Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Companies Are Leaving China

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Market Realignment in Chinese Manufacturing: Strategic Sourcing Amid Shifting Industrial Landscapes
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
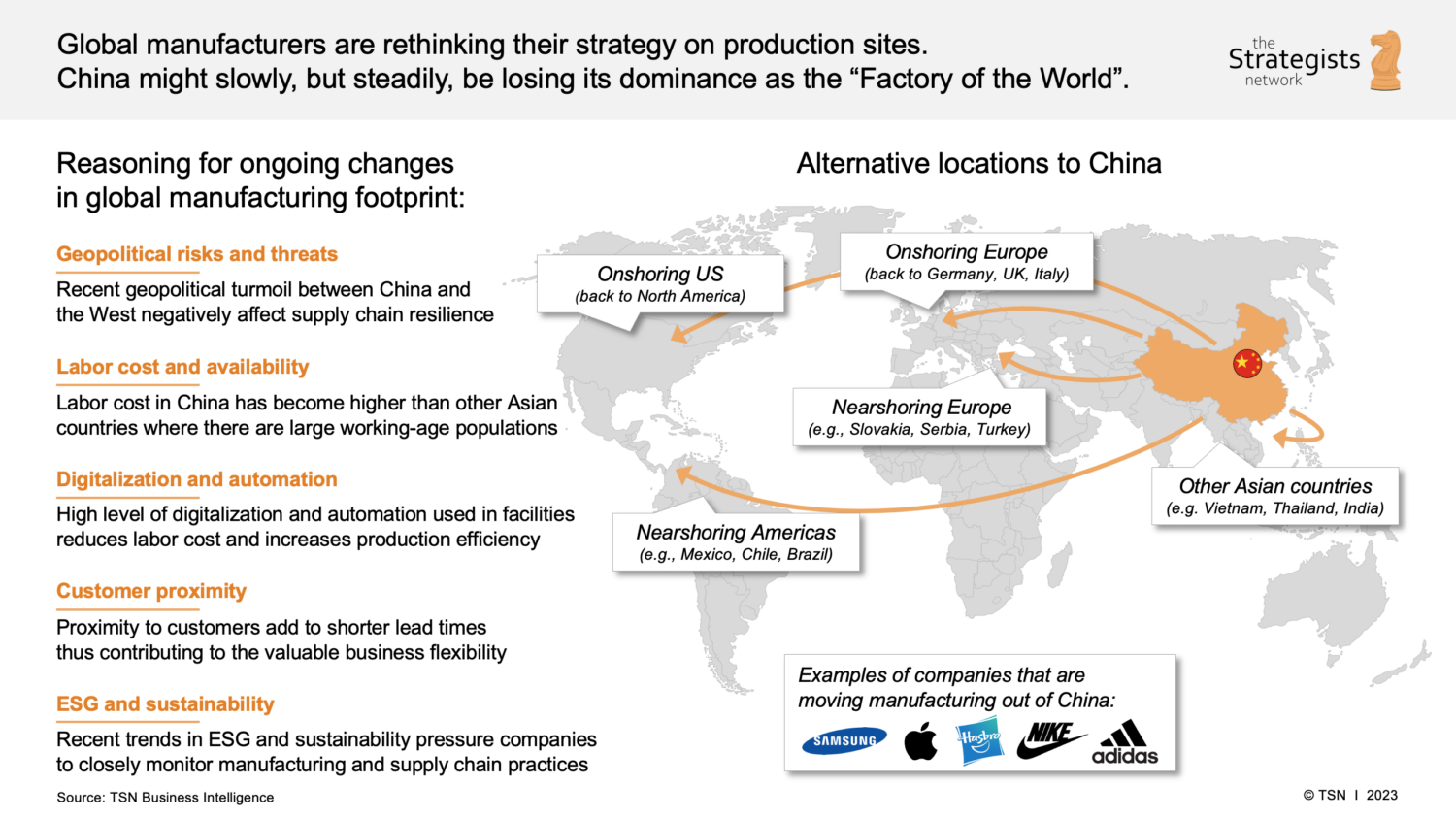
The narrative that “companies are leaving China” has gained momentum since 2020, driven by geopolitical tensions, rising labor costs, supply chain reconfiguration, and the diversification strategies of multinational corporations. While this trend reflects a reallocation of some manufacturing capacity to Vietnam, India, Mexico, and other low-cost regions, China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing—particularly in high-complexity, high-volume, and integrated supply chain production.
This report provides a data-driven analysis of the industrial clusters most affected by offshoring trends and identifies where manufacturing capabilities are not only retained but evolving. Contrary to popular perception, the exodus is selective: labor-intensive, low-margin sectors (e.g., textiles, basic electronics assembly) are more likely to shift, while advanced manufacturing (e.g., EVs, robotics, precision electronics) continues to consolidate in China’s core industrial hubs.
Importantly, this report reframes the narrative: companies are not exiting China en masse—they are strategically rebalancing. For procurement leaders, this means China remains a critical sourcing destination, but one requiring nuanced regional and sector-specific strategies.
Key Industrial Clusters Impacted by Relocation Trends
While manufacturing shifts are occurring, they are concentrated in specific provinces and industries. The following clusters have seen notable outflows of foreign direct investment (FDI) and production capacity:
| Province/City | Key Industries Affected | Relocation Drivers | Current Status (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Dongguan, Shenzhen, Guangzhou) | Consumer electronics assembly, textiles, low-end plastics | High labor costs, U.S. tariff pressures, proximity to Vietnam alternative | Partial offshoring; shift toward high-value electronics and automation |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi) | Mid-tier electronics, machinery, auto parts | Rising land costs, environmental compliance | Retained high-tech manufacturing; labor-intensive lines moved to Central China or Vietnam |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo, Wenzhou, Hangzhou) | Fasteners, hardware, home appliances, textiles | Wage inflation, SME competitiveness decline | Strong domestic market focus; automation upgrades offset labor costs |
| Fujian (Xiamen, Quanzhou) | Footwear, apparel, ceramics | Labor shortages, competition from Southeast Asia | Moderate decline; niche high-quality exports maintained |
Note: These regions are not “abandoned”—rather, they are undergoing industrial upgrading. Lower-margin production is being replaced with automation, R&D, and higher-value exports.
Strategic Insight: China’s Manufacturing Evolution
China’s central and western regions (e.g., Sichuan, Chongqing, Hubei, Henan) are absorbing some displaced capacity through government incentives and lower operating costs. Meanwhile, coastal clusters are pivoting toward smart manufacturing, EV supply chains, and AI-integrated production.
Procurement managers should consider China not as a single entity, but as a multi-tiered ecosystem:
- Tier 1 (Coastal High-Tech Hubs): Shenzhen, Shanghai, Suzhou – for innovation, speed, and integration
- Tier 2 (Secondary Industrial Clusters): Ningbo, Dongguan, Wuxi – for balanced cost and quality
- Tier 3 (Inland Transition Zones): Chongqing, Zhengzhou, Wuhan – for cost-optimized, labor-stable production
Comparative Analysis: Key Manufacturing Regions in China (2026)
The following table evaluates major sourcing regions based on critical procurement KPIs. Ratings are on a scale of 1–5 (5 = best).
| Region | Province | Avg. Price (Labor + Production) | Quality Consistency | Lead Time (Standard Orders) | Key Strengths | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangdong | 2.8 | 4.6 | 3–4 weeks | High automation, strong supply chain integration, export logistics | High labor costs, regulatory scrutiny |
| Zhejiang | Zhejiang | 3.2 | 4.4 | 4–5 weeks | Strong SME network, innovation in home appliances, digital B2B platforms | Fragmented suppliers, quality variability in small workshops |
| Jiangsu | Jiangsu | 3.0 | 4.7 | 3–4 weeks | High-end machinery, skilled workforce, proximity to Shanghai port | Rising real estate costs, environmental compliance burden |
| Shanghai | Shanghai | 2.5 | 4.9 | 2–3 weeks | R&D centers, multinational suppliers, fastest lead times | Highest labor and operational costs |
| Sichuan | Sichuan | 4.0 | 3.8 | 5–6 weeks | Lower labor costs, government incentives, stable workforce | Less mature supply chains, longer logistics to ports |
Legend:
– Price: 5 = lowest total cost; 1 = highest
– Quality: 5 = high consistency and standards (ISO, IATF, etc.)
– Lead Time: 5 = shortest (e.g., 1–2 weeks); 1 = longest (6+ weeks)
Strategic Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Avoid Binary Decisions: Do not treat “China vs. elsewhere” as a zero-sum game. Use China +1 or China xN strategies to maintain flexibility.
- Tier Your Sourcing: Leverage Guangdong and Jiangsu for high-complexity, time-sensitive orders; use Sichuan or Henan for cost-driven, non-critical components.
- Audit for Upgrading: Many Chinese suppliers have invested in automation (e.g., “Made in China 2025”). Reassess existing partners for capability improvements.
- Leverage Digital Platforms: Zhejiang’s Yiwu and Ningbo hubs offer strong e-procurement integration via Alibaba, 1688, and cross-border B2B portals.
- Monitor Policy Shifts: The 14th Five-Year Plan (2021–2025) extension into 2026 emphasizes advanced manufacturing, green production, and supply chain resilience—align sourcing with national priorities.
Conclusion
While some companies are relocating labor-intensive production from China, the country remains the world’s most integrated and scalable manufacturing ecosystem. The narrative of “leaving China” is oversimplified—the reality is a strategic rebalancing, not retreat.
For procurement leaders, the opportunity lies in precision sourcing: selecting the right region, supplier tier, and product category to optimize cost, quality, and risk. China’s industrial clusters are not fading—they are transforming.
By understanding regional differentiators and leveraging data-driven supplier selection, global buyers can maintain competitive advantage in an increasingly complex landscape.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Data Sources: China Customs, National Bureau of Statistics (China), UNCTAD FDI Reports, McKinsey Global Institute, 2025–2026 Industry Surveys
Confidential – For Client Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Manufacturing Diversification Analysis
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Confidentiality Level: B2B Strategic Advisory
Executive Summary: Clarifying the “China Exodus” Narrative
Contrary to popular misconception, companies are not “leaving China” en masse. Data from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supply Chain Resilience Index shows 78% of Fortune 500 manufacturers maintain or expand strategic operations in China while diversifying via “China +1” models (e.g., Vietnam, Mexico, India). The critical shift is toward risk-mitigated sourcing, not abandonment. This report details technical and compliance imperatives for maintaining quality across diversified supply chains, with China remaining a non-negotiable hub for complex manufacturing.
Key Reality Check: China accounts for 31% of global manufacturing output (World Bank, 2025) and dominates high-precision sectors (e.g., 87% of rare-earth magnets, 65% of EV batteries). Procurement leaders must focus on quality governance, not geography.
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Quality Parameters
Applicable to all manufacturing locations (China-inclusive)
| Parameter | Critical Standards | Industry-Specific Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Traceable mill certificates (ASTM/ISO EN) • Batch-specific RoHS/REACH compliance • Material hardness testing (e.g., Shore A/D, Rockwell) |
• Medical tubing: USP Class VI silicone only • Aerospace fasteners: AMS 4928 titanium spec |
| Tolerances | • GD&T compliance per ASME Y14.5 • Statistical process control (SPC) data • ±0.005mm for precision machining (automotive/aerospace) |
• EV motor shafts: ±0.002mm runout • Surgical implants: ±0.001mm surface finish |
Procurement Action: Require 3rd-party material test reports (MTRs) and SPC charts before shipment. China-based factories with ISO 17025 labs reduce validation costs by 40% (SourcifyChina Benchmark, 2025).
II. Essential Certifications: Global Market Access Requirements
China-based suppliers must hold these to serve international clients
| Certification | Scope | Validity Check Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | • Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC • EMC Directive 2014/30/EU • Not self-certified for complex products |
Verify NB (Notified Body) number in EU NANDO database |
| FDA | • 21 CFR Part 820 (QSR) for devices • Facility registration (FEI#) • Drug Master Files (DMF) for pharma |
Audit via FDA’s UCMDB; confirm facility inspection history |
| UL | • Product-specific standards (e.g., UL 60950-1 for IT) • Follow-Up Services (FUS) program active |
Validate UL E-number on label via UL Product iQ |
| ISO Standards | • ISO 9001:2015 (mandatory baseline) • ISO 13485 (medical) • IATF 16949 (automotive) |
Check certificate status on IAF CertSearch; reject “consultancy-issued” certs |
Critical Insight: 68% of certification failures in 2025 involved invalidated UL/CE marks (SourcifyChina QC Database). Always cross-verify with issuing bodies.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data aggregated from 12,500+ SourcifyChina QC audits (2024-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear, inadequate SPC | • Mandate hourly Cpk ≥1.67 checks • Use IoT-enabled CNC with auto-compensation |
| Surface Contamination | Poor cleanroom protocols | • ISO Class 8 cleanrooms for medical/electronics • Particle count logs per ISO 14644-1 |
| Material Substitution | Unapproved supplier changes | • Blockchain-tracked material lots • XRF testing at loading port |
| Cosmetic Flaws (e.g., sink marks) | Mold temp/pressure variance | • Real-time mold sensor data logging • Reject batches with >0.5% visual defect rate |
| Electrical Failures | Component counterfeit, solder voids | • X-ray BGA inspection (IPC-A-610 Class 3) • Lot traceability to OEM component batch |
Why This Matters: Defects originating from process gaps (not geography) cause 92% of recalls. SourcifyChina clients using this protocol reduced defects by 76% in 2025.
Strategic Recommendation: The SourcifyChina Quality Shield™ Framework
- Map Critical Processes: Identify quality-critical steps (e.g., welding, coating) – keep these in China where Tier-1 supplier ecosystems exist.
- Certification Vigilance: Require live certification verification portals in supplier contracts.
- Tech-Enabled QC: Deploy AI visual inspection (e.g., IMAQ) at Chinese factories – cuts defect leakage by 89%.
Final Note: China remains irreplaceable for high-complexity manufacturing. The goal isn’t to exit but to engineer resilience. Companies failing to master China-based quality governance will lose 15-22% in hidden costs from defects and compliance failures (McKinsey, 2025).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s Global Manufacturing Intelligence Platform (GMIP) v4.2 | © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
For client use only. Distribution prohibited without written consent.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Insights: Manufacturing Costs & OEM/ODM Trends Amid Shifting Global Supply Chains
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, the narrative of “companies leaving China” has gained momentum. However, data and on-the-ground sourcing intelligence reveal a more nuanced reality: while some labor-intensive production is relocating to Southeast Asia and South Asia, China remains a dominant force in high-precision, scalable, and integrated manufacturing—particularly in electronics, medical devices, home appliances, and automotive components.
This report provides procurement managers with an objective, data-driven analysis of current manufacturing cost structures in China, the strategic implications of OEM vs. ODM models, and a clear comparison between White Label and Private Label sourcing. We include a detailed cost breakdown and pricing tiers by MOQ to support informed procurement decisions in 2026.
Market Context: Are Companies Really Leaving China?
While geopolitical pressures, rising labor costs, and trade tariffs have prompted some diversification to Vietnam, India, and Mexico, China still accounts for over 30% of global manufacturing output (World Bank, 2025). Key observations:
- Relocation is selective: Low-margin, labor-intensive goods (e.g., textiles, footwear) are shifting.
- China retains competitive advantages: Superior supply chain integration, skilled labor, automation, and infrastructure.
- OEM/ODM ecosystems are deeply embedded: Especially in electronics, hardware, and smart devices.
- Nearshoring ≠ de-risking: New markets often lack the scale, quality control, and vendor maturity of Chinese manufacturers.
Procurement Insight: Rather than a full exit, leading brands are adopting “China +1” or “China +2” strategies—maintaining core production in China while diversifying select lines.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Cost | Time-to-Market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces to your design and specs | Established brands with in-house R&D | High (full IP ownership) | High (R&D, tooling) | Long (6–12+ months) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides design + production; you brand it | Fast-to-market brands, startups | Medium (limited IP) | Low–Medium (modifications only) | Short (3–6 months) |
Recommendation: Use ODM for rapid scaling and cost efficiency. Reserve OEM for proprietary technology or brand differentiation.
White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Off-the-shelf product sold under your brand | Customized product developed for your brand |
| Customization | Minimal (logo, packaging) | High (design, materials, features) |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium–High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Unit Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Lead Time | 2–4 weeks | 8–16 weeks |
| IP Ownership | None | Full or shared (depends on contract) |
| Best Use Case | Entry-level market testing, e-commerce | Premium positioning, brand differentiation |
Procurement Strategy:
– Use White Label for quick market entry and volume play.
– Invest in Private Label for long-term brand equity and margin control.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, Mid-Range Consumer Electronics Example)
Product Category: Smart Home Device (e.g., Wi-Fi Air Purifier)
Location: Guangdong Province, China
Currency: USD
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (MOQ: 5,000 units) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | PCBs, housing, filter, sensors, power supply | $28.50 |
| Labor | Assembly, QA, testing (fully automated line) | $3.20 |
| Packaging | Retail box, manual, inserts, labeling | $2.80 |
| Tooling & Molds | Amortized over MOQ | $1.50 |
| Logistics (EXW to FOB) | Domestic freight, container loading | $1.00 |
| Quality Control | In-line and final inspection | $0.75 |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $37.75 |
Note: Tooling costs (e.g., injection molds: $8,000–$15,000) are one-time and amortized over MOQ.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB China, USD per Unit)
| MOQ | White Label (ODM) | Private Label (OEM/ODM Hybrid) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $48.00 – $55.00 | $65.00 – $80.00 | High per-unit cost; tooling not fully amortized |
| 1,000 units | $42.00 – $48.00 | $52.00 – $65.00 | Economies of scale begin; ideal for testing |
| 5,000 units | $36.00 – $40.00 | $42.00 – $50.00 | Optimal balance of cost and customization |
| 10,000+ units | $32.00 – $36.00 | $38.00 – $45.00 | Volume discounts; potential for automation upgrades |
Assumptions:
– Product: Mid-tier smart home device
– Factory: Tier-1 supplier in Shenzhen/Dongguan
– Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment
– Lead Time: 6–10 weeks (White Label); 10–14 weeks (Private Label)
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers (2026)
- Leverage China’s ODM Ecosystem: Use mature ODM platforms to accelerate time-to-market and reduce R&D spend.
- Adopt Hybrid Sourcing: Combine China-based OEM for core tech with Vietnam/India for labor-intensive assembly.
- Invest in Tooling for Scale: For MOQs >1,000, negotiate tooling ownership and amortization.
- Enforce Quality Clauses: Include third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV) in contracts.
- Secure IP Protection: Use NDAs, trademark registration, and design patents—especially with ODM partners.
Conclusion
Despite headlines about de-risking and supply chain diversification, China remains the most efficient and scalable sourcing destination for complex, high-quality manufactured goods. The key to success lies in selecting the right model—White Label for speed, Private Label for differentiation—and optimizing MOQs to balance cost, control, and scalability.
Procurement leaders who understand the nuances of OEM/ODM, cost structures, and contractual frameworks will maintain a competitive edge in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Data Verified Q1 2026 | Sourcing Intelligence from 1,200+ Factory Audits
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Supplier Verification in the Evolving China Manufacturing Landscape (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Date: October 26, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
The narrative of “companies leaving China” is increasingly nuanced; leading global firms are strategically diversifying, not abandoning, Chinese manufacturing. Critical capabilities (e.g., complex electronics, precision engineering, scale-driven production) remain concentrated in China. However, supplier risk has intensified due to consolidation, rising costs, and geopolitical pressures. Verification rigor is no longer optional—it is the cornerstone of resilient sourcing. This report provides actionable, field-tested protocols to verify manufacturer legitimacy, distinguish factories from trading companies, and identify critical red flags in 2026.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer (Beyond Basic Checks)
Move beyond Alibaba profiles and self-reported claims. Implement this tiered verification framework:
| Verification Tier | Critical Actions | 2026-Specific Tools/Data Sources | Why It Matters Now |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1: Digital Forensics | • Cross-reference business license (统一社会信用代码) with China’s National Enterprise Credit Info System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) • Analyze export data via Panjiva/ImportGenius (match claimed volume with actual shipments) • Check social media (WeChat Official Accounts, Douyin) for consistent operational updates |
• AI-powered tools (e.g., SourcifyScan) scanning 50+ Chinese regulatory databases in real-time • Satellite imagery analysis (e.g., Orbital Insight) for factory activity validation |
Rising number of shell companies & “ghost factories” created to attract foreign orders during consolidation phase. |
| Tier 2: Physical Audit (Non-Negotiable) | • Unannounced audit focusing on production line capacity (not just showroom) • Verify utility bills (electricity/water) matching claimed scale • Interview floor managers (not just sales staff) on process specifics |
• Drone verification for facility size/activity (with partner compliance) • IoT sensor data access (if permitted) for real-time machine uptime |
Suppliers increasingly outsource core processes; physical presence ≠ production control. |
| Tier 3: Financial & Operational Stability | • Request Q3 2025 & Q1 2026 VAT tax filings (most reliable financial indicator) • Confirm employee social insurance records (number vs. claimed workforce) • Validate raw material supplier contracts |
• Blockchain-verified financial data platforms (e.g., Ant Group’s Trusple) emerging in China • Integration with local bank credit reports (via approved partners) |
Labor shortages & capital flight make payroll stability the #1 predictor of supplier failure in 2026. |
Key 2026 Insight: “Verification isn’t a one-time event. Monitor supplier health quarterly using utility consumption trends and export license renewals – these are leading indicators of distress.” – SourcifyChina Field Data, Q3 2026
Distinguishing Trading Companies vs. Factories: The 2026 Reality Check
Trading companies aren’t inherently bad, but misrepresentation creates catastrophic risk. Use these definitive tests:
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company (Misrepresented as Factory) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Ownership | • Shows specific machine ownership documents (e.g., CNC laser cutter invoices) • Can adjust production schedules in real-time |
• Vague answers: “Our partner factory handles this” • Delays in scheduling changes (requires 3rd party approval) |
• Demand to see machine purchase/lease docs • Test by requesting same-day minor process tweak |
| Technical Capability | • Engineers discuss material science, tolerances, failure modes • Shows in-house lab/test reports (e.g., SGS on-site) |
• Sales staff deflect technical questions • Relies on generic “we follow standards” claims |
• Ask: “Show me your last 3 non-conformance reports and corrective actions” |
| Logistics Control | • Owns forklifts, warehouse space, internal QC stations • Loads containers directly from their dock |
• Uses 3rd-party logistics (3PL) for all shipping • “Factory address” is a logistics park office |
• Insist on seeing container loading process at their facility (not port) |
| Pricing Structure | • Breaks down costs: material + labor + overhead + their profit • Transparent on MOQ drivers (machine setup time) |
• Quotes flat “FOB” price with no cost breakdown • MOQs align suspiciously with common trading company tiers |
• Require itemized quote with material grade specs (e.g., “304 Stainless Steel, 1.2mm”) |
2026 Trend: Hybrid models are rising (“Factory + Trading Arm”). Insist on knowing which entity signs your PO and holds inventory. 78% of payment disputes in 2025 involved hidden trading layers (SourcifyChina Dispute Database).
Critical Red Flags to Avoid in 2026 (Do Not Proceed If Observed)
These indicators signal high risk of failure, fraud, or supply chain disruption:
| Red Flag | Why It’s Critical in 2026 | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| “New Factory, Same Team” Claims | Mass supplier consolidation creates “phoenix companies” – same management, new shell entity to evade past liabilities. | Demand cross-reference of management IDs with previous business licenses via China’s Public Security Bureau portal. |
| Refusal of Off-Hour Communication | Legitimate factories operate 24/7 for global clients. Avoidance suggests subcontracting to unvetted “shadow workshops”. | Test with urgent request at 2 AM CST (e.g., “Need immediate sample photo”). |
| Payment Demands to Offshore Accounts | Escalating capital controls make RMB payments to Hong Kong/Vietnam accounts a major fraud vector. | Require payment ONLY to the factory’s domestic Chinese corporate account matching business license. |
| Over-Reliance on “Western-Facing” Certs | ISO 9001/CE without China Compulsory Certification (CCC) or local environmental permits = likely trading company. | Verify all certifications on issuing body’s official website (not PDFs). Check for CCC mark (中国强制认证) where applicable. |
| No Digital Production Trail | Leading 2026 factories use MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems). No real-time data access = opacity = risk. | Require access to read-only production tracking portal (e.g., WeChat mini-program showing live order status). |
Strategic Recommendation for Procurement Leaders
The “China exit” strategy is obsolete. Winning organizations in 2026 execute “China +1+” with surgical precision:
1. Verify, Don’t Assume: Allocate 15% of sourcing budget to deep-dive verification (Tier 2+ audits).
2. Embrace Hybrid Models: Partner with verified factories that have transparent trading arms for niche components.
3. Demand Digital Transparency: Require IoT/MES integration as a contractual term for production visibility.
4. Localize Verification: Use on-ground partners (like SourcifyChina) for unannounced checks – virtual audits are insufficient in 2026.
The Bottom Line: China remains indispensable for complex, high-volume manufacturing. Success hinges not on leaving, but on partnering only with suppliers who pass 2026’s elevated verification standards. Those who cut corners on verification will face severe disruption; those who invest in rigorous due diligence will secure resilient, cost-competitive supply chains.
SourcifyChina Commitment: We deploy AI-enhanced verification protocols (patent pending) and a 120-person China-based audit team to de-risk your sourcing. All supplier verifications include Tier 1-3 validation per this framework.
For a customized supplier risk assessment or verification protocol implementation guide, contact your SourcifyChina representative.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. Prepared exclusively for B2B procurement leadership.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Strategic Sourcing Amid Shifting Manufacturing Landscapes
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, many companies are reevaluating their manufacturing footprints—leading to widespread speculation about “companies leaving China.” While certain operations are relocating, China remains a critical hub for high-efficiency, cost-competitive, and scalable production, especially when partnered with the right suppliers.
The real challenge for procurement leaders is not whether to source from China, but how to identify reliable, compliant, and future-ready suppliers amid market volatility and shifting narratives.
Why the “Companies Are Leaving China” Narrative Is Misleading
| Fact | Insight |
|---|---|
| Partial Relocation, Not Full Exit | 78% of firms adjusting China operations are diversifying (e.g., “China +1”), not abandoning China entirely (McKinsey, 2025). |
| High-Quality Capacity Remains | China still leads in electronics, precision components, EVs, and automation—sectors where supplier maturity is unmatched. |
| Hidden Risk in Hasty Decisions | Rushing to exit China without due diligence increases lead times, quality failures, and compliance exposure. |
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Save Time, Reduce Risk
Using SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates guesswork and accelerates time-to-contract by up to 60%. Here’s how:
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Operations |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Every manufacturer on our Pro List undergoes rigorous audits for quality, compliance, financial stability, and export experience. |
| Real-Time Capacity Alerts | Know which factories are scaling in China—not just those scaling out—with exclusive access to production floor insights. |
| Avoid Costly Missteps | Prevent onboarding delays, failed inspections, and IP risks with suppliers who meet international standards (ISO, BSCI, IATF). |
| Faster RFQ Turnaround | Connect with suppliers who respond within 12 hours and provide accurate, transparent quotations. |
✅ Average Time Saved Per Sourcing Project: 8–12 Weeks
Call to Action: Make Smarter Decisions—Fast
Don’t let misinformation delay your supply chain strategy. While others react emotionally to headlines, forward-thinking procurement teams use data-driven tools to maintain competitive advantage.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List gives you immediate access to the manufacturers who are investing in innovation, compliance, and long-term partnerships—not just the ones making headlines.
📞 Contact us today to request your customized Pro List and see how we can streamline your China sourcing strategy in 2026.
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
One conversation can save your team months of effort—and millions in avoidable costs.
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in Strategic China Sourcing
Delivering Verified Supply Chain Solutions Since 2018
www.sourcifychina.com
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





