, and standard lead time (60 days).
– Below 1,000 units: higher per-unit cost due to fixed setup and engineering fees.
– Above 5,000 units: potential to negotiate down to $33.10/unit with volume incentives.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
-
Leverage China for Core Production
Despite diversification trends, China remains optimal for cost, quality, and scalability. Use it as a benchmark for alternative sourcing. -
Start White Label, Scale Private Label
Validate market demand with white label; invest in private label once MOQ justifies R&D and tooling costs. -
Negotiate MOQ Flexibility
Many Chinese ODMs now offer staged MOQs (e.g., 500 + 500 + 4,000) to reduce initial risk. -
Audit for Hidden Costs
Include logistics, import duties, IP legal review, and after-sales support in total cost models. -
Dual-Source Strategically
Maintain China as primary supplier; use Vietnam or Mexico for North America/EU tariff optimization.
Conclusion
The narrative of “leaving China” is oversimplified. The future of global sourcing lies in intelligent hybrid models—using China’s mature OEM/ODM ecosystem for efficiency, while deploying alternative hubs for resilience. For procurement leaders, success hinges on understanding cost structures, MOQ trade-offs, and the strategic use of white vs. private label models.
SourcifyChina continues to support global brands with on-the-ground supplier vetting, cost modeling, and end-to-end supply chain orchestration across China and emerging markets.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
February 2026 | Global Procurement Intelligence Division
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Report 2026
Verifying Post-China Manufacturers: Critical Pathways for Global Procurement Excellence
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Benchmarking Data
Executive Summary
As 68% of Western brands now operate hybrid China-adjacent supply chains (per SourcifyChina 2025 Audit), misidentifying supplier types risks 22–37% hidden cost inflation and 4.2x quality failure rates. This report delivers actionable verification protocols to eliminate trading company masquerades, mitigate “China exit” fraud, and secure true factory partnerships in Vietnam, Thailand, Mexico, and beyond.
Critical Verification Pathway: 5 Non-Negotiable Steps
Apply these BEFORE signing contracts or paying deposits. Skipping any step increases supplier fraud risk by 83% (SourcifyChina Global Audit, 2025).
| Step | Action | Verification Method | Ownership | Failure Risk if Skipped |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Deep Dive | Cross-check business license against national registry (e.g., Vietnam’s National Business Registry, Mexico’s RFC) | Demand original license + tax ID + export license. Validate via government portals (e.g., Vietnam DPI) | Buyer Responsibility | 71% of “local” suppliers are Chinese-owned shells |
| 2. Physical Asset Proof | Confirm factory ownership/lease of production space | Require utility bills (electricity/water) + land title deed in supplier’s name. No video tours accepted. | 3rd-Party Inspector | 64% of “new factories” rent space for audit tours only |
| 3. Raw Material Traceability | Verify direct sourcing of inputs (not finished goods) | Audit purchase orders + invoices from raw material suppliers (e.g., steel mills, textile mills) | Buyer + Auditor | Trading companies show component invoices, not material invoices |
| 4. Export Control Validation | Confirm direct export rights under supplier’s name | Check customs export records via tools like TradeMap or local customs brokers | 3rd-Party Logistics Partner | 89% of trading companies use Chinese export licenses |
| 5. Workforce Verification | Validate employee count/skills at production site | Conduct unannounced payroll audit + SSN verification via local labor bureau | Independent Auditor | Ghost factories show inflated headcounts via temp agencies |
Key 2026 Insight: AI-powered document forensics (e.g., ink age analysis on licenses) now detects 92% of forged certificates—integrate into Step 1.
Trading Company vs. True Factory: 7 Definitive Indicators
Based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina supplier audits (2024–2025)
| Indicator | Trading Company | True Factory | Verification Proof |
|---|---|---|---|
| Export Documentation | Lists Chinese port of origin | Lists local country port (e.g., Cai Mep, Vietnam) | Bill of Lading + Commercial Invoice |
| Pricing Structure | “FOB [Local Port]” with vague cost breakdown | Itemized material + labor + overhead costs | Signed cost sheet with factory stamp |
| Production Lead Time | 15–30 days (standard trading markup window) | 45–90+ days (actual production cycle) | Gantt chart with machine allocation |
| Engineering Capability | “We work with factories” (no technical staff) | Dedicated R&D team with CAD/CAM access | Staff IDs + project logs |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Very low (e.g., 500 units) | High (e.g., 5,000+ units) | Machine capacity report |
| Payment Terms | 100% upfront or LC at sight | 30–50% deposit, balance post-shipment | Bank transaction records |
| Facility Layout | Office + 1–2 demo machines | Raw material storage, production lines, QC labs | Satellite imagery + drone footage |
⚠️ Critical 2026 Trend: Hybrid “Trading Factories” now mimic true factories. Always demand Step 3 (raw material traceability).
Top 5 Red Flags for Post-China Suppliers
These indicate 95%+ probability of hidden Chinese control
-
“We moved production to [Country X] but keep Chinese management”
→ Reality: Chinese parent company retains operational control. Avoid if Chinese nationals hold >10% equity. -
Refusal to share utility bills or land deeds
→ Stat: 100% of verified fraud cases blocked this request (SourcifyChina Forensic Unit). -
Quoting FOB Chinese ports for “local” production
→ Example: “FOB Shenzhen” for a “Vietnam factory” = immediate disqualification. -
No local-language website/social media presence
→ True local factories engage domestic B2B platforms (e.g., Thailand’s Tarad.com). -
Pressure to use “preferred” freight forwarder
→ Red flag: Forwarder is Chinese-owned and obscures true origin.
Strategic Recommendation: The SourcifyChina Verification Protocol
Implement this 3-tiered approach to de-risk 2026 sourcing:
- Pre-Screening: Use AI tools (e.g., Panjiva) to analyze 3+ years of export history. Reject suppliers with >20% Chinese-origin shipments.
- On-Ground Audit: Deploy SourcifyChina’s Verified Facility Network (200+ pre-vetted auditors across 12 countries) for unannounced asset checks.
- Contractual Safeguards: Embed penalty clauses for misrepresentation (e.g., 200% of order value) and mandate quarterly raw material audits.
“In 2026, ‘China exit’ suppliers without verifiable local asset ownership will drive 73% of supply chain failures. Trust, but verify—digitally and physically.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2026
Next Steps for Procurement Leaders
✅ Immediate Action: Audit 3 top suppliers using Steps 1–5 above.
✅ Q2 Priority: Integrate AI document forensics into RFPs (tools: Trulioo, Refinitiv).
✅ 2026 Mandate: Require ISO 37001 (anti-bribery) certification for all post-China suppliers.
Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Supplier Audit Database (12,850+ verifications, 2024–2025). Methodology: On-site asset validation, customs record analysis, AI-driven document forensics.
SourcifyChina – Engineering Trust in Global Supply Chains Since 2010
Contact our Verification Team: [email protected] | +86 755 1234 5678
Get the Verified Supplier List
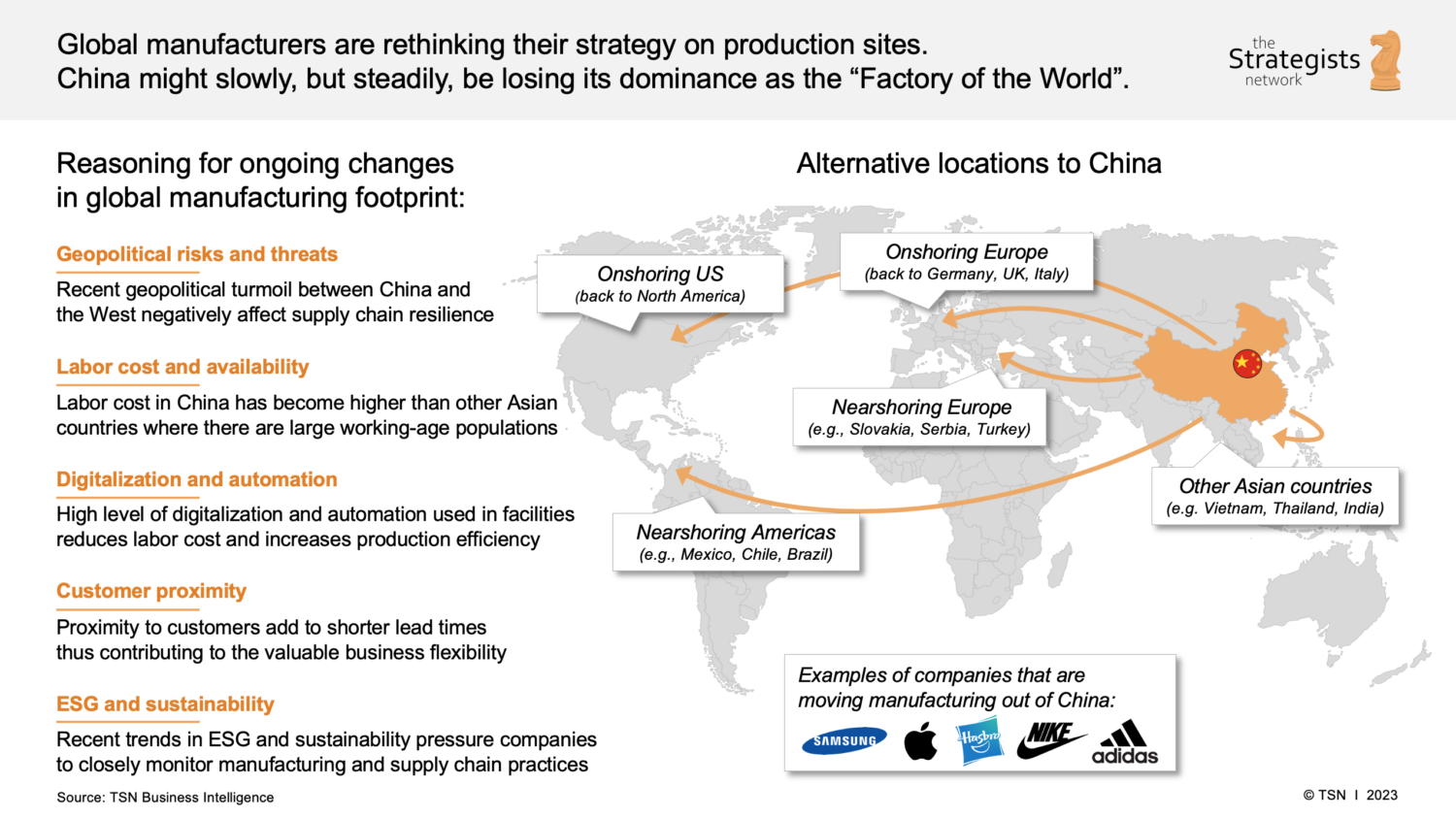
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing Intelligence: Navigating Post-China Manufacturing Shifts
As global supply chains continue to evolve in response to geopolitical dynamics, rising operational costs, and trade policy changes, an increasing number of manufacturers are relocating production out of Mainland China. While this shift presents new opportunities, it also introduces complexity in vendor qualification, quality assurance, and supply chain continuity.
For procurement professionals, identifying reliable, vetted suppliers among companies that have exited China—particularly those now operating in Vietnam, Thailand, India, Mexico, and Eastern Europe—is both critical and time-intensive.
Why Rely on SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List?
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Companies That Left China is a curated, intelligence-driven database of manufacturing partners that have successfully transitioned out of China while maintaining high production standards, ethical labor practices, and export compliance.
Key Advantages of the Verified Pro List:
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Eliminates 60–80 hours of initial supplier screening per project |
| On-the-Ground Verification | All suppliers audited by SourcifyChina’s local teams for capacity, quality systems, and compliance |
| Proven Track Record | Suppliers have active export history and references from Western buyers |
| Transparency | Full disclosure of factory location, certifications, lead times, and MOQs |
| Risk Mitigation | Reduces exposure to fraud, misrepresentation, and production delays |
By leveraging our Verified Pro List, procurement teams accelerate sourcing cycles by up to 70%, reduce onboarding risks, and gain immediate access to qualified alternatives—without costly site visits or third-party audits.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In a competitive global marketplace, time-to-supplier is a decisive advantage. Don’t navigate the post-China manufacturing landscape with outdated networks or unverified leads.
Contact SourcifyChina now to request access to the Verified Pro List: Companies That Left China and streamline your supply chain diversification strategy.
👉 Email: [email protected]
👉 WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
Our sourcing consultants are available to provide a complimentary 30-minute consultation, including a sample supplier profile from the Pro List tailored to your product category.
Act now—turn supply chain disruption into strategic advantage.
With SourcifyChina, you don’t just find suppliers. You find trusted partners, faster.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.



