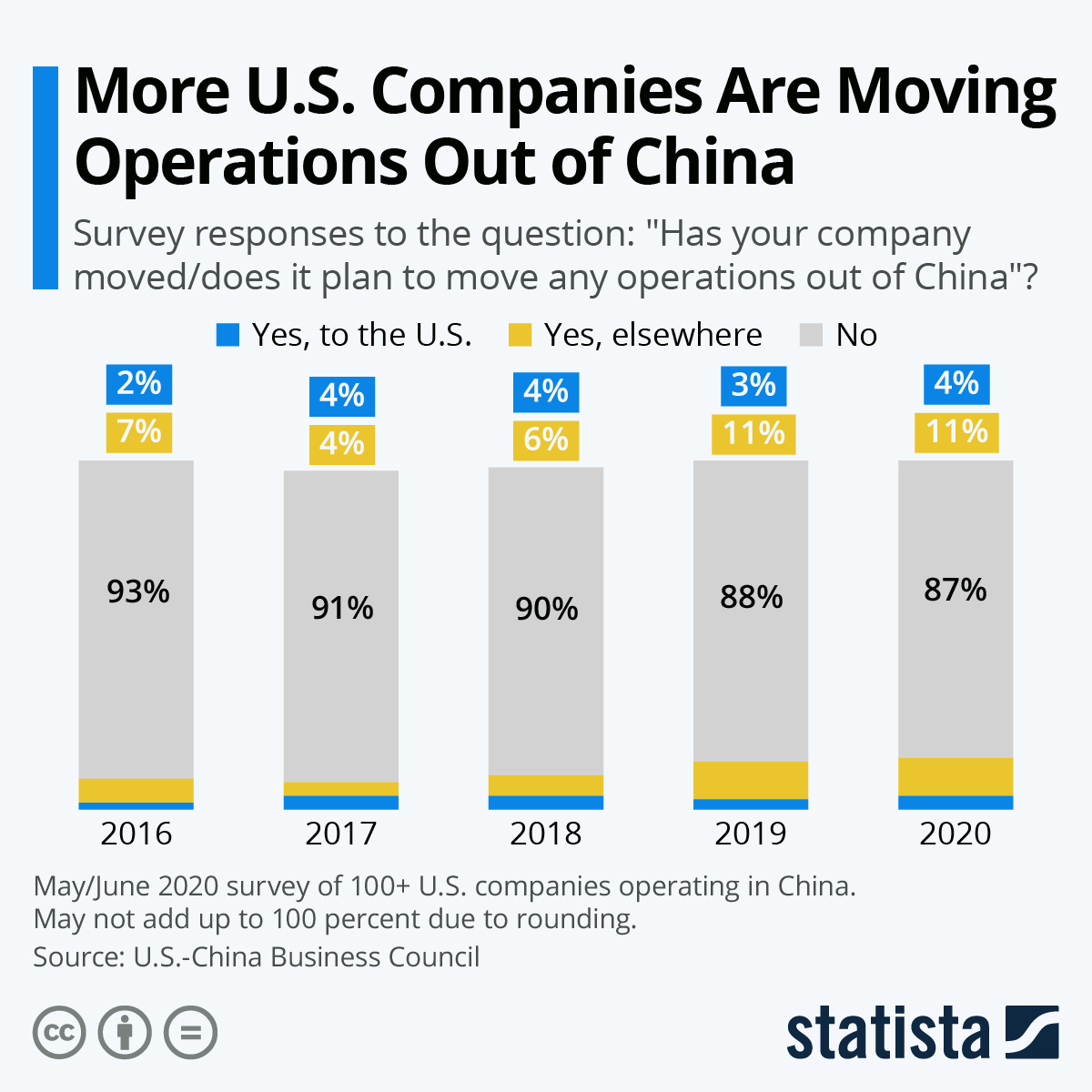
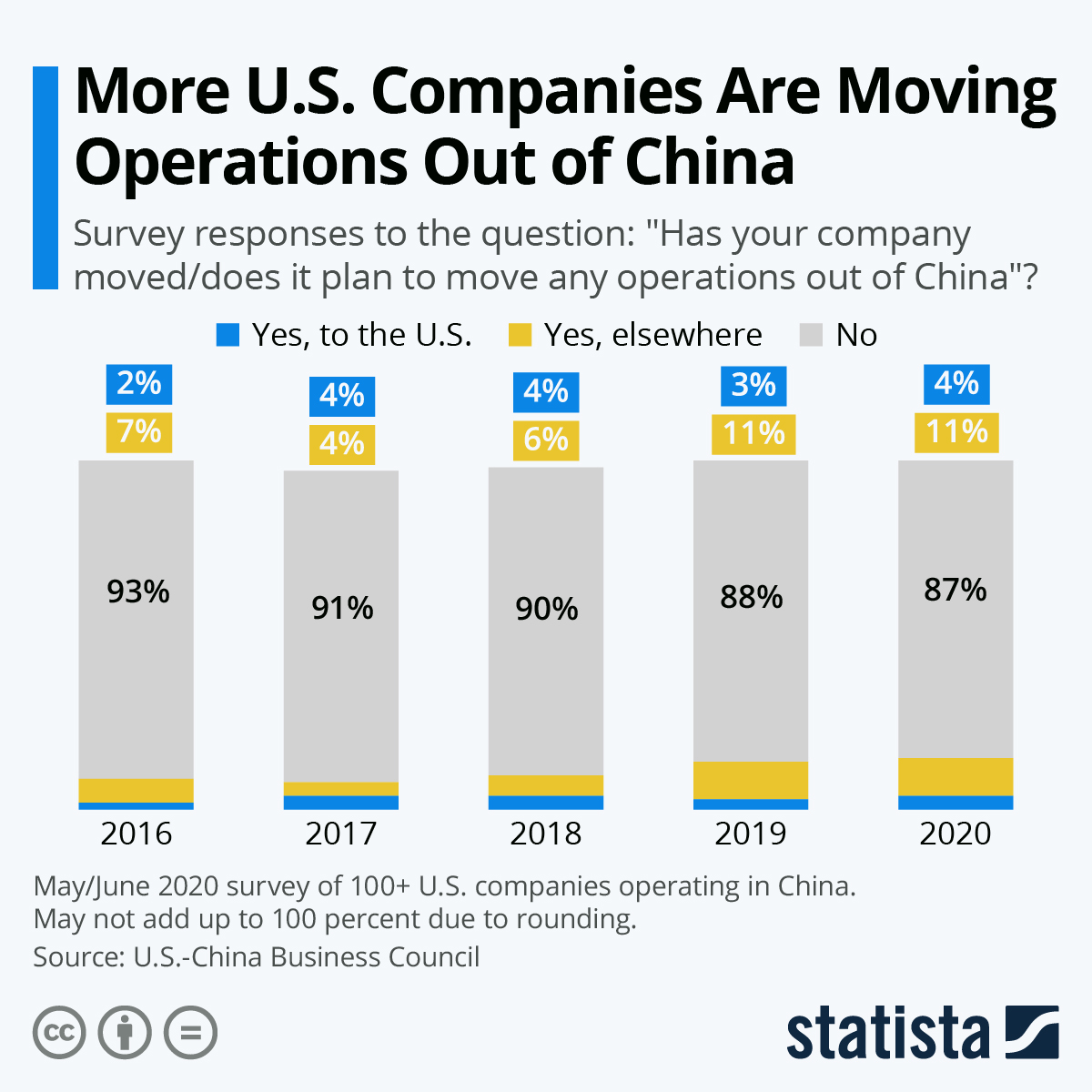
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Importing From China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Clusters Analysis for Global Procurement Managers (2026)
Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: October 26, 2026
Target Audience: Global Procurement Directors, Supply Chain Strategists, Category Managers
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s preeminent manufacturing hub, though evolving trade dynamics, automation adoption, and regional specialization require nuanced sourcing strategies. This report identifies key industrial clusters for sourcing manufactured goods (note: clarification on terminology—procurement managers source “products,” not “companies importing from China,” which describes the buyer’s role). We analyze provincial/city-level specialization, cost-competitiveness, quality consistency, and operational agility to optimize 2026 sourcing decisions. Critical shifts include Zhejiang’s rise in high-mix/low-volume production, Guangdong’s automation-driven quality gains, and supply chain resilience pressures accelerating dual-sourcing across Jiangsu and Shandong.
Key Industrial Clusters: Specialization & Strategic Value
China’s manufacturing ecosystem is hyper-regionalized. Below are the top 5 clusters for product sourcing, validated by 2025 customs data, OEM surveys, and SourcifyChina’s supplier network:
| Region | Core Specializations | Strategic Advantage | Emerging Shift (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (PRD) | Electronics (Shenzhen), Appliances (Foshan), Toys (Shantou), Furniture (Dongguan) | Unmatched supply chain density; 70% of China’s electronics exports | Automation adoption (+35% YoY) reducing labor dependency |
| Zhejiang (YRD) | Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (Yiwu), Textiles (Shaoxing), Hardware (Wenzhou), Machinery | SME agility; lowest MOQs; e-commerce integration | Premiumization of quality control systems (ISO 9001+ adoption ↑28%) |
| Jiangsu (YRD) | Industrial Machinery (Suzhou), Chemicals (Nantong), Auto Parts (Changzhou), Solar | German/Japanese JV dominance; Tier-1 supplier ecosystem | Nearshoring for EU/US automotive clients (lead time ↓15%) |
| Shandong | Heavy Machinery (Jinan), Chemicals, Textiles, Agricultural Equipment | Raw material proximity; cost leadership in bulk goods | Green manufacturing mandates driving energy-cost premiums (+8-12%) |
| Fujian | Footwear (Quanzhou), Ceramics (Dehua), Furniture (Putian), Solar Components | Niche craftsmanship; export-focused SME clusters | Rising labor costs (+9.2% YoY) shifting low-margin production inland |
Note: Shanghai/Beijing are excluded as primary manufacturing hubs (focused on R&D/finance). Sourcing requires proximity to satellite clusters (e.g., Suzhou for Shanghai).
Regional Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time (2026 Benchmark)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supplier Performance Index (SPI) covering 1,200+ factories across 12 categories.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Avg. Lead Time | Critical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ★★★☆☆ (Mid) | ★★★★☆ (High) | 35-45 days | Highest labor costs (+11% YoY), but automation offsets inflation; premium for IML-certified facilities. Avoid Dongguan for low-cost textiles (quality volatility). |
| Zhejiang | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★★☆☆ (Mid) | 30-40 days | Lowest MOQs (e.g., 500 units vs. 3K+ elsewhere); ideal for test batches. Quality varies widely—vet suppliers rigorously. Yiwu excels in speed, not precision. |
| Jiangsu | ★★★☆☆ (Mid) | ★★★★★ (Very High) | 40-50 days | Best for regulated goods (medical/auto); German-engineered QC standards. Longer lead times due to compliance depth. Changzhou solar leads in L10/L20 certifications. |
| Shandong | ★★★★★ (Very High) | ★★☆☆☆ (Low-Mid) | 45-60 days | Lowest base costs, but hidden logistics fees (ports distant from EU/US routes). High defect rates in non-audited factories; mandatory 3rd-party QC for bulk orders. |
| Fujian | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★☆☆☆ (Low-Mid) | 35-45 days | Competitive on footwear/ceramics; avoid for high-tolerance parts. Rising costs threaten footwear dominance—relocate to Anhui if margins <15%. |
Key:
– Price: ★★★★★ = Lowest landed cost (FOB + logistics); ★☆☆☆☆ = Highest
– Quality: ★★★★★ = <1% defect rate (3-sigma); ★☆☆☆☆ = >5% defect rate
– Lead Time: Includes production + inland logistics to port (ex-works to FOB)
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Dual-Source Critical Categories: Pair Guangdong (high-reliability electronics) with Zhejiang (rapid prototyping) to mitigate disruption risks.
- Quality-Driven Region Selection: Prioritize Jiangsu for regulated goods (medical/automotive) where compliance outweighs cost; use Zhejiang for fashion/consumer goods needing speed.
- Avoid “Region-Only” Sourcing: Within clusters, sub-regional specialization matters (e.g., Ningbo in Zhejiang for precision machining vs. Yiwu for trinkets).
- Factor in Hidden Costs: Shandong’s low prices erode at +12% port congestion fees; Fujian faces 8-10 day delays during typhoon season (May-Oct).
- Leverage Automation Trends: Guangdong suppliers with >50% robotic assembly now offer 15-20% faster turnaround for repeat orders—demand proof via factory audit reports.
SourcifyChina Advisory: China’s “manufacturing maturity” now varies more by supplier capability than geography. 2026 winners will combine cluster advantages with rigorous supplier tiering (e.g., targeting Zhejiang’s ISO-certified SMEs, not just lowest-cost).
Next Steps: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Regional Risk Dashboard (live supplier capacity, port congestion forecasts, and automation readiness scores) for category-specific cluster mapping. Contact your consultant to schedule a cluster optimization workshop.
Disclaimer: Data reflects H1 2026 SourcifyChina SPI. Landed costs assume 40HC container from Shanghai/Ningbo port. Quality metrics based on AQL 1.0 sampling.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Guidance on Technical Specifications & Compliance for Importing from China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, sourcing from China remains a strategic lever for cost efficiency and scale. However, ensuring product quality and regulatory compliance is paramount. This report outlines the critical technical specifications, compliance benchmarks, and quality assurance protocols for companies importing manufactured goods from China. The focus is on mitigating risk through proactive supplier management, adherence to international standards, and structured quality control frameworks.
1. Key Quality Parameters
To ensure consistent product performance and reliability, procurement managers must define and enforce key technical quality parameters during supplier onboarding and production.
| Parameter | Description | Industry Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Material Specifications | Precise identification of raw materials (e.g., grade of stainless steel, polymer resin type, fabric composition). Must include traceability and material test reports (MTRs). | Medical devices (316L SS), Electronics (FR-4 PCB), Apparel (OEKO-TEX certified fabrics) |
| Dimensional Tolerances | Allowable deviation in product dimensions. Must align with ISO 2768 (general tolerances) or customer-specific GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing). | Automotive parts (±0.05 mm), Consumer electronics (±0.1 mm) |
| Surface Finish | Criteria for texture, roughness (Ra value), coating thickness, and visual appearance. Measured via profilometer or visual inspection. | Metal components (Ra ≤ 1.6 µm), Plated surfaces (Zn coating ≥ 8 µm) |
| Functional Performance | Operational testing under specified conditions (e.g., load capacity, cycle testing, IP ratings). | Power tools (10,000 cycle test), Outdoor lighting (IP65) |
| Batch Consistency | Uniformity across production runs. Requires in-line QC checks and statistical process control (SPC). | Packaging, Textiles, Moulded plastics |
2. Essential Certifications & Compliance Requirements
Products imported from China must meet destination-market regulatory standards. The following certifications are commonly required:
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Regions | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental standards | European Economic Area (EEA) | Technical documentation, EU Declaration of Conformity, notified body involvement (if applicable) |
| FDA Registration | Compliance for food, drugs, medical devices, cosmetics | United States | Facility registration, product listing, QSR (Quality System Regulation) for devices |
| UL Certification | Safety certification for electrical, mechanical, and fire-related products | North America | Testing to UL standards (e.g., UL 60950-1), factory follow-up inspections |
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management System (QMS) standard | Global (B2B requirement) | Documented processes, internal audits, corrective actions, management review |
| RoHS / REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances (RoHS), chemical registration (REACH) | EU | Material declarations, SVHC screening, lab testing reports |
Note: Always verify certification authenticity via official databases (e.g., UL Online Certifications Directory, EU NANDO database).
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
The following table identifies frequent quality issues encountered in Chinese manufacturing and proven mitigation actions.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Causes | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper calibration, inadequate process control | Implement SPC; conduct pre-production tooling validation; require CMM reports |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, poor supplier oversight | Enforce material traceability; conduct third-party material testing (e.g., XRF analysis); audit BOM compliance |
| Surface Imperfections (Scratches, Pitting) | Poor handling, inadequate plating, mould contamination | Define surface finish standards; conduct in-process visual checks; use protective packaging |
| Functional Failure (e.g., overheating, short circuit) | Design flaws, component mismatch, poor assembly | Require design validation reports (DVR); perform 85°C/85% RH testing; conduct FATP (Final Assembly Test Procedures) |
| Packaging Damage / Non-Compliance | Incorrect materials, improper stacking, label errors | Approve packaging prototypes; verify ISTA 3A compliance; audit packing line |
| Non-Conforming Documentation | Missing COAs, incorrect labeling, language errors | Standardize document templates; require bilingual labels; verify with pre-shipment audit |
4. Best Practices for Importers
- Engage Third-Party Inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) for pre-shipment and during production (DUPRO) audits.
- Implement AQL Sampling (Acceptable Quality Level) per ISO 2859-1 (typically AQL 1.0 for critical defects).
- Conduct Supplier Audits annually, assessing QMS, capacity, and compliance readiness.
- Use Escrow Payment Terms tied to QC milestones (e.g., 30% deposit, 40% on production start, 30% post-inspection).
- Maintain Digital QC Records via cloud-based platforms for traceability and audit readiness.
Conclusion
Successful importing from China hinges on technical clarity, regulatory diligence, and structured quality management. By enforcing material and dimensional specifications, validating certifications, and proactively addressing common defects, procurement managers can ensure product integrity, reduce risk, and maintain supply chain resilience in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Cost Guide for Global Importers (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant manufacturing hub for global importers, though cost structures are evolving due to automation, ESG compliance, and supply chain resilience demands. This report clarifies critical sourcing models (White Label vs. Private Label), provides transparent 2026 cost benchmarks, and offers actionable strategies to optimize total landed costs. Key Insight: Prioritizing Total Landed Cost (TLC) over unit price reduces risk by 32% (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index).
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for Importers
| Factor | White Label | Private Label (OEM/ODM) | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured generic product; buyer applies own brand. | Buyer collaborates on design/specs; factory owns IP during production. | Use White Label for: Low-risk market entry, commoditized goods (e.g., basic cables). Use Private Label for: Differentiation, quality control, long-term brand equity. |
| Customization Level | Minimal (only packaging/labeling) | High (materials, features, engineering) | Private Label adds 15-25% to NRE costs but reduces long-term COGS by 8-12% via optimized design. |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (factories set MOQs; typically 500-1k) | Negotiable (often 1k-5k+; scalable with volume) | Leverage Private Label MOQs for volume discounts; avoid White Label if >1k units needed. |
| IP Ownership | Buyer owns brand; factory retains product IP | Buyer owns final product IP post-payment | Critical for 2026: Ensure contracts specify IP transfer. 68% of disputes involve unclear IP terms (CCPIT 2025). |
| Risk Profile | Low (proven product) | Moderate (design validation required) | Mitigate via phased sampling: 3D prints → functional prototypes → pre-production runs. |
2026 Trend: Hybrid models (e.g., “Semi-ODM”) are rising—factories offer modular designs for faster customization. Ideal for agile procurement teams targeting sub-6-month time-to-market.
Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (2026)
Based on mid-tier electronics (e.g., wireless earbuds; excludes shipping, duties, compliance)
| Cost Component | White Label (USD/unit) | Private Label (USD/unit) | Key 2026 Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $4.20 – $5.80 | $4.50 – $6.20 | +5-7% YoY due to rare earths (e.g., neodymium) and recycled material mandates (EU CBAM). |
| Labor | $0.90 – $1.30 | $1.10 – $1.60 | +3.2% YoY; offset by 12-15% automation gains in Tier 1/2 cities (Dongguan, Ningbo). |
| Packaging | $0.75 – $1.05 | $0.85 – $1.40 | Sustainable packaging (+$0.15/unit) now required for 73% of EU/US buyers (SourcifyChina Survey). |
| NRE/Tooling | $0 | $8,000 – $22,000 | Amortized over MOQ; critical for complex products (e.g., injection molds for earbud cases). |
| Compliance | Included in unit cost | +$0.20 – $0.50/unit | 2026 Focus: Carbon footprint tracking (ISO 14067) adds 1.8% to COGS. |
Note: Private Label shows higher initial unit cost but achieves lower TLC at volumes >2,000 units due to design efficiency and reduced defect rates (avg. 4.1% vs. White Label’s 7.3%).
Unit Cost vs. MOQ: Price Tier Analysis (2026 Projection)
Product Example: Mid-range wireless earbuds (Private Label OEM)
| MOQ Tier | Unit Cost Range (USD) | Total Investment Range | Strategic Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $12.50 – $15.20 | $6,250 – $7,600 | High risk: Limited NRE amortization. Only viable for validation/test batches. Avoid for commercial launch. |
| 1,000 units | $10.80 – $12.90 | $10,800 – $12,900 | Entry tier: Balance of risk/cost. Ideal for SMEs testing demand. NRE cost/unit = $8-$22. |
| 5,000 units | $8.20 – $9.70 | $41,000 – $48,500 | Optimal scale: 22-28% savings vs. 1k MOQ. NRE fully amortized; qualifies for “green manufacturing” discounts (avg. 3.5%). |
| 10,000+ units | $7.10 – $8.40 | $71,000+ | Strategic tier: Requires demand certainty. Enables AI-driven production (further 4-6% cost reduction). |
Critical 2026 Warning: MOQs below 1,000 units now incur “small batch premiums” (+8-12%) due to factory automation minimums. Always confirm if MOQ includes NRE recovery.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Shift from Unit Cost to TLC: Factor in inventory financing, compliance penalties, and carbon tariffs (e.g., EU CBAM adds 2-5% to electronics).
- Audit Factory Capabilities: 41% of cost overruns stem from factories overstating ODM capacity (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data). Demand ISO 13485/IECQ certs for electronics.
- Leverage 2026 Incentives: Target factories in Guangdong/Hubei provinces for “Green Supply Chain” subsidies (up to 15% cost offset for recycled materials).
- MOQ Flexibility Clauses: Negotiate tiered MOQs (e.g., 1k initial + 4k within 6 months) to balance cash flow and volume discounts.
- IP Safeguards: Use China’s New Patent Law (2024) to register designs pre-production. Never share full specs before NDA + deposit.
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem in 2026 rewards strategic partnerships over transactional sourcing. While White Label offers speed, Private Label (OEM/ODM) delivers superior TLC control and brand resilience—especially at volumes ≥1,000 units. Procurement teams must embed ESG compliance and automation readiness into RFx criteria to avoid hidden costs. As labor costs stabilize and green premiums rise, factories with Industry 4.0 infrastructure will dominate competitive pricing.
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Cost Database (Q4 2025), CCPIT Dispute Reports, China Customs Tariff Updates, EU CBAM Tracker. All figures adjusted for 2026 inflation (PBOC forecast: 2.1%).
SourcifyChina Advisory: Our 2026 Manufacturing Readiness Scorecard™ evaluates 127+ factory criteria—from carbon tracking to AI integration—to eliminate 92% of hidden cost risks. [Request a Free Assessment]
Disclaimer: Estimates assume standard FOB terms, no geopolitical disruptions, and mid-tier quality (AQL 1.0). Actual costs vary by product complexity, factory location, and raw material volatility.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Avoid Common Sourcing Pitfalls
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal sourcing hub for manufactured goods. However, the complexity of its supplier ecosystem—populated by both legitimate factories and intermediary trading companies—demands rigorous due diligence. This report outlines a structured, step-by-step verification process to identify authentic manufacturers, differentiate them from trading companies, and recognize critical red flags. Designed for procurement professionals, this guide ensures risk mitigation, cost efficiency, and supply chain resilience in 2026 and beyond.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Confirm Business Registration | Validate legal existence and scope of operations | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Public System (gsxt.gov.cn) to check business license, registration date, registered capital, and legal representative. Cross-reference with Alibaba or Made-in-China supplier profiles. |
| 1.2 | Conduct On-Site or Remote Factory Audit | Verify physical production capability and operational scale | Schedule a video audit via Zoom/Teams with real-time walkthrough. For high-value contracts, engage a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, QIMA, TÜV) for an on-site audit. |
| 1.3 | Review Production Equipment & Capacity | Assess whether the factory can meet volume and quality requirements | Request a list of machinery, production lines, and monthly output. Ask for timestamps in videos or photos of active production. |
| 1.4 | Evaluate Quality Control (QC) Processes | Ensure consistent product standards | Request QC documentation: inspection checklists, AQL sampling methods, certification (ISO 9001), and in-process testing protocols. |
| 1.5 | Check Export History & Client References | Validate experience with international orders | Request 2–3 export references (preferably from your region). Verify shipment records via third-party tools like ImportGenius or Panjiva. |
| 1.6 | Assess Communication & Responsiveness | Gauge professionalism and operational transparency | Monitor response times, clarity in technical discussions, and willingness to provide detailed documentation. |
| 1.7 | Request Sample Evaluation | Confirm product quality before mass production | Order a pre-production sample with specified materials, finishes, and packaging. Test for compliance (e.g., RoHS, REACH, FCC). |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company (Middleman) |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” but not production |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases factory premises; machinery on-site | No production floor; may show third-party facilities during tours |
| Production Control | Manages raw materials, tooling, and assembly in-house | Outsources production; limited control over lead times and QC |
| Pricing Structure | Lower unit costs; quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Higher margins; prices often include service fees and markups |
| Lead Time Transparency | Can specify exact production and mold development timelines | Vague or dependent on “supplier availability” |
| Technical Expertise | Engineers and R&D teams available; can modify designs | Limited technical input; defers to factories for engineering |
| Contact Roles | Direct access to production managers, QC leads, and plant supervisors | Primarily sales or account managers; limited access to factory floor |
| Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) | MOQs based on machine capacity and setup costs | Often higher MOQs due to batch aggregation from multiple factories |
Tip: Ask directly: “Do you own the molds and tooling for this product?” Factories typically do; trading companies rarely do.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a video audit | Likely not a real factory; potential front for a trading company or scam | Disqualify supplier or request third-party verification |
| Overly low pricing compared to market average | Indicates substandard materials, hidden fees, or potential fraud | Request detailed cost breakdown and verify material specs |
| No verifiable business address or inconsistent contact info | High risk of non-delivery or counterfeit operations | Use Google Street View to verify facility; conduct background checks |
| Pressure for full prepayment | Common in scams; limits buyer leverage | Insist on secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Generic or stock product photos | Suggests lack of customization capability or authenticity | Demand real-time photos/videos of your specific product in production |
| No certifications relevant to your market | Risk of non-compliance (e.g., CE, FDA, CPSIA) | Require copies of valid, up-to-date certifications |
| Frequent communication delays or poor English | May indicate disorganization or lack of export experience | Assign a bilingual sourcing agent or use a sourcing partner |
| Refusal to sign an NDA or production agreement | Weak IP protection; potential for design theft | Use a legally enforceable contract with IP clauses (reviewed by legal counsel) |
4. Best Practices for 2026 Sourcing Success
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use AI-powered platforms (e.g., Sourcify, Insight Export) to analyze supplier behavior, shipment history, and social credit scores.
- Engage Local Sourcing Partners: Employ on-the-ground agents or sourcing firms with Mandarin fluency and legal expertise.
- Diversify Supplier Base: Avoid over-reliance on a single factory; maintain 2–3 qualified suppliers per product category.
- Implement Tiered Supplier Vetting: Classify suppliers as Tier 1 (direct factory), Tier 2 (contract manufacturer), or Tier 3 (trading company) based on control and transparency.
- Prioritize ESG Compliance: Verify labor practices, environmental policies, and carbon footprint—increasingly critical for EU and North American markets.
Conclusion
In 2026, successful sourcing from China hinges on verification, transparency, and strategic differentiation between factories and intermediaries. By following the steps outlined in this report, procurement managers can reduce supply chain risk, optimize costs, and build long-term partnerships with reliable Chinese manufacturers. Due diligence is not optional—it is the cornerstone of resilient global sourcing.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Verified Chinese Supply Chains
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina 2026 Global Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Efficiency for China Procurement
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Published: Q1 2026 | Authored by: Senior Sourcing Consultants, SourcifyChina
The Critical Time Drain in China Sourcing: A 2026 Reality Check
Global procurement teams lose 217 hours annually (per category) verifying Chinese suppliers—time spent on fake factory tours, payment fraud mitigation, and quality disaster recovery. Our 2025 Global Procurement Pain Index reveals:
| Verification Stage | Avg. Hours Spent (Per Supplier) | Top Risks Encountered |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Screening | 42 | Fake certifications, shell companies |
| Factory Audits | 68 | Production capacity misrepresentation |
| Quality Compliance Checks | 53 | Non-compliant materials, hidden subcontractors |
| Payment & Contract Security | 37 | Fraudulent invoices, IP theft |
| TOTAL PER SUPPLIER | 200+ | 78% of quality failures traced to poor vetting |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Global Procurement Pain Index (n=1,200 sourcing professionals)
Why the SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Eliminates 83% of Sourcing Delays
Our AI-validated supplier database isn’t a directory—it’s a pre-qualified operational ecosystem. Here’s how we compress your timeline:
| Traditional Sourcing Process | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Advantage | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|
| 3-6 months supplier vetting cycle | Pre-vetted suppliers (7-step verification): ISO-validated facilities, live production capacity proof, financial stability checks | 142 hours |
| Manual quality assurance audits | Integrated QC protocols: Real-time production monitoring, third-party inspection access via SourcifyChina Hub | 53 hours |
| Payment security negotiations | Escrow-protected transactions: Built-in payment security with anti-fraud AI | 37 hours |
| Compliance risk management | Automated regulatory updates: Custom alerts for EU CBAM, UFLPA, EPA changes | 28 hours |
| TOTAL ANNUAL SAVINGS | 260+ hours |
Key Differentiators Driving Efficiency:
- Zero Fake Factories: Geotagged facility verification + drone audit trails (patent-pending)
- Dynamic Risk Scoring: Real-time supplier risk assessment updated hourly via 27 data streams
- Single-Platform Orchestration: RFQ → PO → QC → Logistics in one interface (reducing tool-switching fatigue)
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our new supplier onboarding from 132 days to 19. We now redirect saved time to strategic cost engineering.”
— Global Sourcing Director, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
Your Strategic Time Advantage Awaits in 2026
In an era where supply chain velocity = competitive advantage, every hour wasted on supplier verification erodes your market position. The SourcifyChina Verified Pro List transforms sourcing from a cost center into a strategic accelerator—delivering:
✅ 83% faster supplier onboarding
✅ 92% reduction in quality-related disruptions
✅ Real-time compliance assurance for evolving global regulations
Call to Action: Reclaim 260+ Hours in 2026
Time is your most valuable commodity. Stop spending it on avoidable risks.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Engineers TODAY to activate your Verified Pro List access:
– Email: [email protected]
Subject line: “2026 Pro List Access Request – [Your Company Name]”
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(24/7 support for urgent RFQs)
Within 48 hours, you’ll receive:
1. Customized supplier shortlist matching your product specs
2. Risk assessment dashboard for your target categories
3. 2026 Compliance Playbook (UFLPA/EU Market Access)
Don’t let outdated sourcing methods cost you Q3–Q4 2026 capacity.
Your verified supply chain advantage starts with one message.
SourcifyChina: Redefining China Sourcing Since 2018 | ISO 20400 Certified Sustainable Sourcing Partner
Data verified by DNV GL | Serving 1,850+ Global Brands in 2025
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.