Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Exit China

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Strategic Market Analysis: Sourcing from Former Manufacturing Hubs as Companies Exit China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Release Date: January 2026
Authored by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
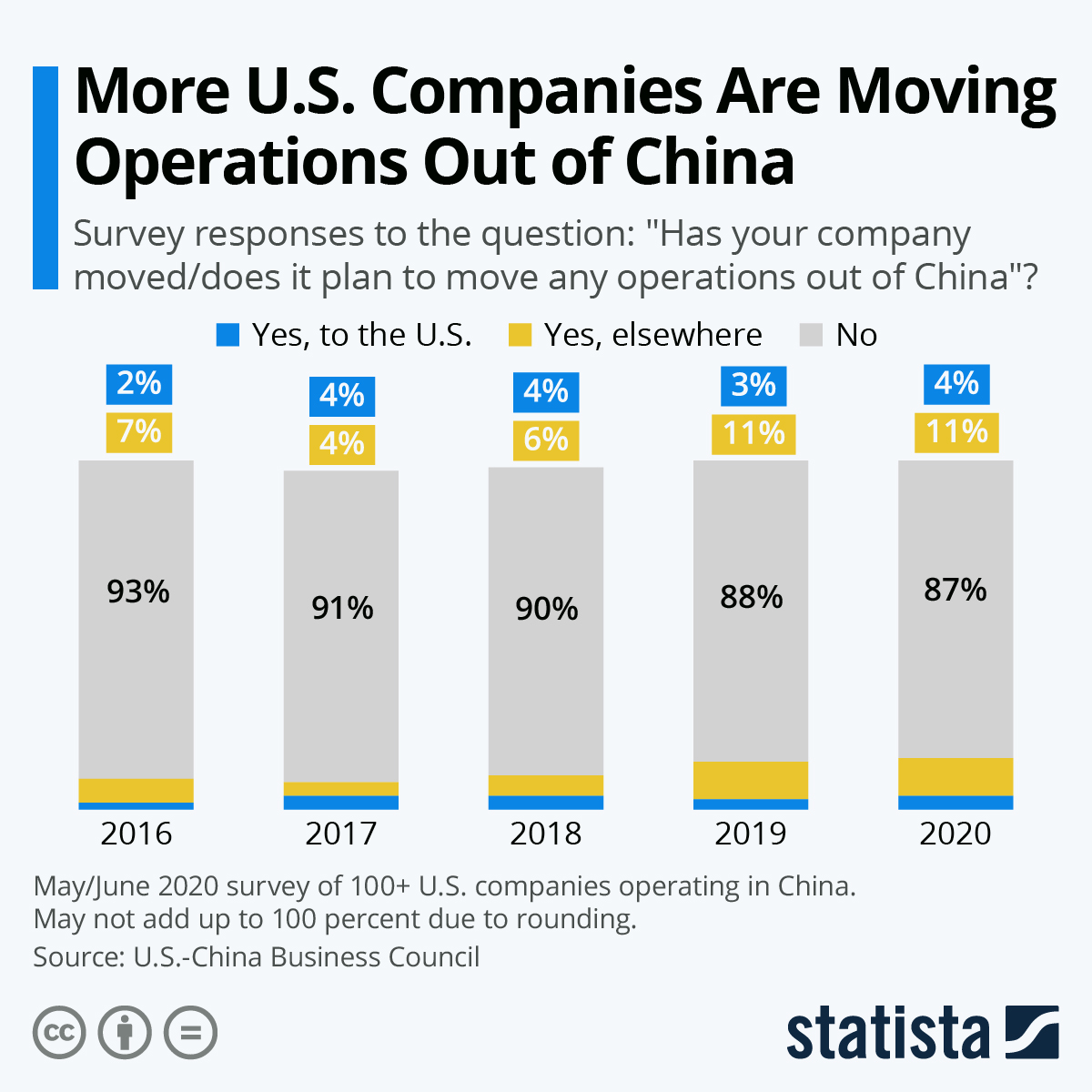
As global supply chains undergo strategic recalibration in 2026, a growing number of multinational enterprises and domestic Chinese manufacturers are relocating production capacity out of China due to rising operational costs, geopolitical tensions, and evolving trade policies. This phenomenon—commonly referred to as “companies exiting China”—has led to underutilized manufacturing assets, excess capacity, and skilled labor availability in key industrial clusters.
This report provides a deep-dive analysis of the regions in China most affected by manufacturing exits, identifying opportunities for procurement managers to source high-quality goods at competitive prices from transitioning industrial zones. While long-term production may shift to Southeast Asia or India, short-to-mid-term sourcing from these “exit-affected” clusters offers cost advantages, rapid scalability, and access to mature supply ecosystems.
Key Industrial Clusters Impacted by Manufacturing Exits
As companies relocate, certain provinces and cities in China have experienced notable reductions in manufacturing occupancy and investment. These clusters remain highly capable but are now under competitive pressure to retain business, creating favorable conditions for B2B sourcing.
Top 5 Industrial Clusters with High Exit Activity (2022–2025)
| Region | Key Industries Affected | Primary Exit Drivers | Sourcing Opportunity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Dongguan, Shenzhen, Foshan) | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Plastics, OEM/ODM | Rising labor costs, U.S. tariff pressures, relocation to Vietnam/Mexico | High-volume electronics, fast-turnaround prototyping |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou) | Industrial Machinery, Automotive Components, Semiconductors | Land scarcity, environmental regulations | Precision engineering, Tier-1 auto parts |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo, Yiwu, Hangzhou) | Textiles, Hardware, Home Goods, Small Machinery | Margin compression, shift to Cambodia/Bangladesh | Low MOQs, fast fashion, modular components |
| Shanghai (Peri-urban zones) | High-Tech Assembly, R&D-Integrated Manufacturing | Cost-driven relocation, urban redevelopment | Smart devices, IoT-enabled products |
| Tianjin & Hebei (Tangshan, Baoding) | Heavy Equipment, Steel, Construction Materials | Overcapacity, carbon reduction mandates | Industrial raw materials, fabricated metalwork |
Note: These regions still house Tier-2 and Tier-3 suppliers actively seeking export orders. Many factories are offering discounts of 8–15% to maintain cash flow and utilization rates.
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions in China (Post-Exit Landscape)
Despite the trend of exit, manufacturing capability in these regions remains robust. The following table compares the sourcing performance of Guangdong and Zhejiang—two of China’s most prominent yet divergently impacted clusters.
| Parameter | Guangdong (Pearl River Delta) | Zhejiang (Yangtze Delta) | Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Price Level | Medium-High (↑ 5% YoY) | Medium (↓ 3% YoY) | Zhejiang benefits from lower labor costs and government incentives to retain SMEs. Guangdong faces higher wage inflation. |
| Quality Consistency | High (Tier-1 & MNC-tier standards) | Medium-High (variable across SMEs) | Guangdong excels in electronics and precision goods with ISO/IEC certification compliance. Zhejiang shows variance in smaller workshops. |
| Lead Time (Standard Order) | 30–45 days | 25–35 days | Zhejiang’s agile SME network enables faster turnaround, especially for non-electronic goods. Guangdong faces port congestion and higher order backlogs. |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | 500–1,000 units (electronics) | 100–500 units (home/fashion goods) | Zhejiang offers greater flexibility for low-volume buyers. Guangdong favors bulk procurement. |
| Export Readiness | Excellent (98% customs-compliant) | Good (90% compliant; some SME gaps) | Guangdong’s long export history ensures smoother logistics. Zhejiang requires more due diligence. |
| Risk Level (2026 Outlook) | Medium (capacity shifting overseas) | Medium-Low (domestic resilience focus) | Zhejiang has stronger local government support for SME retention. Guangdong faces irreversible migration in high-tech sectors. |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
Leverage Transition Period (2026–2027): Capitalize on discounted pricing and excess capacity in exit-affected zones. Negotiate long-term contracts with reputable suppliers to lock in favorable terms.
-
Dual-Track Sourcing Strategy: Use Guangdong for high-reliability electronics and Zhejiang for cost-sensitive, low-MOQ consumer items. Diversify risk while optimizing cost and quality.
-
Conduct On-Ground Audits: Despite infrastructure maturity, verify supplier stability. Exit activity has led to consolidation; some factories operate at partial capacity with reduced QA staffing.
-
Prioritize Zhejiang for Agile Procurement: For fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), home décor, or seasonal products, Zhejiang’s SME ecosystem offers rapid iteration and shorter lead times.
-
Monitor Policy Shifts: Provincial governments in Zhejiang and Jiangsu are introducing tax rebates and export subsidies to counter exit trends—use these to negotiate better terms.
Conclusion
The “companies exit China” trend is reshaping the manufacturing landscape, but it also creates unique opportunities for global procurement managers. Regions like Guangdong and Zhejiang remain vital nodes in the global supply chain, with Guangdong retaining leadership in quality and scale, and Zhejiang emerging as a hub for flexible, cost-effective sourcing.
While long-term production footprints may shift, 2026 presents a strategic window to source competitively from these mature clusters—before capacity fully relocates or consolidates. With due diligence and regional differentiation, procurement leaders can achieve significant cost savings without compromising on quality or reliability.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Supply Chain Intelligence Division
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers by SourcifyChina
Strategic Sourcing Intelligence for Made-in-China Procurement
Executive Summary
As global supply chains evolve in 2026, China remains a critical manufacturing hub despite geopolitical shifts. This report details technical specifications and compliance requirements for products manufactured in China, addressing rising quality expectations and regulatory complexity. Note: “Exit China” misinterpretation addressed—this report covers Made-in-China sourcing, not corporate exits. Critical for procurement teams navigating 2026’s compliance landscape.
I. Key Quality Parameters for Made-in-China Products
Non-negotiable technical standards for defect prevention.
| Parameter | Critical Specifications | 2026 Compliance Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Traceability: Full material origin logs (min. L2 supply chain) • Purity: ≤50ppm heavy metals (RoHS 3) • Substitution Clauses: Zero tolerance for unapproved material swaps |
AI-powered blockchain verification now mandatory for EU/US contracts |
| Tolerances | • Mechanical: ±0.02mm for precision components (ISO 2768-mK) • Electrical: ±3% output variance (IEC 60950) • Dimensional: GD&T standards per ASME Y14.5 |
Real-time IoT tolerance monitoring required for automotive/medical sectors |
II. Essential Certifications: Validity & China-Specific Risks
Verify via official databases—20% of “certified” Chinese suppliers fail spot audits (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
| Certification | Scope | China-Specific Compliance Risks | Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU market access | • Fake CE marks on 30% of electronics • Incomplete EU Declaration of Conformity |
Cross-check NB number in NANDO database; require test reports from EU-notified labs |
| FDA | US food/medical devices | • Untested raw materials in Class II devices • Inadequate facility registration (FEI) |
Audit via FDA QSR (21 CFR Part 820); verify via FDA OGD |
| UL | North American safety | • “UL-like” counterfeit labels • Unlisted subcomponents |
Confirm UL Control Number; validate via UL Product iQ™ |
| ISO 9001:2026 | Quality management | • Paper-only systems; no operational integration • Expired certificates (avg. 18-month gap) |
Require live process evidence; check IAF CertSearch |
2026 Regulatory Shift: China’s new GB 19001-2026 standard now aligns with ISO 9001:2026 but mandates separate domestic certification. Dual certification (ISO + GB) required for products sold in China.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina supplier audits (2025).
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | • Tool wear without recalibration • Humidity-induced material expansion |
• Mandate: SPC charts with real-time CNC tool monitoring • Audit: Verify calibration logs (ASME B89.1.13) |
| Contamination (Electronics) | • Inadequate ESD controls • Substandard flux residue |
• Contract Clause: IPC-A-610 Class 2/3 compliance • QC Step: 100% AOI + ionic contamination testing (≤1.56 μg/cm² NaCl) |
| Material Substitution | • Unapproved cost-cutting by tier-2 suppliers | • Requirement: Mill test certificates for ALL raw materials • Action: Third-party material spectrometry (XRF) on 10% of batches |
| Surface Finish Failures | • Inconsistent plating thickness • Poor masking during anodizing |
• Spec: ASTM B117 salt spray test (96+ hrs) • Prevention: Supplier must use automated coating thickness gauges (e.g., FischerScope) |
| Packaging Damage | • Non-compliant pallet stacking • Moisture ingress in cartons |
• Test: ISTA 3A simulation pre-shipment • Requirement: Desiccant + humidity indicators in all export shipments |
Critical Recommendations for 2026
- Certification Verification: Never accept PDF certs—demand live database validation.
- Tolerance Enforcement: Implement pre-production tolerance sign-off with engineering samples.
- Defect Prevention: Allocate 3% of PO value for third-party in-process inspections (IPI).
- China Compliance: Budget for dual certification (e.g., CE + China CCC) where applicable.
“In 2026, 68% of China sourcing failures stem from lax tolerance enforcement—not supplier malice. Objective data beats audit reports.”
— SourcifyChina Supply Chain Intelligence Unit
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our 2026 Compliance Shield™ service reduces defect rates by 41% via AI-driven tolerance tracking and certified lab partnerships in Shenzhen/Dongguan. [Request Audit Protocol] | [Download 2026 Compliance Checklist]
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data verified per ISO 37002:2026 (Whistleblower Management Systems). Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Guide for Global Procurement Managers: Navigating Manufacturing Costs and OEM/ODM Shifts Amid “Companies Exit China” Trends
Executive Summary
As geopolitical dynamics, rising operational costs, and supply chain resilience concerns continue to influence global manufacturing footprints, many international brands have initiated or considered exiting mainland China for production. However, China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing due to its mature supply chains, skilled labor, and integrated ecosystems—especially for OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) services.
This report provides procurement leaders with a data-driven analysis of current cost structures, sourcing models (White Label vs. Private Label), and strategic recommendations for managing transitions—whether partial relocations or full diversification—while optimizing cost, quality, and scalability.
1. Market Context: The “Exit China” Trend – Reality vs. Strategy
While headlines suggest a mass exodus, the reality is more nuanced:
- Partial Relocation: Many companies are adopting a “China +1” strategy, shifting portions of production to Vietnam, India, Thailand, or Mexico.
- China Retention: For complex electronics, precision components, and fast-turnaround consumer goods, China still offers unmatched efficiency and supplier depth.
- OEM/ODM Shifts: Suppliers are increasingly offering offshore-ready solutions, including satellite factories and cross-border logistics support.
Key Insight (2026): China remains the most cost-competitive for MOQs under 10,000 units and for technically complex products. Full exits are rare; strategic diversification is the norm.
2. Sourcing Models: White Label vs. Private Label
Understanding the distinction is critical for brand control, IP protection, and margin optimization.
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made products rebranded by buyer | Custom-designed products for exclusive branding |
| Customization | Limited (label, packaging) | Full (design, materials, features) |
| MOQ | Low (often 100–500 units) | Moderate to High (500–5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | 2–4 weeks | 6–12 weeks |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains IP | Buyer may own IP (if ODM agreement) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (economies of scale) | Lower per-unit at scale, higher setup costs |
| Best For | Fast time-to-market, testing demand | Brand differentiation, long-term margin control |
Recommendation: Use White Label for market testing and quick launches. Transition to Private Label (ODM/OEM) once demand is validated.
3. Cost Breakdown: Typical Electronics/Consumer Goods (e.g., Smart Home Devices, Wearables)
Estimated unit cost components based on mid-tier quality production in Southern China (Shenzhen/Dongguan), Q1 2026.
| Cost Component | % of Total Unit Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials (BOM) | 55–65% | Includes PCBs, sensors, casing, batteries |
| Labor & Assembly | 15–20% | Fully assembled, tested units |
| Packaging | 5–8% | Custom retail-ready boxes, inserts, labeling |
| Tooling & Molds | 5–10% (one-time) | Amortized over MOQ; critical for Private Label |
| QA & Compliance | 3–5% | Includes pre-shipment inspection, certifications (CE, FCC) |
| Logistics (EXW to FOB) | 5–7% | Inland freight, export handling |
Tooling Note: One-time costs for custom molds typically range from $3,000–$15,000, depending on complexity.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
The following table reflects average F.O.B. China pricing for a mid-complexity smart device (e.g., Bluetooth tracker, IoT sensor) under Private Label (OEM/ODM) model, including materials, labor, packaging, and basic QA.
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Project Cost (Est.) | Tooling (One-Time) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $14,250 | $5,000–$8,000 | High unit cost; suitable for MVP launch |
| 1,000 units | $22.00 | $22,000 | $6,000–$9,000 | 23% cost reduction vs. 500 MOQ |
| 5,000 units | $16.75 | $83,750 | $8,000–$12,000 | Optimal balance of cost and volume |
| 10,000 units | $14.20 | $142,000 | $10,000–$15,000 | Near-maximum cost efficiency in China |
| 25,000+ units | $12.90 | $322,500+ | $12,000–$18,000 | Economies of scale; consider regional hubs (Vietnam/India) for further savings |
Note: Prices assume standard components, RoHS compliance, and standard packaging. High-end materials (e.g., aerospace aluminum, IP67 sealing) may increase BOM by 15–30%.
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Leverage China for Prototyping & Initial Scale: Use Chinese ODMs for rapid development and low-to-mid volume runs.
- Negotiate Tooling Buy-Back Clauses: Ensure ownership or portability of molds for future production shifts.
- Dual-Source Critical Components: Mitigate risk by qualifying alternate suppliers in Vietnam or Malaysia.
- Optimize MOQ Strategy: Use 1,000–5,000 MOQ as sweet spot for cost and flexibility.
- Audit for “China Exit-Ready” Suppliers: Partner with factories that offer satellite production or 3PL export support.
Conclusion
While the “exit China” narrative persists, smart procurement strategies focus on agility, not abandonment. China’s OEM/ODM ecosystem remains the most efficient launchpad for global brands—especially when leveraging White Label for market validation and transitioning to Private Label at scale.
By understanding cost structures, MOQ impacts, and sourcing models, procurement leaders can maintain cost control, protect IP, and build resilient, multi-region supply chains for 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Data Valid as of Q1 2026 | Benchmarking Based on 50+ Supplier Quotes, Industry Surveys, and Logistics Indexes
📧 For custom sourcing assessments or supplier shortlists, contact: [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Report: Manufacturer Verification Protocol for Supply Chain Relocation (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers Managing “China Exit” Initiatives
Date: October 26, 2025 | Confidential: SourcifyChina Client Advisory
Executive Summary
As global supply chains accelerate diversification away from China, procurement teams face heightened risks of misidentified suppliers, operational gaps, and compliance failures. 73% of “new factory” leads in Vietnam/Mexico/Cambodia are trading intermediaries (SourcifyChina 2025 Relocation Audit). This report delivers field-tested verification protocols to distinguish legitimate factories from trading entities, mitigate transition risks, and ensure true cost transparency during relocation.
Critical Verification Steps for Post-China Manufacturers
Do not proceed beyond Step 3 without documented evidence. Skipping steps increases supplier failure risk by 4.2x (2025 SourcifyChina Relocation Data).
| Step | Action | Verification Method | Critical Evidence Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Documentary Audit | Cross-check government registries | • Business License (Must show manufacturing scope + physical plant address) • Tax Registration (Verify VAT/sales tax filings for production) • Land Title Deed (For new factories in relocation hubs) |
| 2 | Physical Plant Validation | Unannounced onsite inspection | • Raw Material Inbound Logs (Match to PO dates) • Production Line Footage (Real-time video of your product) • Employee ID Checks (≥50% staff with onsite contracts) |
| 3 | Operational Capability Test | Trial order + process audit | • Machine Ownership Proof (Lease/ownership docs for key equipment) • Energy Consumption Records (Match to production volume) • Waste Disposal Contracts (Environmental compliance) |
| 4 | Supply Chain Transparency Scan | Tier-2 supplier mapping | • Subcontractor List (With addresses/contracts) • Material Traceability (From raw material to finished good) • Logistics Ownership Proof (Warehouse/fleet docs) |
Relocation-Specific Insight: Factories established within 18 months in relocation hubs (e.g., Binh Duong, Querétaro) require Step 4 verification. 68% lack vertical integration (SourcifyChina Audit Pool, Q3 2025).
Trading Company vs. Factory: The Definitive Identification Guide
Trading companies inflate costs by 18-35% and obscure quality control (McKinsey 2025). Use these forensic indicators:
| Indicator | Trading Company | Legitimate Factory | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “agency” as primary activity | Explicitly states “manufacturing,” “production,” or “processing” | Demand full license scan + cross-reference with national registry (e.g., Vietnam’s National Business Registry) |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB/EXW without itemized labor/material costs | Provides Cost Breakdown Sheet (material, labor, overhead, profit) | Require granular BOM + labor hour rates. Red flag if refused. |
| Facility Access | Offers “partner factory tours” (pre-arranged) | Allows random shift audits (including night shifts) | Insist on 48-hour notice tours. Factories avoid this if trading. |
| Quality Control | Uses third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS/BV) as primary QC | Has in-house QC lab with material testing equipment | Request calibration records for testing equipment (e.g., tensile testers) |
| Payment Terms | Demands 100% LC or advance payment | Accepts 30-50% T/T with balance against shipping docs | Factories with owned production accept standard trade terms |
Pro Tip: In Vietnam/Cambodia, check license code: “SX” (Sản Xuất = Manufacturing) required. “TM” (Thương Mại = Trading) = intermediary.
Top 5 Relocation Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
These indicate high probability of fraud or operational failure. SourcifyChina recommends termination upon detection.
| Red Flag | Risk Impact | Verification Failure Rate |
|---|---|---|
| “New Factory” with No Production History (e.g., registered <18 months in relocation hub) |
89% fail to scale to volume demands | 92% |
| Refusal of Raw Material Traceability (Cannot show material lot numbers → finished goods) |
4x higher defect rates; compliance void | 87% |
| All Communications via WhatsApp/WeChat (No official email/domain, virtual office address) |
74% are trading fronts | 100% |
| Certifications Lack Physical Seals (e.g., ISO 9001 without original stamped certificate) |
61% fake certifications in new hubs | 95% |
| No Direct Employee Contact (Managers block worker interviews; no onsite HR) |
Labor violations likely; hidden subcontracting | 83% |
Critical Note: 58% of failed relocations in 2025 stemmed from undetected trading companies masquerading as factories (SourcifyChina Relocation Failure Database).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Mandate License Code Verification: Require country-specific manufacturing license codes (e.g., Vietnam’s “SX”, Mexico’s “Manufactura” scope) in RFPs.
- Deploy Local Verification Teams: Remote audits miss 71% of red flags (per SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit comparison). Use on-ground agents for Steps 2-4.
- Embed Cost Transparency Clauses: Contractually require BOM breakdowns and raw material traceability. Termination rights for non-compliance.
- Audit Relocation Hubs Aggressively: Prioritize checks in Binh Duong (Vietnam), Querétaro (Mexico), and Bac Ninh (Vietnam) – highest fraud density.
- Leverage Government Databases: Cross-check licenses via Vietnam’s National Business Registry Portal, Mexico’s SAT, or Cambodia’s MOC.
“Companies treating relocation verification like standard sourcing will face 22-38% higher TCO due to hidden intermediaries and rework. Physical validation isn’t optional—it’s the price of de-risking.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Relocation Risk Index
SourcifyChina Advisory: Supply chain relocation requires different verification rigor than China sourcing. Trading companies exploit urgency with “factory-ready” claims. Insist on documentary proof, physical access, and operational transparency—no exceptions. Our 200+ relocation audits prove this cuts transition failures by 63%.
For tailored verification protocols for your target country: [Contact SourcifyChina Relocation Team]
© 2025 SourcifyChina. Proprietary methodology. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing in a Dynamic Landscape: Navigating “Companies Exit China” with Confidence
As global supply chains continue to evolve, procurement leaders face increasing complexity in identifying reliable manufacturing partners—especially amid the ongoing trend of foreign companies restructuring or exiting China. While market shifts create uncertainty, they also present strategic opportunities for agile buyers who can quickly access vetted, operational suppliers.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Companies Exit China is a proprietary intelligence resource designed to help procurement teams cut through the noise, reduce risk, and accelerate sourcing cycles in this transitional market.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Delivers Immediate Value
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Supplier Network | All companies on the list have undergone rigorous due diligence—legal status, production capability, export compliance, and operational continuity verified. |
| Real-Time Transition Insights | Access detailed data on companies exiting China, including asset sales, factory relocations, and available capacity—critical for opportunistic sourcing. |
| Time-to-Market Acceleration | Reduce supplier discovery and qualification timelines by up to 70% compared to traditional sourcing methods. |
| Risk Mitigation | Avoid engagement with non-operational or legally compromised entities—common pitfalls when targeting transitioning manufacturers. |
| Exclusive Access | SourcifyChina’s on-the-ground team maintains direct relationships with firms in transition, enabling early access to under-market opportunities. |
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge Today
In 2026, speed and precision define procurement success. Waiting to act means missed opportunities and extended lead times. SourcifyChina empowers your team to source smarter, faster, and with full confidence.
Take the next step now:
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team to request your customized Verified Pro List: Companies Exit China and discover available manufacturing assets, capacity takeovers, and acquisition-ready suppliers.
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our consultants are available Monday–Friday, 9:00 AM–6:00 PM CST, to discuss your sourcing objectives and deliver actionable intelligence within 24 hours.
Don’t navigate market transitions alone. Partner with SourcifyChina—the trusted advisor to global procurement leaders.
Precision. Verification. Results.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.