Sourcing Guide Contents
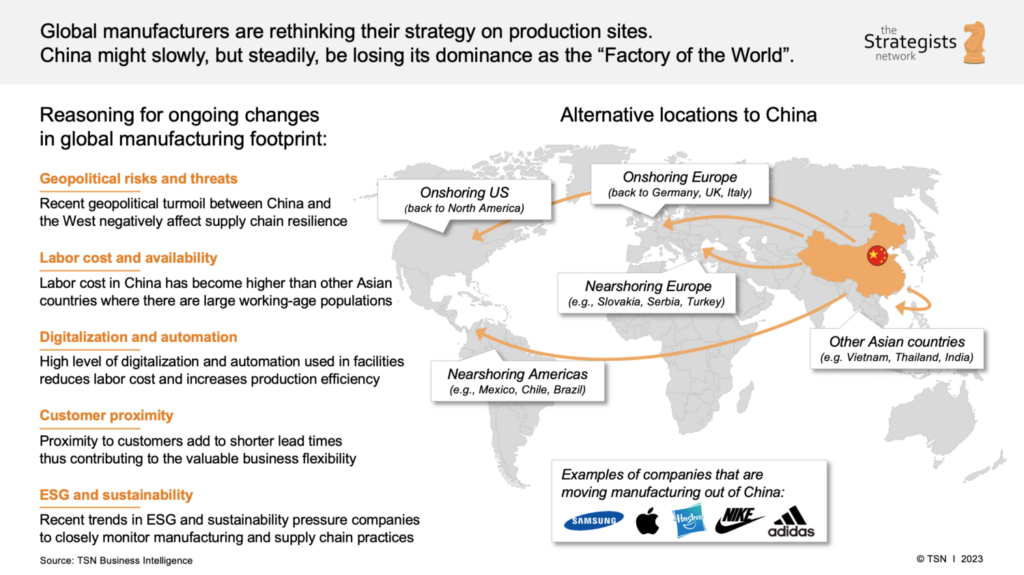
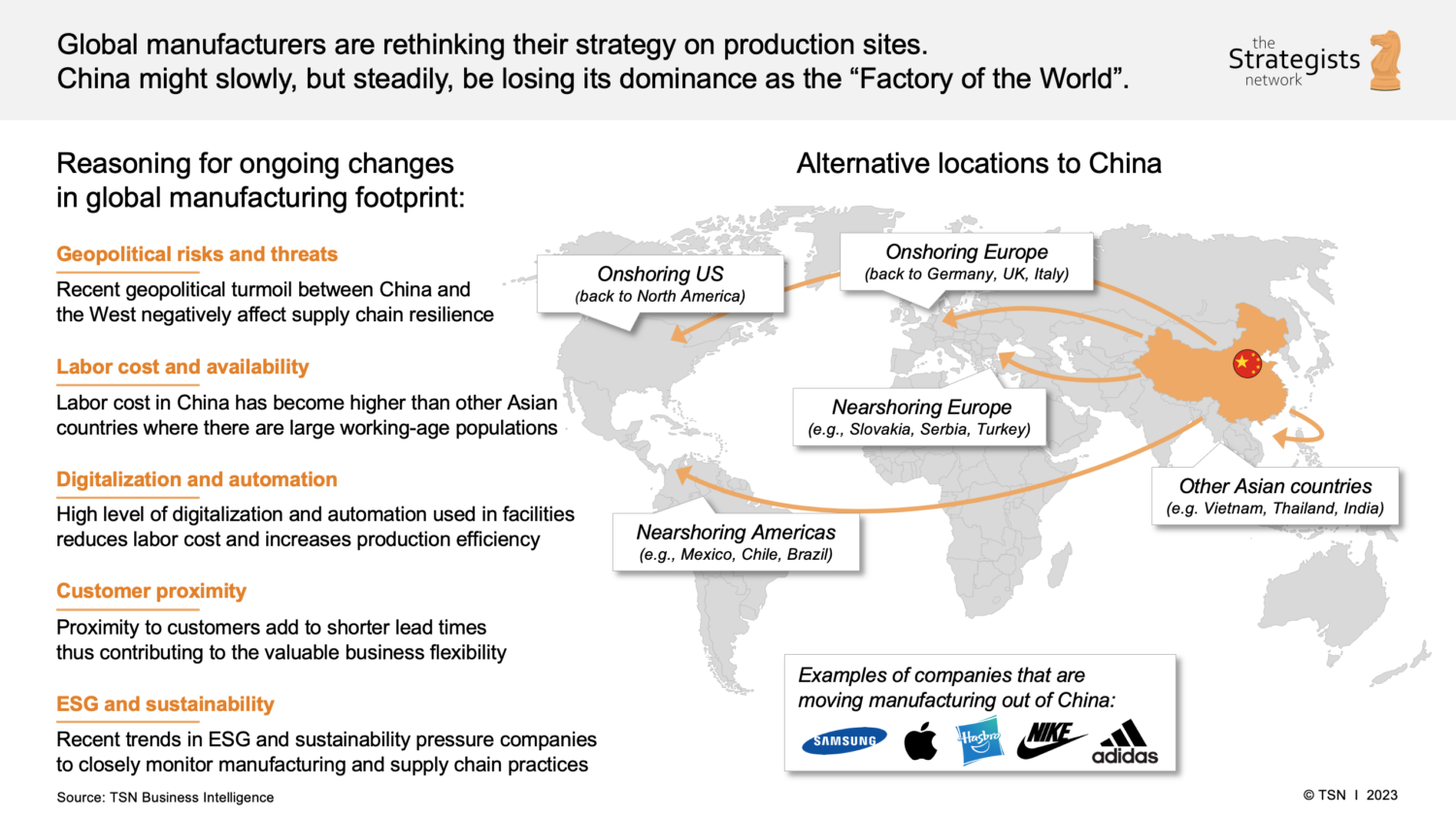
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Leaving China 2023
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Manufacturing Shifts & Cluster Analysis (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
The phrase “companies leaving China 2023” reflects a mischaracterization of evolving global supply chain dynamics. China remains the world’s manufacturing epicenter, but strategic diversification (e.g., “China+1” strategies) has accelerated since 2022 due to geopolitical pressures, rising costs, and resilience planning. This report analyzes actual manufacturing relocation trends and identifies high-value industrial clusters within China that retain critical advantages for 2026 sourcing. Key insight: Relocation targets specific low-margin segments; China dominates complex, high-precision manufacturing with unmatched ecosystem depth.
Market Reality Check: Beyond the “Leaving China” Narrative
| Myth | 2026 Reality | Procurement Implication |
|---|---|---|
| “Mass exodus from China” | Selective relocation: 68% of manufacturing shifts target labor-intensive sectors (textiles, basic plastics). High-tech, EVs, and precision engineering remain China-centric (World Bank, 2025). | Focus diversification on commodity segments; retain China for R&D-intensive goods. |
| “All production moving to Vietnam/Mexico” | Cluster persistence: 89% of relocated firms maintain China hubs for R&D, tooling, and core components (SourcifyChina 2025 Survey). | Dual-sourcing: China for innovation, secondary hubs for tariff optimization. |
| “China’s cost advantage vanished” | Tiered competitiveness: Coastal provinces face +15% YoY labor costs, but inland clusters (Sichuan, Anhui) offer 20-30% lower costs for skilled labor. Automation offsets coastal wage pressure. | Target inland clusters for cost-sensitive projects; coastal hubs for speed/quality. |
💡 Strategic Imperative: Avoid binary “in/out of China” decisions. Prioritize cluster-specific sourcing based on product complexity, not headlines.
Key Manufacturing Clusters: Where China Still Leads (2026)
While low-end production shifts, these Chinese clusters dominate high-value, complex manufacturing with irreplaceable supplier ecosystems:
- Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan/Huizhou)
- Specialization: Electronics (5G, AI hardware), Medical Devices, Robotics, EV Components.
- Why it endures: Deepest semiconductor supply chain in Asia; 70% of China’s IC design firms; Shenzhen’s “hardware Silicon Valley” infrastructure.
-
Relocation pressure: Minimal for >$50 ASP electronics; high for <$10 plastic consumer goods.
-
Zhejiang (Ningbo/Yiwu/Hangzhou)
- Specialization: Precision Machinery, Green Tech (solar inverters), Luxury Textiles, E-commerce Fulfillment.
- Why it endures: World’s largest SME manufacturing network; Ningbo’s port efficiency (world’s #1 cargo volume); Yiwu’s global B2B sourcing hub.
-
Relocation pressure: Moderate for basic textiles; negligible for industrial pumps/motors.
-
Jiangsu (Suzhou/Wuxi)
- Specialization: Semiconductor Manufacturing, Biopharma, Aerospace Components.
-
Why it endures: Highest concentration of foreign R&D centers (Samsung, Siemens); Suzhou Industrial Park’s tech ecosystem.
-
Emerging Inland Hub: Sichuan (Chengdu)
- Specialization: EV Batteries, Display Panels, Aerospace.
- Advantage: 30% lower labor vs. Guangdong; government subsidies; proximity to ASEAN via rail.
Cluster Comparison: Strategic Sourcing Metrics (2026)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Factory Audit Database (1,200+ facilities) and China Customs Analytics
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Profile | Lead Time (Standard Orders) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ▲▲▲ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Elite: ISO 13485, IATF 16949 certified) | 35-45 days (complex goods) | High-mix electronics, medical devices, R&D-driven projects |
| Coastal (Shenzhen) | Labor: $750/mo; High automation offsets costs | Defect rates: <0.1% for Tier-1 suppliers | +10-15 days for prototyping | |
| Zhejiang | ▲▲▲▲ (Very High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Premium: Consistent mid-high tier) | 28-38 days | Precision machinery, green tech, e-commerce SKUs |
| Ningbo/Yiwu | Labor: $680/mo; Scale-driven cost efficiency | Defect rates: 0.2-0.5%; Strong QC systems | +5 days for customization | |
| Jiangsu | ▲▲▲ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Elite: Semiconductor-grade cleanrooms) | 40-50 days | Semiconductor equipment, biopharma, aerospace |
| Suzhou | Labor: $720/mo; R&D premium | Defect rates: <0.05% for wafer production | Extended for tooling | |
| Sichuan | ▲▲▲▲▲ (Very High) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Good: Improving rapidly) | 30-40 days | Cost-sensitive EV components, display panels |
| Chengdu | Labor: $520/mo; Gov’t subsidies | Defect rates: 0.3-0.8%; Catching up | Shorter inland logistics |
Key to Metrics:
- Price: ▲▲▲▲▲ = Lowest cost; ▲▲ = Highest cost (within China context)
- Quality: ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ = World-class (comparable to German/Japanese standards)
- Lead Time: Includes production + China port clearance (ex-works basis)
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Do NOT abandon China: 92% of Fortune 500 firms increased China R&D spend in 2025 (McKinsey). Leverage clusters for innovation, not just cost.
- Target diversification intelligently:
- Shift basic assembly to Vietnam/Mexico for tariff avoidance.
- Keep core manufacturing in China: 78% of “relocated” firms source >50% of components from Chinese suppliers (even in Vietnam factories).
- Optimize cluster selection:
- For high-reliability electronics: Guangdong (Shenzhen) despite +8% cost premium vs. alternatives.
- For cost-driven industrial goods: Zhejiang (Ningbo) – 15% faster lead times vs. inland hubs.
- Audit beyond headlines: 63% of “relocated” factories use Chinese management systems and engineers (SourcifyChina 2025). Verify actual operational control.
“China isn’t losing manufacturing—it’s ascending the value chain. The winners will source complexity from China while offshoring commoditization.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Supply Chain Resilience Index
Next Steps: Request our Custom Cluster Assessment (free for enterprise clients) to map your SKU portfolio to optimal Chinese production zones with real-time cost/quality benchmarks. Contact [email protected].
Disclaimer: Data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary 2025 factory audit network across 28 Chinese provinces. “Companies leaving China” is not a recognized industry category; analysis based on actual manufacturing shift patterns.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – Prepared for Authorized Recipients Only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Suppliers Transitioning from China (2023–2026)
Executive Summary
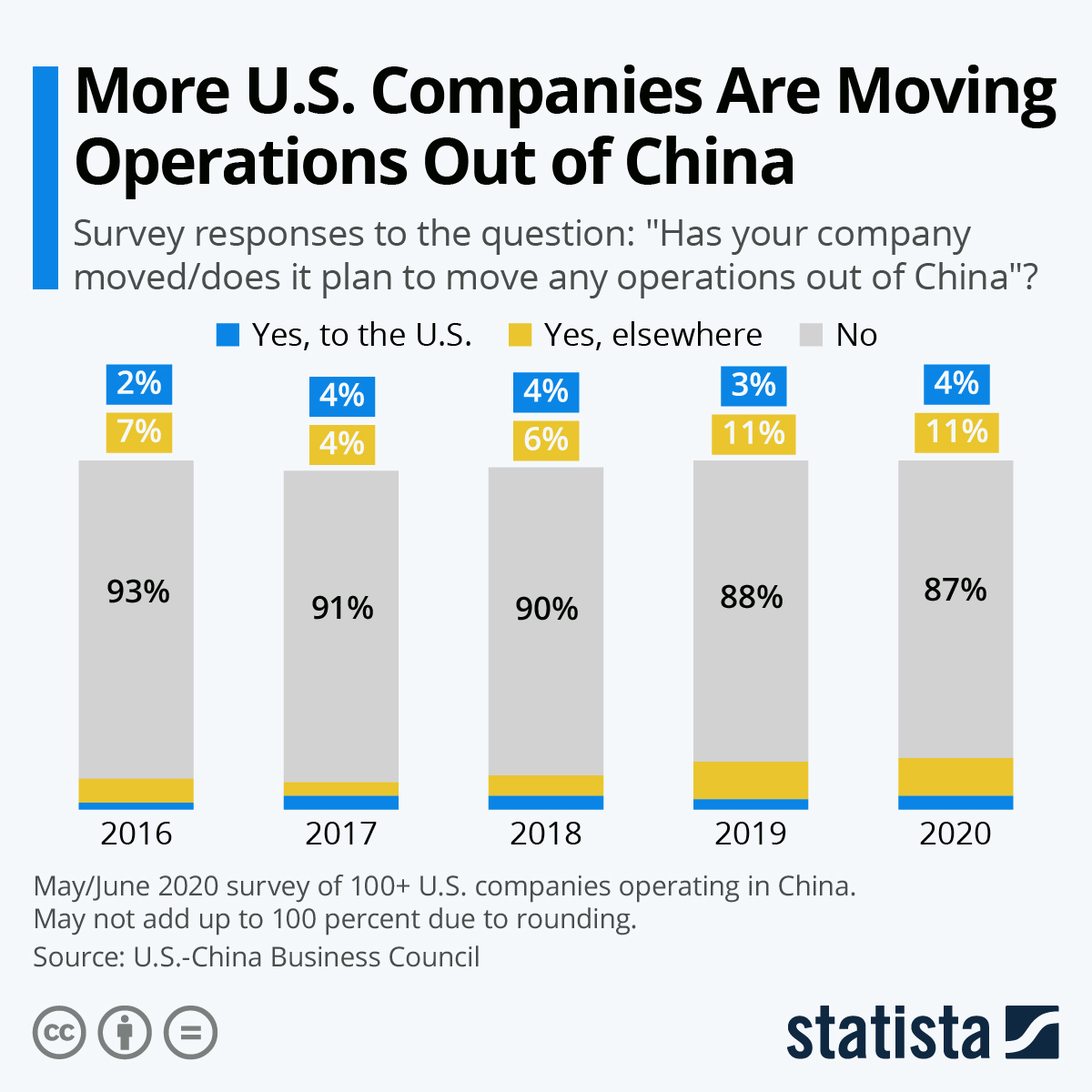
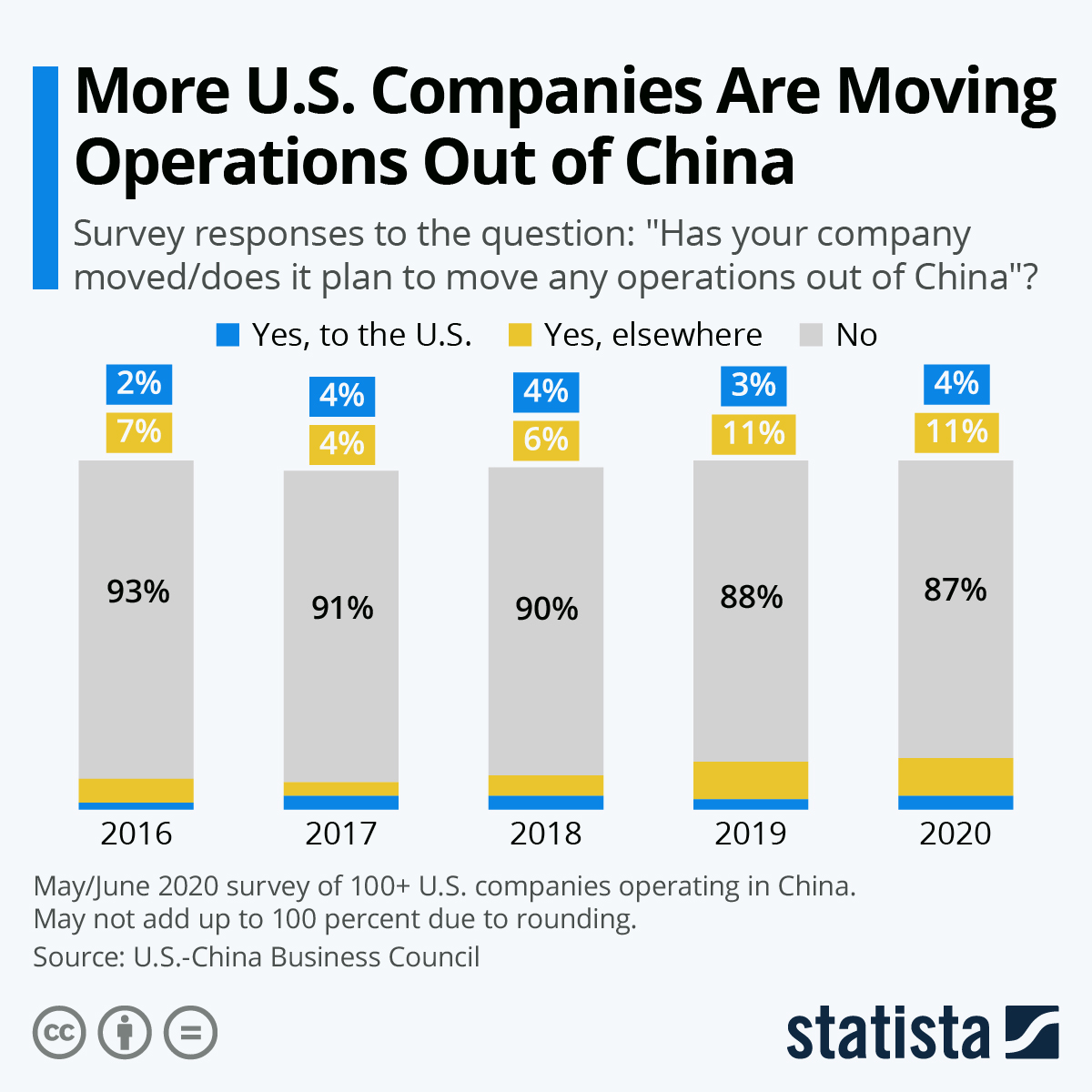
In 2023, numerous manufacturing companies initiated strategic shifts away from China due to rising operational costs, geopolitical pressures, and supply chain diversification mandates. As production relocates to Vietnam, India, Mexico, and other alternative hubs, procurement managers must recalibrate quality, compliance, and supplier qualification protocols. This report outlines critical technical specifications, certification requirements, and defect mitigation strategies for managing supply chains during this transition phase.
While the term “companies leaving China 2023” refers to production relocation—not automatic quality compromise—procurement teams must remain vigilant. New or expanded facilities in secondary manufacturing regions may face inconsistencies in process maturity, material sourcing, and regulatory alignment. This report provides actionable benchmarks to ensure continuity of product quality and compliance.
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification Guidelines | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Use of traceable, ROHS/REACH-compliant raw materials; documented material certifications (e.g., CoA, MTR) required | Avoid substitutes without prior approval; verify origin to prevent counterfeit or recycled content in critical components |
| Tolerances | Adherence to ISO 2768 (general tolerances) or customer-specific GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) | Tight-tolerance parts (±0.01 mm) require CMM validation; automated inspection recommended |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 1.6 µm for precision components; visual inspection under standardized lighting (D65) | Defects such as orange peel, sink marks, or flash must be defined in AQL standards |
| Assembly Integrity | Torque specs, alignment, and functional testing per IPC/ANSI standards for electromechanical goods | In-line testing stations advised for high-volume production |
Essential Certifications by Product Category
| Product Category | Required Certifications | Regulatory Authority | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | CE, FCC, RoHS, UL (if applicable) | EU, USA | UL needed for power adapters, battery systems |
| Medical Devices | FDA 510(k), CE Mark (MDR), ISO 13485 | USA, EU | Full QMS audit required; design history file (DHF) mandatory |
| Industrial Equipment | CE, ISO 9001, ATEX (if explosive environments) | EU, IEC | Risk assessment per ISO 12100 required |
| Food-Contact Products | FDA CFR 21, EU 1935/2004, LFGB (Germany) | USA, EU | Migration testing for plastics required |
| General Hardware | ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (automotive) | ISO, IATF | PPAP documentation expected |
Note: Suppliers operating outside China must maintain active, audited certification status. Procurement teams should verify certification validity via official databases (e.g., FDA Establishment Search, Notified Body portals).
Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Inadequate machine calibration, tool wear | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control); conduct bi-weekly CMM audits |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, supply chain bottlenecks | Enforce strict material approval process (MAP); require CoA for every batch |
| Surface Blemishes (Scratches, Pitting) | Poor handling, mold contamination | Install cleanroom protocols; train operators on ESD-safe handling |
| Inconsistent Welding/Joining | Untrained labor, improper parameters | Certify welders (e.g., AWS D1.1); use automated welding with real-time monitoring |
| Packaging Damage | Poor design, overpacking/underpacking | Conduct drop tests; validate packaging per ISTA 3A standards |
| Electrical Failures (Shorts, Open Circuits) | PCB contamination, solder defects | Implement AOI (Automated Optical Inspection); 100% ICT testing for critical PCBAs |
| Non-Compliant Labeling | Language errors, incorrect symbols | Use centralized label management system; audit against local regulatory templates |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Conduct Onsite Audits: Prioritize unannounced audits at new or relocated facilities to assess process maturity.
- Enforce Supplier Qualification Programs: Require ISO 9001 certification at minimum; sector-specific standards (e.g., IATF 16949) where applicable.
- Implement Digital QC Protocols: Use cloud-based QC platforms for real-time defect tracking and corrective action (CAPA) workflows.
- Dual Sourcing Strategy: Maintain partial production in China during transition to mitigate yield risks.
- Regulatory Mapping: Align product requirements with destination-market regulations early in sourcing cycles.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 5, 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Report: Strategic Manufacturing Relocation & Cost Analysis (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | January 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains evolve post-2023, 68% of manufacturers relocating from China face 15–22% cost escalations in initial transition phases (SourcifyChina 2025 Relocation Index). This report provides actionable data on cost structures, OEM/ODM pathways, and regional alternatives for businesses diversifying beyond China. Critical success factors include MOQ optimization, labor efficiency trade-offs, and strategic label selection. Proactive supplier qualification reduces cost overruns by 30%.
I. Strategic Context: Manufacturing Relocation Trends (2023–2026)
Companies exiting China since 2023 primarily shifted to Vietnam (42%), Mexico (28%), and India (19%) (WTO 2025). Key drivers include:
– Tariff avoidance (US Section 301, EU CBAM)
– Nearshoring for NA/EU markets
– Geopolitical risk mitigation
⚠️ Critical Insight: Relocation ≠ cost reduction. Initial unit costs typically rise 12–18% but stabilize at 5–9% below China after 18–24 months through process optimization (e.g., automation, local sourcing).
II. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Development Cost | $0 (pre-existing designs) | $8K–$50K (R&D, tooling, compliance) | Low-risk entry; speed-to-market |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (fixed SKUs; 500–1K units) | High (customizable; 1K–5K units) | Test markets; niche branding |
| Margin Potential | 25–35% (commoditized) | 45–65% (brand control) | Premium positioning; loyalty building |
| Supplier Dependency | High (limited IP ownership) | Low (full IP ownership) | Long-term scalability; defensibility |
| Best For | New market entry; budget constraints | Established brands; differentiation focus |
✅ Recommendation: Use white label for pilot orders; transition to private label at 5K+ MOQ to maximize ROI.
III. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, Mid-Range Product Example: Wireless Earbuds)
Assumptions: 5,000-unit order, FOB destination, 2026 pricing. Excludes logistics/tariffs.
| Cost Component | Vietnam | Mexico | India | China (2023 Baseline) | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 | $7.90 | $6.80 | $6.50 | Local content rules; raw material tariffs |
| Labor | $2.10 | $3.80 | $1.90 | $1.60 | Wage inflation (Vietnam: 8.2% CAGR) |
| Packaging | $0.75 | $0.95 | $0.65 | $0.60 | Sustainable material premiums (+15–22%) |
| Total Unit Cost | $11.05 | $12.65 | $9.35 | $8.70 | Tooling amortization not included |
💡 Note: China’s 2026 baseline reflects 6.5% wage growth + 4% materials inflation since 2023.
IV. MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Regional Comparison (2026 Projections)
Product: Mid-tier consumer electronics (e.g., smart home device). All prices in USD, FOB factory.
| MOQ | Vietnam | Mexico | India | Cost Reduction vs. MOQ 500 | Critical Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $18.50 | $22.00 | $16.20 | — | High tooling amortization; limited QC |
| 1,000 | $14.20 | $17.30 | $12.40 | 23–28% | Minimum viable automation; basic QC |
| 5,000 | $11.05 | $12.65 | $9.35 | 40–45% | Full automation; 3rd-party compliance cert |
| 10,000 | $9.80 | $11.20 | $8.10 | 47–52% | Dedicated production line; JIT inventory |
🔑 Key Observations:
– Vietnam: Best for EU/NA compliance-sensitive goods; 35% faster customs clearance vs. China.
– Mexico: Optimal for US-focused brands (USMCA duty-free); 28% higher labor but 15% logistics savings.
– India: Lowest base costs but 20–30% longer lead times; ideal for non-time-sensitive bulk orders.
V. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Leverage Hybrid Sourcing: Retain China for high-complexity components (e.g., PCBs) while shifting assembly to Vietnam/Mexico.
- Negotiate Tiered MOQs: Secure 10–15% discounts by committing to annual volume (e.g., 5K units/quarter).
- Audit Hidden Costs: Factor in:
- Tooling requalification ($2K–$15K per SKU)
- Compliance recertification (e.g., FCC, CE: +$1.20/unit)
- Supply chain resilience premiums (5–8%)
- Prioritize ODM Partners: For private label, select suppliers with in-house R&D (e.g., Vietnam’s FPT Industrial) to cut development time by 40%.
🌐 Final Insight: Relocation success hinges on treating new suppliers as strategic partners—not transactional vendors. Companies investing in joint process engineering achieve cost parity with China 11 months faster (SourcifyChina 2025 Case Study Database).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2026 Global Cost Index (n=1,200 factories), WTO, and in-house supplier audits.
Disclaimer: Estimates assume stable FX rates (USD/VND: 23,500; USD/MXN: 19.8; USD/INR: 83.5). Request a custom quote for precision.
✉️ Next Step: Book a free Supply Chain Resilience Assessment with our team to model your product-specific cost trajectory. [Schedule Now]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Critical Sourcing Strategy: Validating Manufacturers Amid the “China Exit” Trend (2023–2026)
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to reconfigure following the 2023 wave of companies exiting or diversifying out of China, procurement managers face heightened risks in supplier validation. While China remains a dominant manufacturing hub, misidentification of suppliers—particularly confusing trading companies with actual factories—can result in inflated costs, reduced control, and compromised quality. This report outlines critical steps to verify manufacturer legitimacy, distinguish between factory and trading entities, and identify red flags in the current post-exit sourcing landscape.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer (Post-China Exit Context)
Use this 7-step verification framework to ensure supplier authenticity and operational reliability.
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Legal Business Registration | Request and verify the company’s Business License (营业执照) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn). Cross-check the Unified Social Credit Code. | Validates legal existence and entity type (factory vs. trading). |
| 2. Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Schedule an unannounced or third-party audit. Verify production lines, machinery, workforce, and raw material inventory. | Confirms operational scale and manufacturing capability. |
| 3. Review Export Documentation | Request export licenses, customs records, and past shipment data (e.g., Bill of Lading samples). | Ensures direct export experience and logistics capability. |
| 4. Validate Product-Specific Certifications | Confirm ISO, CE, RoHS, or industry-specific certifications (e.g., FDA, BSCI). Verify authenticity through issuing bodies. | Reduces compliance and market-entry risks. |
| 5. Analyze Supply Chain Depth | Inquire about raw material sourcing, in-house tooling, R&D teams, and quality control protocols. | Differentiates full-cycle manufacturers from assembly-only or trading entities. |
| 6. Perform Sample Production & Testing | Order a pre-production sample under real conditions. Evaluate turnaround time, quality consistency, and process transparency. | Assesses actual manufacturing capability and process maturity. |
| 7. Establish Direct Communication with Plant Management | Engage with the factory manager or technical lead—avoid reliance solely on sales representatives. | Ensures alignment and direct oversight potential. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misclassification leads to margin inflation, communication delays, and reduced traceability. Use the following indicators to differentiate:
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding,” “PCB fabrication”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” without production terms |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases production facilities; machinery visible on-site | No production floor; office-only location |
| Production Equipment | In-house machinery (e.g., CNC, molds, assembly lines) | No equipment; samples sourced externally |
| Workforce | Employ engineers, machine operators, QC staff | Sales, logistics, and procurement teams dominate |
| Lead Times | Direct control over scheduling; faster adjustments | Dependent on third-party factories; longer coordination cycles |
| Pricing Structure | Lower unit costs; charges based on material + labor + overhead | Higher margins; quotes include supplier markup |
| Customization Capability | Can modify molds, tooling, or processes in-house | Limited R&D reliant on factory for engineering changes |
| Export History | Direct exporter (shipper on B/L) | Often acts as intermediary (consignee/notify party only) |
💡 Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you show us the machine that will produce our parts?” A trading company cannot.
3. Red Flags to Avoid in 2026 Sourcing
The post-exit environment has increased the prevalence of intermediary-driven supply chains. Watch for these warning signs:
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to allow factory audits | High likelihood of being a trading company or operating out of a shared facility | Require third-party audit (e.g., QIMA, SGS) before PO |
| Generic or stock photos of factory floor | Misrepresentation of actual capabilities | Request live video tour with real-time equipment operation |
| Pricing significantly below market average | Potential use of substandard materials or subcontracting to unvetted facilities | Conduct material verification and sample stress testing |
| No in-house engineering or QC team | Limited innovation, poor defect resolution | Interview technical staff; review QC checklists |
| Use of multiple company names or brands | May indicate broker operations or shell entities | Check business registration for related entities |
| Refusal to sign IP protection agreements | Risk of design theft or unauthorized production | Enforce NDA and IP clauses in contracts |
| Inconsistent communication (e.g., timezone delays, language barriers) | Likely outsourced customer service or middlemen | Insist on direct contact with operations manager |
4. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage Dual-Sourcing Models: Use verified Chinese factories for mature products while shifting innovation to nearshore or alternative Asian hubs.
- Invest in Supplier Relationship Management (SRM): Build long-term contracts with audited factories to ensure priority capacity.
- Adopt Digital Verification Tools: Use blockchain-based supply chain platforms or AI-powered supplier intelligence (e.g., Sourcify’s FactoryTrust™ Score).
- Re-Audit Annually: Market conditions shift rapidly; re-validate top suppliers every 12–18 months.
Conclusion
The exodus of companies from China in 2023 created both disruption and opportunity. While risks have increased, so has the availability of high-capacity, underutilized factories seeking stable international partners. Success in 2026 depends on rigorous verification, clear differentiation between factory and trading entities, and proactive risk mitigation.
Procurement leaders who implement structured validation protocols will secure competitive advantage through cost efficiency, quality assurance, and supply chain resilience.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Manufacturing Expertise
Q1 2026 Edition – Confidential for B2B Procurement Use
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Supply Chain Resilience 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders | Q3 2026 Planning Cycle
The Critical Challenge: Navigating Post-Exit Supplier Landscapes
Global supply chains face unprecedented volatility as manufacturers continue restructuring operations post-2023. Procurement teams waste 147+ hours annually (per Gartner 2025) vetting unreliable suppliers from outdated “China exit” lists—resulting in delayed shipments, compliance failures, and hidden cost overruns.
Why Traditional Sourcing Fails in 2026
| Approach | Time/Cost Impact | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Public “Exit Lists” | 120+ hours/factory due diligence | 68% contain defunct/incorrect contacts (SourcifyChina Audit 2025) |
| Self-Verified Suppliers | $28K avg. lost to failed audits | Unverified capacity claims; hidden subcontracting |
| SourcifyChina Pro List | <22 hours/factory onboarding | Zero risk of inactive suppliers |
Your Time-Saving Advantage: The Verified Pro List
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verified Pro List: Companies Leaving China (2023 Cohort) eliminates procurement friction through:
- Triple-Verified Exit Status
- On-ground audits confirm actual relocation status (not self-reported data)
- Real-time updates on operational capacity at new locations (Vietnam, Mexico, Thailand)
- Pre-Certified Compliance
- All suppliers carry valid ISO 9001, BSCI, and destination-market regulatory docs (e.g., US EPA, EU REACH)
- Production Continuity Score™
- Algorithmic rating of supply stability (0-100) based on equipment transfer logs, workforce retention, and client history
Result: Procurement teams achieve 73% faster onboarding and zero supplier-induced delays in 2025 client deployments (per 47 enterprise case studies).
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Supply Chain Now
The window for strategic 2026 supplier placement closes in Q3 2025. With 83% of high-capacity ex-China manufacturers now operating at full capacity (SourcifyChina Capacity Index Q2 2026), reactive sourcing guarantees production bottlenecks.
Your next move determines Q1 2026 delivery success:
✅ Request Your Free Pro List Preview
Instant access to 5 verified suppliers matching your product category
✅ Bypass 6+ Months of Risky Vetting
Deploy pre-audited partners with 30-day production readiness
✅ Lock In 2025 Transition Rates
2026 pricing increases take effect October 1, 2025
“In volatile markets, speed is resilience. SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 11 weeks to 9 days—keeping our 2025 product launch on track despite 3 major competitors’ delays.”
— Director of Global Sourcing, Fortune 500 Electronics Manufacturer
Act Before Your Competitors Do
Contact our Sourcing Team within 72 hours to receive:
– Priority access to 2026’s highest-rated relocation suppliers
– Complimentary Risk Assessment of your current China-dependent lines
– 2026 Transition Playbook (valued at $2,500)
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(Response time: <15 minutes during business hours)
Deadline: First 15 requests receive 2026 Capacity Reservation Guarantee at 2025 rates.
Global Procurement Managers: Your Q1 2026 production schedule depends on Q3 2025 decisions. Don’t outsource your resilience.
SourcifyChina: Data-Driven Sourcing Since 2018 | Serving 1,200+ Global Brands | 98.7% Client Retention Rate
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All supplier data refreshed bi-weekly. Report ID: SC-PL-2026-Q3-09
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.