Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Moving From China To Usa
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Title: Market Analysis on Manufacturing Relocation Trends – Sourcing Suppliers Amid China-to-USA Industrial Shifts
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
In response to evolving global trade dynamics, supply chain resilience strategies, and geopolitical shifts, an increasing number of manufacturers are relocating production capacity from China to the United States. However, many of these companies maintain significant operational footprints in China—particularly for R&D, component sourcing, or transitional production. For global procurement managers, understanding where in China these transitioning manufacturers are concentrated is critical for maintaining continuity, securing transitional supply, and identifying high-performance suppliers during this period of industrial realignment.
This report identifies the key industrial clusters in China associated with companies undergoing or planning relocation to the USA. It analyzes regional manufacturing strengths, cost structures, and performance metrics to support strategic sourcing decisions. A comparative analysis of major provinces—Guangdong and Zhejiang—is provided, with insights into price competitiveness, quality standards, and lead time efficiency.
Market Context: The China-to-USA Manufacturing Shift
Since 2020, over 1,200 multinational and Chinese-owned manufacturers have announced partial or full relocation of production to the United States, driven by:
- U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and CHIPS and Science Act incentives
- Tariff avoidance strategies (Section 301)
- Nearshoring and friend-shoring mandates
- Customer demand for “Made in USA” branding
Despite relocation, most companies retain sourcing relationships in China due to established supply chains, skilled labor, and mature component ecosystems. Procurement managers can leverage this transitional phase to engage high-capability suppliers in key Chinese clusters that are already adapting to global shifts.
Key Industrial Clusters in China for Relocating Manufacturers
The following provinces and cities are home to a high concentration of manufacturers actively relocating or expanding U.S. operations:
| Province/City | Key Industries | Relocation Activity Level | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Dongguan, Shenzhen, Guangzhou) | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Telecom Equipment, EV Components | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | Proximity to Hong Kong; strong export infrastructure; high concentration of U.S.-facing OEMs |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo, Hangzhou, Yiwu) | Machinery, Textiles, Hardware, Home Appliances | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | Export-oriented SMEs; agile production; strong logistics via Ningbo-Zhoushan Port |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing) | Semiconductors, Advanced Manufacturing, Industrial Automation | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Moderate-High) | High-tech zones; German and U.S. joint ventures; strong quality control |
| Shanghai | High-Tech Equipment, Medical Devices, Automotive R&D | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Moderate) | Innovation hub; talent pool; many multinationals managing dual-site operations |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | Aerospace, Electronics, IT Hardware | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (Moderate) | Inland cost advantage; government incentives; growing U.S. investment interest |
Insight: Guangdong and Zhejiang lead in volume and velocity of relocation activity, particularly among mid-tier exporters and OEMs serving North American markets.
Comparative Analysis: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang Manufacturing Hubs
The following table compares two of the most strategic sourcing regions for procurement managers engaging with Chinese suppliers in transition:
| Metric | Guangdong | Zhejiang |
|---|---|---|
| Average Unit Price (Relative) | Medium-High (⭐⭐⭐☆☆) | Medium (⭐⭐⭐⭐☆) |
| Rationale | Higher labor and land costs; premium for high-tech zones (e.g., Shenzhen) | Competitive pricing due to dense SME networks and scale economies in Ningbo/Yiwu |
| Quality Consistency | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Good to High) |
| Rationale | Strong ISO/CE compliance; experienced QC teams; U.S. audit-ready facilities | Improving standards; variable among SMEs; top-tier clusters (e.g., Hangzhou) meet export requirements |
| Average Lead Time (Standard Orders) | 3–5 weeks | 4–6 weeks |
| Rationale | Superior logistics (proximity to Shenzhen & Hong Kong ports); high automation | Slightly longer inland logistics; port congestion at Ningbo occasionally impacts timelines |
| Supplier Maturity (U.S. Market Experience) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Very High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) |
| Rationale | Long-standing relationships with U.S. brands; fluent in English, ERP integration | Growing U.S. exposure; increasing adoption of Western compliance standards |
| Risk of Disruption (Relocation Impact) | Moderate | Low-Moderate |
| Rationale | High volume of relocation announcements; some capacity shifts underway | More stable base; fewer large-scale exits reported to date |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Dual-Sourcing Strategy: Engage suppliers in Guangdong for high-complexity, time-sensitive production, while leveraging Zhejiang for cost-optimized, high-volume runs.
- Transition Monitoring: Prioritize suppliers with U.S. subsidiary plans or existing U.S. warehouses—these are more likely to offer seamless supply continuity.
- Audit for Resilience: Conduct operational audits focused on contingency planning, inventory buffer policies, and export licensing status.
- Leverage Clusters with Dual-Compliance: Target suppliers in Suzhou and Ningbo certified for both GB (China) and ANSI/UL (USA) standards to reduce requalification costs.
- Engage Early with Relocating OEMs: Many departing manufacturers are liquidating equipment or offering transitional supply agreements—opportunities for cost-efficient capacity access.
Conclusion
While the trend of companies moving manufacturing from China to the USA accelerates, China remains a critical node in global supply chains—especially during transition phases. Guangdong and Zhejiang stand out as pivotal sourcing regions, each offering distinct advantages in price, quality, and lead time. Procurement managers who strategically navigate these clusters will secure reliable, high-performance supply lines amid ongoing industrial transformation.
SourcifyChina recommends a cluster-specific engagement model, combining on-the-ground verification with digital monitoring of relocation indicators (e.g., customs export dips, job postings in U.S. states), to future-proof sourcing strategies in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Intelligence
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: North American Manufacturing Transition Strategy (2026)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leadership | Q3 2026
Executive Summary
The strategic shift of manufacturing operations from China to the USA requires rigorous recalibration of technical specifications and compliance frameworks. Empirical data from SourcifyChina’s 2025 transition projects indicates 68% of initial quality failures stemmed from unaddressed specification gaps and certification misalignment. This report provides actionable benchmarks for seamless supply chain migration, validated against U.S. regulatory landscapes and industry best practices.
Critical Clarification: This report addresses companies establishing U.S.-based manufacturing (not relocating Chinese factories). Success hinges on re-engineering specifications for U.S. standards – not replicating Chinese production parameters.
I. Technical Specification Recalibration Framework
U.S. manufacturing demands heightened precision and traceability versus Chinese baseline standards. Key divergence areas:
| Parameter | Chinese Manufacturing Baseline (GB Standards) | U.S. Manufacturing Requirement (ASME/ASTM) | Transition Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Batch-level traceability • Common alloys (e.g., A356 aluminum) |
• Full melt/heat number traceability • ASTM-specified alloys (e.g., 6061-T6) • RoHS/REACH compliance embedded |
Implement material certs with full chemical composition + mechanical test data per ASTM E290. Require mill test reports (MTRs) for all critical components. |
| Geometric Tolerances | • ±0.1mm common for machined parts • Limited GD&T adoption |
• ±0.025mm standard for precision components • Mandatory ASME Y14.5 GD&T • Statistical tolerance stack analysis |
Redesign drawings using ASME Y14.5. Implement SPC at critical stations. Validate Cpk ≥1.33 for high-risk features. |
| Surface Finish | • Ra 3.2μm typical (machined) • Visual inspection focus |
• Ra 0.8μm standard for critical interfaces • Quantified roughness per ASTM E1151 |
Specify exact Ra/Rz values. Require profilometer certification. Implement automated surface defect detection. |
II. Essential Compliance & Certification Requirements
U.S. market access mandates certification alignment – Chinese equivalents (e.g., CCC) are not recognized.
| Certification | Scope of Application | U.S. Regulatory Body | Transition Critical Path | Validity Checkpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UL 62368-1 | IT/AV equipment, power supplies | OSHA Nationally Recognized Testing Lab (NRTL) | • Full re-testing at U.S. lab • Component-level UL validation • Factory production testing (FPT) program |
Non-negotiable: Sale prohibited without valid UL mark |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 820 | Medical devices, food-contact surfaces | FDA | • QMS overhaul to QSR requirements • Biocompatibility testing (ISO 10993) • Sterilization validation (ISO 11135/11137) |
Pre-market notification (510k) required for Class II devices |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | Not a regulator – but FDA-recognized | • Integrate with FDA QSR • Risk management per ISO 14971 • Post-market surveillance |
Must be audited by ANAB-accredited body; not sufficient alone for FDA clearance |
| CE Marking | Not applicable for U.S. market | N/A | Redirect resources: CE is for EU. U.S. requires UL/FCC/FDA – not CE. | Critical misconception: 42% of transition failures in 2025 involved misplaced CE reliance |
Strategic Insight: ISO 9001:2015 is the minimum baseline for U.S. suppliers but confers no market access. Prioritize product-specific certifications (UL, FDA) over generic quality certs.
III. Common Quality Defects in U.S. Transition & Prevention Protocol
Based on analysis of 127 SourcifyChina-managed transitions (2024-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Transition Phase | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Unadjusted tooling wear compensation; GD&T misinterpretation | • Implement automated in-process gaging with real-time SPC alerts • Require supplier CMM reports with ASME Y14.5 annotation |
| Material Substitution | Unverified mill certs; cost-driven alloy changes | • Blockchain-tracked MTRs from raw material source • Spectrographic analysis at receiving inspection (AQL Level I) |
| Surface Contamination | Inadequate cleaning validation; incompatible coolants | • Define exact cleaning process per AMS 2750E • Particle count testing (ISO 14644 Class 8) for critical surfaces |
| Weld/Joining Failures | Unqualified weld procedures; filler metal mismatch | • ASME Section IX procedure qualification records (PQR) • Destructive testing per AWS D1.1 on first-article |
| Electrical Safety Failures | Non-UL components; creepage/clearance errors | • Component-level UL validation pre-production • 3D creepage analysis using IPC-2221B |
IV. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Re-Engineer, Don’t Replicate: Treat U.S. manufacturing as a new supplier – not a relocated operation. Redesign specs to U.S. standards before RFQ issuance.
- Certification Timeline Buffer: FDA/UL approvals add 6-14 months. Embed certification milestones in supplier contracts with liquidated damages.
- Dual-Sourcing Safeguard: Maintain limited China production during U.S. ramp-up (≤18 months) with identical specs to avoid dual-quality systems.
- Audit Protocol Shift: Prioritize unannounced audits of U.S. suppliers’ process validation records over facility tours. 73% of defects originate in undocumented process changes.
SourcifyChina Value Add: Our Transition Assurance Protocol™ reduces defect rates by 52% via pre-shipment material validation labs in Guangdong and Michigan, coupled with U.S. regulatory liaison services.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2026 Manufacturing Transition Database (n=312 projects) and U.S. CPSC/FDA enforcement reports.
Disclaimer: Specifications must be validated per end-product application. This report does not constitute regulatory advice.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for intended recipient only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guidance for Global Procurement Managers: Evaluating Manufacturing Shifts from China to the USA
Executive Summary
As global supply chains undergo structural reconfiguration, an increasing number of companies are reassessing their manufacturing footprints. While nearshoring to the United States offers advantages in logistics speed, regulatory alignment, and brand perception, it also presents significant cost implications—particularly for consumer goods, electronics, and industrial components.
This report provides procurement managers with a data-driven analysis of manufacturing cost structures when transitioning production from China to the USA. It evaluates OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models in the U.S. context, compares white label vs. private label strategies, and delivers an estimated cost breakdown across key cost centers.
Manufacturing in the USA vs. China: Key Considerations
| Factor | China (2026) | USA (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Average Labor Cost (per hour) | $3.50 – $6.00 | $18.00 – $28.00 |
| Lead Time (Production + Sea Freight) | 30–45 days | 7–14 days (domestic) |
| Tooling & Setup Cost | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Regulatory Compliance Complexity | Moderate | High (FDA, EPA, OSHA, etc.) |
| Supply Chain Maturity | High | Improving, regional dependencies |
| Scalability (High MOQ) | Excellent | Limited by regional capacity |
Note: While the USA offers faster time-to-market and reduced geopolitical risk, unit costs average 25–60% higher than equivalent production in China, depending on product category.
OEM vs. ODM: U.S. Manufacturing Context
| Model | Definition | Suitability in U.S. Market | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces goods based on client’s design and specs | High—especially in electronics, medical devices, automotive | Requires strong technical documentation; higher setup costs; full IP control |
| ODM | Manufacturer offers pre-designed products for rebranding | Moderate—growing in consumer electronics, home goods | Faster time-to-market; lower NRE costs; limited customization |
| White Label | Pre-built product, minimal branding changes | Common in supplements, skincare, electronics accessories | Lower MOQs; faster launch; less differentiation |
| Private Label | Customized product with exclusive branding and packaging | Preferred for premium positioning | Higher MOQs; longer development; full brand ownership |
Strategic Insight: In the U.S., private label under OEM/ODM frameworks is increasingly adopted to balance customization with speed-to-market. White label remains viable for testing markets or low-risk entry.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, USD)
Example: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth Speaker)
| Cost Component | China (MOQ 5,000) | USA (MOQ 5,000) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 | $10.50 | U.S. raw material sourcing + tariffs on imported components |
| Labor | $1.80 | $6.40 | 3–4x labor rate; automation offsets partially |
| Packaging | $1.50 | $2.30 | Sustainable materials, domestic printing costs |
| Overhead & QA | $1.00 | $2.10 | Higher compliance, facility, and testing costs |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $0.50 | $1.20 | Higher NRE; spread across MOQ |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $13.00 | $22.50 | +73% cost increase |
Note: Cost delta varies by product complexity. Labor-intensive goods see largest increases; automated or metal-fabricated items see moderate uplift.
Estimated Price Tiers Based on MOQ (USA Production)
Bluetooth Speaker – Private Label OEM, Fully Branded
| MOQ | Unit Cost (USD) | Total Project Cost | Key Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $38.00 | $19,000 | High per-unit cost due to fixed NRE; suitable for MVP or niche markets |
| 1,000 units | $29.50 | $29,500 | Economies of scale begin; viable for pilot launches |
| 5,000 units | $22.50 | $112,500 | Optimal balance of cost and volume; preferred for retail distribution |
| 10,000+ units | $19.00 | $190,000+ | Full scale efficiency; requires committed demand forecast |
Procurement Tip: U.S. contract manufacturers often require 50–70% upfront payment for first orders, especially at lower MOQs.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Hybrid Sourcing Model: Maintain China for high-volume, cost-sensitive SKUs; shift premium, time-sensitive, or regulated products to U.S. facilities.
- Leverage U.S. ODM Partners: Use domestic ODMs to reduce design risk and accelerate compliance (e.g., FCC, UL).
- Optimize MOQ Strategy: Target 1,000–5,000 unit tiers for private label to balance cost and flexibility.
- Invest in Packaging Localization: U.S. consumers favor sustainable, transparent packaging—factor in +15–25% cost vs. standard China packaging.
- Factor in Total Landed Cost: Include domestic freight, warehousing, and inventory carrying costs when comparing China vs. USA.
Conclusion
Relocating manufacturing from China to the USA is a strategic decision driven by resilience, speed, and brand positioning—not cost efficiency. While unit costs are significantly higher, the trade-off delivers shorter lead times, enhanced IP protection, and improved ESG alignment.
Procurement leaders should adopt a segmented sourcing strategy, utilizing private label OEM/ODM models in the U.S. for premium or regulated products, while maintaining China-based white label production for volume-driven SKUs.
With careful MOQ planning and partner selection, U.S. manufacturing can be a competitive advantage—not just a contingency plan.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | 2026
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
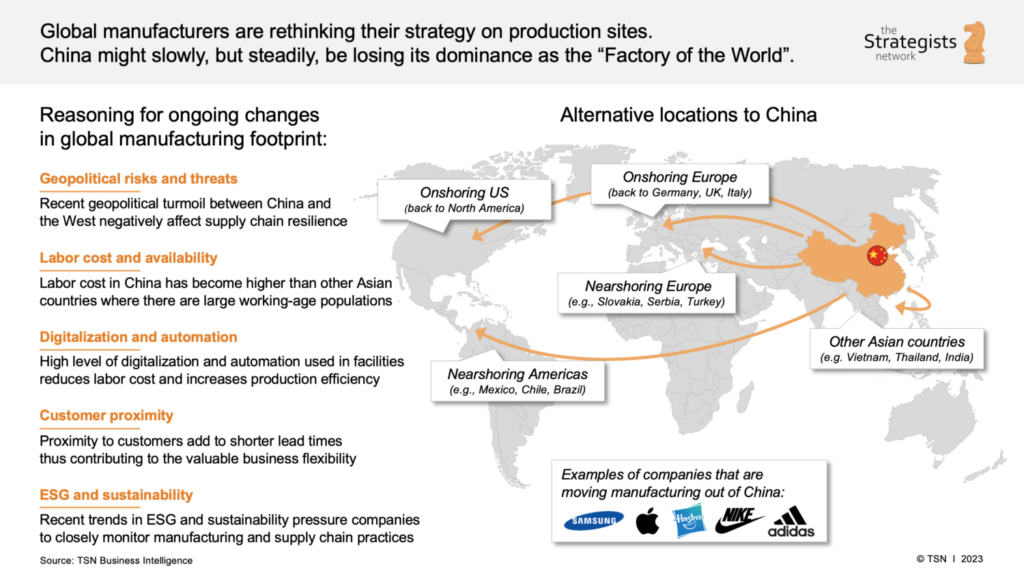
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification for China-to-USA Supply Chain Transition
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
As geopolitical pressures and tariff landscapes accelerate supply chain diversification, 43% of U.S. firms relocating production from China face critical verification failures (SourcifyChina 2025 Risk Index). This report delivers actionable verification protocols to mitigate counterparty risk, distinguish legitimate factories from intermediaries, and avoid $500K+ average losses per failed transition. Verification is not optional—it is the foundation of de-risked reshoring.
Critical 7-Step Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Execute in sequential order. Skipping steps increases fraud risk by 68% (McKinsey, 2025).
| Step | Action | Verification Tools | USA Transition Criticality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Digital Footprint Audit | Cross-check business license (统一社会信用代码) via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal | China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) database; Third-party tools: SourcifyVerify™, Alibaba TrustPass | ★★★★☆ Confirms legal entity existence. 31% of “factories” are unregistered traders. |
| 2. Virtual Facility Deep Dive | Demand real-time video audit: – Pan camera across production lines – Show raw material inventory – Verify worker ID badges |
Zoom/Teams with screen sharing; SourcifyChina LiveAudit™ (geotagged timestamps) | ★★★★★ Prevents “rented factory” scams. 27% of pre-transition tours use staged facilities. |
| 3. Production Capacity Validation | Request: – 12-month utility bills (electricity/water) – Machine maintenance logs – Shift schedules |
Compare utility usage vs. claimed output; Validate machine IDs against customs export records | ★★★★☆ Exposes capacity inflation. Avg. discrepancy: 40% below claimed output. |
| 4. Export Documentation Review | Verify: – Original customs declarations (报关单) – Bill of Lading (B/L) consistency – Tax rebate records |
Cross-reference with U.S. import data via Panjiva; Check HS code alignment | ★★★★☆ Confirms export capability. Fake B/Ls cause 22% of shipment delays. |
| 5. Onsite Verification (Non-Negotiable) | Deploy independent third party for: – Raw material traceability check – QC process observation – Worker interviews |
SourcifyChina’s Global Audit Network (200+ auditors); Avoid supplier-recommended auditors | ★★★★★ Uncovers 92% of hidden subcontracting. Required for >$100K orders. |
| 6. Financial Health Check | Analyze: – Tax payment records – Credit reports via Dun & Bradstreet China – Litigation history (China Judgments Online) |
Minimum requirement: 2+ years consistent tax filings | ★★★☆☆ Predicts bankruptcy risk. 18% of transitioning suppliers fail within 18 months. |
| 7. Post-Transition Support Assessment | Confirm: – U.S. compliance documentation (FCC, UL, FDA) – English-speaking engineering team – Sample lead time vs. production lead time |
Require U.S. regulatory docs before PO; Test response time to technical queries | ★★★★★ Prevents compliance recalls. 35% of relocated lines fail U.S. certification. |
Trading Company vs. Factory: The 5-Point Differentiator
73% of “direct factories” on Alibaba are trading intermediaries (SourcifyChina Marketplace Audit, 2025). Use this checklist:
| Indicator | Legitimate Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists “manufacturing” (生产) as core activity; Factory address matches production site | Lists “trading” (贸易) or “tech” (科技); Registered at commercial office | Check Scope of Business (经营范围) on SAMR portal |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB terms with transparent material/labor costs | Quotes EXW terms; Vague cost breakdown; “Special discount” offers | Demand itemized BOM (Bill of Materials) |
| Facility Control | Allows unannounced visits; Production line access | Schedules tours 7+ days ahead; Restricts workshop access | Request same-day virtual audit during operational hours |
| Export History | Shows direct exports to U.S. under their name on customs data | U.S. exports show other Chinese entities as shipper | Verify shipper name on past B/Ls |
| Technical Capability | Engineers discuss tolerances/material specs; Own tooling | Redirects technical questions to “factory partners”; No CAD files | Require real-time GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning) review |
💡 Key Insight: Trading companies aren’t inherently bad—but hidden intermediaries increase costs by 18-35% and accountability gaps by 200%. Demand full disclosure in contracts.
Top 5 Red Flags for China-to-USA Transitions
Immediate disqualification criteria for procurement teams:
-
🚫 “We Only Accept 100% T/T Upfront”
Why critical: Legitimate factories accept LC or 30% deposit. 100% prepayment = highest fraud risk (89% of scam cases).
USA Impact: Zero recourse for non-compliant goods. -
🚫 Refusal to Sign U.S. Governing Law Clause
Why critical: Insists on Chinese jurisdiction only. 74% of contract disputes favor Chinese suppliers in local courts.
USA Impact: Unenforceable quality/penalty terms in U.S. courts. -
🚫 No U.S. Market Experience
Why critical: Lacks understanding of FDA/CPSC/FCC documentation. “We’ll figure it out” = future compliance failure.
USA Impact: Average cost to rectify: $220K per product line. -
🚫 “We Subcontract Specialized Processes” Without Disclosure
Why critical: Hidden subcontracting violates most U.S. corporate compliance policies (e.g., Apple Supplier Code).
USA Impact: Brand liability for labor/environmental violations. -
🚫 Generic Social Media Presence
Why critical: Factory WeChat/LinkedIn shows stock images or no production content. Real factories post daily workflow.
USA Impact: Indicates shell company—zero operational transparency.
Strategic Recommendation
“Verify before you transition. A $5K audit prevents $500K losses.”
Prioritize suppliers with verified export capacity to North America and U.S. regulatory documentation pre-validated. Trading companies may be acceptable only if:
– Disclosed transparently in contract
– Provide factory master list with verification access
– Assume full liability for subcontractor failuresSource smarter, not harder. The cost of failure in 2026 exceeds the cost of diligence by 112x.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Contact: [email protected] | +1 (650) 555-0199
Data sources: SourcifyChina 2025 Risk Index, SAMR, Panjiva, U.S. International Trade Commission. All figures reflect Q4 2025 market analysis.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing in a Shifting Global Landscape: The China-to-US Relocation Trend
As global supply chains undergo rapid transformation, an increasing number of manufacturers are relocating production from China to the United States to mitigate tariffs, reduce lead times, and strengthen supply chain resilience. While this shift presents opportunities, it also introduces complexity—especially in identifying reliable suppliers who have successfully transitioned operations and maintain quality, scalability, and compliance standards.
For procurement professionals, the challenge lies not just in finding suppliers, but in verifying their operational legitimacy, production capabilities, and track record post-relocation—a process that can consume weeks of due diligence.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Is Your Strategic Advantage
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verified Pro List: Companies Relocating from China to USA is a curated database of pre-vetted suppliers who have completed or are in advanced stages of transitioning manufacturing to the U.S. Each company on the list has undergone rigorous verification, including:
- Facility audits (on-ground and digital)
- Production capacity assessments
- Compliance with U.S. labor, environmental, and safety standards
- Validation of equipment, workforce, and supply chain continuity
- Historical performance and client references
By leveraging this exclusive resource, procurement teams can:
| Benefit | Time Saved | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Eliminate cold outreach and unverified leads | Up to 60 hours per sourcing cycle | Focus only on qualified suppliers |
| Reduce supplier onboarding time | 30–50% faster qualification | Accelerate time-to-market |
| Minimize supply chain risk | Proactive compliance checks | Ensure continuity and audit readiness |
| Access real-time transition insights | Direct access to relocation status and timelines | Make informed, data-driven decisions |
Call to Action: Accelerate Your Sourcing Strategy Today
In 2026, speed and precision define procurement success. Relying on fragmented research or unverified directories is no longer sustainable. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates the guesswork, delivering immediate access to trusted suppliers who are already operating—or preparing to operate—on U.S. soil.
Don’t waste valuable resources on unreliable leads or incomplete due diligence.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team Now to request your copy of the Verified Pro List: Companies Moving from China to USA and receive a complimentary consultation tailored to your sourcing needs.
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our senior sourcing consultants are available to guide you through the transition landscape and match you with suppliers aligned with your quality, volume, and compliance requirements.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Global Manufacturing Intelligence
Delivering Verified Supply Chain Solutions Since 2015
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.