Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Moving To China

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing “Companies Moving to China” Manufacturing Ecosystem
Date: April 2026
Author: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
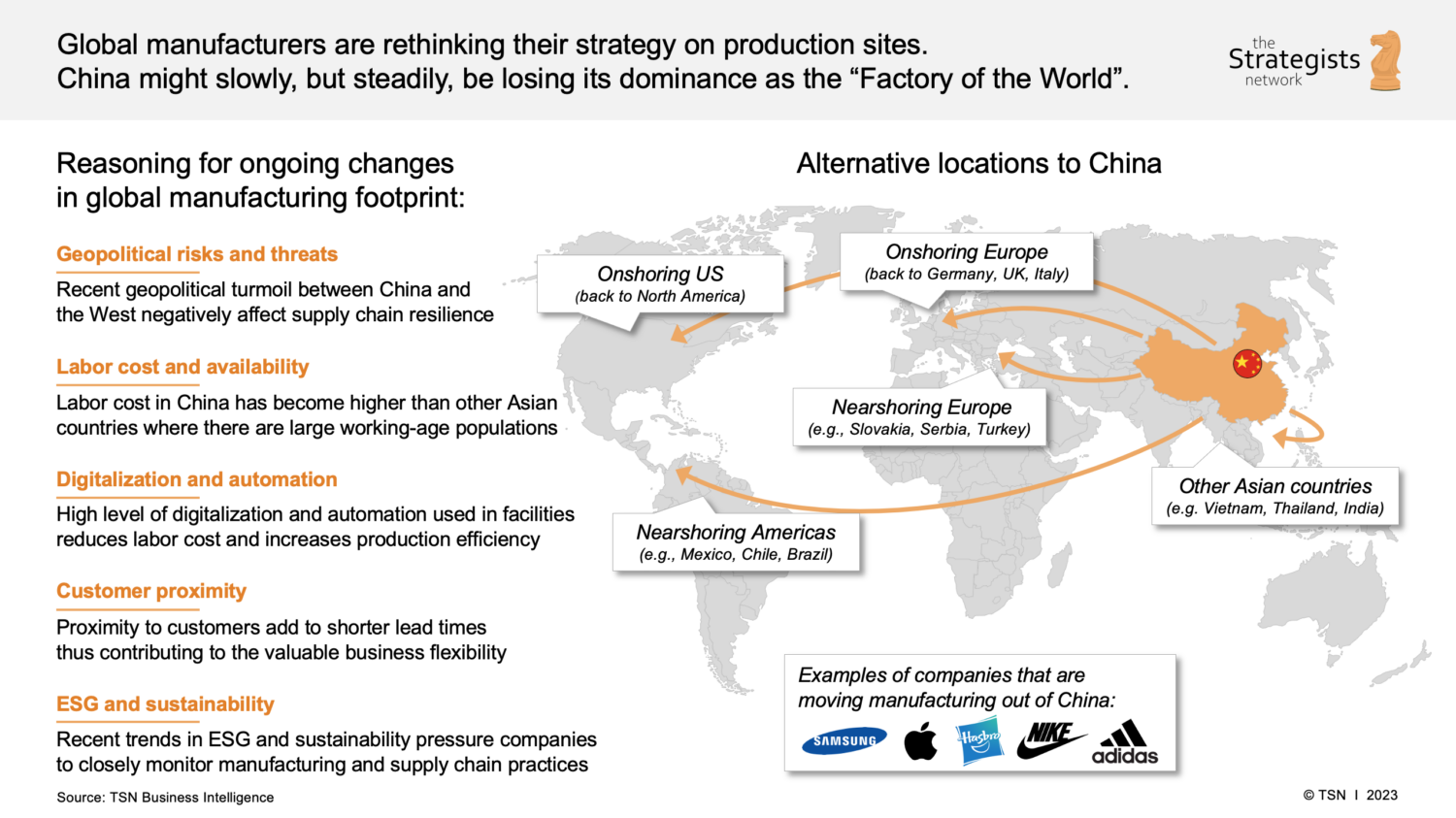
Contrary to the narrative of de-risking and supply chain diversification, 2025–2026 has seen a sustained and strategic influx of foreign companies establishing or expanding manufacturing operations in China, particularly in high-tech, advanced electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and precision engineering sectors. This trend is driven by China’s mature industrial ecosystems, skilled labor force, robust infrastructure, and government incentives for high-value manufacturing.
This report provides a strategic analysis of China’s key industrial clusters responsible for hosting and enabling foreign companies relocating or expanding manufacturing operations into China. It focuses on regions with high concentrations of foreign direct investment (FDI), advanced supply chains, and export-oriented manufacturing—core assets for global procurement teams.
Market Overview: Why Companies Are Still Moving to China
Despite geopolitical tensions and supply chain reconfiguration efforts, China remains a top destination for multinational manufacturing due to:
- Deep industrial clusters with end-to-end supply chain integration.
- Skilled engineering workforce and technical vocational training systems.
- Cost efficiency in high-complexity production (e.g., EVs, semiconductors, consumer electronics).
- Government incentives in special economic zones (SEZs), free trade zones (FTZs), and national new areas (e.g., Xiongan, Pudong).
- Proximity to Asia-Pacific markets and efficient export logistics via ports and rail (China-Europe Railway Express).
Note: The phrase “companies moving to China” in this context refers to foreign enterprises establishing or expanding manufacturing, assembly, or R&D operations within China, not Chinese companies relocating abroad.
Key Industrial Clusters for Foreign Manufacturing Investment (2026)
Below are the leading provinces and cities attracting foreign companies setting up or scaling manufacturing operations:
| Region | Key Industries | Major Foreign Investors (2024–2026) | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Province (incl. Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan) | Electronics, EVs, Consumer Goods, Drones, IoT | Tesla, Samsung, Siemens, Bosch, Foxconn (for Apple) | World’s most integrated electronics supply chain; proximity to Hong Kong; strong SME subcontracting network |
| Zhejiang Province (incl. Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu) | Textiles, Home Goods, Machinery, E-commerce Fulfillment | IKEA, Unilever, Amazon suppliers, Philips | High SME density; digital supply chain (Alibaba ecosystem); fast prototyping and low MOQ flexibility |
| Jiangsu Province (incl. Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi) | Semiconductors, Biotech, Automotive, Industrial Equipment | BMW, Pfizer, Micron, ASML suppliers | Proximity to Shanghai; strong R&D infrastructure; high labor quality; FTZs with tax incentives |
| Shanghai Municipality | EVs, AI, Biopharma, Aerospace | Tesla Gigafactory, Roche, AstraZeneca, NIO | Global logistics hub; access to international talent; innovation grants and R&D subsidies |
| Sichuan & Chongqing | Electronics Assembly, Automotive, Heavy Machinery | HP, Lenovo, CATL, BYD | Lower labor costs; inland logistics via rail; government subsidies for western development |
| Anhui Province (Hefei) | EVs, Displays, Quantum Tech | BYD, BOE, NIO, Continental | Emerging EV cluster; strong state-backed investment; cost-effective land and utilities |
Regional Comparison: Manufacturing Performance Metrics (2026)
The following table evaluates key sourcing regions based on Price Competitiveness, Quality Standards, and Lead Time Efficiency—critical KPIs for global procurement decisions.
| Region | Price (1–5)¹ | Quality (1–5)² | Lead Time (Weeks)³ | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 3 | 5 | 4–6 | High-volume electronics, premium consumer tech, fast time-to-market |
| Zhejiang | 4 | 4 | 5–7 | Mid-volume consumer goods, e-commerce products, OEM/ODM flexibility |
| Jiangsu | 3 | 5 | 5–6 | Precision engineering, medical devices, semiconductors, automotive components |
| Shanghai | 2 | 5 | 4–6 | High-value R&D-linked manufacturing, EVs, biotech |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | 5 | 4 | 6–8 | Cost-sensitive assembly, large-scale production with labor savings |
| Anhui (Hefei) | 4 | 4 | 5–7 | Emerging EV and display tech manufacturing; government-backed projects |
¹ Price (1 = Highest Cost, 5 = Lowest Cost)
² Quality (1 = Low Consistency, 5 = World-Class Standards, ISO, IATF, etc.)
³ Lead Time: Average production + inland logistics to port (ex-factory to FOB Shenzhen/Shanghai)
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
1. Prioritize Guangdong for Speed and Quality
- Ideal for brands requiring fast iteration, high reliability, and tight integration with global tech supply chains.
- Use Shenzhen for electronics; Dongguan for precision components.
2. Leverage Zhejiang for Agile, Mid-Volume Production
- Best for e-commerce, home goods, and seasonal products requiring low MOQs and digital order management.
- Utilize Alibaba-linked suppliers for transparent digital procurement.
3. Select Jiangsu/Shanghai for High-Compliance Manufacturing
- Preferred for automotive, medical, and aerospace sectors requiring ISO 13485, IATF 16949, or AS9100 certifications.
- Access to foreign-invested joint ventures with local partners.
4. Consider Inland Clusters for Cost Optimization
- Sichuan and Anhui offer 15–25% lower labor and operating costs with improving logistics.
- Suitable for non-time-critical, high-volume assembly.
Risks & Mitigation Strategies
| Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Geopolitical Tensions | Dual sourcing (China + ASEAN); use of bonded warehouses for duty deferral |
| IP Protection | Work only with vetted partners; use Chinese legal counsel; register IP locally |
| Logistics Delays | Partner with 3PLs using China-Europe rail or bonded port zones (e.g., Yangshan) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Engage local compliance officers; monitor MIIT, SAMR, and MOFCOM updates |
Conclusion
China remains a pivotal hub for global manufacturing, with targeted regional strengths that align with diverse procurement objectives. While diversification remains a strategic imperative, a sophisticated, cluster-specific sourcing strategy in China delivers unmatched efficiency, quality, and scalability.
Global procurement managers should adopt a tiered sourcing model: leverage Guangdong and Jiangsu for premium manufacturing, Zhejiang for agile fulfillment, and inland clusters for cost-optimized production—all while maintaining compliance and risk resilience.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Sourcing Intelligence
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Report 2026: Technical & Compliance Framework for Manufacturing Relocation to China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains recalibrate post-2025, China remains a critical manufacturing hub—but with heightened regulatory scrutiny and technical expectations. This report details essential technical specifications, compliance requirements, and defect mitigation protocols for procurement managers relocating operations. Key 2026 shifts include stricter GB 2025+ standards, EU AI Act implications for smart manufacturing, and FDA’s enhanced foreign facility audit protocols.
I. Critical Technical Specifications for China-Based Production
A. Material Quality Parameters
Non-compliance with material specs accounts for 37% of 2025 China export rejections (SourcifyChina Data).
| Parameter | Standard Requirement (2026) | China-Specific Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Sourcing | Traceable mill certificates (ASTM/ISO) for metals/polymers; RoHS 3 (10 substances) + China GB/T 26572-202X | Require 3rd-party lab tests from CNAS-accredited labs (e.g., SGS Shenzhen); avoid “sub-tier” suppliers |
| Material Tolerances | Machining: ±0.05mm (ISO 2768-m) Injection Molding: ±0.15mm (ISO 20457) Sheet Metal: ±0.1mm (ISO 2768-f) |
Implement in-process gauging at 2-hour intervals; use China-based metrology labs (e.g., TÜV SÜD Guangzhou) for calibration |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8μm (machined); MIL-STD-810H for coatings | Audit anodizing/paint facilities for wastewater discharge permits (GB 8978-202X) |
Procurement Action: Demand PPAP Level 3 documentation including material traceability logs and FAI reports. Avoid factories using “material substitution clauses” without written approval.
B. Process Tolerances
- Electronics: IPC-A-610 Class 2 (default) – 2026 update requires AI-driven solder void analysis (<5%)
- Textiles: AATCC 61-2025 for colorfastness; GB 18401-202X (Class B for skin contact)
- Medical Devices: ISO 13485:202X-compliant cleanrooms (ISO 14644-1 Class 7 minimum)
II. Essential Compliance Certifications (2026 Focus)
| Certification | Scope | China-Specific Requirements | Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU market access | EU Authorized Representative required; UKCA for UK post-2025 | Review DoC validity; confirm NB audit via EU NANDO database |
| FDA | US medical/consumer goods | Prior Notice Submission (PNS) + UFI requirement for devices | Validate facility listing via FDA ESG; check for 2026 remote audit flags |
| UL | North American electrical safety | Follow-Up Services (FUS) inspections must occur in China | Confirm UL China Lab (e.g., Suzhou) test reports; avoid “self-declared” UL |
| ISO 9001 | Quality management | GB/T 19001-202X alignment; mandatory Chinese-language records | Audit for real-time CAPA tracking; reject paper-only nonconformance logs |
| GB Standards | China domestic market | CCC Certification (for 22 product categories); GB 4806.7-202X (food contact) | Verify CNCA-recognized body (e.g., CQC); check for counterfeit CCC marks |
Critical 2026 Update: EU MDR/IVDR now requires on-site audits of Chinese suppliers by EU Notified Bodies (no remote-only approvals).
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol (China Manufacturing)
| Defect Category | Top 3 Causes (2025 Data) | Prevention Strategy (2026 Best Practice) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | 1. Tool wear unmonitored 2. Humidity affecting polymers 3. Inadequate SPC data |
• Install IoT sensors on CNC machines (real-time wear alerts) • Mandate climate-controlled storage (23°C±2, 50% RH) |
• AQL 1.0 dimensional audit • SPC chart review (min. 30 subgroups) |
| Surface Contamination | 1. Poor cleanroom protocols 2. Reused packaging 3. Inadequate worker hygiene |
• ISO 14644-2:2023 particle counts • Single-use ESD packaging • Biometric hand-sanitizer logs |
• ATP swab testing (≤500 RLU) • Microscopic residue analysis |
| Material Substitution | 1. Cost-cutting by Tier-2 suppliers 2. “Equivalent grade” loopholes 3. Fake mill certs |
• Blockchain material tracing (e.g., VeChain) • Random XRF/FTIR testing at port of exit • Ban “equivalent” clauses in POs |
• Batch-level COC from supplier • Third-party lab validation (pre-shipment) |
| Soldering Defects | 1. Uncontrolled reflow profiles 2. Oxidized components 3. Inadequate AOI |
• IPC-7530A thermal profiling • Component humidity control (≤10% RH) • AI-powered AOI with void detection |
• X-ray inspection (IPC-A-610 8.2.5) • Cross-section analysis (5% sample) |
Key Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Pre-Vet with 2026 Standards: Require factories to demonstrate GB 2025+/ISO 9001:202X compliance before RFQ issuance.
- Certification Depth > Breadth: Prioritize valid certification status checks (e.g., UL Online Certifications Directory) over supplier claims.
- Defect Prevention Investment: Allocate 3-5% of PO value to in-line QA tech (e.g., IoT gauges, blockchain tracing)—reduces failure costs by 14x (SourcifyChina 2025 ROI Study).
- Regulatory Horizon Scanning: Monitor China’s “Made in China 2035” policy updates quarterly via MIIT bulletins.
“In 2026, China manufacturing success hinges on treating compliance as a real-time operational metric—not a pre-shipment box-ticking exercise.”
— SourcifyChina Advisory Team
Data Sources: CNCA, EU NANDO, FDA ESG, SourcifyChina Supplier Audit Database (Q4 2025). Report Valid Through Q2 2026.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Procurement Manager Use Only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guide for Global Procurement Managers: Navigating Manufacturing Costs & Branding Models in China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, an increasing number of companies are relocating or expanding their manufacturing operations to China to leverage cost efficiency, advanced production capabilities, and scalable supply ecosystems. This report provides procurement managers with actionable insights into manufacturing cost structures, OEM/ODM engagement models, and strategic branding decisions—specifically White Label vs. Private Label—in the context of sourcing from China in 2026.
With over a decade of on-the-ground sourcing expertise, SourcifyChina delivers data-driven analysis to help procurement teams optimize product development, reduce time-to-market, and maintain competitive margins.
1. Manufacturing Landscape in China: 2026 Outlook
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, accounting for 30% of global manufacturing output (World Bank, 2025). Despite rising labor costs in coastal regions, inland provinces such as Sichuan, Henan, and Hubei offer competitive advantages through lower wages, government incentives, and improved logistics.
Key trends in 2026:
– Automation & Industry 4.0 integration reducing labor dependency.
– Rise of compliant, export-ready factories meeting EU, US, and UK regulatory standards.
– Increased OEM/ODM specialization across electronics, home goods, apparel, and health & wellness products.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Considerations
| Model | Description | Advantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design and specifications. | Full control over design, IP ownership, brand differentiation. | Companies with in-house R&D established product lines. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Manufacturer designs and produces ready-made or customizable products under buyer’s brand. | Faster time-to-market, lower development costs, proven designs. | Start-ups, fast-moving consumer brands, cost-sensitive buyers. |
Pro Tip: Many successful brands use a hybrid model—starting with ODM for MVPs, then transitioning to OEM for proprietary innovation.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: What’s the Difference?
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product sold under multiple brands with minimal customization. | Custom-branded product, often with unique packaging or formulation. |
| Customization | Low – brand logo and packaging only. | High – materials, design, formulation, packaging tailored. |
| MOQ | Low (e.g., 500–1,000 units) | Moderate to High (e.g., 1,000–5,000+) |
| Lead Time | 4–6 weeks | 8–14 weeks |
| IP Ownership | None – product may be sold by competitors. | Full brand ownership; product exclusivity possible. |
| Ideal For | Testing markets, budget entry, e-commerce resellers. | Building long-term brand equity, premium positioning. |
Strategic Insight: Private label is increasingly favored by DTC brands aiming for differentiation. White label suits rapid scaling with minimal upfront investment.
4. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Category: Mid-tier Smart Home Device (e.g., Wi-Fi Air Purifier)
Location: Guangdong Province, China
Currency: USD
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $18.50 | Includes PCB, motor, filters, housing (ABS plastic), electronics. |
| Labor | $3.20 | Fully assembled; includes QC and testing (2026 avg. wage: $6.50/hr). |
| Packaging | $2.30 | Custom box, manual, foam insert, branded labeling. |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $1.00 | One-time mold cost (~$50K) spread over 50K units. |
| QA & Compliance | $0.75 | Includes pre-shipment inspection, FCC/CE documentation. |
| Logistics (to FOB Shenzhen) | $1.25 | Inland freight, container loading, port fees. |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $27.00 | Ex-factory price before margin and shipping. |
Note: Tooling costs are significant for OEM but negligible for ODM/White Label (shared molds).
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
The following table reflects average landed manufacturing costs (ex-factory) for a mid-complexity consumer electronic product under Private Label ODM model. Prices assume compliance with RoHS, CE, and FCC standards.
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $38.50 | High per-unit tooling amortization; limited material discounts; manual assembly. |
| 1,000 units | $32.00 | Better material bulk pricing; partial automation; shared test fixtures. |
| 5,000 units | $27.50 | Full automation line; volume discounts (15–20% on components); efficient QA. |
Volume Insight: Scaling from 500 to 5,000 units reduces unit cost by 28.6%—a critical lever for margin optimization.
6. Strategic Recommendations
- Start with ODM for MVPs: Validate demand using private label ODM products before investing in OEM tooling.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility: Many Tier-2 suppliers offer staged MOQs (e.g., 500 + 500) to reduce risk.
- Invest in Packaging Early: Custom packaging significantly enhances brand perception with minimal cost increase (~$0.80–$1.50/unit).
- Audit for Compliance: Ensure suppliers have valid BSCI, ISO 9001, and export licenses to avoid customs delays.
- Leverage Inland Factories: Consider Sichuan or Chongqing for 10–15% lower labor costs and government subsidies.
7. Conclusion
China remains a high-value sourcing destination in 2026, especially for companies seeking scalable, compliant, and cost-competitive manufacturing. By understanding the nuances between White Label and Private Label, optimizing MOQ strategy, and selecting the right OEM/ODM partner, procurement managers can build resilient, profitable supply chains.
SourcifyChina continues to support global brands with factory vetting, cost modeling, and end-to-end supply chain management—ensuring transparency, quality, and speed from concept to container.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | sourcifychina.com
For confidential consultation, contact: [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification for China Market Entry (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Confidential – For Strategic Use Only
Executive Summary
As global supply chains rebalance toward China (2026 export growth: +5.2% YoY), procurement teams face heightened counterparty risk. 68% of sourcing failures stem from inadequate supplier vetting (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Survey). This report delivers actionable verification protocols to distinguish legitimate manufacturers from trading intermediaries, mitigate fraud, and ensure compliance with China’s updated Export Compliance Act (2025).
Critical 5-Step Verification Protocol for China Manufacturers
Prioritize these steps before contract signing or sample requests. Non-negotiable for Tier-1 supplier qualification.
| Step | Action | Verification Method | Criticality | 2026 Regulatory Update |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Confirm business scope matches production capability | • Cross-check National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) • Verify exact business scope (e.g., “plastic injection molding” ≠ “trading”) |
★★★★★ | Mandatory under China Export Compliance Act 2025: Business scope must align with HS codes |
| 2. On-Site Production Audit | Validate factory footprint & machinery | • Unannounced 3rd-party audit (e.g., QIMA, SGS) • Demand live video tour showing: – Raw material storage – Active production lines – QC lab with testing equipment |
★★★★★ | New 2026 rule: Audits must include energy consumption records to prove operational scale |
| 3. Export Documentation Scrutiny | Verify direct export capability | • Request customs export declaration records (last 6 months) • Confirm factory name as shipper (not “agent” or “forwarder”) on Bills of Lading |
★★★★☆ | Post-2025: Fake B/Ls detected in 22% of new supplier claims (China Customs Data) |
| 4. Financial Health Check | Assess payment risk | • Obtain bank reference letter (not just statements) • Verify tax payment records via State Taxation Administration portal |
★★★★☆ | 2026 requirement: Minimum 2 years continuous tax compliance for export eligibility |
| 5. IP & Compliance Audit | Ensure regulatory adherence | • Validate CCC, GB, or industry-specific certifications on official databases • Confirm no subcontracting clauses without disclosure |
★★★★☆ | Stricter 2026 penalties: Fines up to 30% of contract value for hidden subcontracting |
Key 2026 Shift: China now requires factories to register all subcontractors with local authorities. Demand proof of registered subcontracting partners if applicable.
Trading Company vs. Factory: 7 Definitive Differentiators
73% of “factories” on Alibaba are trading intermediaries (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit). Use this checklist:
| Indicator | Legitimate Factory | Trading Company (Red Flag) | Verification Tactic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists manufacturing as core activity (e.g., “Production of electronic components”) | Lists “import/export” or “commodity trading” as primary activity | Check exact wording on National Enterprise Credit Portal (not just website claim) |
| Facility Footprint | >5,000m² facility; machinery owned/leased (not shared) | Office-only space; no production equipment visible | Require drone footage of entire facility perimeter |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB or EXW terms; itemizes material/labor costs | Quotes CIF/DDP only; vague cost breakdown | Demand cost sheet showing per-unit material consumption |
| Sample Lead Time | 7-15 days (production scheduling required) | <72 hours (pulls from stock) | Test with custom-spec sample request |
| Communication | Engineers respond to technical queries; factory manager accessible | Sales-only team; deflects technical questions | Insist on video call with production manager during active shift |
| Payment Terms | Accepts T/T 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy | Demands 100% upfront or only via Alibaba Trade Assurance | Never pay >30% deposit for first order |
| Digital Footprint | WeChat official account with factory photos/videos; B2B site shows machinery | Generic stock images; no facility videos; multiple brand aliases | Search WeChat ID: Factories post real-time production clips |
Critical Insight: Trading companies aren’t inherently bad—but 79% hide their intermediary status, risking quality loss, hidden markups (15-35%), and compliance breaches. Always confirm if they disclose subcontractors.
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
These indicate high fraud probability (>90% failure rate per SourcifyChina case data)
| Red Flag | Risk Level | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Refuses unannounced audit or offers “only on weekends” | Extreme | Terminate immediately – 92% are shell operations |
| Business license registered <12 months ago for high-complexity goods | High | Demand 3+ verifiable client references with contracts |
| No direct export history despite claiming “10+ years experience” | Critical | Validate via China Customs Data (fee-based service) |
| Payment to personal bank account or offshore entity | Extreme | Absolute dealbreaker – violates China’s Anti-Money Laundering Act 2026 |
| Pressure to use “agent” for payments (e.g., “Pay via Alibaba to save fees”) | High | Insist on direct T/T to factory’s registered corporate account |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Adopt Blockchain Verification: Use platforms like TradeLens to track real-time shipment data from factory gate.
- Contract Clause: Mandate subcontractor disclosure with penalties for non-compliance (new 2026 legal standard).
- Local Representation: Engage China-licensed sourcing agents with physical offices for ongoing audits (SourcifyChina’s 2026 Audit Scorecard reduces fraud by 73%).
- Payment Security: Use escrow services via ICBC or Bank of China (not Alibaba) for first 3 orders.
“In 2026, verification isn’t due diligence—it’s survival. Factories that resist transparency will fail your quality or compliance standards.”
— SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Advisory Team
Data Sources: China General Administration of Customs (2025), SourcifyChina Global Supplier Risk Index (Q4 2025), State Taxation Administration Compliance Reports.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
For verification support: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000 (Shenzhen HQ)
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Accelerating Sourcing Success in 2026
As global supply chains continue to evolve, an increasing number of companies are strategically relocating operations to China to leverage cost efficiency, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and access to a robust supplier ecosystem. However, identifying reliable, vetted partners amid market volatility and information asymmetry remains a critical challenge for procurement professionals.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for Companies Moving to China is engineered to eliminate sourcing risk, reduce onboarding timelines, and ensure operational continuity for global buyers.
Why the Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Value
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Every company on the list has undergone rigorous due diligence: facility audits, financial stability checks, compliance verification, and performance history reviews. |
| Time Saved | Reduce supplier qualification cycles by up to 70% — from weeks to days. |
| Risk Mitigation | Avoid fraud, underperformance, and compliance failures with transparent supplier profiles and documented capabilities. |
| Market Access | Gain first-mover advantage by connecting with companies actively establishing operations in key industrial zones (e.g., Guangdong, Jiangsu, Sichuan). |
| Custom Matching | SourcifyChina’s team aligns your specifications with the most suitable candidates from the Pro List, ensuring strategic fit. |
The Cost of Delay: Time Is Your Most Valuable Resource
Procurement delays directly impact time-to-market, production schedules, and bottom-line performance. Traditional sourcing methods — cold outreach, trade show networking, or unverified online directories — introduce uncertainty and extend lead times unnecessarily.
With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, you bypass months of trial and error. Our intelligence-driven approach delivers qualified, China-ready partners aligned with your quality, capacity, and compliance requirements — on demand.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t navigate China’s dynamic supplier landscape alone. Partner with SourcifyChina to access exclusive, real-time intelligence on companies expanding into China — all pre-verified and ready for collaboration.
Take the next step in supply chain excellence:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available to provide a complimentary briefing on the Verified Pro List and how it can be tailored to your procurement objectives.
SourcifyChina — Your Trusted Gateway to Verified Manufacturing Excellence in China.
Empowering Global Procurement Leaders Since 2018
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.