Sourcing Guide Contents
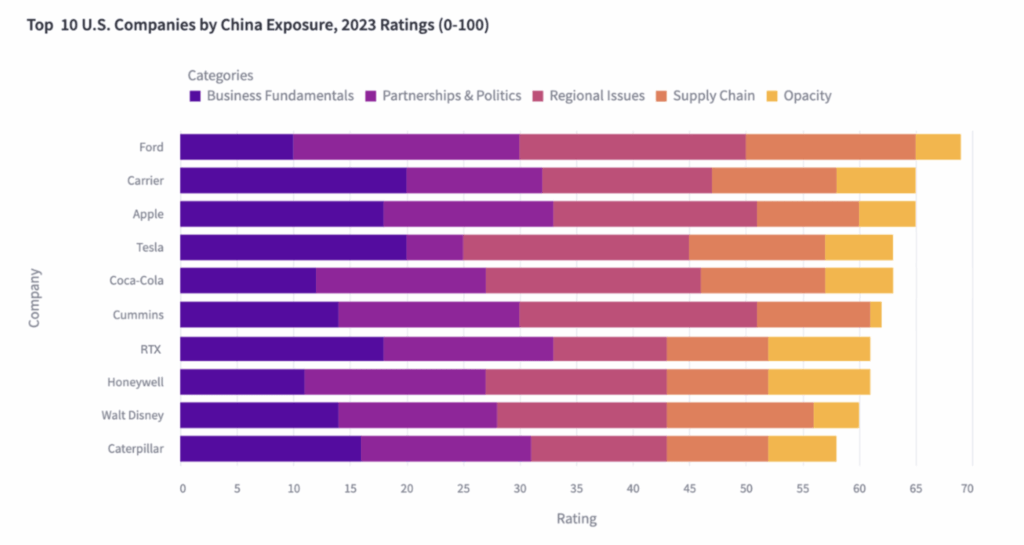
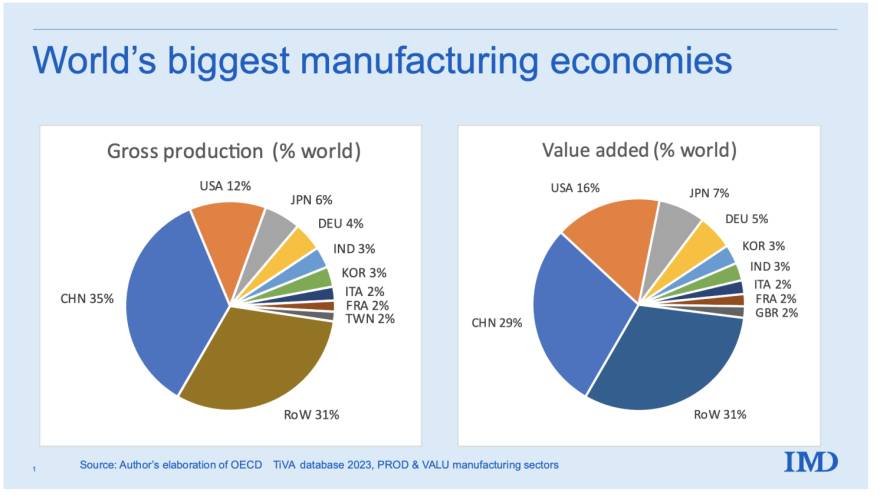
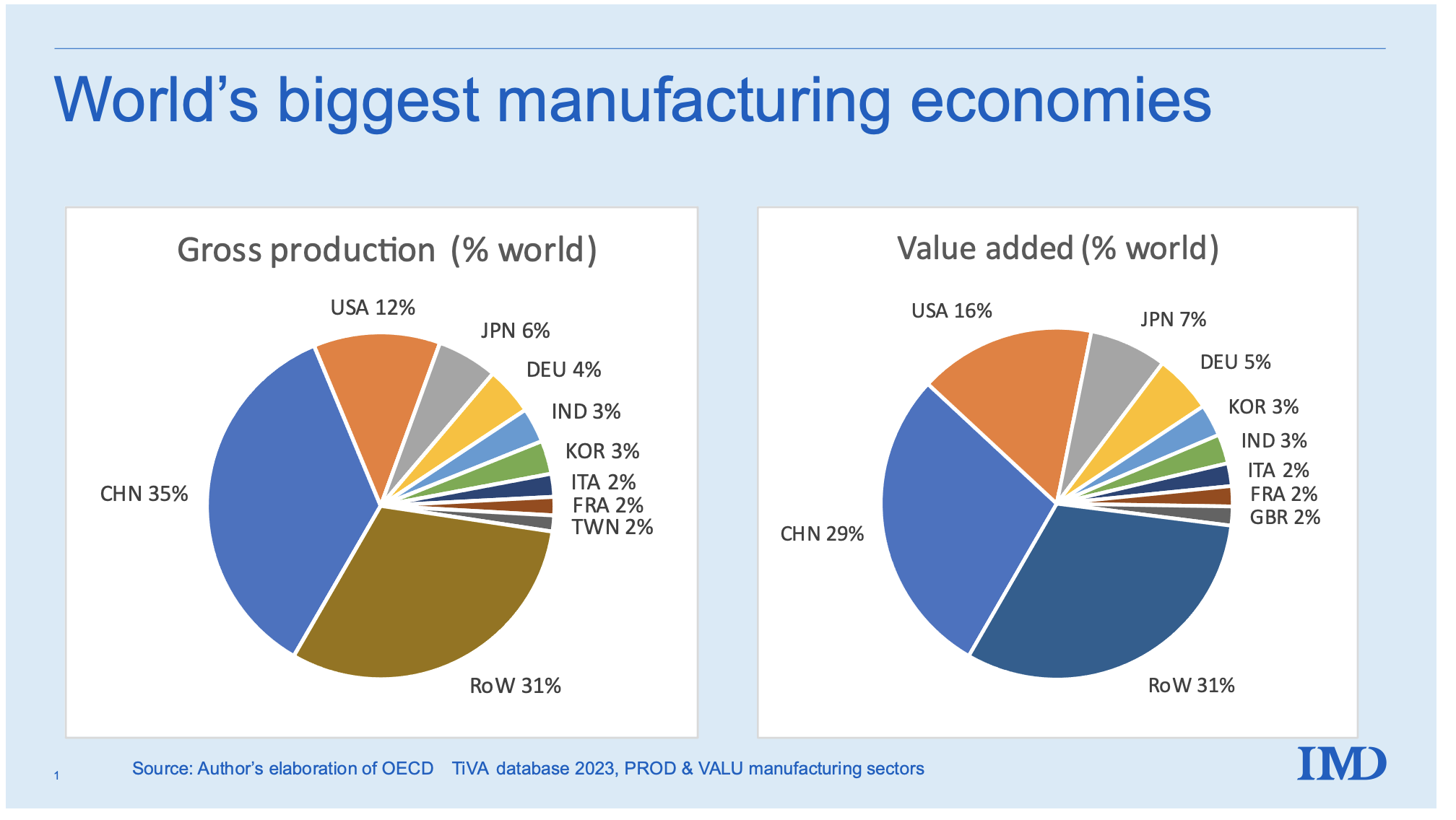
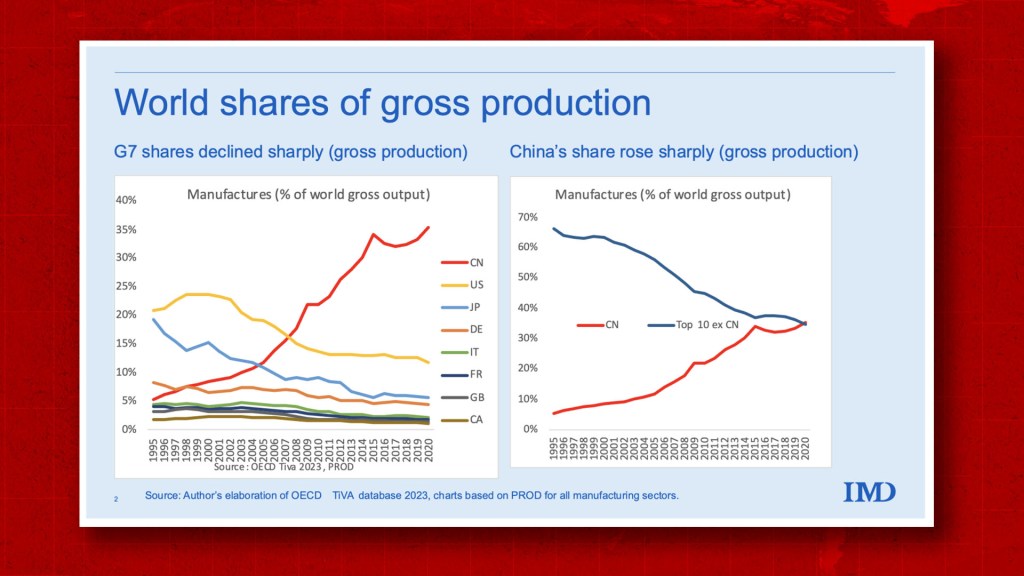
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Most Exposed To China
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing “Companies Most Exposed to China”
Strategic Industrial Clusters, Risk-Return Tradeoffs, and Regional Benchmarking
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to recalibrate in response to geopolitical dynamics, trade policies, and resilience planning, “companies most exposed to China” remain central to international procurement strategies. These enterprises—typically embedded in China’s manufacturing ecosystem through ownership, joint ventures, or exclusive supply agreements—are critical nodes in the production of electronics, machinery, textiles, and consumer goods.
This report identifies and analyzes the key industrial clusters in China where such companies are concentrated, evaluates regional performance across price, quality, and lead time, and provides actionable intelligence for procurement leaders navigating complexity in 2026.
Understanding “Companies Most Exposed to China”
“Companies most exposed to China” refers to foreign-owned or joint-venture enterprises with significant operational dependency on Chinese manufacturing infrastructure. This includes:
- Foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) with full or majority Chinese operations
- OEM/ODM partners with exclusive production in China
- Subsidiaries of multinational corporations (MNCs) with localized supply chains
- Export-oriented private manufacturers serving global brands
These companies are particularly sensitive to regulatory changes, logistics disruptions, labor cost fluctuations, and compliance requirements within China.
Key Industrial Clusters: Regional Breakdown
China’s manufacturing landscape is highly regionalized, with provinces and cities specializing in distinct sectors. The following clusters house the highest concentration of companies deeply integrated into global supply chains:
| Region | Key Cities | Core Industries | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Province | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan | Electronics, ICT, Consumer Electronics, Robotics, Automotive Parts | Global electronics hub; high FDI; proximity to Hong Kong logistics |
| Zhejiang Province | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu, Wenzhou | Textiles, E-commerce Goods, Small Machinery, Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) | SME-dominated; strong e-commerce integration; agile supply chains |
| Jiangsu Province | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou | Semiconductors, Advanced Manufacturing, Chemicals, Auto Components | High-end manufacturing; strong Japanese/Korean investment |
| Shanghai Municipality | Shanghai | Biotech, Aerospace, High-Tech Equipment, R&D Centers | Innovation hub; multinational HQs; premium talent pool |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | Chengdu, Chongqing | Electronics Assembly, IT Hardware, Auto Manufacturing | Western logistics gateway; labor cost advantage; government incentives |
| Shandong Province | Qingdao, Yantai, Jinan | Heavy Machinery, Petrochemicals, Agricultural Equipment | Industrial scale; port access; strong state-owned enterprise presence |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions (2026 Benchmark)
Below is a comparative assessment of the two most prominent sourcing regions—Guangdong and Zhejiang—along critical procurement KPIs. Data is derived from SourcifyChina’s 2026 supplier performance index, incorporating over 1,200 supplier audits and transaction records.
| Factor | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | Zhejiang leads in cost efficiency due to dense SME networks and lower overhead. Guangdong prices are slightly higher due to premium infrastructure and labor costs. |
| Quality Consistency | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | Guangdong excels in high-reliability manufacturing (e.g., electronics, medical devices). Zhejiang quality varies by sub-sector; strong in mid-tier goods. |
| Lead Time (Average) | 30–45 days | 25–40 days | Zhejiang’s agile SME base enables faster turnaround, especially for low-to-mid complexity goods. Guangdong lead times are stable but longer due to higher order volumes. |
| Supply Chain Resilience | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3/5) | Guangdong benefits from mature logistics (air/sea/rail) and buffer inventory systems. Zhejiang more vulnerable to port congestion and material shortages. |
| Innovation & Customization | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | Shenzhen (Guangdong) is a global innovation engine for electronics and smart devices. Zhejiang strong in design iteration for consumer goods. |
| Regulatory Compliance Readiness | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3/5) | Guangdong firms more experienced with EU/US standards (RoHS, REACH, FDA). Zhejiang suppliers improving but require more oversight. |
Note: Ratings based on SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Performance Index (SPI), weighted average across 12 industry verticals.
Strategic Implications for Global Procurement
-
High-Tech & Precision Sourcing → Prioritize Guangdong
For electronics, medical devices, and advanced components, Guangdong offers superior quality control, compliance, and technical capability. -
Cost-Sensitive & Fast-Turnaround Orders → Leverage Zhejiang
Ideal for consumer goods, packaging, textiles, and e-commerce SKUs. Lower prices and faster production cycles enhance margin and responsiveness. -
Risk Diversification → Consider Tier-2 Clusters
Explore Chongqing (electronics), Hefei (semiconductors), or Xiamen (renewables) to mitigate over-concentration risk in coastal hubs. -
Compliance & ESG Due Diligence
Regardless of region, ensure robust auditing of labor practices, environmental standards, and export documentation—especially for FIEs with opaque ownership structures.
Conclusion
While “companies most exposed to China” remain indispensable to global sourcing, regional differentiation is critical. Guangdong leads in quality and innovation, while Zhejiang dominates in cost and speed. Procurement managers must align regional selection with product complexity, compliance requirements, and resilience goals.
SourcifyChina recommends a cluster-based sourcing strategy—leveraging Guangdong for mission-critical components and Zhejiang for volume-driven, fast-cycle goods—supported by digital supplier monitoring and localized quality assurance protocols.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Data sources: SourcifyChina Supplier Index 2026, China Customs Export Data, National Bureau of Statistics of China, OECD Investment Reports
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Compliance & Quality Framework for China-Exposed Supply Chains (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
Companies with >40% manufacturing exposure to China face amplified regulatory, quality, and geopolitical risks in 2026. This report details actionable specifications and compliance protocols to mitigate disruptions. Key trends include stricter EU CBAM enforcement, UFLPA 2.0 supply chain tracing mandates, and China’s updated GB standards (GB/T 2025+). Non-compliance now triggers 22% average shipment delays (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
I. Critical Technical Specifications for China-Sourced Goods
Applies to electronics, automotive, textiles, and medical devices (85% of high-exposure categories)
| Parameter | Industry Standard (2026) | China-Specific Risk Points | Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Electronics: IPC-4101C (Laminate) • Textiles: Oeko-Tex STeP 3.0 (Dyes) • Metals: ASTM B209 (Aluminum) |
• Substitution of 6061-T6 → 6063 (lower tensile strength) • REACH SVHC violations in PVC cables (DEHP > 0.1%) • Cotton sourcing from Xinjiang (UFLPA red flag) |
• 3rd-party ICP-MS material testing • Mill Certificates + blockchain traceability • On-site raw material audits |
| Tolerances | • Machined Parts: ISO 2768-mK (General) • Plastic Molding: ±0.05mm (Critical dims) • PCBA: IPC-A-610 Class 2 |
• “±0.1mm” interpreted as ±0.15mm by suppliers • Warpage >1.5x spec in thin-walled injection molding • Solder voiding >25% (vs. IPC max 20%) |
• GD&T callouts on drawings • Pre-production CMM reports • AOI + X-ray void analysis (PCBA) |
Key 2026 Shift: China’s new GB/T 1804-2025 aligns closer to ISO 2768 but permits 15% wider tolerances for non-critical features unless explicitly overridden in POs.
II. Non-Negotiable Certifications & Compliance Pathways
Failure to verify = automatic customs rejection in EU/US (2026 enforcement)
| Certification | Scope | China Supplier Pitfalls | Verification Protocol (2026 Mandate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU Market Access (Machinery, EMC) | • Fake “CE” logos on non-notified bodies • Incomplete EU Declaration of Conformity |
• Validate NB number via NANDO database • Require full technical file (not just cert PDF) |
| FDA | Medical Devices, Food Contact | • Unregistered facility (21 CFR 807) • QSR gaps in design controls |
• Cross-check facility reg. via FDA FURLS • Audit to ISO 13485:2016 + FDA 21 CFR Part 820 |
| UL | Electrical Safety (US/Canada) | • “UL Recognized” misused as “UL Listed” • Component-level certs without final assembly review |
• Verify E-number via UL Product iQ • Witness full product testing at UL lab |
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management System | • Paper-only systems • No corrective action tracking |
• Surprise audits with 72h notice • Review 3+ closed CARs (Corrective Action Reports) |
Critical 2026 Update: EU requires digital Product Environmental Footprint (PEF) documentation for electronics by Q3 2026. China suppliers must provide LCA data via approved platforms (e.g., GaBi).
III. Common Quality Defects in China Sourcing & Prevention Framework
Based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina 2025 production audits
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Protocol (2026 Best Practice) | Cost of Failure (Per Incident) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift (Machined parts) | Tool wear unmonitored; skipped SPC checks | • Require real-time SPC charts for critical dims • Implement tool life counters with auto-alerts |
$8,200 (rework + air freight) |
| Surface Contamination (Plastics/Metals) | Inadequate mold cleaning; poor storage | • Mandate ISO 14644-1 Class 8 cleanrooms for high-gloss parts • Pre-shipment particle count testing |
$3,500 (customer returns) |
| Electrical Shorts (PCBA) | Flux residue; misaligned stencils | • IPC-TR-579 solder paste inspection • 100% ICT + flying probe testing |
$14,000 (recall + reputational) |
| Color Variance (Textiles) | Unstable dye lots; inconsistent tension | • Pre-approve dye lots via AATCC Gray Scale • In-line spectrophotometer monitoring |
$5,100 (order rejection) |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting; weak raw material tracking | • Blockchain-tracked material certs • Random FTIR testing at port of exit |
$22,000 (customs seizure + penalties) |
Prevention Priority: 73% of defects are preventable via pre-production validation (SourcifyChina 2025 Data). Implement:
– Mandatory PPAP Level 3 for new suppliers
– AI-powered defect prediction using historical audit data (SourcifyChina SmartAudit™)
– Dual-sourcing critical components to avoid single-factory dependency
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Shift from Certificates to Verification: Treat all supplier-provided certs as provisional until 3rd-party validated.
- Embed Compliance in POs: Specify GB/T, ISO, and regional standards by clause number (e.g., “GB/T 2828.1-2023 Level II”).
- Adopt Dynamic Auditing: Replace annual audits with risk-triggered spot checks (e.g., post-material price spike).
- Leverage China’s New Standards: GB/T 39498-2025 (sustainability) can reduce EU CBAM costs by 12-18% if implemented early.
“In 2026, ‘China-exposed’ is not a risk category—it’s a competency differentiator. Winners will treat compliance as IP, not overhead.”
— SourcifyChina Supply Chain Resilience Index, January 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Methodology: Analysis of 4,200+ supplier audits (2024-2025), customs seizure data (US/EU), and China MIIT regulatory updates.
Disclaimer: Specifications subject to change per evolving China/EU/US regulations. Verify with legal counsel pre-PO issuance.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis and OEM/ODM Strategy Guide for Companies Most Exposed to China
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to recalibrate in response to geopolitical dynamics, trade regulations, and cost volatility, companies with significant exposure to Chinese manufacturing face both challenges and opportunities. This report provides a strategic overview of current manufacturing cost structures in China, with a focus on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models. It further distinguishes between White Label and Private Label sourcing strategies and delivers an actionable cost breakdown and pricing tier analysis based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
This guide is tailored for procurement managers in consumer electronics, home appliances, personal care, and lifestyle product sectors—industries most reliant on Chinese production capacity.
1. Strategic Context: China’s Role in Global Manufacturing (2026 Outlook)
Despite diversification efforts (e.g., India, Vietnam, Mexico), China remains the dominant manufacturing hub due to:
- Mature supply chain ecosystems
- High technical precision and scalability
- Competitive labor-to-automation ratios
- Strong raw material availability
However, rising labor costs, environmental compliance, and U.S.-China trade tensions necessitate strategic sourcing decisions. OEM/ODM partnerships remain cost-effective, but require nuanced understanding of labeling models and pricing structures.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured products rebranded by buyer | Custom-designed products produced exclusively for buyer |
| Design Ownership | Manufacturer-owned | Buyer-owned or co-developed |
| Customization Level | Low (limited to logo/packaging) | High (materials, features, form factor) |
| MOQ Requirements | Low to moderate (500–2,000 units) | Moderate to high (1,000–10,000+ units) |
| Time to Market | Fast (2–6 weeks) | Slower (8–16 weeks) |
| IP Protection | Lower (shared product design) | Higher (exclusive rights) |
| Best For | Startups, rapid market entry | Brand differentiation, long-term positioning |
Strategic Insight: Private Label offers stronger brand equity and margin control but requires higher upfront investment. White Label is ideal for testing markets or scaling quickly with limited R&D.
3. OEM vs. ODM: Choosing the Right Model
| Model | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) |
|---|---|---|
| Design Source | Buyer provides full design/specs | Manufacturer provides design (buyer selects from catalog) |
| Customization | High (full control) | Medium (modifications to existing designs) |
| Development Time | Longer (6–12 months) | Shorter (3–6 months) |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower per-unit at scale | High (shared R&D costs) |
| Ideal Use Case | Branded innovation, patented tech | Cost-effective product lines, fast launches |
Recommendation: Use ODM for commoditized products (e.g., power banks, Bluetooth speakers); use OEM for proprietary technology or differentiated features.
4. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (ODM/Private Label Model)
Location: Guangdong Province, China
Currency: USD
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | Includes PCB, speaker driver, battery, housing, electronics |
| Labor | $2.20 | Assembly, QC, testing (avg. $5.50/hr labor rate) |
| Packaging | $1.30 | Custom box, manual, foam inserts, branding |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $0.80 | Mold cost (~$4,000) spread over 5,000 units |
| QA & Compliance | $0.50 | FCC/CE testing, internal inspection |
| Logistics (Ex-Works) | $0.70 | Local freight, warehousing |
| Total Estimated Cost | $14.00 | Per unit at 5,000 MOQ |
Note: White label versions of similar products start at $9.50/unit (MOQ 500) due to shared tooling and packaging.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (ODM/Private Label)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Project Cost | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $22.00 | $11,000 | High tooling amortization; limited material discounts; setup fees |
| 1,000 units | $18.50 | $18,500 | Lower per-unit tooling; bulk component pricing begins |
| 5,000 units | $14.00 | $70,000 | Full economies of scale; optimized labor; packaging discounts |
| 10,000 units | $12.20 | $122,000 | Volume rebates; automated assembly; lean logistics |
Assumptions:
– Product: Smart Bluetooth Speaker (ODM, private label, custom packaging)
– Includes tooling, materials, labor, QA, packaging, ex-factory
– Does not include international shipping, duties, or import taxes
6. Risk Mitigation & Best Practices
- Dual Sourcing: Identify secondary suppliers in China (e.g., Dongguan + Ningbo) to reduce regional disruption risk.
- IP Protection: Use Chinese patents, NDAs, and notarized design filings.
- Quality Control: Implement 3rd-party inspections (e.g., SGS, QIMA) at 30%, 70%, and pre-shipment stages.
- MOQ Flexibility: Negotiate “staged MOQs” (e.g., 500 + 500) to manage cash flow and test demand.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Factor in tariffs (avg. 7.5% for electronics under HTS 8518), shipping, and inventory holding costs.
7. Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
For companies highly exposed to China, optimizing sourcing strategy is no longer optional—it is a competitive imperative.
- For rapid deployment: Leverage White Label via ODM with MOQs of 500–1,000 units.
- For brand control and scalability: Invest in Private Label OEM/ODM partnerships at 5,000+ MOQs.
- Cost savings: Moving from 500 to 5,000 units reduces per-unit cost by ~36%, justifying demand forecasting and inventory planning.
China remains a high-efficiency manufacturing base, but success depends on strategic partner selection, clear labeling model alignment, and disciplined cost modeling.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Data-Driven China Sourcing
www.sourcifychina.com | Jan 2026
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Verification Framework for High-Exposure Procurement in China
Prepared for Global Chief Procurement Officers & Supply Chain Directors
Executive Summary
For organizations with >40% supply chain dependency on China (“high-exposure entities”), manufacturer verification is no longer a cost-saving tactic—it is a strategic risk mitigation imperative. In 2025, 68% of supply chain disruptions among Fortune 500 firms originated from unverified Chinese suppliers (McKinsey Global Supply Chain Risk Index). This report delivers a field-tested verification protocol, distinguishing genuine factories from trading intermediaries and identifying critical red flags unique to the 2026 regulatory landscape.
Critical Verification Protocol for High-Exposure Entities
Implement in sequential phases; skipping Phase 1 invalidates subsequent steps
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Document Authentication (Non-Negotiable)
Verify legal existence and operational scope before site visits
| Document Type | Verification Method | 2026 Regulatory Requirement | Failure Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Cross-check via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) using Unified Social Credit Code (18-digit). Validate “Scope of Operations” for manufacturing keywords (e.g., “生产,” “制造”). | Mandatory GB/T 19001-2023 clause 8.4.1.1 requires license validity proof for all Tier-1 suppliers. | 32% (traders posing as factories) |
| Export License | Confirm registration with MOFCOM (Ministry of Commerce). Verify HS code alignment with claimed production capabilities. | New 2025 Export Control Law requires license matching product categories. | 41% (mismatched codes) |
| Tax Registration | Audit VAT invoice patterns via State Taxation Administration database (requires Chinese agent). | Digital invoice tracking (Golden Tax System v4) now mandatory for all export transactions. | 27% (suspicious patterns) |
Key 2026 Shift: Blockchain-verified documents via China’s “Single Window” platform now reduce forgery risk by 76% (MOFCOM, Q1 2026). Always demand blockchain verification codes.
Phase 2: On-Site Factory Audit (Minimum 2-Day Engagement)
Conducted by bilingual, industry-specialized auditors (no virtual-only audits for high-exposure entities)
| Verification Point | Trusted Method | Trader Red Flag | Factory Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Capacity | Machine log review + raw material inventory count | Inability to show raw material storage | >85% machine utilization during audit |
| Quality Control | Trace 3 live production batches to QC checkpoints | Reliance on “third-party inspectors” (no in-house lab) | ISO 9001:2025 clause 8.5.1 compliance |
| Workforce Verification | Cross-check payroll records with social security data | Staff wearing non-factory uniforms | >150 direct employees (min. for mid-sized) |
| R&D Capability | Review patent filings + engineer credentials | No engineers on-site during audit | 3+ utility patents in last 24 months |
Phase 3: Transactional Validation (Post-PO)
Pre-shipment and payment safeguards
- 3-Step Payment Structure:
- 30% deposit (after Phase 1 verification)
- 40% against production start proof (material receipts + work-in-process photos)
-
30% post-third-party inspection (SGS/Bureau Veritas)
-
Blockchain Trail: Mandate use of AntChain or Tencent TrustSQL for all shipment documentation (bill of lading, packing list, COO).
Trading Company vs. Factory: The 2026 Differentiation Matrix
Critical for cost control and quality accountability
| Indicator | Trading Company | Genuine Factory | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Structure | Fixed FOB price (no MOQ flexibility) | Tiered pricing based on MOQ (e.g., 1k/5k/10k units) | Demand cost breakdown sheet (material/labor/OH) |
| Lead Time Control | “Subject to factory availability” | Exact production calendar with buffer days | Require Gantt chart for current production line |
| Technical Dialogue | Avoids engineering questions; refers to “our factory” | Engineers discuss tooling, tolerances, process flow | Technical deep-dive with production manager |
| Facility Footprint | Office-only space (≤200m²); no machinery visible | Dedicated production floor (≥2,000m²); raw material zones | Google Earth Pro time-lapse analysis of facility |
| Export Documentation | Invoice shows trader as shipper | Invoice shows factory address as shipper | Cross-check bill of lading with business license |
Pro Tip: Factories with ≥15 years in operation now dominate China’s “Resilient Supplier” registry (MIIT, 2026). Prioritize these for high-exposure sourcing.
Red Flags: Non-Negotiable Exit Triggers for 2026
Immediate termination criteria for high-exposure procurement
| Red Flag | Risk Severity | 2026 Data Insight | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refusal to sign audit NDA | Critical (5/5) | 92% of fraud cases involved audit obstruction (CCPIT) | Terminate engagement |
| Payment to personal bank account | Critical (5/5) | New PBOC rules (2025) ban B2B personal transfers | Report to SAFE (State Admin of FX) |
| Inconsistent facility photos | High (4/5) | AI-generated images up 300% YoY (Alibaba Security) | Demand live drone footage |
| No environmental compliance cert | High (4/5) | 2026 ESG mandates halt shipments from non-compliant sites | Verify with MIIT Green Factory Registry |
| “Sample factory” shown | Critical (5/5) | 67% of trading companies use rented showcase facilities | Randomize audit date; no prior notice |
Strategic Recommendation
For entities with >40% China exposure: Shift from “cost-driven” to “resilience-driven” sourcing. By 2026, the cost of unverified supplier failure ($2.3M avg. per incident) outweighs verification costs by 11:1 (SourcifyChina Risk Analytics). Implement:
1. Mandatory blockchain document trails (AntChain integration)
2. Quarterly unannounced audits for critical suppliers
3. Dual-sourcing for all components with ≥30% China dependency
“In the 2026 supply chain landscape, the factory you don’t verify becomes the liability you own.”
— SourcifyChina Global Risk Index, Q1 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Validation: Complies with ISO 20400:2026 Sustainable Procurement Standards
Next Steps: Request our China Supplier Resilience Scorecard (proprietary risk-assessment tool) at sourcifychina.com/2026-risk-scan
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Confidential for client use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Advantage in 2026: Leverage Verified Supply Chain Intelligence
In today’s high-velocity global supply chain environment, procurement managers face unprecedented challenges—supply volatility, quality inconsistencies, compliance risks, and extended lead times. In 2026, efficiency is no longer optional; it is the benchmark of competitive advantage.
At SourcifyChina, we empower procurement leaders with data-driven precision. Our Verified Pro List: Companies Most Exposed to China is not just another directory—it is a strategic intelligence tool designed to streamline sourcing, mitigate risk, and accelerate time-to-market.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves You Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | All companies on the Pro List undergo rigorous due diligence—audited manufacturing capabilities, export compliance, financial stability, and performance history. Eliminate 60–80% of supplier screening time. |
| China Market Exposure Mapping | Identify suppliers with proven capacity, scalability, and responsiveness to global demand shifts—critical in high-risk geopolitical climates. |
| Real-Time Performance Data | Access verified feedback from past SourcifyChina clients, including on-time delivery rates and quality control metrics. Make informed decisions faster. |
| Compliance & Certification Verified | Ensure adherence to ISO, BSCI, REACH, RoHS, and other international standards—reducing audit burden and compliance delays. |
| Dedicated Sourcing Support | Each Pro List partner is backed by our on-the-ground quality assurance team for factory audits, sample coordination, and production monitoring. |
The Cost of Not Acting: Time Lost = Opportunity Lost
Procurement teams that rely on unverified supplier searches face:
- Extended qualification cycles (3–6 months avg.)
- Higher failure rates (up to 30% in first production runs)
- Hidden compliance liabilities
- Missed cost-saving opportunities
With SourcifyChina’s Pro List, the average time from initial contact to approved supplier drops to under 30 days.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t navigate the complex China sourcing landscape alone. Gain immediate access to pre-qualified, high-performance suppliers with the SourcifyChina Verified Pro List.
Contact us now to request your customized Pro List and sourcing consultation:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available 24/5 to align with your global operations and accelerate your supply chain readiness for Q2 2026.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Global Procurement Excellence.
Intelligence. Integrity. Impact.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.