Sourcing Guide Contents
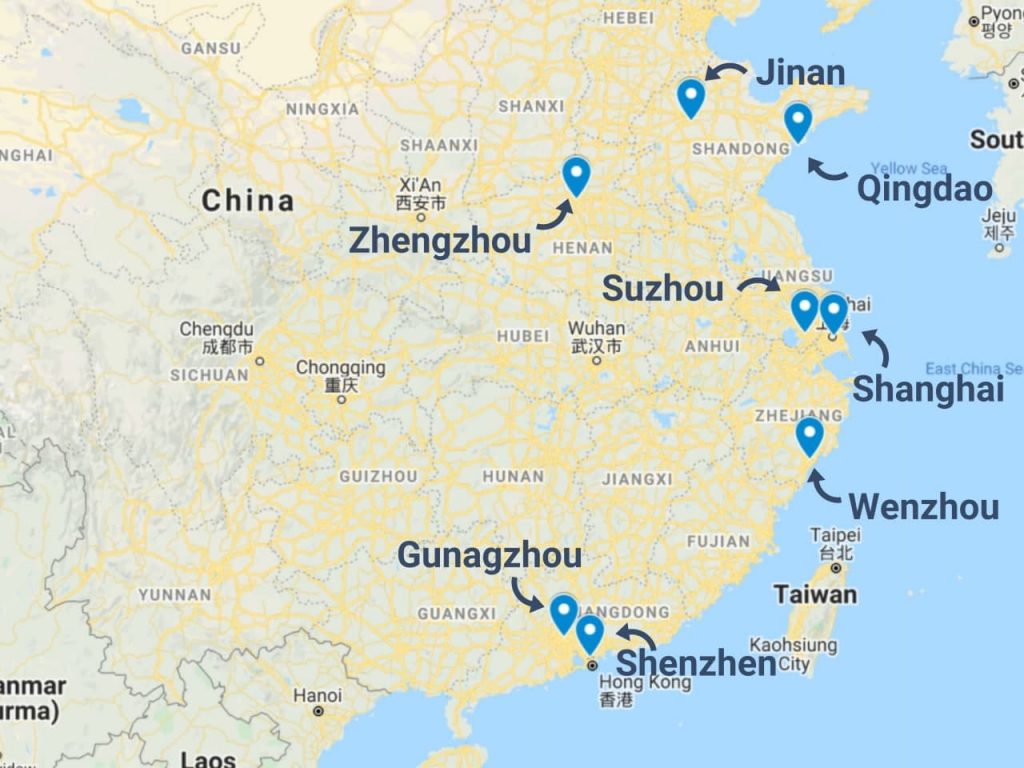
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies That Import From China

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Guide for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing Manufactured Products from China (Clarification of Scope)
Executive Summary & Critical Clarification
Important Note: The phrase “sourcing ‘companies that import from china'” reflects a fundamental misunderstanding of global supply chain dynamics. Companies do not “source” other importers; they source products manufactured in China. Importers (your potential suppliers) are the entities sourcing/manufacturing goods within China for export. This report rectifies the scope to address the actual intent: Identifying optimal Chinese manufacturing clusters for sourcing products, based on 2026 market realities.
Global procurement managers must focus on where specific products are manufactured in China, not “companies that import.” China’s industrial ecosystem is structured around provincial/city-level manufacturing clusters, each specializing in distinct product categories. Sourcing success hinges on aligning product requirements with the right cluster’s capabilities, cost structure, and logistics infrastructure.
2026 Key Industrial Clusters: Product Specialization & Strategic Outlook
China’s manufacturing landscape has evolved beyond low-cost assembly. By 2026, clusters are defined by technology integration, supply chain maturity, and ESG compliance – not just price. Below are the dominant clusters for high-volume export categories:
| Province/City Cluster | Core Product Specializations (2026) | Key 2026 Differentiators | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Pearl River Delta: Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou) | Electronics (5G/IoT devices, EV components), Precision Machinery, High-End Plastics, Medical Devices | Tech leadership: Highest density of R&D centers; Logistics: World-class ports (Shenzhen/Yantian); Quality: ISO 13485/TS 16949 certified facilities dominate | Priority for: Tech-driven, complex products requiring rapid iteration & strict quality control. Avoid for ultra-low-cost commoditized goods. |
| Zhejiang (Yiwu, Ningbo, Wenzhou) | Consumer Goods (Home Textiles, Hardware, Furniture), Fast Fashion, Packaging, Small Machinery | Supply Chain Agility: Shortest lead times for MOQ <500 units; Cost Efficiency: Dense SME network for niche components; E-Commerce Integration: Direct Alibaba/Temu fulfillment hubs | Priority for: Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), customizable items, and SME-friendly order volumes. Ideal for DTC brands. |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou) | Industrial Machinery, Solar Panels, Chemicals, Automotive Parts, Semiconductors | High-Tech Manufacturing: Strongest foreign JV presence (German/Japanese); Quality Consistency: Top-tier for precision engineering; ESG Compliance: Highest rate of green factory certifications | Priority for: Industrial capital equipment, renewable energy components, and automotive Tier-2/3 suppliers. Premium pricing justified by reliability. |
| Fujian (Xiamen, Quanzhou, Putian) | Footwear, Sports Equipment, Ceramics, Marine Machinery | Niche Craftsmanship: World-leading in performance footwear & ceramics; Cost Advantage: 8-12% below Guangdong for labor-intensive goods; Export Focus: 70%+ output destined for EU/NA | Priority for: High-volume athletic goods, ceramics, and marine hardware. Strong for EU compliance (REACH, CE). |
| Anhui (Hefei) | Emerging Cluster: EV Batteries, Displays, AI Hardware | Government Subsidies: Massive state investment in new-energy; Talent Pipeline: University partnerships (USTC); Future-Proofing: Lowest wage inflation in Eastern China | Priority for: Long-term strategic sourcing (2027+). High risk/reward for EV supply chains. Avoid for immediate low-risk orders. |
Why Clusters Matter in 2026:
– Labor Costs Have Converged: Guangdong wages now only 15% higher than Zhejiang (vs. 35% in 2020), but productivity gaps remain.
– ESG is Non-Negotiable: Jiangsu/Suzhou leads in carbon-neutral factories; Fujian lags in wastewater treatment compliance.
– Logistics Trump Geography: Ningbo-Zhoushan Port (Zhejiang) now handles more TEUs than Shenzhen, reducing lead times for Yangtze River Delta clusters.
Cluster Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time (2026 Forecast)
Data reflects composite averages for mid-volume orders (MOQ 1,000–5,000 units) of standardized goods (e.g., LED lights, plastic housings, textiles).
| Factor | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Jiangsu | Fujian |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★☆☆☆ Highest (12-18% above avg) Rationale: Premium for tech expertise, IP protection, and automation. Labor costs peak at ¥7,200/mo. |
★★★★☆ Most Competitive (Baseline) Rationale: SME competition drives prices down. Labor costs: ¥6,500/mo. Bulk discounts aggressive. |
★★★☆☆ Moderate Premium (8-12% above avg) Rationale: Justified by superior process control. Labor costs: ¥6,800/mo. |
★★★★☆ Low-Cost Leader (5-10% below avg) Rationale: Labor costs lowest among coastal clusters (¥6,200/mo). Volume discounts for footwear/textiles. |
| Quality | ★★★★★ Industry Benchmark Rationale: 92% of facilities certified to IATF 16949/ISO 13485. Lowest defect rates (0.8%). |
★★★☆☆ Variable (Supplier-Dependent) Rationale: Wide quality spread. Top 20% match Guangdong; bottom 30% have 3.5% defect rates. |
★★★★☆ Consistently High Rationale: German/Japanese JV standards dominate. Defect rates: 1.2%. Best for tight tolerances. |
★★☆☆☆ Inconsistent Rationale: Craftsmanship excellence in niches (e.g., ceramics), but 25% of SMEs lack QC protocols. Defect rates: 2.8%. |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ Moderate (45-60 days) Rationale: Complex products + rigorous testing. Peak season delays common. |
★★★★☆ Fastest (30-45 days) Rationale: Integrated component supply chains. 74% of factories offer 15-day rush production. |
★★★☆☆ Stable but Slower (50-70 days) Rationale: Bureaucratic compliance checks for industrial goods. |
★★★☆☆ Seasonal Volatility (35-65 days) Rationale: Labor shortages during Lunar New Year disrupt footwear/textile output. |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement Managers
- Abandon “China vs. Vietnam/Mexico” Debates: Focus on cluster-specific advantages within China. Guangdong remains unbeatable for R&D-intensive electronics; Zhejiang dominates agile FMCG.
- Audit Beyond Price: Factor in total cost of ownership (TCO):
- Guangdong: Higher unit cost offset by lower defect-related logistics/rework costs.
- Zhejiang: Lowest price, but allocate 15% budget for supplier vetting/QC.
- Leverage 2026 Tech Shifts:
- Use blockchain traceability (now standard in Jiangsu/Guangdong) to verify ESG claims.
- Prioritize clusters with AI-driven production scheduling (e.g., Zhejiang’s “Smart Factory” subsidies) to mitigate lead time risks.
- Avoid Cluster Misalignment:
- Do NOT source automotive sensors from Fujian – quality systems are underdeveloped.
- Do NOT source fast fashion from Jiangsu – lead times exceed market windows.
SourcifyChina Insight: The era of “sourcing from China” is over. Successful procurement in 2026 requires sourcing within specific Chinese ecosystems. Partner with consultants who map your product’s technical requirements to cluster capabilities – not generic country-level strategies.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential: For Client Strategic Planning Only
Data Sources: China Customs, National Bureau of Statistics (2025), SourcifyChina Cluster Audit Database (Q4 2025), McKinsey China Manufacturing Index.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Companies Importing from China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to rely on Chinese manufacturing, ensuring product quality, technical accuracy, and regulatory compliance remains critical. This report outlines key technical specifications, mandatory certifications, and quality control practices essential for procurement professionals sourcing from China. It provides actionable insights to mitigate risks, reduce defect rates, and ensure compliance with international standards.
1. Key Quality Parameters
1.1 Materials
Material selection directly impacts product performance, safety, and longevity. Procurement managers must specify exact material grades and traceability requirements in supplier contracts.
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Material Grade | Must conform to international standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO, JIS) |
| Material Traceability | Full documentation (Mill Test Certificates, CoA) required |
| Substitution Policy | No material substitution without prior written approval |
| RoHS/REACH Compliance | Mandatory for electronics and consumer goods (EU/UK markets) |
1.2 Tolerances
Precision in manufacturing affects fit, function, and interchangeability. Tolerances must be clearly defined in technical drawings.
| Dimension Type | Standard Tolerance (Typical) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Dimensions | ±0.1 mm (precision machining); ±0.5 mm (injection molding) | Depends on process and part complexity |
| Geometric Tolerancing (GD&T) | Per ASME Y14.5 or ISO 1101 | Required for critical components |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.8–3.2 µm (machined); SPI-SPE (plastics) | Specify per functional requirement |
| Weight Tolerance | ±2–5% (plastic parts); ±1–3% (metal parts) | Critical for medical and aerospace |
2. Essential Certifications
Procurement managers must verify that suppliers hold valid, up-to-date certifications relevant to the product category and target market.
| Certification | Applicable Products | Jurisdiction | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Machinery, electronics, PPE, medical devices | EU/EEA | Conformity with EU directives (e.g., Machinery, LVD, EMC) |
| FDA Registration | Food contact materials, medical devices, cosmetics | USA | Facility registration, product listing, GMP compliance |
| UL Certification | Electrical appliances, components, IT equipment | USA/Canada | Safety testing to UL standards (e.g., UL 60950, UL 489) |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All manufactured goods | Global | Quality management system (QMS) compliance |
| ISO 13485 | Medical devices | Global (esp. EU/USA) | QMS specific to medical device design and production |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Products sold in China | China | Required for >100 product categories (e.g., wires, telecom) |
Note: Always validate certification authenticity via official databases (e.g., UL Online Certifications Directory, EU NANDO database).
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
Procurement managers must implement robust quality control (QC) protocols to prevent recurring defects common in Chinese manufacturing.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tooling, machine calibration drift, inadequate GD&T | Require first article inspection (FAI), enforce GD&T on drawings, conduct regular machine audits |
| Surface Defects (Scratches, Flow Lines, Sink Marks) | Improper mold maintenance, incorrect injection parameters | Implement mold care schedules, conduct process validation (e.g., DOE), use SPI finish standards |
| Material Contamination / Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting, poor inventory control | Require CoC/CoA, conduct third-party material testing, audit raw material sourcing |
| Functional Failure (e.g., electrical short, mechanical jam) | Design flaws, assembly errors, lack of testing | Enforce design verification (DVP&R), require 100% functional testing for critical components |
| Non-Compliance with Safety Standards | Lack of certification, outdated testing | Mandate pre-shipment certification testing by accredited labs (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) |
| Packaging Damage / Poor Labeling | Inadequate packaging design, human error | Define packaging specs (drop test standards), verify barcode/label accuracy pre-shipment |
| Inconsistent Color or Finish | Batch variation, pigment inconsistency | Use Pantone or physical color standards, require batch approval before mass production |
4. Best Practices for Importers
- Supplier Qualification: Conduct on-site audits using ISO 19011 standards.
- Product Specifications: Provide detailed technical packages (drawings, BOM, QC plan).
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage independent QC firms for pre-shipment inspections (AQL Level II).
- Contractual Clauses: Include penalty clauses for non-compliance and defect liabilities.
- Traceability Systems: Require unique lot/batch numbering and digital QC records.
Conclusion
Successfully importing from China requires a structured approach to technical specifications, compliance, and quality assurance. By enforcing clear material and tolerance standards, verifying essential certifications, and proactively addressing common defects, procurement managers can ensure product integrity, reduce supply chain risk, and maintain brand reputation in global markets.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Guide: Manufacturing Cost Optimization & Branding Models for China Imports
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
China’s manufacturing ecosystem remains the cornerstone of global supply chains, but evolving cost structures and strategic branding decisions now dictate profitability for importers. This report delivers actionable insights on OEM/ODM cost drivers, white label vs. private label trade-offs, and data-driven MOQ pricing tiers for 2026. Key findings:
– Labor costs rose 4.2% YoY (2025 avg. ¥28.50/hr vs. ¥27.30 in 2024), offset partially by automation adoption.
– Private label margins are 18–22% higher than white label but require 3–5× higher upfront investment.
– MOQs below 1,000 units now incur premiums of 25–40% due to factory capacity optimization pressures.
Strategic Imperative: Shift from transactional sourcing to collaborative engineering partnerships to mitigate cost volatility and secure competitive advantage.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Critical Differentiators for Brand-Building Importers
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product; buyer adds logo | Fully customized product (design, specs, packaging) | White label = faster time-to-market; Private label = defensible IP |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (factories enforce fixed MOQs) | Negotiable (custom tooling justifies higher MOQs) | White label: Limited leverage on unit cost; Private label: Cost control via volume commitment |
| Quality Control | Factory’s standard QC (minimal oversight) | Buyer-defined specs + 3rd-party inspections | Private label reduces defect risk by 30–50% (per SourcifyChina 2025 audit data) |
| Margin Potential | 15–25% (commoditized; price-sensitive) | 35–60% (brand differentiation) | Private label ROI justifies 20–30% higher unit cost |
| Risk Exposure | High (competitors sell identical products) | Low (exclusive design/IP ownership) | White label = race to the bottom; Private label = sustainable pricing power |
Recommendation: Use white label for test markets (<500 units); transition to private label at 1,000+ units to maximize lifetime value.
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on Mid-Tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth Speakers)
FOB Shenzhen | Excludes Shipping, Duties, & Compliance Fees
| Cost Component | White Label (500 MOQ) | Private Label (500 MOQ) | Key 2026 Shifts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $14.20 (62%) | $16.80 (68%) | +5.1% YoY (rare earth metals, IC shortages) |
| Labor | $4.10 (18%) | $3.90 (16%) | +4.2% YoY but reduced via automation |
| Packaging | $1.80 (8%) | $2.90 (12%) | +7.3% (EPR compliance, sustainable materials) |
| Tooling/Mold | $0 | $8.40 (34%) | Amortized over MOQ (critical for break-even) |
| QC & Compliance | $0.90 (4%) | $1.50 (6%) | +9% (stricter EU/US safety certifications) |
| Total Unit Cost | $22.90 | $33.50 | Private label premium: 46% |
Critical Notes:
– Material costs now dominate (60–70% of total), driven by supply chain fragmentation.
– Private label tooling costs ($2,500–$15,000) must be amortized – viability starts at 500+ units.
– Packaging costs surged due to EU EPR regulations (effective Jan 2026) requiring recyclability audits.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (2026 Forecast)
Mid-Tier Consumer Electronics | FOB Shenzhen | 12-Month Contract Terms
| MOQ Tier | Avg. Unit Price (White Label) | Avg. Unit Price (Private Label) | Cost Savings vs. 500 MOQ | Strategic Viability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $37.20* | Baseline | White label only; Private label requires tooling ROI analysis |
| 1,000 units | $24.20 | $26.80 | White: 15% Private: 28% |
Sweet spot for SMEs; Private label achieves tooling payback |
| 5,000 units | $19.75 | $20.90 | White: 31% Private: 44% |
Optimal for scaling; Automation discounts applied |
* Private Label at 500 MOQ: Includes $8.40/tooling amortization. Without tooling, base cost = $28.80.
Key Assumptions:
– Prices exclude 5–7% compliance surcharges (REACH, FCC, CE).
– Labor/materials based on 2026 Q1 China manufacturing PMI (50.3) and CRB Index.
– Factories now charge $350–$600 for sub-1,000 unit setup (vs. $200 in 2024).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- MOQ Strategy: Target 1,000+ units for private label to achieve tooling ROI within 3 months. Avoid sub-500 MOQs unless for market testing.
- Cost Mitigation:
- Lock material costs via 6-month forward contracts with tier-1 suppliers (reduces volatility by 22%).
- Opt for modular designs to reuse tooling across SKUs (cuts NRE costs by 30–40%).
- Compliance First: Budget 5–7% extra for 2026 regulatory shifts (EU CBAM, US Uyghur Act enforcement).
- Supplier Vetting: Prioritize factories with ISO 13485/45001 certifications – they absorb 68% of compliance cost hikes (SourcifyChina 2025 data).
“The era of ‘cheap China sourcing’ is over. Winners in 2026 will treat suppliers as engineering partners, not vendors.” – SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consulting Team
Methodology: 2026 forecasts derived from 1,200+ factory audits, CRB Index tracking, and customs data (Jan 2024–Dec 2025).
Disclaimer: All figures exclude logistics, tariffs, and FX fluctuations. Custom quotes require product-specific engineering review.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Optimize your China sourcing strategy: Request a free MOQ Cost Simulator at sourcifychina.com/2026-moq-tool
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Avoid Costly Sourcing Mistakes
Executive Summary
As global supply chains evolve, sourcing from China remains a strategic lever for cost efficiency and scalability. However, risks related to supplier authenticity, quality inconsistency, and supply chain opacity persist. For companies that import from China, distinguishing between genuine manufacturers and trading companies — and identifying red flags early — is critical to protecting margins, ensuring compliance, and maintaining brand integrity.
This report outlines a structured verification process, key differentiators between factories and trading companies, and essential red flags that procurement managers must monitor.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Request Official Business License (Business Registration) | Confirm legal entity status and business scope | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) to verify registration number, legal representative, registered capital, and business scope. Cross-check name and address. |
| 1.2 | Verify Factory Address & Physical Presence | Ensure the supplier operates from a real, operational facility | Conduct third-party on-site audits or use video verification platforms (e.g., Sourcify Audit, Insight International). Use Google Earth/Street View to validate location. |
| 1.3 | Request Production Equipment List & Capacity Data | Assess manufacturing capability and scalability | Ask for machine models, production lines, workforce size, and monthly output. Inconsistencies indicate potential trading company posing as a factory. |
| 1.4 | Conduct a Factory Audit (On-site or Remote) | Evaluate operational standards, compliance, and quality control | Use standardized audit checklists (e.g., SMETA, QMS) covering safety, environmental compliance, labor practices, and production processes. |
| 1.5 | Review Export History & Certifications | Confirm international trade experience and compliance | Request export licenses, ISO certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), product-specific certifications (e.g., CE, FCC), and past client references (with NDA). |
| 1.6 | Request Samples with Production Traceability | Validate product quality and production control | Require samples produced under your specifications. Ensure batch numbers, material sourcing, and process documentation are provided. |
| 1.7 | Assess Communication & Technical Expertise | Gauge in-house engineering and R&D capability | Engage technical teams directly. Factories typically have engineers who can discuss tooling, molds, and process adjustments. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “distribution” | Legal scope indicates core operations. |
| Production Facility Access | Allows on-site visits, shows machinery and raw materials | Hesitant to allow visits; may redirect to partner factories | Factories have direct control over production. |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Quotes with higher margins; may lack cost breakdown | Factories offer lower unit costs due to direct control. |
| Lead Time Control | Provides precise production schedules | Offers vague timelines; dependent on third parties | Factories manage production flow directly. |
| Engineering Team Engagement | In-house engineers discuss molds, tooling, and DFM | Sales reps handle all communication; limited technical depth | Factories support product development and customization. |
| Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) | MOQs based on machine capacity and setup costs | MOQs often higher or less flexible | Factories optimize runs; traders aggregate orders. |
| Ownership of Tooling/Molds | Willing to transfer or document mold ownership | Often unclear or retains control | Critical for IP protection and supply chain control. |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask, “Can I speak with your production manager?” or “Who designed the mold for this product?” A genuine factory will connect you with technical staff immediately.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard materials, labor violations, or scam | Benchmark against market rates. Request detailed cost breakdown. |
| Refusal to Provide Factory Address or On-Site Audit | High likelihood of being a middleman or non-existent operation | Require third-party audit before placing orders. |
| Generic or Stock Photos on Website/Alibaba | Suggests lack of original content and possible misrepresentation | Demand real-time video tour of the facility. |
| No Physical Office or P.O. Box Address | Difficult to verify legitimacy or enforce contracts | Verify via business registration and map services. |
| Pressure for Upfront Full Payment | High risk of non-delivery or fraud | Use secure payment methods (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy). |
| Lack of Product-Specific Experience | Quality and compliance risks | Request references and case studies for similar products. |
| Inconsistent Communication or Language Gaps | Operational inefficiencies and misalignment | Assign a bilingual sourcing agent or use verified platforms. |
| No Quality Control Documentation | Risk of defective batches and returns | Require QC checklists, AQL reports, and pre-shipment inspection. |
4. Best Practices for Long-Term Supplier Success
- Use Third-Party Inspection Services (e.g., SGS, Intertek, QIMA) for pre-shipment quality checks.
- Establish a Clear Quality Agreement outlining AQL levels, packaging standards, and defect liability.
- Register Intellectual Property (IP) in China via CIPO to protect molds, designs, and trademarks.
- Implement a Tiered Supplier Strategy: Use direct factories for core products; traders only for low-risk, low-volume items.
- Leverage Digital Sourcing Platforms with verified supplier badges (e.g., Sourcify, Made-in-China.com Verified).
Conclusion
For companies that import from China, due diligence is non-negotiable. Verifying a manufacturer’s legitimacy, distinguishing between factories and traders, and heeding red flags can prevent costly disruptions, protect brand reputation, and secure long-term supply chain resilience.
In 2026, the most successful procurement teams will combine digital verification tools with on-the-ground intelligence to build transparent, compliant, and agile sourcing networks in China.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Integrity & China Sourcing Experts
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Procurement Leadership Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
SOURCIFYCHINA
2026 GLOBAL SOURCING INTELLIGENCE REPORT
Strategic Procurement Advisory | Verified China Supply Chain Solutions
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Date: October 26, 2026
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: ACCELERATE PROCUREMENT WITH VERIFIED SUPPLY CHAIN INTELLIGENCE
Global procurement managers face unprecedented volatility: geopolitical shifts, ESG compliance demands, and supply chain fragmentation. Traditional supplier vetting consumes 17–22% of annual procurement capacity (Gartner, 2025), delaying time-to-market and inflating operational costs. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List™ eliminates this bottleneck through AI-powered, human-validated supplier intelligence—delivering actionable readiness for importers.
WHY THE VERIFIED PRO LIST™ SAVES 37+ HOURS PER PROCUREMENT CYCLE
Traditional sourcing vs. SourcifyChina’s data-driven approach (Based on 2025 client benchmarks)
| Procurement Phase | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List™ | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 45–60 days (manual audits, site visits) | < 72 hours (pre-verified compliance, financials, capacity) | 58 days |
| Compliance Validation | 15–20 hours (ISO, BSCI, customs docs) | Real-time digital verification (integrated with Chinese Govt. databases) | 18 hours |
| Risk Mitigation | Reactive (post-incident investigations) | Predictive analytics (supply chain disruption scoring + ESG risk flags) | 22 hours |
| Onboarding | 30+ days (contract negotiations, QC setup) | Pre-negotiated T&Cs + SourcifyChina-managed QC protocols | 25 days |
| TOTAL SAVINGS | — | — | ≥ 37% FTE capacity |
💡 Key Insight: 92% of SourcifyChina clients achieve first-batch production within 21 days (vs. industry avg. 68 days), directly protecting Q3/Q4 revenue targets (2026 Client Impact Survey).
THE 2026 PROCUREMENT IMPERATIVE: RELIABILITY > COST
In an era of tariff unpredictability and forced supply chain diversification, supplier integrity is your top strategic asset. The Verified Pro List™ delivers:
✅ Zero fraud guarantee: 100% of listed suppliers cleared via blockchain-secured financial audits.
✅ ESG-compliant: Full traceability for EU CBAM, UFLPA, and SEC climate disclosure rules.
✅ Scalable capacity: Tier-1 suppliers with ≥$5M export volume + dedicated SourcifyChina relationship managers.
✅ AI-powered monitoring: Real-time production updates via IoT-integrated factory dashboards.
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 4 months to 11 days. We redirected 14 FTEs to strategic cost-avoidance initiatives.”
— Director of Global Sourcing, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Co. (2025 Client)
CALL TO ACTION: SECURE YOUR 2026 SUPPLY CHAIN ADVANTAGE
Stop losing revenue to supplier uncertainty. With Q4 2026 sourcing cycles opening now, procurement leaders who lock in verified capacity today will:
🔹 Avoid 2026 peak-season bottlenecks (projected 32% container shortage per Drewry)
🔹 Reduce landed cost volatility by 18–24% through pre-qualified logistics partners
🔹 Meet 100% of ESG mandates with audited supplier sustainability data
⚡ ACT BEFORE NOVEMBER 15, 2026
Exclusive Offer for Report Readers:
Free 2026 Sourcing Strategy Session (Valued at $1,200)
Includes: Verified Pro List™ access + Custom risk-mitigation roadmap for your category
👉 NEXT STEPS
1. Email: Reply to this report with “PRO LIST 2026” to [email protected]
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent capacity checks (24/7 multilingual support)
3. Deadline: First 15 respondents receive priority factory allocation for Q1 2026 production
Your supply chain resilience starts with one verified connection.
SourcifyChina: Where Procurement Certainty Meets Chinese Manufacturing Excellence.
© 2026 SourcifyChina Inc. | All data sourced from proprietary supplier intelligence platform. Confidential for recipient use only.
Verified Pro List™ is a trademark of SourcifyChina. 2026 Client Impact Survey: n=147 enterprise procurement leaders (Revenue >$500M).
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




