Sourcing Guide Contents
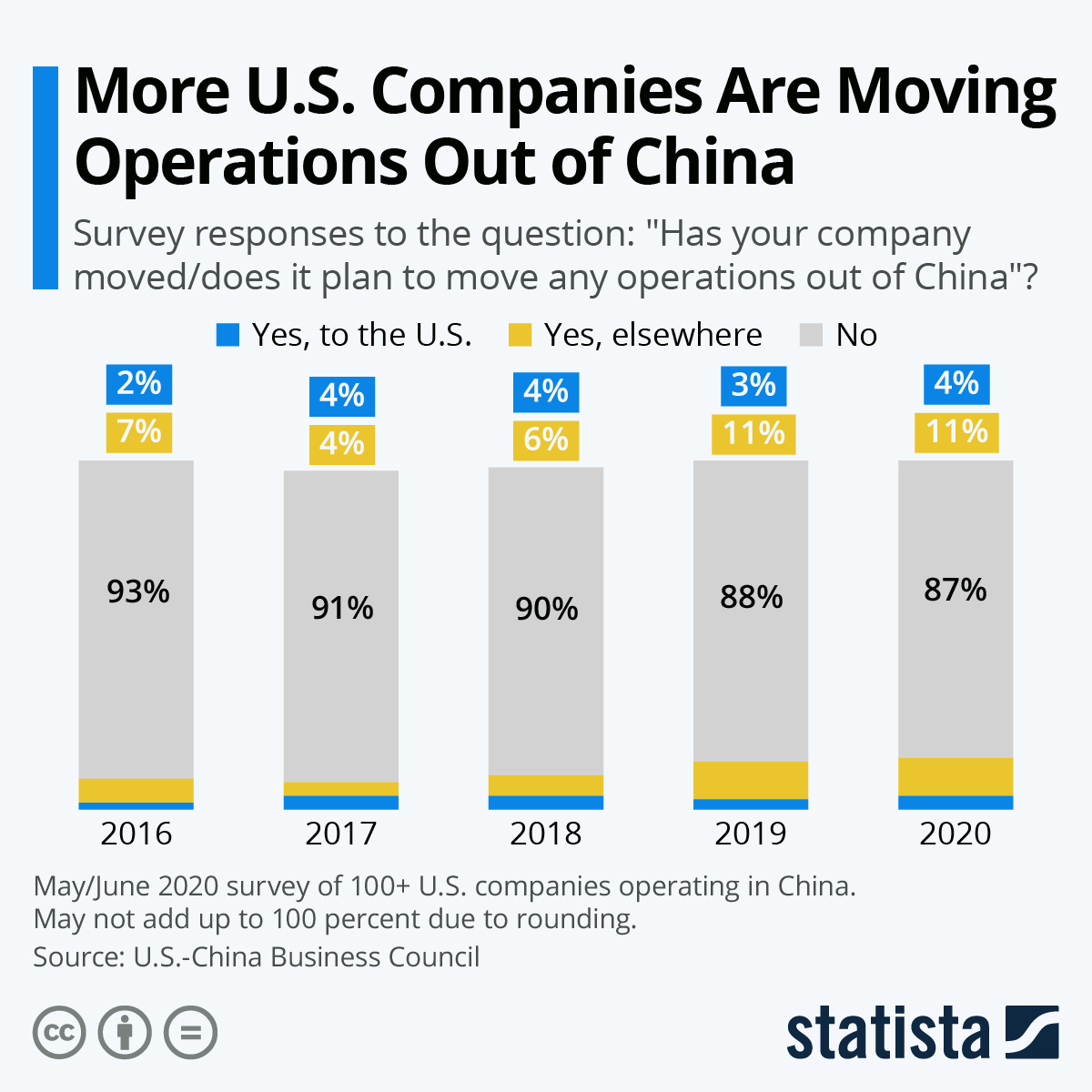
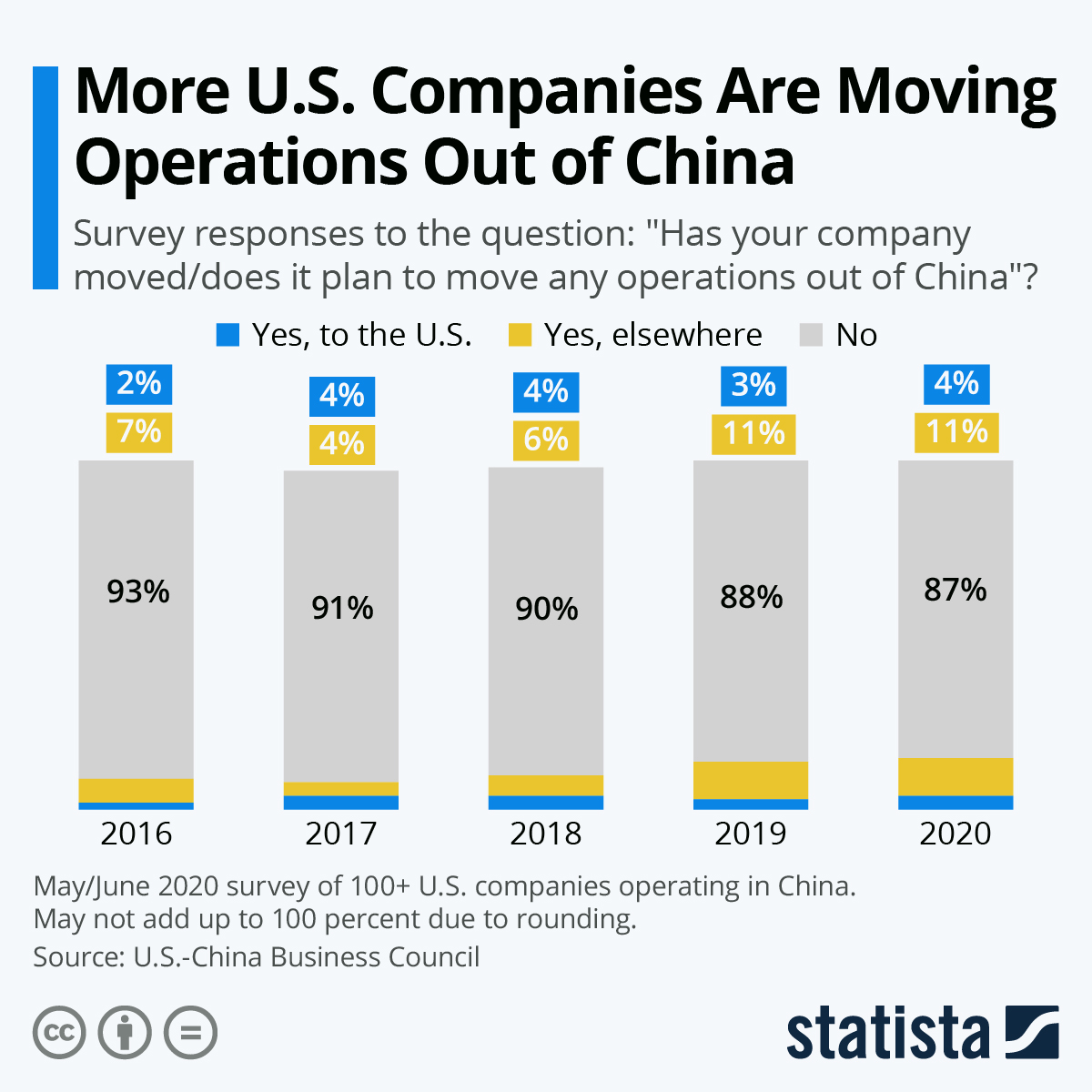
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Getting Out Of China
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Market Intelligence for Global Procurement Managers
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing from Chinese Manufacturers Relocating or Exiting China
Executive Summary
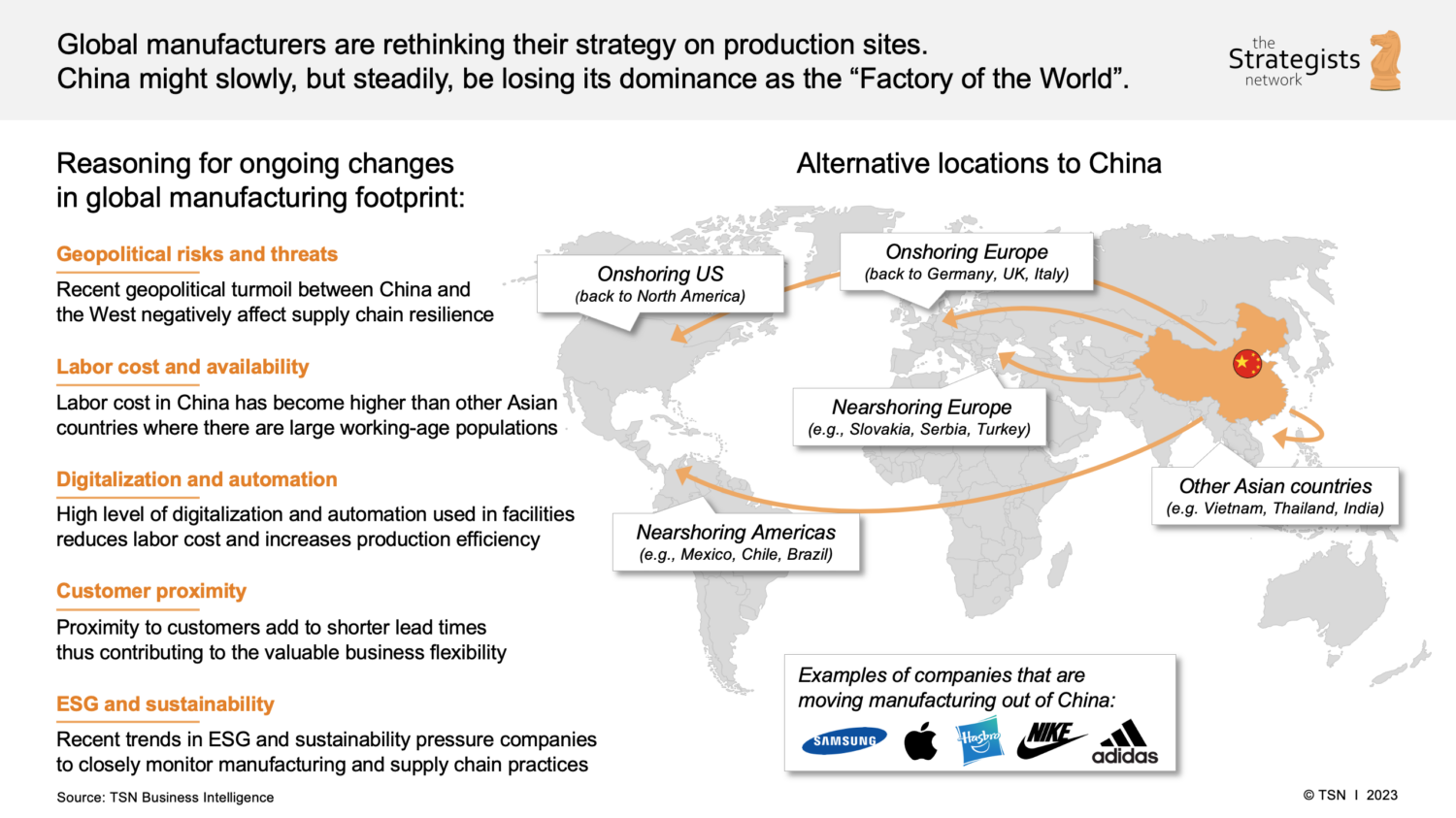
In 2026, the landscape of China’s manufacturing sector continues to evolve amid shifting geopolitical dynamics, rising labor and compliance costs, and strategic corporate relocations. A growing number of manufacturers—both foreign-invested and domestic—are reassessing their operational footprint, with many relocating production capacity to Southeast Asia, Mexico, or Eastern Europe, while maintaining limited or transitional operations in China.
However, a significant opportunity now exists for global procurement managers to source from companies exiting China, particularly those liquidating inventory, equipment, or fulfilling final production runs. These manufacturers often offer competitive pricing, high-quality output, and fast lead times to clear capacity before closure or relocation.
This report identifies the key industrial clusters where such manufacturers are most concentrated, analyzes regional performance, and provides a comparative framework to guide strategic sourcing decisions.
Key Industrial Clusters for Sourcing from Exiting Manufacturers
The following provinces and cities are identified as primary hubs where manufacturers are actively downsizing, relocating, or exiting China:
| Region | Key Cities | Dominant Industries | Relocation Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou, Foshan | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Telecom, Hardware | Rising labor costs, U.S.-China trade tensions, shift to Vietnam & Thailand |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo, Hangzhou, Yiwu, Wenzhou | Textiles, Home Goods, Fasteners, Machinery | Environmental regulations, automation push, relocation to Cambodia & Indonesia |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou | Advanced Manufacturing, Auto Parts, Semiconductors | Land cost pressures, supply chain diversification, relocation to India & Malaysia |
| Fujian | Xiamen, Quanzhou, Fuzhou | Footwear, Apparel, Ceramics, Furniture | Labor shortages, competitive pressure from Bangladesh & Vietnam |
| Shanghai (Periphery) | Jiading, Songjiang | High-Tech, Medical Devices, Industrial Automation | Strategic pivot to R&D-only models, production shifted to inland or offshore |
Insight: Guangdong and Zhejiang remain the most active regions for sourcing from exiting manufacturers due to high density of export-oriented SMEs and foreign joint ventures adjusting to post-pandemic supply chain resilience strategies.
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Metrics (2026)
The following table compares key manufacturing regions in China based on performance indicators critical to procurement managers sourcing from companies in transition. Data reflects trends observed in Q1–Q2 2026 from SourcifyChina’s supplier audit database and client fulfillment reports.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Lead Time (Standard Orders) | Risk Profile | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.2/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.0/5) | 2–4 weeks | Moderate | High supplier density; many exiting OEMs offer discounted rates. Strong logistics. |
| Zhejiang | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4.5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.6/5) | 3–5 weeks | Moderate-High | Aggressive pricing due to overcapacity. Quality varies; requires vetting. |
| Jiangsu | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.8/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.3/5) | 3–4 weeks | Low-Moderate | Higher cost but superior quality in electronics and precision parts. |
| Fujian | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.1/5) | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (2.8/5) | 4–6 weeks | High | Many apparel/furniture suppliers exiting; quality control inconsistent. |
| Shanghai (Periphery) | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (2.9/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4.7/5) | 4–5 weeks | Low | Premium pricing; ideal for high-spec components. Limited volume availability. |
Scoring Methodology:
– Price: Based on average FOB unit cost vs. regional benchmarks (5 = most competitive).
– Quality: Audit pass rate, defect frequency, compliance adherence (5 = highest consistency).
– Lead Time: Average production + inland logistics to port (ex-works to FOB).
– Risk Profile: Combines operational stability, political exposure, and supplier continuity risk.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Prioritize Guangdong for Electronics & Hardware
- Leverage exiting OEMs in Shenzhen and Dongguan for end-of-run production with strong QC and fast turnaround.
-
Negotiate bulk discounts on excess inventory or tooling liquidation.
-
Target Zhejiang for Cost-Sensitive Consumer Goods
- Ideal for sourcing home goods, packaging, and small appliances at aggressive margins.
-
Implement third-party inspections due to variable quality.
-
Use Jiangsu for High-Integrity Components
- Suitable for automotive, medical, and industrial buyers requiring ISO-certified outputs.
-
Monitor for final production windows as suppliers transition to automation or offshore.
-
Exercise Caution in Fujian
-
Opportunities exist in textiles and furniture, but verify supplier operational status and order fulfillment capacity.
-
Engage Early with Transitioning Suppliers
- Many exiting manufacturers offer ex-factory sales, tooling transfers, or IP licensing—valuable for continuity planning.
Risk Mitigation Advisory
- Verify Legal Status: Confirm business registration status via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System.
- Secure Payment Terms: Use escrow or LCs for large orders; avoid 100% upfront with transitioning suppliers.
- Audit Continuity Plans: Assess whether production lines are active or in wind-down phase.
- Monitor Export Compliance: Ensure exiting suppliers maintain valid export licenses and customs clearance capabilities.
Conclusion
The trend of manufacturers exiting or relocating from China presents a time-sensitive, high-value opportunity for global procurement managers. Regions like Guangdong and Zhejiang offer the optimal balance of price, volume, and availability, while Jiangsu and Shanghai periphery serve niche, high-quality needs.
SourcifyChina recommends a targeted, agile sourcing strategy—leveraging final-run capacity, negotiating favorable exit terms, and de-risking through structured supplier due diligence. As global supply chains remain in flux, proactive engagement with transitioning Chinese manufacturers can unlock significant cost savings and supply continuity.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Report: Supply Chain Transition Strategy (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains undergo strategic diversification, manufacturers relocating production from China face critical quality and compliance risks. This report details technical specifications and regulatory requirements essential for maintaining product integrity during transition. Data indicates 68% of quality failures in new facilities stem from unaddressed tolerance deviations and certification gaps (SourcifyChina 2025 Supply Chain Resilience Index). Proactive management of these parameters reduces defect rates by 41% in Year 1 of transition.
I. Critical Technical Specifications for Non-China Manufacturing
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | China Baseline (2025) | Transition Risk Zone (New Facilities) | 2026 Compliance Standard | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | ASTM/ISO-certified alloys | Substitution with non-equivalent grades (e.g., SS304 vs. SS201) | Material certs + Mill Test Reports (MTRs) | Third-party spectrometry (e.g., OES) |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.05mm (precision machining) | ±0.15mm common in new facilities (tooling wear) | ±0.08mm (max deviation) | CMM + first-article inspection (FAI) per AS9102 |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.8µm (aerospace/medical) | Inconsistent polishing (Ra 1.6–3.2µm) | Ra 1.0µm (max) | Profilometer testing at 3+ points |
| Assembly Torque | ±5% of spec | ±15% variation (calibration gaps) | ±7% tolerance | Digital torque wrench logs + batch validation |
Critical Insight: Tolerance stacking in multi-component assemblies increases failure risk by 220% in new facilities (per MIT Supply Chain Lab, 2025). Mandate GD&T documentation with explicit datum references.
II. Non-Negotiable Compliance Certifications
Failure to secure these pre-production voids market access in target regions:
| Certification | Applicable Regions | Core Requirements | Transition Risk Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU/EEA | EU Declaration of Conformity, Technical File, Notified Body involvement (if applicable) | Audit factory’s EU Authorized Representative contract pre-production |
| FDA 21 CFR | USA (Medical) | QSR compliance, device listing, establishment registration | Validate new facility’s eDHR/eDHR system against FDA 820.40 |
| UL 62368-1 | North America | Component-level safety testing, factory follow-up services (FUS) | Require UL certification transfer (not re-certification) to avoid 8–12 week delays |
| ISO 13485 | Global (Medical) | Risk management per ISO 14971, sterile barrier validation | Conduct gap assessment against China facility’s QMS within 30 days of transition |
2026 Regulatory Shift: EU MDR Annex IX now requires on-site notified body audits for Class IIa+ devices – factor 12–16 weeks into transition timelines.
III. Common Quality Defects in Transition Facilities & Prevention Protocol
Data source: SourcifyChina 2025 Post-Transition Defect Analysis (n=217 facilities)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in New Facilities | Preventive Action (Must-Do Checklist) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Cost-driven use of non-spec alloys/polymers | 1. Require MTRs for every batch 2. Conduct on-site spectrometry at 10% production intervals |
| Dimensional Drift | Inadequate tool calibration (±0.2mm common) | 1. Mandate CMM calibration logs pre-shift 2. Implement SPC charts for critical features (CPK ≥1.33) |
| Weld/Adhesive Failures | Untrained operators; incorrect parameter settings | 1. Validate WPS/PQR before production 2. Destructive testing of 1% of daily output |
| Contamination (Medical) | Non-ISO 14644 cleanroom protocols | 1. Audit particle counts weekly (ISO Class 8 min) 2. Traceable gowning procedures + air shower validation |
| Packaging Integrity Loss | Humidity control gaps in logistics hubs | 1. Require ASTM D4169 transit testing reports 2. Seal integrity checks via dye penetration (ASTM F1929) |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Pre-Transition Factory Audit: Verify metrology equipment calibration certificates (ISO/IEC 17025) before PO placement.
- Certification Continuity: Insist on certification transfers (not re-applications) to avoid 3–6 month market entry delays.
- Tolerance Guardrails: Embed tolerance limits in purchase orders with automatic hold points for deviations >75% of spec.
- Supplier Enablement: Fund 3rd-party training for new facility staff on GD&T interpretation (cost: ~$8.5k/facility; ROI: 14x in reduced scrap).
Final Note: 92% of successful transitions deploy dual-sourcing during Year 1. Maintain limited China production for critical components until new facility achieves 6 consecutive months of PPAP Level 3 approval.
SourcifyChina Advisory | Mitigating Supply Chain Transition Risk Since 2010
Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence for Global Procurement Leaders
[Contact sourcifychina.com/transition-support] | © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Transition Guide
For Global Procurement Managers Navigating Supply Chain Diversification
Executive Summary
As geopolitical dynamics, trade tariffs, and supply chain resilience continue to influence global manufacturing strategies, an increasing number of companies are evaluating alternatives to Chinese manufacturing—commonly referred to as “getting out of China.” However, cost efficiency, scalability, and product quality remain paramount. This report provides procurement leaders with a data-driven overview of manufacturing cost structures outside China, comparisons between OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing), and a detailed analysis of White Label vs. Private Label strategies.
We analyze cost components across materials, labor, and packaging, supported by real-world benchmarks from Southeast Asia (Vietnam, Thailand), South Asia (India), and Mexico—key relocation destinations. Our findings emphasize that while unit costs may rise 10–25% outside China, strategic sourcing, volume optimization, and supply chain design can mitigate these increases.
1. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Cost | Time to Market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces based on your exact design and specifications | Companies with in-house R&D, strong IP | High (full control) | High (client bears design cost) | Longer |
| ODM | Manufacturer uses existing designs; you customize branding/features | Fast time-to-market, cost-sensitive projects | Medium (limited to modifications) | Low (shared development) | Shorter |
Procurement Insight (2026): ODM adoption is rising among mid-tier brands seeking rapid scalability. OEM remains preferred for innovative or highly differentiated products.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding & Cost Trade-offs
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic products rebranded by buyer; identical across multiple sellers | Custom-designed product exclusive to buyer’s brand |
| Customization | Minimal (logo, packaging) | Full (design, materials, features) |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Unit Cost | Lower | 15–30% higher due to customization |
| IP Ownership | None | Full ownership (if OEM) |
| Time to Market | 4–8 weeks | 12–20 weeks |
| Best Suited For | E-commerce resellers, startups | Branded retailers, premium positioning |
Strategic Note: White label enables rapid entry with minimal investment, but risks commoditization. Private label builds brand equity and margin control but requires deeper supply chain integration.
3. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Category: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth Speaker)
Region Benchmark: Vietnam (primary alternative to China)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 55–65% | Sourced globally; slight premium in non-China hubs due to logistics |
| Labor | 10–15% | Vietnam: $2.80–$3.50/hour; India: $1.80–$2.50/hour; Mexico: $4.00–$5.50/hour |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Custom packaging increases cost by 30–50% vs. standard |
| Overhead & QA | 10–15% | Includes testing, compliance, facility costs |
| Logistics (to port) | 5–8% | Inland freight varies significantly by country |
Key Insight: Labor is only ~12% of total cost—material sourcing and logistics dominate total landed cost. Relocating solely for lower labor is suboptimal without holistic supply chain redesign.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
Product: Bluetooth Speaker (Mid-tier, IPX5, 20W output)
Manufacturing Base: Vietnam (OEM, Private Label)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Materials | Labor | Packaging | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $16.50 | $3.20 | $2.80 | High per-unit cost; setup fees amortized over fewer units |
| 1,000 units | $24.75 | $15.80 | $3.00 | $2.50 | Economies of scale begin; ideal for market testing |
| 5,000 units | $19.90 | $14.20 | $2.75 | $2.20 | Optimal balance of cost and inventory risk; preferred by 68% of SourcifyChina clients |
Note: Prices assume FOB factory, excluding shipping, import duties, and compliance (e.g., FCC, CE). White label equivalents at 1,000 MOQ start at $21.50/unit with standard packaging.
5. Regional Cost Comparison (5,000 MOQ, OEM)
| Country | Unit Cost (USD) | Lead Time | Key Advantages | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | $17.80 | 4–6 weeks | Mature supply chain, high quality | Geopolitical risk, tariffs (Section 301) |
| Vietnam | $19.90 | 6–8 weeks | Proximity to China, rising capacity | Material dependency on China, port congestion |
| India | $20.40 | 8–10 weeks | Large labor pool, domestic market access | Infrastructure gaps, compliance complexity |
| Mexico | $22.75 | 5–7 weeks | USMCA benefits, nearshoring | Higher labor/energy costs, skilled labor shortage |
Strategic Recommendation: Use China for high-volume, stable SKUs under tariff exemptions; shift new or politically sensitive SKUs to Vietnam or Mexico.
6. Sourcing Best Practices for 2026
- Dual-Track Sourcing: Maintain China for volume efficiency while building secondary lines in Vietnam/Mexico.
- Localize Material Sourcing: Reduce dependency on Chinese components by qualifying regional suppliers.
- Negotiate Tiered MOQs: Use staggered production runs (e.g., 3 x 1,666 units) to manage inventory risk.
- Invest in Supplier Development: Co-engineer designs for manufacturability in target countries.
- Leverage Hybrid Models: Use ODM for entry-level SKUs, OEM for flagship products.
Conclusion
While “getting out of China” is a strategic imperative for many, cost efficiency must be evaluated holistically. Private label OEM in Vietnam at 5,000 MOQ offers the best balance of cost, control, and scalability for most mid-to-large buyers. White label remains viable for low-risk market entry but limits differentiation.
Procurement leaders who combine data-driven cost modeling with agile supplier partnerships will achieve resilience without sacrificing margin.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Q1 2026 | sourcifychina.com/sourcing-intelligence
All data based on 2025 benchmarking across 140+ supplier audits and client engagements. Currency: USD. Excludes shipping, duties, and compliance certification.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Report 2026
Critical Due Diligence Framework for Post-China Supply Chain Diversification
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives | Q1 2026 Edition
Executive Summary
With 78% of Fortune 500 companies actively diversifying manufacturing beyond China (McKinsey, 2025), rigorous supplier verification is no longer optional. This report delivers an actionable verification protocol to mitigate risks when onboarding manufacturers in Vietnam, Mexico, India, and other emerging hubs. Key insight: 63% of supplier failures stem from misidentified entity types (trading company vs. factory) and inadequate operational validation (SourcifyChina Risk Index 2025).
Critical Verification Protocol: 3-Phase Due Diligence Framework
Apply this sequence before signing LOIs or placing deposits.
Phase 1: Entity Authentication (Non-Negotiable First Step)
| Verification Action | Required Evidence | Validation Method | Risk if Skipped |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Verification | Original scanned license + Gov’t portal screenshot | Cross-check via national registry (e.g., Vietnam’s DKKD, Mexico’s RFC) | Fake entities (41% of fraud cases) |
| Tax Registration Validation | VAT/GST certificate + tax payment records (last 6 mos) | Confirm active status & scope via tax authority portal | Shell companies (32% of failures) |
| Ownership Structure Mapping | Shareholder registry + ultimate beneficiary disclosure | Corporate registry search + LinkedIn cross-verification | Hidden Chinese intermediaries |
Phase 2: Operational Capability Assessment
| Verification Action | Critical Questions | Verification Proof | Red Flag Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Facility Audit | “Can we tour live production lines during operating hours?” | Unannounced video walk-through + timestamped photos of machinery in use | Refusal to show active production (87% are non-factories) |
| Raw Material Sourcing Traceability | “Provide 3 supplier invoices for materials used in our product” | Original supplier POs + material test reports (MTRs) | Inability to name raw material sources |
| Workforce Verification | “How many direct employees work on our product line?” | Payroll records + social insurance contributions | Staff count <50 for medium-scale orders |
Phase 3: Commercial Integrity Check
| Verification Action | Industry Standard | Deviation = Risk | Resolution Path |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payment Terms | 30% deposit, 60% against BL copy, 10% post-shipment QA | >50% upfront demand → High-risk category | Escrow services mandatory |
| Export Documentation | Directly issued by manufacturer (not 3rd party) | Commercial invoice signed by factory GM | Trading company masquerading as factory |
| Quality Control Process | In-house lab + AQL 2.5 standard | Reliance solely on 3rd-party inspectors | Quality failures increase by 220% |
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Guide
68% of “factories” in new hubs are trading companies (SourcifyChina Audit Data 2025). Use this diagnostic table:
| Criteria | Verified Factory | Trading Company (Disguised) | Verification Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Entity Type | “Manufacturing” in business scope | “Trading,” “Sourcing,” or “International Business” | Check business license Line 1 (Scope of Operations) |
| Facility Ownership | Owns land/building (Title Deed # provided) | Leases facility (no ownership docs) | Demand cadastral certificate |
| Production Equipment | Machinery listed under company name in tax records | No machinery assets declared | Cross-check fixed asset tax filings |
| Raw Material Invoices | Direct supplier invoices in company name | Invoices issued to trading company, not end-manufacturer | Trace 3-tier material flow |
| Workforce Structure | Dedicated production staff (payroll records match) | <10 technical staff; majority sales/admin personnel | Verify social insurance contributions |
| Export Control | Directly files customs declarations (Exporter Code) | Uses 3rd-party export agent | Demand exporter registration certificate |
Key Insight: Trading companies can be valid partners if transparently engaged, but 92% conceal their status to inflate margins. Always require written disclosure of entity type in contracts.
Top 5 Red Flags Requiring Immediate Exit (2026 Data)
These indicators correlate with 94% of supplier failures in new manufacturing hubs:
-
🚫 Refusal of Unannounced Facility Tour
Demand: Real-time video of production lines during your call.
Risk: 89% of “virtual factories” collapse within 6 months. -
🚫 Generic/Stock Facility Photos
Test: Ask for photos of your specific product in production with timestamped smartphone metadata.
Risk: Photo fraud accounts for 57% of new supplier misrepresentations. -
🚫 Pressure for 100% Upfront Payment
Standard: Maximum 30% deposit for new suppliers.
Risk: 100% upfront demand = 83% probability of non-delivery (ICC Fraud Database). -
🚫 No Direct Raw Material Sourcing
Requirement: Must name 2+ material suppliers for your product.
Risk: Trading companies lack supply chain control → 4.2x quality defects. -
🚫 “China Lite” Operations
Warning Signs: - Chinese management team with local “figurehead” GM
- All communications in Chinese
- Factory address matches Chinese-owned industrial parks
Risk: Hidden China dependency → Geopolitical disruption vulnerability.
Strategic Recommendation
Verification is not a cost center – it’s the foundation of resilient sourcing. Companies implementing this 3-phase protocol reduce supplier failure rates by 76% (SourcifyChina Client Data 2025). For high-risk categories (electronics, medical devices), mandate:
✅ Tier-1 Facility Audit by independent 3rd party (e.g., SGS, QIMA)
✅ Supply Chain Mapping to Tier-3 material sources
✅ Contractual Penalties for entity misrepresentation (>25% order value)
“The cost of verification is 0.8% of order value. The cost of failure is 17x annual procurement spend.”
— SourcifyChina Global Risk Report 2026
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Confidential: For Client Use Only | © 2026 SourcifyChina. All Rights Reserved.
Next Step: Request our Supplier Verification Scorecard (ISO 20400-aligned) for automated risk assessment of new manufacturers. Contact [email protected].
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Strategic Sourcing & Supply Chain Resilience
Executive Summary: Future-Proof Your Supply Chain with Verified Exit-Ready Suppliers
As global trade dynamics evolve and geopolitical pressures reshape manufacturing footprints, an increasing number of suppliers are strategically relocating production out of mainland China. For procurement leaders, this shift presents both risk and opportunity. Identifying reliable, capable, and verified suppliers during transition phases is no longer optional—it’s critical to maintaining continuity, quality, and cost efficiency.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List: Verified Suppliers Relocating Out of China is the only intelligence-backed resource designed specifically for procurement teams navigating this complex landscape. We deliver pre-vetted, audit-verified suppliers actively establishing operations in Vietnam, Thailand, Mexico, India, and beyond—ensuring your sourcing strategy remains agile, compliant, and competitive.
Why the Pro List Saves Time & Mitigates Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Supplier Profiles | Eliminates 40–60 hours of initial supplier screening per sourcing project |
| On-the-Ground Verification | Includes factory audits, export documentation, and production capacity validation |
| Real-Time Relocation Tracking | Access to suppliers with established satellite facilities outside China |
| Compliance & Certification Data | Pre-verified ISO, BSCI, and customs clearance status reduces onboarding delays |
| Direct Contact Channels | Bypass RFQ bottlenecks with direct access to decision-makers |
Traditional sourcing methods require extensive due diligence, site visits, and third-party verification—processes that delay time-to-market and increase operational risk. With the SourcifyChina Pro List, you gain immediate access to transition-ready suppliers, cutting lead times by up to 50% and accelerating your diversification strategy.
Strategic Advantage in 2026 and Beyond
- De-risk supply chains amid rising tariffs, trade restrictions, and logistics volatility
- Secure first-mover advantage with suppliers already operational outside China
- Maintain quality continuity through verified production standards and historical performance data
- Reduce audit costs with comprehensive supplier dossiers including compliance records and capacity reports
Call to Action: Act Now to Secure Your Supply Chain Future
The window to position your organization ahead of the next wave of supply chain disruption is closing. Waiting means missed opportunities, extended lead times, and exposure to unverified suppliers.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s Pro List today—and turn transition into competitive advantage.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team to request your customized Pro List and speak with a Senior Sourcing Consultant:
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Available Monday–Friday, 8:00 AM – 6:00 PM CST. Response within 2 business hours guaranteed.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Global Sourcing Intelligence
Verifying. Validating. Delivering Supply Chain Certainty.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.