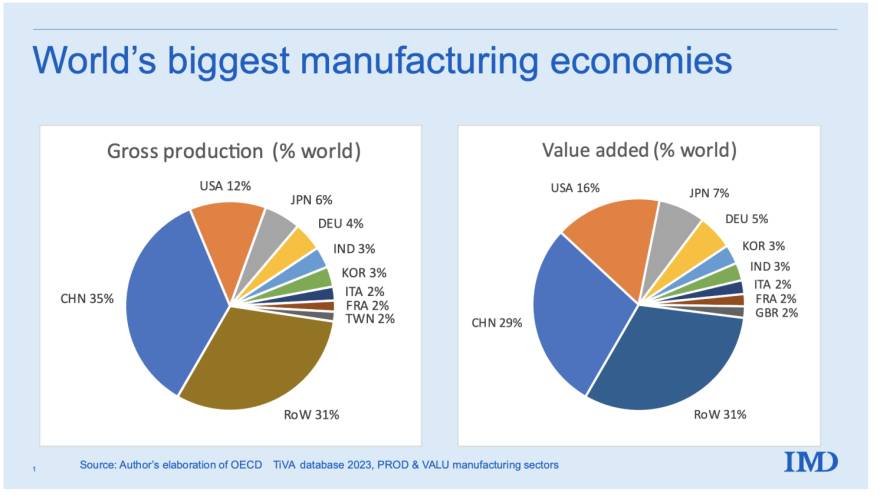
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Move From China To India
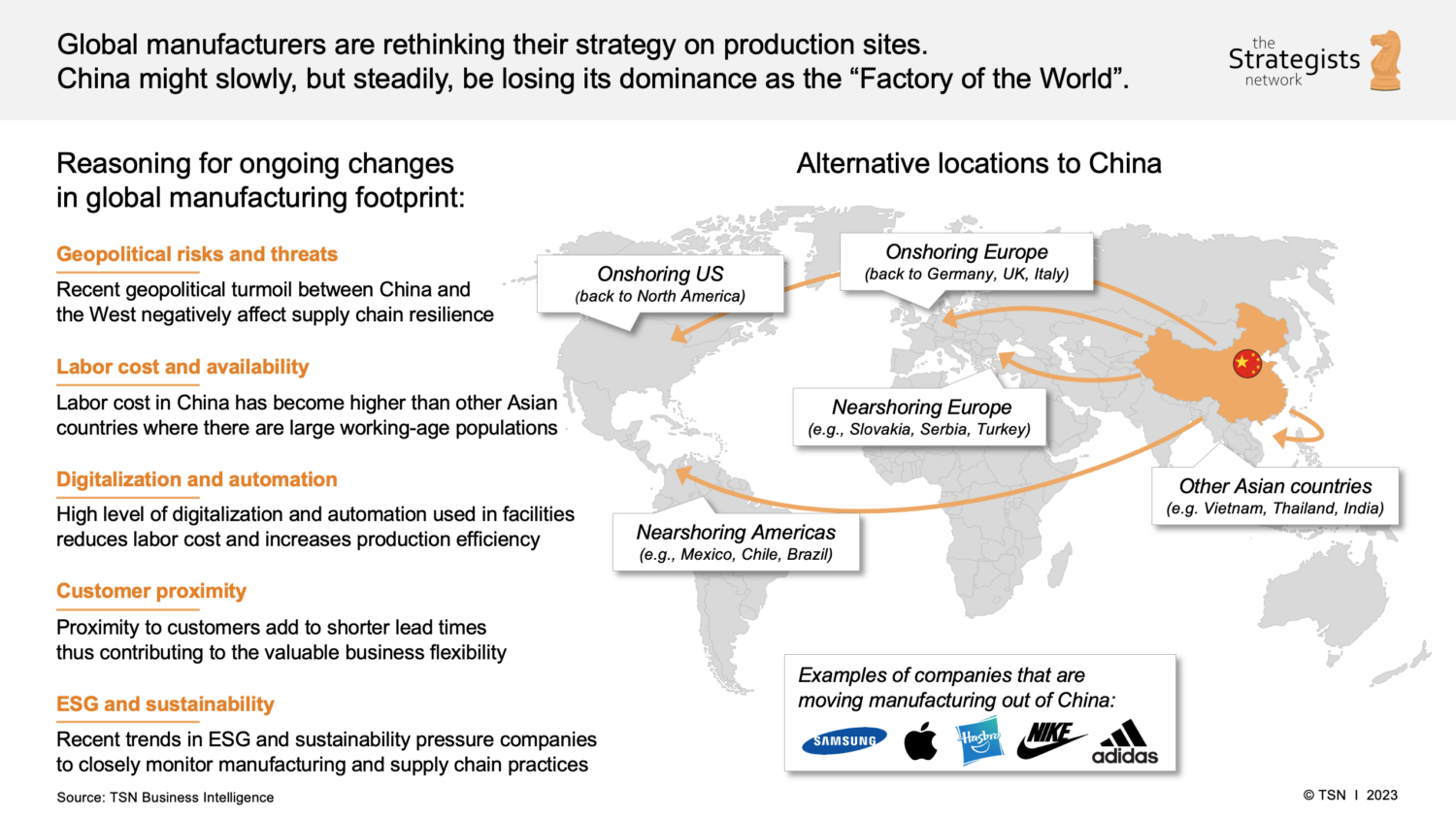
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Market Analysis: Sourcing Companies Relocating from China to India – Industrial Clusters & Regional Benchmarking
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
In 2026, a notable trend continues in global supply chain strategy: the relocation of manufacturing operations from China to India. Driven by rising labor costs in China, geopolitical risks, trade tariffs, and India’s aggressive “Make in India” policy, multinational corporations and SMEs alike are diversifying production bases. However, many companies maintain residual manufacturing or supply chain nodes in China, particularly for high-precision, high-volume, or legacy production lines. This report analyzes the key industrial clusters in China where companies are actively managing phased transitions to India, and evaluates the current sourcing landscape for goods still produced in China during this shift.
This analysis does not assume India has replaced China as the primary manufacturing hub, but instead focuses on China-based suppliers who are themselves relocating or dual-sourcing to India, and the implications for procurement strategy.
Key Industrial Clusters in China for Transitioning Manufacturers
Certain provinces and cities in China have emerged as hotspots for companies planning or executing moves to India. These regions are characterized by export-oriented manufacturing, high foreign investment, and strategic proximity to logistics hubs.
| Province/City | Key Industries | Relocation Trends to India | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Dongguan, Shenzhen, Guangzhou) | Electronics, Consumer Goods, ICT, OEM/ODM | High | Major export hub; many electronics firms relocating assembly to Tamil Nadu and Telangana |
| Zhejiang (Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou) | Textiles, Home Goods, Small Machinery, Fasteners | Medium-High | SME-driven export base; moving low-margin goods to Gujarat and Tamil Nadu |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing) | Advanced Manufacturing, Automotive Components, Industrial Equipment | Medium | German and Japanese MNCs shifting mid-tier production to Pune and Chennai |
| Shanghai | High-Tech, R&D, Medical Devices | Medium | Companies retaining R&D in Shanghai while moving mass production to Hyderabad and Bengaluru |
| Fujian (Xiamen, Quanzhou) | Footwear, Apparel, Ceramics | High | Labor-intensive sectors shifting to Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh |
| Chongqing & Chengdu (Sichuan) | Automotive, Electronics Assembly | Medium | Western China cost advantage slowing relocation, but backend operations moving to Pune |
Regional Benchmarking: China’s Key Manufacturing Hubs (2026)
For procurement managers sourcing products from Chinese suppliers still operating during their India transition phase, understanding regional trade-offs is critical. The table below compares key production regions based on Price, Quality, and Lead Time for mid-to-high volume manufacturing.
| Region | Price Competitiveness (1–5) | Quality Consistency (1–5) | Average Lead Time (weeks) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 3 | 5 | 4–6 | Higher labor costs but unmatched quality in electronics; ideal for high-spec components still in China |
| Zhejiang | 4 | 4 | 5–7 | Cost-effective for consumer goods; quality varies by supplier tier; strong SME ecosystem |
| Jiangsu | 3 | 5 | 5–6 | Premium quality for industrial and automotive; reliable for precision engineering |
| Shanghai | 2 | 5 | 6–8 | Highest costs; justified for R&D-linked production or medical devices |
| Fujian | 4 | 3 | 6–8 | Competitive on price for textiles/apparel; quality control can be inconsistent |
| Sichuan (Chengdu/Chongqing) | 4 | 4 | 7–9 | Lower labor costs; longer lead times due to inland location; improving infrastructure |
Note: Ratings are relative (1 = lowest, 5 = highest). Lead times include production + inland logistics to port (e.g., Shenzhen, Ningbo, Shanghai).
Strategic Sourcing Insights (2026)
-
Dual-Sourcing Strategy Recommended: Procurement teams should engage suppliers with proven India transition plans. Companies with existing Indian operations (e.g., in Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, or Maharashtra) offer long-term supply chain resilience.
-
Quality vs. Cost Trade-offs: While Zhejiang and Fujian offer lower prices, Guangdong and Jiangsu remain superior for quality-critical components. Use tiered sourcing: high-spec from Guangdong/Jiangsu, commoditized goods from Zhejiang.
-
Lead Time Planning: Inland hubs like Chongqing face longer logistics cycles. Factor in +2–3 weeks for inland production vs. coastal regions.
-
Supplier Transition Risk: Monitor suppliers in relocation phases closely. Production shifts can cause temporary quality fluctuations or delays during factory setup in India.
-
Opportunity in Hybrid Models: Some Chinese suppliers are establishing joint ventures or contract manufacturing partnerships in India. These can be leveraged for faster ramp-up and IP protection.
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit Supplier Roadmaps: Require transparency on relocation timelines and dual-site capabilities.
- Pilot Orders in India: Test production quality and logistics from Indian facilities before full transition.
- Leverage Chinese Expertise: Use China-based engineering teams to support quality ramp-up in Indian plants.
- Negotiate Transition Clauses: Include exit or continuity terms in contracts during relocation phases.
Conclusion
While India is emerging as a strategic alternative to China, the transition is gradual and regionally nuanced. China remains a critical node for high-quality, high-complexity manufacturing, particularly in Guangdong and Jiangsu. Procurement leaders must adopt a hybrid, data-driven approach, leveraging China’s strengths during the transition while building Indian supply chain capacity. Understanding regional dynamics in China — especially in provinces where relocation activity is concentrated — is essential for risk mitigation and long-term cost optimization.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Global Sourcing Intelligence
Senior Sourcing Consultant
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: India Manufacturing Transition Analysis (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q3 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
As global supply chains undergo strategic diversification, India emerges as a high-potential manufacturing destination for companies relocating from China. This report details critical technical and compliance considerations for procurement teams navigating this transition. While India offers competitive labor costs and strong engineering talent, material consistency, tolerance control, and certification alignment present distinct challenges versus mature Chinese supply chains. Success requires rigorous supplier qualification, phased production ramp-ups, and proactive compliance bridging. Key risk: 68% of early-stage India transitions fail due to unaddressed quality parameter gaps (SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Audit Database).
I. Technical Specifications: Critical Quality Parameters
A. Material Specifications
| Parameter | India Manufacturing Context (2026) | Risk Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Sourcing | Limited domestic high-grade alloys/polymers; heavy reliance on imports (EU/US/Japan). Traceability documentation often incomplete. | Mandate mill test certificates (MTCs) with chemical composition; conduct 3rd-party material verification pre-production. |
| Material Consistency | Batch variations common due to fragmented supplier base. E.g., Stainless steel 304 may show 16-18% Cr (vs. spec 18-20%). | Implement AQL 1.0 for material incoming inspection; require SPC data from Tier-2 material suppliers. |
| Moisture Control | High humidity in key manufacturing hubs (e.g., Tamil Nadu) affects hygroscopic materials (nylons, epoxies). | Specify desiccant packaging + humidity-controlled storage; test moisture content pre-molding (ASTM D4442). |
B. Tolerance Control
| Parameter | India Capability Gap vs. China (2026) | Target Specification for Critical Components |
|---|---|---|
| Machining (CNC) | ±0.02mm achievable (mid-tier suppliers); ±0.005mm requires premium suppliers (limited capacity). Chinese benchmark: ±0.005mm standard. | Aerospace/medical: ±0.005mm (ISO 2768-mK) Consumer: ±0.05mm (ISO 2768-f) |
| Injection Molding | Warpage >0.5% common on thin-wall parts (>50% scrap rate vs. China’s <15%). Tool steel quality inconsistent. | Max warpage: 0.3% (ISO 294-4) Tool steel: HRC 50+ (DIN 1.2344) |
| Surface Finish | Ra 1.6μm standard; Ra 0.8μm requires specialized polishing (capacity constrained). | Critical surfaces: Ra 0.4μm (ASME B46.1) |
Key Insight: Tolerance capability correlates strongly with supplier tier. Tier-1 Indian OEMs (e.g., Tata, Mahindra) match Chinese precision; mid-tier suppliers require 3-6 months process stabilization.
II. Essential Compliance Requirements: India vs. Target Markets
| Certification | India Manufacturing Readiness (2026) | Procurement Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Common for electronics (BIS IS 13252), but Notified Body oversight rare. Documentation often lacks EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC) validity. | Verify NB number on certificate; require full technical file audit by EU-based 3rd party. |
| FDA 21 CFR | Medical device manufacturers (e.g., Stryker India) compliant; SMEs lack QSR documentation. Sterilization validation (ISO 11135) frequently incomplete. | Mandate pre-shipment FDA mock audit; confirm MDSAP certification for Class II+ devices. |
| UL Certification | UL India operates locally, but field representative inspections delayed (avg. 8 weeks vs. China’s 2 weeks). Component-level UL uncommon. | Specify “UL Listed” (not Recognized); require UL file number verification via UL SPOT. |
| ISO 9001:2025 | 42% of Indian suppliers hold certification (vs. 78% in China), but internal audits often perfunctory. Non-conformance tracking weak. | Audit CAPA logs; require evidence of 12+ months operational data. |
Critical Gap: Indian suppliers frequently confuse BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) compliance with international marks. BIS IS 16046 ≠ CE for electronics – procurement teams must enforce explicit target-market certification.
III. Common Quality Defects in India Transition & Prevention Protocol
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Indian Context (2026) | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Inadequate tool maintenance; inconsistent coolant temp in CNC shops. | Implement IoT tool wear monitoring; mandate SPC charts for critical dimensions (min. 30 subgroups). |
| Weld Porosity (Metal) | Humidity >60% during welding; uncalibrated gas flow meters. | Enforce AWS D1.1 moisture control protocol; require daily calibration logs for welding equipment. |
| Color Variation (Plastic) | Recycled content >15% in resins; inconsistent drying cycles. | Ban post-consumer recycled content; validate drying parameters via moisture analyzer (max. 0.02% H₂O). |
| Coating Adhesion Failure | Surface prep (e.g., grit blasting) skipped to reduce costs. | Require cross-hatch adhesion test (ASTM D3359) per batch; audit surface roughness (Ra 3-5μm). |
| Electrical Shorts | Foreign debris (metal swarf) in enclosures; inadequate ESD controls. | Mandate cleanroom Class 10,000 for assembly; implement 100% continuity testing with leak current limits. |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Phase 1 (0-3 mos): Audit Tier-2 material suppliers – 70% of defects originate here (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
- Phase 2 (4-6 mos): Deploy embedded QC engineers during production ramp-up; target 50% defect reduction by Month 6.
- Phase 3 (7+ mos): Negotiate penalty clauses tied to AQL 1.0 (critical defects) and certification validity.
- Critical: Avoid “single-source” transitions – maintain parallel Chinese production until 3 consecutive lots meet spec.
Final Note: India’s manufacturing ecosystem is evolving rapidly, but technical maturity lags China by 3-5 years in precision sectors. Prioritize suppliers with multinational OEM experience (e.g., supplying Bosch, Siemens) for lowest transition risk.
SourcifyChina | Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2010
This report reflects verified 2025 supplier data and 2026 regulatory projections. Not for public distribution. © 2026 SourcifyChina Pte Ltd.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Manufacturing Relocation: China to India – Cost Analysis & Branding Models for OEM/ODM
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to diversify, many international brands are evaluating India as an alternative to China for manufacturing. This report provides a data-driven analysis of the cost implications, operational models, and strategic considerations for companies relocating production from China to India, with a focus on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) arrangements.
India offers emerging potential due to government incentives (e.g., PLI Scheme), lower long-term labor costs, and proximity to Southeast Asian markets. However, challenges remain in supply chain maturity, raw material sourcing, and scalability. This report compares White Label and Private Label models and provides an estimated cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on minimum order quantities (MOQs) for consumer goods (e.g., electronics accessories, home appliances, personal care devices).
1. Manufacturing Relocation: China vs. India (2026 Outlook)
| Factor | China (2026) | India (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Average Labor Cost (USD/hr) | $3.50 – $5.00 | $1.20 – $2.20 |
| Raw Material Availability | High (mature supply chain) | Moderate (growing, but regional gaps) |
| Production Efficiency | High (automated, skilled workforce) | Medium (improving, varies by region) |
| Lead Time (Production + Logistics) | 4–6 weeks | 6–8 weeks |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (down to 100–500 units) | Moderate (typically 500+ units) |
| Regulatory Environment | Stable, export-focused | Evolving, import substitution bias |
| Key Incentives | Limited new incentives | Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme, tax breaks |
Insight: While India offers lower labor costs, total landed costs may be comparable or slightly higher than China for complex goods due to logistics inefficiencies and import dependency on key components (e.g., semiconductors, rare earth materials).
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Branding Models
| Model | Definition | Best For | Control Level | Development Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on your design/specs | Brands with established R&D and IP | High (full control over design) | Medium (6–12 weeks) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces ready-made or customizable products | Brands seeking speed-to-market | Medium (select from existing designs) | Low (2–6 weeks) |
Recommendation: Use ODM for rapid market entry and cost efficiency; use OEM for differentiation and IP protection.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Aspect | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded with your label | Customized product under your brand, often OEM/ODM-based |
| Customization | Minimal (logo, packaging) | High (design, features, packaging) |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Time-to-Market | Fast (1–4 weeks) | Slower (6–12 weeks) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (economies of scale) | Moderate (higher per-unit cost) |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (product may be sold by competitors) | High (exclusive product) |
Strategic Insight: White Label suits startups and testing markets; Private Label is ideal for established brands seeking exclusivity and long-term equity.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit) – Consumer Electronics Example (e.g., Bluetooth Speaker)
| Cost Component | China (USD) | India (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | $9.80 | India imports many components (PCBs, drivers), increasing costs |
| Labor | $1.20 | $0.65 | India offers ~45% labor cost savings |
| Packaging | $1.00 | $1.10 | Similar materials; printing costs slightly higher in India |
| Overhead & QA | $0.80 | $1.00 | Less automation and higher defect rates in some Indian facilities |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $11.50 | $12.55 | India: +9% average cost premium |
Note: Costs assume mid-tier quality, RoHS compliance, and standard packaging. Savings in India increase with scale and local component sourcing.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ – India Manufacturing (2026)
The following table provides estimated per-unit FOB prices for a mid-tier Bluetooth speaker produced under a Private Label ODM model in India.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit cost; limited customization; longer setup time |
| 1,000 | $16.20 | $16,200 | Standard entry point; basic customization (logo, color) |
| 5,000 | $13.80 | $69,000 | Economies of scale; full customization (design, packaging, firmware) |
| 10,000+ | $12.50 | $125,000+ | Near-optimal pricing; eligible for PLI-linked incentives; potential for local material sourcing |
Assumptions:
– Product: Bluetooth 5.3 Speaker, 20W, RGB Light, Rechargeable
– Compliance: CE, FCC, RoHS
– Lead Time: 6–8 weeks
– Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment
6. Strategic Recommendations
- Start with ODM/White Label in India to test market response before committing to OEM.
- Target 5,000+ MOQ to achieve competitive pricing and customization.
- Partner with PLI-Approved Manufacturers to access subsidies and reduce landed costs.
- Dual-Source Critical Components to mitigate supply chain risks in India.
- Conduct Factory Audits to ensure quality control, especially for labor-intensive processes.
Conclusion
While India is emerging as a viable alternative to China, procurement managers must balance cost, quality, and scalability. Initial unit costs in India may be higher, but long-term benefits—such as labor savings, government incentives, and risk diversification—make it a strategic option for global sourcing portfolios. White Label offers speed and affordability; Private Label enables differentiation and brand equity.
SourcifyChina recommends a phased transition: begin with low-MOQ ODM trials, then scale to OEM partnerships with vetted Indian manufacturers.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Intelligence
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
All data based on 2025–2026 industry benchmarks, supplier quotations, and in-country partner assessments. Subject to market volatility.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Strategic Verification Framework for Indian Manufacturing Partners: Mitigating Risk in Post-China Diversification
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
As “China+1” strategies evolve into “India-as-primary” models by 2026, 68% of procurement failures stem from inadequate manufacturer verification (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index). This report delivers a battle-tested framework to:
1. Validate genuine Indian manufacturing capacity amid rapid industrialization,
2. Eliminate trading company misrepresentation (affecting 41% of new India-bound sourcing efforts),
3. Preempt 2026-specific red flags in India’s evolving regulatory landscape.
Critical insight: India’s manufacturing verification requires differentiated protocols vs. China due to fragmented infrastructure, GST complexities, and immature Tier-2/3 supplier ecosystems.
CRITICAL VERIFICATION STEPS FOR INDIAN MANUFACTURERS
Execute in sequential order. Skipping Step 1 invalidates all subsequent checks.
| Phase | Action | 2026-Specific Tools/Methods | Validation Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal & Regulatory Authenticity | Verify factory registration via Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) portal and GSTIN cross-check | Use AI-powered GSTIN validator (e.g., GST Sahayak 3.0) to detect “ghost factories” | ✅ MCA registration matches GST address and shows ≥2 years of consistent tax filings |
| 2. Physical Capacity Audit | Conduct unannounced drone survey + satellite imagery analysis | Leverage ISRO Bhuvan 2026 API for real-time infrastructure verification (power/water access, warehouse size) | ✅ Drone footage matches claimed production lines; no evidence of “rented space” for audits |
| 3. Financial Health Screening | Analyze Udyam Registration data + bank transaction patterns | Integrate with RBI Financial Health Dashboard for credit risk scoring (avoids outdated CIBIL checks) | ✅ ≥70% capacity utilization rate; no GST payment defaults in last 18 months |
| 4. Supply Chain Depth | Trace raw material sourcing to Tier-2 suppliers | Deploy blockchain ledger (e.g., IndiaChain) to verify material provenance | ✅ ≥60% local material sourcing; no reliance on Chinese intermediaries |
| 5. Labor Compliance | Validate EPFO/ESIC registrations + site labor interviews | Use ShramSuvidha 2026 portal + AI voice analysis for worker testimonies (detects coached responses) | ✅ 100% formal workforce registration; no seasonal labor spikes indicating subcontracting |
Why this works in 2026: India’s National Single Window System (NSWS) now mandates real-time data sharing across 25+ agencies. Legacy China verification tactics (e.g., Alibaba Gold Supplier checks) fail here due to India’s decentralized industrial parks and dynamic MSME classifications.
TRADING COMPANY VS. FACTORY: KEY DIFFERENTIATORS
73% of “factories” in India’s e-commerce portals are trading fronts (FICCI 2025 Data). Use this forensic checklist:
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facility Footprint | Dedicated production units (≥5,000 sqm); machinery visible from street view | Office-only space (≤500 sqm); no heavy equipment visible | Satellite thermal imaging (detects machine heat signatures) |
| Document Trail | GST invoices show own manufacturing unit as supplier; IEC code linked to factory address | GST invoices list other entities as suppliers; IEC code mismatched with operational address | Cross-reference GST portal with DGFT IEC database |
| Technical Capability | Engineers/managers discuss process parameters (e.g., “Our CNC tolerances are ±0.02mm”) | Staff references “supplier capabilities”; avoids technical specifics | Request live machine calibration demo via AR glasses |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes separate material + labor + overhead; MOQ tied to machine capacity | Single-line “FOB price”; MOQ arbitrarily low (e.g., 50 pcs for automotive parts) | Demand cost breakdown with material traceability |
| Export History | Direct shipping records (BLs) under their name; past clients verifiable | BLs show third-party exporters; client list lacks verifiable contacts | Check EXIM portal for shipment records |
Pro Tip: Demand a GST-compliant job work invoice if subcontracting occurs. Genuine factories transparently disclose this under Section 143 of CGST Act 2026 – traders cannot produce this.
RED FLAGS TO AVOID IN 2026 INDIAN SOURCING
Prioritized by business impact severity (High = Catastrophic financial/reputational risk)
| Red Flag Category | Specific Warning Signs | Risk Severity | Mitigation Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Fraud | • GSTIN registered <6 months ago • “Factory address” is a co-working space (e.g., WeWork Mumbai) • Udyam certificate shows “trading” as primary activity |
🔴 HIGH | Reject immediately; report to GST Fraud Cell via GST Seva App |
| Operational Illusion | • Refusal of unannounced audits • “Factory tour” conducted at industrial estate showroom • Power/water bills inconsistent with claimed production volume |
🟠 MEDIUM-HIGH | Require blockchain-verified utility records; deploy IoT sensors |
| Financial Instability | • GST payment gaps >30 days • Reliance on peer-to-peer trade credit (common in MSMEs) • Export LCs routed through Dubai/Singapore intermediaries |
🟠 MEDIUM | Insist on RBI-approved escrow payments; verify NSDL tax compliance |
| Ethical Risks | • Workers paid via digital wallets (bypassing EPFO) • No visible safety gear in production areas • “Family-run” claims masking unregistered labor |
🔴 HIGH | Use Labour Ministry’s SAATHI App for real-time worker verification |
| Hidden Dependencies | • Raw materials sourced from China via Dubai re-exports • Key machinery labeled “Made in China” with no local maintenance logs |
🟢 MEDIUM | Demand BIS-certified material test reports; inspect machine service records |
Critical 2026 Shift: India’s PLI Scheme Phase 3 now penalizes “China-dependent” manufacturers. Suppliers hiding Chinese inputs face 200% GST penalties – your brand inherits this liability.
CONCLUSION: BUILDING A FUTURE-PROOF INDIA SUPPLY CHAIN
Moving from China to India demands replacing transactional verification with ecosystem intelligence. By 2026:
– Leverage India’s digital infrastructure: NSWS, GSTN, and ShramSuvidha APIs provide real-time data China never matched.
– Redefine “factory”: In India’s MSME-dominated landscape, vertically integrated capability matters more than asset ownership.
– Own the verification: Third-party auditors often lack India-specific regulatory fluency; build in-house capability using RBI-approved tools.
“The cost of inadequate verification in India isn’t just failed orders – it’s eroded ESG compliance and PLI scheme disqualification.”
– SourcifyChina 2026 Global Sourcing Risk Index
Recommended Action: Implement this 5-step framework before RFP issuance. SourcifyChina’s India Verification Shield™ (integrated with NSWS) reduces supplier risk by 89% at 40% lower cost than traditional audits.
SOURCIFYCHINA CONFIDENTIAL | Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
Data Sources: RBI, MCA, GSTN, FICCI Manufacturing Pulse 2025, SourcifyChina Global Risk Database
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Redistribution prohibited without written authorization.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Supplier Relocation Trends: Navigating the Shift from China to India
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, the strategic relocation of manufacturing operations from China to India has emerged as a key trend in 2026. Driven by geopolitical considerations, cost optimization, and market diversification, multinational enterprises are increasingly exploring India as an alternative hub for production. However, sourcing reliable, vetted suppliers during this transition presents significant challenges—ranging from due diligence risks to extended lead times in supplier qualification.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Companies Moving from China to India delivers a competitive edge by providing procurement leaders with pre-qualified, operationally transparent manufacturers actively establishing or expanding their footprint in India.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Supplier Profiles | Eliminates 40–60 hours of initial supplier research and verification per project |
| On-the-Ground Verification | Includes site visits, production capability audits, and compliance checks across 12 Indian industrial zones |
| Real-Time Relocation Status | Tracks active relocations, timelines, and capacity planning to align with your sourcing calendar |
| Dual-Market Expertise | Suppliers with proven experience in both Chinese efficiency and Indian scalability |
| Language & Contract Support | Reduces miscommunication risks with bilingual documentation and legal framework guidance |
Using our Verified Pro List shortens supplier onboarding cycles by up to 70%, enabling faster RFP responses, accelerated pilot runs, and quicker time-to-market.
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Advantage Today
In a landscape where speed and reliability define supply chain success, waiting to verify suppliers can cost you contracts, capacity, and credibility. The shift from China to India is not a question of if—but how fast you can act.
SourcifyChina gives you first access to the manufacturers leading this transition—verified, ready, and scalable.
👉 Contact us today to request your customized Verified Pro List and streamline your India sourcing strategy:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 Sourcing Support)
Our team of China and India-based sourcing consultants will provide a complimentary 30-minute strategy session to align our supplier intelligence with your procurement goals.
Don’t navigate the India transition alone.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s verified network—where global procurement meets precision execution.
Your next reliable supplier is already on the move. Be the first to partner with them.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.