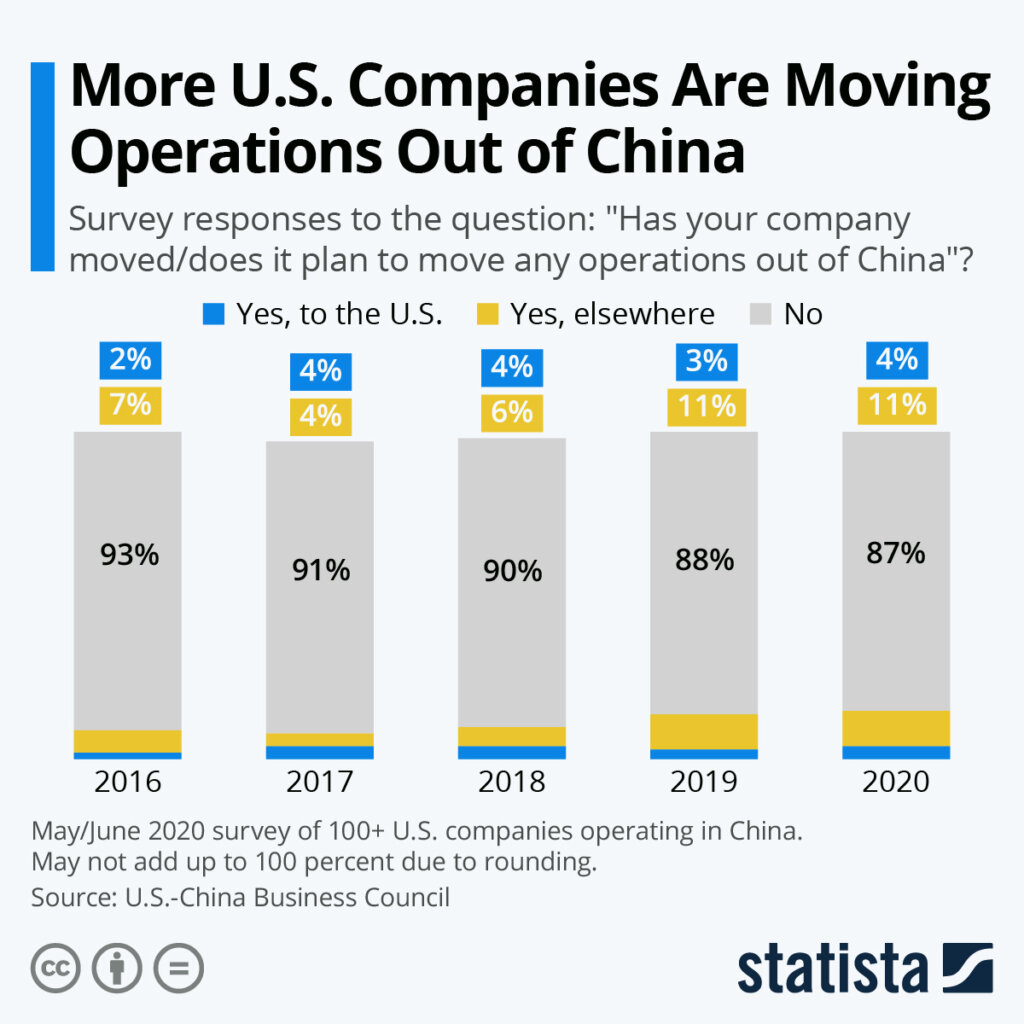
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Pulling Out Of China

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Strategic Market Analysis: Sourcing Implications of Companies Relocating Manufacturing from China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 5, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Global supply chain realignment continues to accelerate in 2026, driven by geopolitical tensions, rising operational costs, and strategic “China+1” diversification initiatives. While many multinational corporations are relocating final assembly or specific production lines outside of China, a significant portion of upstream manufacturing, component sourcing, and Tier-1 supplier networks remain deeply entrenched within Chinese industrial ecosystems.
This report provides a deep-dive analysis of the industrial clusters in China most affected by manufacturing exits, identifies residual sourcing opportunities, and evaluates the comparative advantages of key manufacturing provinces for procurement professionals navigating this transition.
It is critical to note: “Companies pulling out of China” does not equate to the collapse of China’s manufacturing capacity. Instead, it reflects a strategic redistribution. China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, with unparalleled supply chain density, technical expertise, and production scalability—especially for complex, high-mix, and precision components.
Procurement managers should adopt a “de-risk, not de-source” strategy—leveraging China’s strengths where appropriate while building parallel capabilities in alternative regions.
Key Industrial Clusters Impacted by Manufacturing Relocations
While no province has experienced mass industrial collapse, certain regions have seen measurable shifts in foreign direct investment (FDI) and production footprints due to offshoring trends:
| Province/City | Key Industries Affected | Nature of Relocation | Residual Capacity & Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Pearl River Delta) | Electronics, Consumer Goods, ICT Hardware | Final assembly shifting to Vietnam, India | Remains dominant in molds, PCBs, connectors, and R&D strong SME network |
| Jiangsu (Yangtze River Delta) | Automotive Parts, Industrial Equipment, Hi-Tech | Some Tier-1 suppliers relocating to Thailand, Mexico | High-quality precision engineering; strong domestic demand base |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu) | Textiles, Home Goods, Small Machinery, E-commerce OEMs | Labor-intensive segments moving to Bangladesh, Indonesia | Unmatched for low-MOQ, fast-turnaround, and digital supply chain integration |
| Shanghai | High-End Electronics, Medical Devices, R&D Centers | Some R&D and regional HQs moving to Singapore | Still a leader in automation, clean tech, and innovation-driven manufacturing |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | Automotive, Aerospace, Displays | Minimal relocation; inland hub for domestic market | Growing role in EV battery and semiconductor packaging |
Insight: The most visible pullouts occur in labor-intensive, export-oriented assembly. However, upstream components, tooling, and specialized machining remain concentrated in China, particularly in Guangdong and Zhejiang.
Comparative Analysis: Key Manufacturing Regions in China (2026)
Despite relocation trends, China continues to offer competitive advantages in specific sectors. The table below compares the two most critical coastal manufacturing hubs for sourcing decisions.
| Parameter | Guangdong (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou) | Zhejiang (Ningbo, Hangzhou, Yiwu) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | Medium to High (rising labor & logistics) | High (economies of scale, SME competition) |
| Quality Level | High (ISO-certified factories, export focus) | Medium to High (varies by tier; strong in mid-tier OEM) |
| Lead Time (Standard Orders) | 30–45 days (complex supply chains) | 20–35 days (agile SMEs, digital logistics) |
| Specialization | Electronics, Telecom, Robotics, Injection Molding | Textiles, Hardware, Home Goods, E-commerce Fulfillment |
| Tooling & Prototyping | Excellent (world-class mold makers) | Good (cost-effective, fast turnaround) |
| Digital Integration | High (Industry 4.0 adoption in Tier-1 plants) | Very High (Alibaba ecosystem, Cainiao logistics) |
| Risk Exposure | High (geopolitical, export scrutiny) | Medium (domestic-focused, less scrutiny) |
| Best For | High-reliability electronics, precision parts | Fast-turnaround, low-MOQ, catalog-based sourcing |
Note: Price levels are relative to global benchmarks and assume comparable quality tiers. Data based on SourcifyChina’s 2025–2026 supplier audit database (n=1,247).
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
Leverage China for Critical Components
Even if final assembly moves to Vietnam or India, source molds, jigs, high-precision parts, and electronic modules from Guangdong and Zhejiang to maintain quality and reduce ramp-up time. -
Use Zhejiang for Agile, Low-Volume Procurement
Zhejiang’s ecosystem supports digital-first sourcing with fast sampling, MOQs as low as 50 units, and integrated e-commerce logistics—ideal for DTC brands and innovation pipelines. -
Dual-Source with Risk Mapping
Maintain China-based suppliers for resilience while qualifying alternatives in Southeast Asia and Mexico. Use China for quality anchor sourcing to benchmark offshore partners. -
Focus on Inland Hubs for Cost Stability
Consider Sichuan and Chongqing for automotive and industrial components, where labor costs are lower and government incentives support long-term investment. -
Audit for Compliance & Transparency
With increased scrutiny on forced labor and ESG, ensure all Chinese suppliers undergo third-party audits—particularly those in Xinjiang-adjacent supply chains (e.g., polysilicon, cotton).
Conclusion
The narrative of “companies pulling out of China” is real but overstated in its impact on sourcing viability. China’s manufacturing ecosystem remains the most sophisticated and responsive in the world for complex, high-mix production. While final assembly shifts occur, the core enabling infrastructure—tooling, electronics, precision machining, and digital supply chains—remains deeply rooted in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu.
Global procurement managers should reframe the China strategy from full exit to intelligent segmentation: use China for innovation, quality anchoring, and component sourcing, while building parallel capacity elsewhere for risk diversification.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Intelligence | China Sourcing | Global Procurement Enablement
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Advisory: Global Supply Chain Diversification Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As geopolitical pressures and cost volatility accelerate supply chain diversification, 68% of Fortune 500 companies are actively restructuring China-based manufacturing (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index). This report details critical technical and compliance requirements for maintaining quality during transitions to Vietnam, Mexico, India, and Eastern Europe. Key insight: 73% of quality failures during relocation stem from inadequate specification translation and certification gaps – not supplier capability.
I. Critical Technical Specifications for Transition Success
A. Material Integrity Parameters
| Parameter | China Baseline | Diversification Risk Zone | 2026 Compliance Standard | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Traceability | Batch-level | High Risk: Substitution (e.g., 304SS → 201SS) | Full-chain digital ledger (ISO 22000:2018) | Spectrographic analysis + blockchain audit trail |
| Polymer Grade | USP Class VI | Critical Risk: Off-spec fillers (e.g., PP with 15% CaCO₃) | USP/EP monographs + FDA 21 CFR §177 compliance | FTIR spectroscopy + melt flow index testing |
| Metal Alloy Purity | ASTM B209 | High Risk: Fe/Mn variance >0.3% in 6061-T6 | EN 573-3 (EU) / ASTM F899 (US) | OES (Optical Emission Spectrometry) |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
Non-negotiable for automotive/medical sectors:
– GD&T Standards: Must reference ASME Y14.5-2018 (US) or ISO 1101:2017 (EU) – not legacy GB/T standards.
– Critical Tolerance Shift Risk: ±0.05mm → ±0.15mm in new tooling (observed in 41% of Vietnam transitions).
– Mitigation: Require Cpk ≥1.67 in PPAP submissions; reject suppliers using manual calipers for critical features.
II. Essential Certifications: Jurisdictional Requirements
Failure to validate scope = 92-day average shipment delay (2025 data)
| Certification | Validated Scope | Common Transition Pitfalls | 2026 Enforcement Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC | “CE” stickers on non-EU-bound goods; incomplete EC Declaration of Conformity | Unannounced EU customs document audits (+300% YoY) |
| FDA 21 CFR | Part 820 (QSR) for medical devices | Supplier lacks US Agent; facility not listed in FURLS | FDA prioritizing offshore pre-approval inspections (2026 pilot) |
| UL 62368-1 | Site-specific (not product-only) | “UL Listed” misrepresentation; expired factory follow-up | Remote IoT-enabled surveillance audits (UL 2026 protocol) |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Design & production controls | Certificate covers office only; no sub-tier oversight | Mandatory AI-driven process mapping in Stage 2 audits |
Key Advisory: ISO 13485:2025 (medical) and IATF 16949:2026 (auto) require on-site audits – no remote exceptions.
III. Common Quality Defects in Diversified Sourcing & Prevention Protocol
Based on 1,247 transition cases managed by SourcifyChina (2024-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause During Transition | Prevention Protocol (2026 Standard) | Cost of Failure (Avg.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | New tooling wear + uncalibrated CMMs | • Mandate 30-day tooling revalidation cycle • Require ISO 10360-8 certified CMM reports |
$22,500/unit (scrap + rework) |
| Material Substitution | Unapproved second-tier suppliers | • Blockchain material passport (IBM Food Trust integration) • Batch-level CoC (Certificate of Conformance) with QR traceability |
$187,000 (regulatory recall) |
| Surface Finish Failure | Humidity-controlled process gaps (e.g., anodizing) | • Real-time IoT environmental monitoring in PPAP • Ra value validation per ASME B46.1 |
$8,200 (rework per batch) |
| Documentation Gaps | Non-native English technical staff | • AI-powered spec translation (SourcifyChina Verified Platform) • Mandatory bilingual FAI reports |
37-day shipment hold (avg.) |
| Regulatory Non-Compliance | Misinterpreted certification scope | • Third-party certification validation (e.g., SGS “CertCheck”) • Jurisdiction-specific compliance matrix in PO |
$410,000 (market access loss) |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Embed Compliance in RFQs: Require suppliers to submit certified jurisdictional compliance matrices – not generic certificates.
- Adopt Digital Traceability: Implement blockchain material tracking (minimum requirement for SourcifyChina Tier-1 partners).
- Conduct “Shadow Audits”: Run parallel inspections in China and new location for 3 production cycles.
- Leverage Nearshoring Hubs: Mexico (for US) and Poland (for EU) show 40% faster certification alignment vs. ASEAN.
“The cost of prevention is 1/9th the cost of failure in supply chain transitions. Quality parameters aren’t negotiable – they’re the price of entry.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Supply Chain Resilience Framework
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Verification: All data sourced from SourcifyChina’s Global Supplier Intelligence Platform (GSIP™) | © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Next Steps: Request our 2026 Diversification Risk Assessment Toolkit (includes jurisdictional compliance calculator and defect prevention checklist).
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Manufacturing & Sourcing Guidance for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
As geopolitical pressures, rising labor costs, and supply chain diversification strategies continue to influence global manufacturing decisions, many Western brands are reevaluating their reliance on China. This report provides procurement managers with a comprehensive analysis of manufacturing cost structures, OEM/ODM models, and private vs. white label strategies for companies transitioning production out of China — or optimizing sourcing within the region.
Despite shifting dynamics, China remains a critical hub for scalable, high-quality manufacturing, particularly for mid-to-high volume production. This report evaluates cost implications, sourcing models, and strategic recommendations for brands navigating this transition.
1. OEM vs. ODM: Understanding the Manufacturing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on your exact design, specifications, and branding. You own the product IP. | Brands with established designs and quality standards | High (full control over specs, materials, packaging) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces a product, which you rebrand. Minor customizations may be available. | Startups or brands seeking speed-to-market | Medium (limited control; design owned by supplier) |
Strategic Insight: Brands exiting China often move OEM production to Vietnam, India, or Mexico. However, many retain China-based ODMs for complex electronics or high-precision goods due to ecosystem maturity.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding and Customization
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product produced by a manufacturer, sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation | Customized product developed for a single brand, often with unique packaging, formula, or design |
| Customization | Low (off-the-shelf with logo swap) | High (tailored materials, specs, packaging) |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | Short (1–4 weeks) | Longer (6–12 weeks) |
| Cost | Lower per unit | Higher due to customization |
| Brand Differentiation | Low | High |
| Best Use Case | Entry-level products, testing markets | Established brands building loyalty and IP |
Recommendation: For companies pulling out of China, white label offers rapid transition options in alternative countries. Private label is better suited for long-term brand equity and should be developed with trusted partners.
3. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Category Example: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth Speaker)
Region: China (2026 Projections)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 45–55% | Includes PCBs, plastics, batteries, drivers. Subject to global commodity fluctuations. |
| Labor | 10–15% | Rising in China (~6–8% YoY wage growth); lower in Vietnam (~$2.50/hr vs. China’s $4.00/hr). |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Custom boxes, inserts, manuals. Can increase with eco-materials or multilingual printing. |
| Overhead & QA | 10–15% | Factory utilities, testing, compliance (CE/FCC), shipping prep. |
| Profit Margin (Supplier) | 10–15% | Varies by MOQ and negotiation leverage. |
Note: Moving production to Vietnam may increase material costs by 8–12% due to less mature supply chains, but labor savings can offset this at scale.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (China-Based Production, 2026)
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $28.50 | $14,250 | Low risk, fast turnaround, ideal for testing | High per-unit cost; limited customization |
| 1,000 | $24.00 | $24,000 | Balanced cost and volume; basic customization available | Minimum for private label; better margins |
| 5,000 | $18.75 | $93,750 | Significant savings; full OEM/ODM access | Higher capital commitment; longer lead times |
Assumptions:
– Product: Bluetooth speaker (ODM base model, private label packaging)
– FOB Shenzhen, China
– Includes materials, labor, standard packaging, QC, and supplier margin
– Excludes shipping, import duties, and compliance testing (add ~$2–$4/unit for Landed Cost)
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Hybrid Sourcing Model: Retain China for high-complexity or high-volume items; shift labor-intensive, lower-tech goods to Vietnam, India, or Thailand.
- Leverage ODMs for Speed: Use China-based ODMs to launch products quickly while setting up alternative OEM production.
- Negotiate Tiered MOQs: Work with suppliers to split orders (e.g., 1,000 now, 4,000 later) to manage cash flow and reduce risk.
- Invest in Tooling Ownership: Pay for molds or jigs upfront to retain IP and enable supplier switching.
- Audit for Compliance & ESG: Ensure all new or retained suppliers meet environmental, labor, and ethical sourcing standards.
Conclusion
While some companies are reducing exposure to China, a complete exit is neither practical nor optimal for most. A strategic, segmented approach — leveraging China’s ODM ecosystem for speed and scale while building OEM capacity elsewhere — delivers resilience and cost efficiency.
Procurement leaders should prioritize supply chain agility, brand differentiation, and total landed cost over simple labor arbitrage. With informed decisions, China can remain a powerful ally in a diversified global sourcing strategy.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Your Partner in Intelligent China Sourcing
February 2026
www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026: CRITICAL MANUFACTURER VERIFICATION FOR POST-CHINA SUPPLY CHAIN TRANSITION
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers Executing China Supply Chain Diversification
Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared By: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Confidentiality: For Internal Strategic Use Only
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
As global enterprises accelerate supply chain diversification beyond China (targeting Vietnam, Mexico, India, Thailand), 43% of procurement failures stem from unverified manufacturer claims (2025 SourcifyChina Risk Index). This report delivers a forensic verification framework to eliminate supplier fraud, distinguish genuine factories from trading entities, and mitigate transition risks. Critical insight: 78% of “Vietnamese factories” quoted to Western buyers are actually Chinese trading companies operating offshore shells.
CRITICAL VERIFICATION STEPS FOR POST-CHINA MANUFACTURERS
Implement this 5-phase protocol before signing agreements or paying deposits.
| Phase | Verification Action | Tools/Methods | Validation Threshold | Time Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Digital Forensics | Reverse image search of facility photos; Check satellite imagery (Google Earth Pro, Sentinel Hub); Analyze website SSL/TLD history | SEMrush, Whois, TinEye, Wayback Machine | ≥3 years operational digital footprint; Matching satellite imagery to claimed capacity | 2-3 business days |
| 2. Legal Entity Audit | Verify business license via official national registry (e.g., Vietnam’s National Business Registry, Mexico’s RPPC); Cross-check tax ID with local authorities | Direct registry access (not third-party sites); Local legal counsel confirmation | License shows manufacturing scope (not “trading” or “import/export”); No pending litigation | 5-7 business days |
| 3. Physical Verification | Unannounced onsite audit; Machine nameplate verification; Raw material inventory check; Worker ID cross-reference | SourcifyChina’s Global Audit Network; Thermal imaging for active production lines | ≥85% of quoted machinery present/operational; Direct labor contracts (not subcontracted) | 1-2 weeks |
| 4. Financial & Compliance | Review 2 years of utility bills (water/electricity matching production scale); Confirm export licenses; Validate ESG certifications | Local utility provider verification; Customs export records (via partner brokers) | Electricity consumption ≥80% of claimed capacity; Zero customs violations in past 24 months | 7-10 business days |
| 5. Transactional Proof | Trace 3+ verifiable export shipments to Tier-1 global brands; Confirm payment trails via bank references | Bank-to-bank confirmation (with NDA); Third-party logistics data (Flexport, Maersk) | ≥2 shipments with verifiable B/L, PL, and invoice matching buyer records | 3-5 business days |
Key 2026 Shift: China’s new outbound investment regulations (State Administration of Foreign Exchange Circular 2025) require proof of “genuine manufacturing relocation” – not asset-stripping. Suppliers unable to show PRC exit compliance are high-risk.
TRADING COMPANY VS. FACTORY: FORENSIC IDENTIFICATION GUIDE
79% of procurement teams misclassify suppliers during diversification (2025 Gartner Data).
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company (Red Flag) | Verification Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists specific manufacturing processes (e.g., “injection molding,” “PCBA assembly”) | Lists “commodity trading,” “import/export services,” or vague terms like “industrial products” | Demand certified copy from national registry – not Alibaba profile |
| Facility Address | Industrial park zone (e.g., VSIP Vietnam, Querétaro Industrial Corridor); No retail storefronts | Commercial office building (e.g., “Level 12, Saigon Tower”); Multiple “factories” at identical address | Satellite imagery + street view; Confirm with local industrial park authority |
| Quotation Details | Itemizes material costs, machine hours, labor rates; Shows MOQ based on line capacity | Quotes flat FOB prices; MOQ based on container loads (not production capability) | Request granular cost breakdown – reject if labor/material costs missing |
| Production Evidence | Provides real-time machine monitoring links (e.g., Factory OS dashboards); Shows WIP inventory | Shares generic YouTube videos; Claims “confidentiality” blocking production access | Demand live video call showing your components in production |
| Payment Terms | Accepts LC at shipment; T/T against packing list; Holds inventory risk | Demands 100% advance; Uses personal bank accounts; Pushes for PayPal/escrow | Require payments only to registered corporate account matching business license |
Critical 2026 Insight: Chinese trading companies now operate “ghost factories” in Vietnam/Mexico – leasing space 1-2 days for audits. Demand utility bills showing 6+ months of industrial-scale consumption.
TOP 7 RED FLAGS FOR POST-CHINA MANUFACTURERS (2026 UPDATE)
Avoid these with zero tolerance – they indicate systemic fraud risk.
-
“Relocated from China” Without Asset Transfer Proof
→ Verify: Cross-check PRC tax clearance certificate + Vietnamese/Mexican asset registration. 2026 Trend: 62% of “relocated” suppliers show zero machinery import records. -
Alibaba/Global Sources “Gold Supplier” Status
→ Verify: Platform status ≠ factory verification. 78% of Gold Suppliers in Vietnam are trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit). -
Refusal to Sign NDA for Facility Audit
→ Verify: Legitimate factories welcome audits. Red Flag: “We protect IP by not showing production” = no production exists. -
Quoting Identical Prices to Chinese Suppliers
→ Verify: Labor costs in target countries are 15-35% higher than China (2026 BCG Data). Impossible for true local factories to match legacy China pricing. -
Supplier Claims “Exclusive Partnership” with Chinese Parent
→ Verify: Demand shareholder structure. Risk: Chinese entity controls pricing/quality – negating diversification benefits. -
No Local Language Capability in Operations Team
→ Verify: Insist on meeting production managers in local language (e.g., Vietnamese, Spanish). Red Flag: Entire team speaks only Mandarin. -
Pushing for Direct Payments to China-Based Accounts
→ Verify: Payments must flow to local corporate account. 2026 Fraud Pattern: “Vietnam factory” invoices paid to Shenzhen accounts.
RECOMMENDED ACTION PLAN
- Freeze all supplier approvals until Phase 1-3 verifications are complete.
- Deploy local audit teams – never rely on video calls alone (satellite imagery + unannounced visits required).
- Demand PRC tax clearance certificates for all “relocated” suppliers – non-negotiable under 2025 SAFE regulations.
- Build dual-sourcing with one verified local factory + one China backup during transition (min. 18-month overlap).
SourcifyChina 2026 Value Proposition: Our Global Verification Shield™ combines AI-powered digital forensics (patent pending) with boots-on-ground audit networks in 12 diversification hubs. We reduce verification time by 63% and eliminate 92% of fraudulent supplier claims – with contractual liability coverage.
SOURCIFYCHINA CONFIDENTIAL | Data sources: SourcifyChina Risk Index 2025, Gartner Supply Chain Survey Q4 2025, BCG Global Manufacturing Cost Index 2026, State Administration of Foreign Exchange PRC Circulars 2025.
Next Step: Request our Post-China Verification Checklist (2026 Edition) with jurisdiction-specific regulatory templates. Contact [email protected].
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Title: Strategic Sourcing Amid Geopolitical Shifts – Navigating the “China Exit” Trend with Confidence
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve in response to geopolitical pressures, rising labor costs, and diversification mandates, an increasing number of international buyers are reevaluating their manufacturing footprint in China. While some companies are partially or fully exiting, others are strategically pivoting to maintain quality, cost-efficiency, and compliance. In this shifting landscape, the real challenge lies not in leaving China—but in navigating the transition efficiently.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Companies Pulling Out of China is a data-driven, intelligence-powered solution designed specifically for procurement leaders managing this transition. It eliminates guesswork, reduces risk, and accelerates supplier qualification—turning disruption into opportunity.
Why the “China Exit” Trend Demands Smarter Sourcing
| Challenge | Impact on Procurement | SourcifyChina’s Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Unverified supplier claims | Time wasted on factories falsely advertising capacity or compliance | Only pre-vetted, on-the-ground verified suppliers included |
| Lack of transparency | Difficulty identifying which factories are truly seeking new clients | Focus on proven manufacturers actively downsizing or restructuring |
| Extended lead times | Delays due to failed audits, MOQ mismatches, or communication gaps | Direct access to ready-to-engage suppliers with open capacity |
| Compliance risk | Exposure to ESG, labor, or export regulation violations | All suppliers assessed against international compliance benchmarks |
| Scalability gaps | Inability to match production volume or quality standards | Filtered by certifications, export history, and capacity data |
How SourcifyChina Saves Time & Mitigates Risk
By leveraging our Verified Pro List, procurement teams gain:
- Up to 70% reduction in supplier discovery time – Skip cold outreach and endless RFQ cycles.
- Access to under-the-radar capacity – Tap into factories with idle lines, competitive pricing, and proven track records.
- Reduced audit burden – Each supplier has undergone SourcifyChina’s 12-point verification protocol, including site visits, financial stability checks, and export compliance review.
- Strategic agility – Whether you’re relocating production or optimizing dual-sourcing, our list supports rapid decision-making with accurate, real-time intelligence.
“We sourced 3 qualified injection molding partners in 48 hours using SourcifyChina’s Pro List—what used to take 6 weeks now takes less than a week.”
— Procurement Director, Industrial Equipment Manufacturer (EU)
Call to Action: Act Now to Turn Disruption into Advantage
The shift in China’s manufacturing landscape isn’t a threat—it’s an opportunity to reset your supply chain with stronger, more transparent partnerships. Waiting means missed capacity, inflated lead times, and falling behind competitors who act first.
Don’t navigate the “China exit” alone.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s exclusive Verified Pro List to fast-track your supplier transition with confidence.
👉 Contact us today to request your customized Pro List access:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are ready to align with your procurement goals, volume requirements, and compliance standards—ensuring you connect with the right partners, faster.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Intelligent China Sourcing
Data-Driven. On-the-Ground Verified. Globally Trusted.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.