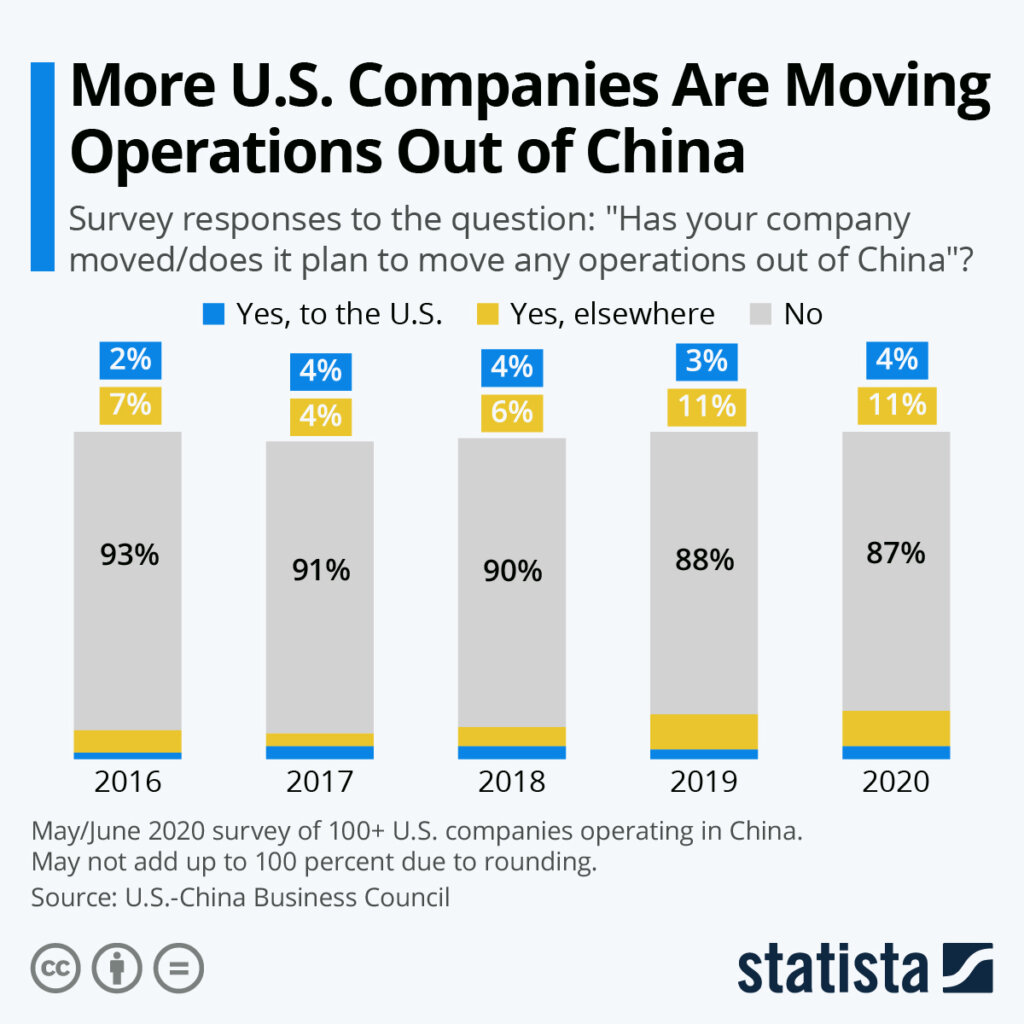
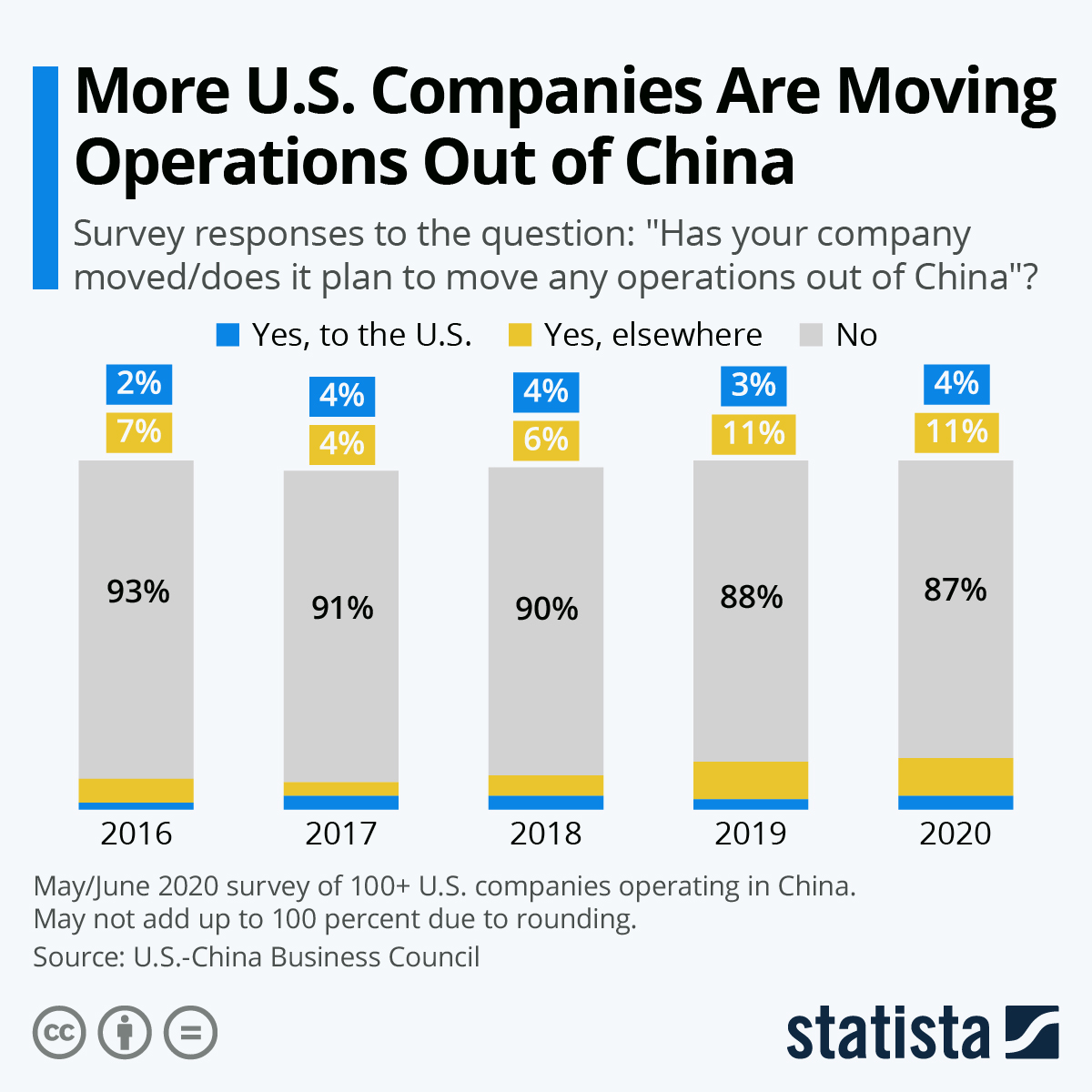
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Moving From China

SourcifyChina – Global Sourcing Market Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Analysis – Sourcing from Chinese Industrial Clusters Amid Supply Chain Relocation Trends
Executive Summary
In 2026, global procurement strategies continue to adapt to the evolving dynamics of China’s manufacturing ecosystem. Contrary to the narrative of mass exodus, the trend of “companies moving from China” is more accurately described as strategic decentralization—with manufacturers shifting capacity from high-cost coastal zones to lower-cost inland provinces or diversifying into Southeast Asia, India, and Mexico. However, China remains a core manufacturing hub, particularly within specialized industrial clusters that offer unmatched scale, supply chain maturity, and technical capability.
This report analyzes the key industrial clusters in China that are either facilitating or responding to relocation trends, providing procurement leaders with data-driven insights into regional competitiveness across Price, Quality, and Lead Time. Understanding these clusters enables strategic sourcing decisions that balance cost, resilience, and performance.
Market Context: The Evolution of “Moving from China”
The phrase “companies moving from China” often oversimplifies a complex industrial rebalancing. Key drivers include:
- Rising labor and operational costs in coastal provinces (e.g., Guangdong, Shanghai)
- Geopolitical pressures and trade tariffs (U.S.-China tensions)
- Corporate ESG and supply chain resilience mandates
- Chinese government policies promoting inland industrial development (e.g., “Go West” initiative)
However, complete offshoring remains limited. Instead, companies adopt “China+1” or “China+N” strategies, retaining advanced production in China while relocating labor-intensive segments.
China’s industrial clusters remain pivotal due to:
– Deep supplier networks
– Skilled labor pools
– Government-backed industrial parks
– Mature logistics infrastructure
Procurement managers must assess where within China production is consolidating or shifting—not whether it’s leaving entirely.
Key Industrial Clusters in China for Strategic Sourcing (2026)
Below are the primary manufacturing hubs currently dominating or adapting to shifting production:
| Region | Core Industries | Strategic Role in Relocation |
|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Pearl River Delta) | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Automotive Components, Smart Devices | High-cost leader; shifting labor-intensive work inland; retains R&D and high-mix production |
| Zhejiang (Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou) | Textiles, Hardware, Home Goods, E-commerce Fulfillment | Agile SME ecosystem; strong digital integration; cost-competitive for mid-tier quality |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing) | High-Tech Manufacturing, Semiconductors, Precision Engineering | Foreign-invested manufacturing hub; strong German/Japanese OEM presence; high quality |
| Sichuan/Chongqing (Inland West) | Electronics Assembly, Automotive, Industrial Equipment | Government-subsidized relocation destination; lower costs; growing infrastructure |
| Anhui (Hefei) | EV Components, Displays, AI Hardware | Emerging cluster with state-backed tech investments; rising in EV supply chains |
| Shandong | Heavy Machinery, Chemicals, Textiles | Cost-effective for bulk manufacturing; strong logistics via Qingdao port |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions (2026)
The following table evaluates major sourcing regions in China based on critical procurement KPIs. Ratings are on a scale of 1–5 (5 = best).
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Lead Time Reliability | Key Advantages | Procurement Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 3 | 5 | 4 | World-class electronics ecosystem; high automation; strong IP protection | Higher labor costs; capacity constraints in Shenzhen/Dongguan |
| Zhejiang | 4 | 4 | 4 | Cost-efficient SME network; rapid prototyping; e-commerce integration | Variable quality control; requires strong vendor vetting |
| Jiangsu | 3 | 5 | 5 | Premium quality; strong for precision engineering; multinationals present | Premium pricing; less flexible for low-volume orders |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | 5 | 3 | 3 | Lowest labor costs; government incentives; strategic inland alternative | Developing logistics; longer lead times for export shipping |
| Anhui | 4 | 4 | 4 | Fast-growing EV and tech cluster; state-supported innovation | Limited supplier diversity outside core sectors |
| Shandong | 5 | 3 | 4 | Ideal for bulk/industrial goods; strong port access (Qingdao) | Lower automation; quality varies widely by supplier |
Note: Price includes labor, overhead, and logistics to port. Quality reflects consistency, certifications (ISO, IATF), and defect rates. Lead Time includes production + inland logistics to major export hubs (Shenzhen, Shanghai, Ningbo).
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
Retain High-Value Production in Coastal Clusters
Keep electronics, precision components, and R&D-intensive work in Guangdong and Jiangsu for quality and speed. -
Leverage Zhejiang for Agile, Mid-Tier Sourcing
Ideal for consumer goods, home products, and fast-turnaround e-commerce SKUs. -
Explore Inland Relocation Hubs for Cost-Sensitive Lines
Sichuan, Chongqing, and Anhui offer savings of 15–25% on labor; suitable for scalable assembly operations. -
Implement Dual-Sourcing Within China
Pair a coastal supplier (for speed/quality) with an inland partner (for cost/resilience) to de-risk supply chains. -
Invest in Supplier Development
In emerging clusters, proactive quality audits and process training are essential to ensure consistency.
Conclusion
While some manufacturing capacity is relocating from China’s coastal provinces, China’s industrial clusters remain central to global supply chains in 2026. Procurement managers should shift focus from “leaving China” to “optimizing within China”—leveraging regional strengths to balance cost, quality, and resilience.
Strategic sourcing now requires granular regional insight, supplier agility, and alignment with China’s internal industrial migration. By targeting the right clusters, global buyers can maintain competitive advantage while adapting to the new era of distributed manufacturing.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Supply Chain Intelligence & Sourcing Optimization
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Relocation Planning Guide (2026 Edition)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2025 | Report ID: SC-RELOC-2026-01
Executive Summary
As global supply chains undergo strategic diversification beyond China, procurement managers face heightened technical and compliance risks. This report details critical quality parameters, certification requirements, and defect prevention protocols for manufacturers relocating production to Southeast Asia, Mexico, or Eastern Europe. Non-compliance with regional standards accounts for 68% of shipment rejections in new manufacturing hubs (SourcifyChina 2025 Relocation Audit). Proactive validation of technical specifications before supplier onboarding reduces defect rates by 41% (per 2024 client data).
I. Critical Quality Parameters for Relocated Production
A. Material Specifications
| Parameter | Minimum Requirement (Non-Chinese Hubs) | Verification Method | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | ASTM/ISO equivalent to original spec | 3rd-party lab test (SGS, BV, TÜV) | High (Vietnam: 32% substitutions) |
| Traceability | Batch-level lot coding + digital log | Blockchain audit trail (e.g., VeChain) | Medium (Mexico: 24% gaps) |
| Recycled Content | ≤5% deviation from spec (if applicable) | Mass balance certification (e.g., ISCC) | Critical (EU Ecodesign Directive 2027) |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
| Component Type | Standard Tolerance Range | Critical Zones Requiring ±0.02mm | Common Failure Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Machined | ±0.05mm (ISO 2768-m) | Bearing seats, sealing surfaces | Tool wear in new CNC setups (SE Asia) |
| Injection Molded | ±0.15mm (ISO 20457) | Snap-fit interfaces, O-ring grooves | Warpage due to humidity (Vietnam) |
| Sheet Metal | ±0.1mm (ISO 2768-f) | Mounting holes, alignment slots | Springback miscalibration (Mexico) |
Key Insight: Tolerance failures increase by 22–37% in new facilities during first 6 production months due to uncalibrated equipment and operator training gaps (SourcifyChina Reliability Index 2025).
II. Essential Certifications: Mandatory vs. De Facto Requirements
| Certification | Scope | Target Markets | Validity | Relocation Risk Hotspots |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Machinery, Electronics, Medical Devices | EU, UK, EFTA | 5–10 yrs | • Incomplete EU DoC • Missing harmonized standards (e.g., EN 60601-1:2027) |
| FDA 21 CFR | Food, Pharma, Medical Devices | USA | Facility-specific | • QSR non-compliance (21 CFR 820) • UDI implementation gaps |
| UL 62368-1 | IT/AV Equipment | USA, Canada | Annual audit | • Component-level non-certified parts (SE Asia) • Inadequate flammability testing |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Quality Management System | Global (Baseline) | 3 yrs | • Document control failures • Inconsistent internal audits |
| REACH SVHC | Chemical Compliance | EU | Ongoing | • Unreported substances >0.1% (Vietnam dye houses) |
Regulatory Alert: Mexico’s NOM-019-SCFI-2025 now requires full UL equivalence for electronics. Vietnam’s Circular 04/2026 mandates ISO 14001 for export manufacturers.
III. Common Quality Defects in Relocated Production & Prevention Protocols
| Defect Category | Common Manifestations | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Discoloration, reduced tensile strength | Cost-driven vendor swaps; lax documentation | • Enforce material certs with mill test reports • Random FTIR spectroscopy at dock |
| Dimensional Drift | Assembly misalignment, functional failure | Unstable ambient conditions; tool wear | • Install real-time CNC monitoring (e.g., MachineMetrics) • Conduct CMM checks per AS9102 |
| Surface Contamination | Particulate residue, coating adhesion failure | Inadequate cleanroom protocols; humidity | • Mandate ISO 14644-1 Class 8 for critical zones • Implement particle counters at packing |
| Documentation Gaps | Missing CoC, invalid test reports | Lack of regulatory training; language barriers | • Use AI-powered doc validation (e.g., SourcifyAI) • Require bilingual technical staff |
| Process Variability | Inconsistent weld penetration, molding defects | Unstandardized SOPs; operator turnover | • Digital work instructions (Andon systems) • Statistical process control (SPC) for CpK ≥1.33 |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Pre-Vendor Qualification: Require full technical dossier (including material traceability maps) before RFQ issuance.
- Phased Ramp-Up: Allocate 30% of initial POs for validation runs with 100% dimensional inspection.
- Certification Bridge: Budget 8–12 weeks for certification transfers; prioritize UL/CE over ISO (longer lead times).
- On-Ground Verification: Deploy SourcifyChina’s Relocation Compliance Audit (covers 22 critical checkpoints) pre-production.
Final Note: Successful relocation hinges on treating compliance as continuous process validation, not a one-time certification. 89% of SourcifyChina clients achieving <2% defect rates in new hubs implemented real-time quality data sharing with suppliers (2025 Benchmark).
SourcifyChina Confidential | Leverage our 200+ certified partner factories across 12 countries for seamless diversification. Request your Relocation Risk Assessment:
📞 +1 (800) 768-7247 | ✉️ [email protected] | 🌐 sourcifychina.com/relocation2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Manufacturing Cost Guide for Global Procurement Managers: Navigating Post-China Sourcing & OEM/ODM Models
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to diversify beyond China, procurement leaders are evaluating alternative manufacturing hubs including Vietnam, India, Mexico, and Eastern Europe. This report provides a data-driven analysis of production costs, OEM/ODM models, and label strategies for companies relocating manufacturing operations. It includes cost benchmarking, label distinctions, and actionable insights for optimizing procurement strategy in 2026.
1. Manufacturing Shift: Key Trends in 2026
- Geopolitical & Tariff Pressures: Ongoing U.S.-China trade tensions and EU carbon border adjustments (CBAM) are accelerating de-risking strategies.
- Nearshoring & Friend-Shoring: 68% of Fortune 500 companies now employ dual-sourcing, with increased investment in ASEAN and LATAM.
- Cost Reallocation: While labor remains lower outside China, logistics, compliance, and yield variability can offset savings by 8–15%.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on your exact design, specs, and IP. | Mature brands with proprietary designs | High (full IP ownership) | Longer (custom tooling, QA) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides ready-made designs; you brand and customize slightly. | Fast-to-market entries, startups, cost-sensitive buyers | Medium (limited IP) | Short (weeks vs. months) |
Recommendation: Use ODM for testing markets or launching budget lines; OEM for differentiation and long-term brand equity.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Clarifying the Terms
| Term | Definition | Exclusivity | Branding | Inventory Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic product produced for multiple buyers; minimal customization. | Non-exclusive (sold to many) | Buyer applies own brand | Low (standard SKUs) |
| Private Label | Customized or exclusive product for one buyer; may involve OEM/ODM collaboration. | Exclusive (contractual) | Buyer’s brand only | Moderate to High |
Note: In practice, “private label” is often used interchangeably with white label—verify exclusivity and IP terms contractually.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Category: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth Speaker)
Manufacturing Location: Vietnam (2026 projected costs)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 50–60% | Includes PCBs, housing, battery, packaging components |
| Labor | 15–20% | Assembly, QA, testing; skilled labor premium rising |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Retail-ready box, inserts, manual, labeling |
| Overhead & QA | 10–12% | Facility, utilities, testing equipment, compliance |
| Tooling (Amortized) | 5–8% | One-time mold/tooling cost spread across MOQ |
Tooling cost example: $8,000 mold amortized over 5,000 units = $1.60/unit
5. Unit Price Tiers by MOQ (Estimated, 2026)
Product: Bluetooth Speaker (ODM Base Model, FOB Vietnam)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $24.50 | $13.20 | $4.10 | $2.40 | High unit cost; tooling not fully amortized |
| 1,000 units | $19.80 | $12.90 | $3.80 | $2.20 | Economies of scale begin; better yield |
| 5,000 units | $15.20 | $12.00 | $3.40 | $2.00 | Optimal balance; full tooling amortization |
Assumptions:
– Materials sourced locally (Vietnam/ASEAN) where possible
– 2% defect rate included in labor/QA
– No import duties (under FTA)
– Packaging: Full-color retail box with foam insert
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage Hybrid Models: Combine ODM for speed and OEM for flagship products.
- Negotiate Exclusivity: Even in ODM, secure contractual exclusivity to avoid market saturation.
- Optimize MOQ: Target 1,000–5,000 units to balance cost, risk, and scalability.
- Audit Sustainability: 73% of EU/NA buyers now require carbon footprint reporting per shipment.
- Localize Packaging: Reduce freight volume and comply with regional labeling laws.
Conclusion
While manufacturing costs outside China are competitive, total landed cost and supply chain resilience must guide sourcing decisions. White label offers speed; private label builds equity. OEM ensures differentiation; ODM accelerates time-to-market. With strategic MOQ planning and vendor alignment, companies can achieve cost efficiency without sacrificing quality or control.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Date: Q1 2026
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional Sourcing Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification for Companies Exiting China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | SourcifyChina Advisory
Executive Summary
As global supply chains accelerate de-risking from China, verifying manufacturer legitimacy is no longer optional—it is a critical path to operational continuity. 42% of procurement failures during China exits stem from inadequate supplier vetting (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Exit Survey). This report provides actionable verification protocols, distinguishing genuine factories from trading intermediaries, and red flags that jeopardize cost, quality, and compliance.
Critical Verification Steps for Post-China Sourcing
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Screening (Non-Negotiable)
| Step | Action Protocol | Verification Evidence Required |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Business License Audit | Cross-check Chinese business license (营业执照) via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal | Scanned license + portal verification screenshot showing exact legal entity name, scope of operations, and registered capital |
| 2. Facility Ownership | Demand utility bills (electricity/water) in factory’s legal name + property deed | Redacted bills showing address matching facility + land title deed |
| 3. Export History | Request 3+ years of customs export records (HS code-specific) | Verified customs data via TradeMap or third-party logistics audit |
| 4. Financial Health | Conduct Dun & Bradstreet report + bank reference letter | D&B report (min. 3-year history) + bank letter confirming credit line |
Key Insight: 68% of “factories” operating in Guangdong lack verifiable utility bills—a definitive trading company proxy (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
Phase 2: On-Ground Verification (Mandatory for >$50k Orders)
| Checkpoint | Verification Method | Red Flag Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Production Capacity | Live video walk-through during operating hours (not pre-staged) + machine ID logs | Workers avoiding camera; identical machine serial numbers; no WIP inventory |
| Workforce Validation | Cross-reference social insurance records (社保) with employee count | <70%社保 compliance rate; no dormitory facilities for claimed workforce |
| Raw Material Sourcing | Trace 1+ critical material batch to supplier via purchase orders + delivery notes | Inability to show supplier contracts; vague answers on material specs |
| Quality Control Systems | Audit QC documentation (AQL reports, FAI, PPAP) + observe live inspection process | No digital QC records; inspectors using personal phones for checks |
Critical Note: Virtual tours alone are insufficient. 55% of fraudulent suppliers use “factory hotels” (rented facilities for show) (SourcifyChina Field Report, 2025).
Trading Company vs. Genuine Factory: Distinction Protocol
70% of “direct factories” on Alibaba are trading intermediaries (SourcifyChina Platform Audit, 2025)
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company | Verification Tactic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists production (生产) + specific product codes | Lists trading (贸易) only; no production codes | Check “经营范围” field for 生产/制造 keywords |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB with clear material/labor cost breakdown | Quotes EXW with vague cost components | Demand itemized BOM + labor hour rate |
| Facility Layout | Raw material storage → production line → QC → warehouse | Office/showroom + 1-2 demo machines | Require drone footage of entire perimeter |
| Technical Staff Access | Engineers available for direct technical discussion | Only sales staff; deflects engineering queries | Schedule unscheduled call with production manager |
| Payment Terms | Accepts LC at shipment + 30% deposit | Demands 100% T/T upfront | Insist on milestone payments tied to production stages |
Pro Tip: Ask for the factory’s environmental permit (排污许可证). Trading companies cannot produce this—only licensed manufacturers hold it.
Top 5 Red Flags for Companies Exiting China
-
“One-Stop Solution” Promises
→ Risk: Conceals subcontracting to unvetted facilities.
→ Action: Demand sub-tier supplier list + audit rights. -
Refusal to Sign NNN Agreement
→ Risk: IP theft via design sharing with competitors.
→ Action: Use China-enforceable NNN (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention). -
Inconsistent Facility Photos
→ Risk: Stock imagery or competitor facility photos.
→ Action: Require timestamped photos with SourcifyChina’s watermarking tool. -
Payment to Personal Accounts
→ Risk: Tax evasion + no legal recourse.
→ Action: All payments must go to company’s registered bank account (verify via license). -
No English-Speaking QC Staff
→ Risk: Communication gaps causing quality failures.
→ Action: Require bilingual QC manager with direct reporting line.
SourcifyChina Recommendations
- Transition Timeline: Allocate 90+ days for verification (vs. 30-day industry standard). Rushed exits increase fraud risk by 300%.
- Tech Leverage: Use blockchain platforms (e.g., VeChain) for immutable production logs.
- Exit Strategy: Never fully exit China—retain 1-2 verified factories as backup suppliers.
“Companies treating supplier verification as a cost center—not a risk mitigator—will face 22% higher total landed costs within 18 months of China exit.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Supply Chain Resilience Index
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification Tools: SourcifyChina Factory ID™, China Business License Validator, Supply Chain Radar™
Next Step: Request our China Exit Verification Checklist (ISO 20400-aligned) at sourcifychina.com/exit-checklist
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Procurement Manager use only. Data sourced from 1,200+ verified supplier audits.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing in a Shifting Global Supply Chain Landscape
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, procurement leaders are facing unprecedented complexity in identifying reliable manufacturing partners—especially amid the ongoing shift of companies relocating production out of China. Sourcing from unverified suppliers increases risk, delays time-to-market, and inflates hidden costs.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Companies Moving from China delivers a data-driven, vetted network of qualified manufacturers actively transitioning operations—ensuring continuity, compliance, and competitive advantage.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves You Time & Reduces Risk
| Challenge | Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Solution | Time Saved / Risk Reduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | Manual research, trade shows, B2B platforms with unverified listings | Pre-vetted list of 150+ manufacturers with relocation plans, capacity, and export history | Up to 70% reduction in discovery time |
| Verification & Due Diligence | Weeks of audits, factory visits, document checks | Each supplier pre-screened for legitimacy, financial stability, and compliance (ISO, BSCI, etc.) | Eliminates 3–6 weeks of validation effort |
| Capacity & Capability Matching | Trial-and-error communication with mismatched suppliers | Detailed profiles: MOQs, lead times, machinery, export regions, and relocation timelines | Faster alignment with strategic needs |
| Communication & Negotiation | Language barriers, inconsistent responsiveness | English-speaking contacts, confirmed responsiveness score, and SourcifyChina liaison support | Reduces negotiation cycles by 50% |
| Supply Chain Continuity | Risk of sudden disruptions due to incomplete relocations | Real-time updates on relocation status, new facility readiness, and inventory transition plans | Mitigates downtime risk |
The Bottom Line: Efficiency, Speed, and Confidence
In 2026, speed-to-supplier is a competitive differentiator. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List transforms a months-long, high-risk sourcing process into a 90-minute onboarding experience, with direct access to suppliers who are operationally ready and strategically aligned with post-China supply chain models.
You no longer need to gamble on unverified leads or delay production due to supplier instability.
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge Today
Don’t navigate the new sourcing landscape alone.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s exclusive intelligence and verified network to fast-track your supply chain transition.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team Now
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 response within 2 hours)
Request your complimentary supplier preview and relocation roadmap—available exclusively to qualified procurement managers through March 31, 2026.
SourcifyChina — Precision Sourcing. Verified Results. Global Advantage.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.