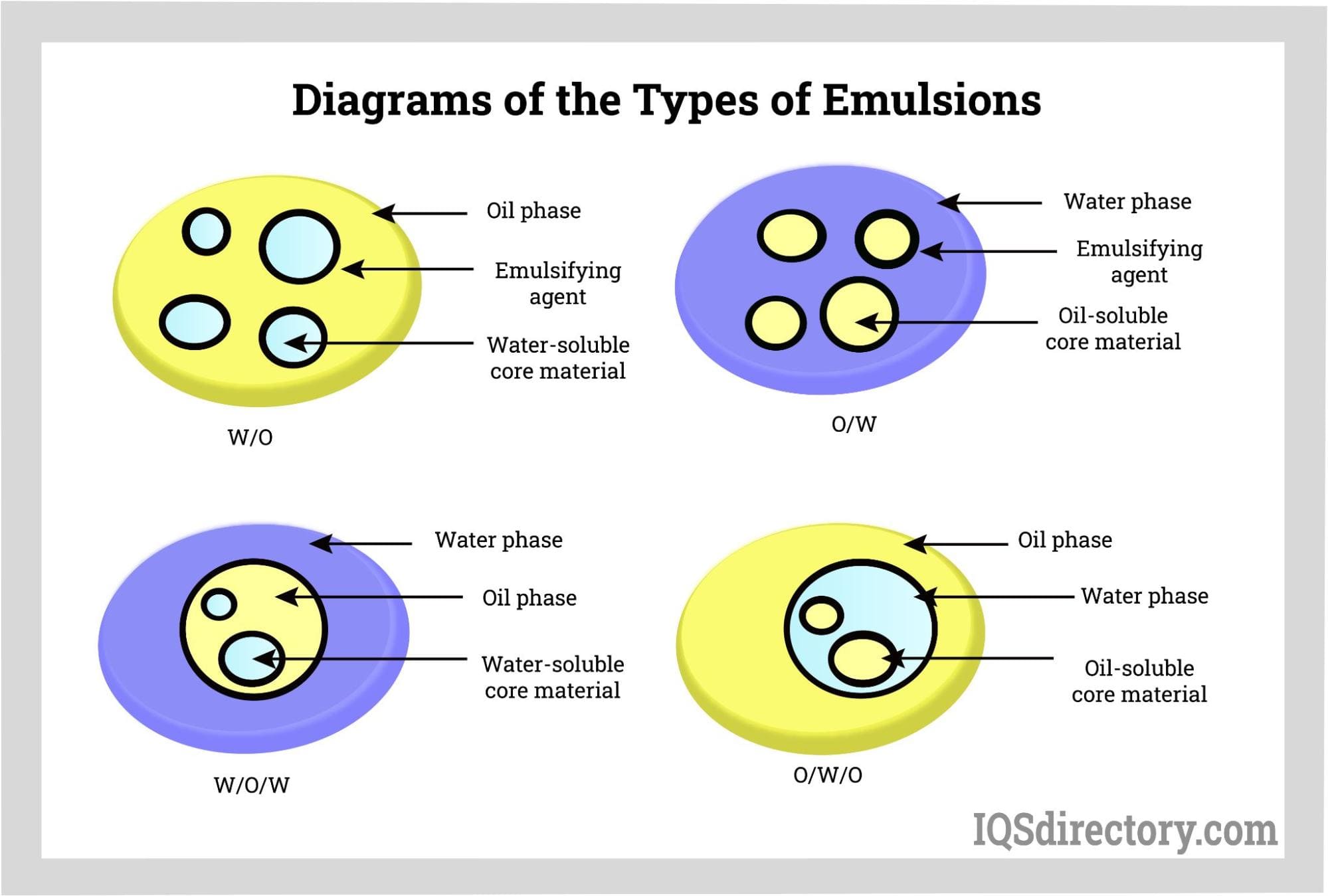
The global emulsifiers market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for processed and convenience foods, coupled with advancements in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations. According to Mordor Intelligence, the emulsifiers market was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by increasing consumer preference for stable, long-lasting textures and extended shelf life in food products, as well as the growing need for efficient delivery systems in personal care and healthcare applications. With major applications in baked goods, dairy, confectionery, and cosmetics, emulsifiers have become indispensable in modern manufacturing. As regulatory standards and clean-label trends influence sourcing strategies, the role of reliable, innovative emulsifier manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. The following list highlights nine of the most prominent emulsifier producers globally—companies that combine scale, technological prowess, and market reach to shape the future of formulation science across industries.
Top 9 Common Emulsifiers Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Dow Inc.
Domain Est. 1992
Website: dow.com
Key Highlights: Dow is a materials science company that offers a wide range of products and services, including agricultural films, construction materials, ……
#2 Bunge
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bunge.com
Key Highlights: Bunge is a premier agribusiness solutions company with the talent and technology to advance the industry….
#3 Emulsifier Suppliers
Domain Est. 2000
Website: industrialmixers.com
Key Highlights: View the country’s top emulsifier manufacturers and suppliers who are leaders in superior products and 24/7 customer support for discount prices….
#4 Emulsifiers Companies
Domain Est. 2009
Website: marketsandmarkets.com
Key Highlights: The emulsifiers market is dominated by key manufacturers including BASF SE (Germany), Archer Daniels Midland (ADM) (US), Cargill, Incorporated (US), Evonik ……
#5 Emulsifiers
Domain Est. 1994
Website: adm.com
Key Highlights: ADM provides consistent, effective, plant-based emulsifiers for a broad range of formulated products and applications….
#6 Emulsifiers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: kerry.com
Key Highlights: Kerry offers texture-optimising food emulsifiers including non-palm emulsifiers. Among our products are emulsifiers in the Myverol™, Admul™ and Myvacet™ ……
#7 How Natural Emulsifiers Support Green Beverage Production
Domain Est. 1998
Website: allanchem.com
Key Highlights: Common examples include soy lecithin, sunflower lecithin, and xanthan gum, each offering unique properties for specific beverage applications….
#8 Food emulsifiers solutions
Domain Est. 2003
Website: lasenor.com
Key Highlights: We create emulsifier solutions that transform recipes into irresistible experiences. Designed for bakery, confectionery, dairy, and savory. Click here!…
#9 Emulsifiers
Domain Est. 2010
Website: food.vantagegrp.com
Key Highlights: These are among the most common emulsifiers used in food manufacturing. Derived from Glycerin, mono- and diglycerides are used to combine ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Common Emulsifiers
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Common Emulsifiers
The global market for common emulsifiers is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving consumer preferences, regulatory changes, technological advancements, and sustainability demands across food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries. Key trends shaping the emulsifier landscape include clean label demand, plant-based innovation, functional versatility, regional market dynamics, and supply chain resilience.
Clean Label and Natural Emulsifiers on the Rise
By 2026, the demand for clean-label and naturally derived emulsifiers is expected to dominate the market. Consumers increasingly favor ingredients with recognizable names and transparent origins. This shift is pushing manufacturers to replace synthetic emulsifiers like polysorbates and DATEM with natural alternatives such as lecithins (especially sunflower and non-GMO soy), mono- and diglycerides from plant sources, and hydrocolloids like gum arabic, pectin, and agar. Clean-label emulsifiers are projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6% from 2022 to 2026, with North America and Western Europe leading adoption.
Plant-Based and Vegan Formulations Driving Innovation
The surge in plant-based diets and vegan product development is reshaping emulsifier demand. With the global plant-based food market expected to exceed $100 billion by 2026, formulators are seeking emulsifiers that stabilize plant proteins, fats, and water in dairy alternatives (e.g., oat milk, vegan cheese) and meat substitutes. Sunflower lecithin, lupin protein isolates, and modified starches are gaining traction due to their compatibility with plant matrices and allergen-free profiles. This trend is particularly strong in Europe and among younger demographics in urban markets.
Functional and Multifunctional Emulsifiers
In 2026, multifunctional emulsifiers that offer enhanced texture, shelf-life extension, and nutritional benefits will gain prominence. For instance, enzymatically modified phospholipids and structured lipids not only stabilize emulsions but also improve bioavailability of nutrients and support gut health. In pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals, emulsifiers like polysorbate 80 and polyglycerol polyricinoleate (PGPR) are being reformulated for improved delivery systems. The trend reflects a broader industry shift toward performance-driven ingredients that support product differentiation.
Regional Market Diversification
While North America and Europe remain strong markets due to high regulatory standards and consumer awareness, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in emulsifier consumption by 2026. Rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and expanding food processing industries in countries like China, India, and Indonesia are fueling demand. Local manufacturers are adapting global emulsifiers to regional tastes, such as using rice lecithin or tapioca-based stabilizers to meet clean label and allergen-free requirements in Asian markets.
Sustainability and Supply Chain Transparency
Sustainability concerns are influencing emulsifier sourcing and production. By 2026, companies are prioritizing traceable, deforestation-free, and ethically sourced raw materials—especially for palm oil derivatives like glyceryl monostearate (GMS) and PGPR. Certification schemes (e.g., RSPO, Fair Trade) are becoming standard. Additionally, innovations in fermentation-derived emulsifiers (e.g., microbial exopolysaccharides) and enzyme-aided synthesis are reducing environmental impact and enhancing production efficiency.
Regulatory Pressures and Health Concerns
Regulatory scrutiny on certain synthetic emulsifiers is expected to increase by 2026, particularly in the EU and Canada, where food safety agencies are reevaluating the long-term health effects of emulsifiers like carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) and polysorbate 80. Emerging research linking some emulsifiers to gut microbiome disruption may accelerate the shift toward safer, natural alternatives. This regulatory landscape will drive innovation in safer emulsifier chemistries and comprehensive safety dossiers.
Conclusion
By 2026, the common emulsifier market will be characterized by a strong pivot toward natural, sustainable, and multifunctional ingredients. Innovation will be centered on meeting consumer demands for transparency, health, and environmental responsibility, while maintaining technical performance across applications. Companies that invest in R&D, sustainable sourcing, and clean-label positioning are likely to lead the evolving emulsifier market.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Common Emulsifiers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing common emulsifiers like lecithins, polysorbates, glycerides, or sorbitan esters is deceptively complex. While they are widely available, overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to significant downstream problems in product performance, regulatory compliance, and legal liability.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Emulsifier Specifications and Purity
* Problem: Suppliers may offer emulsifiers meeting only basic industry standards (e.g., FCC, Ph. Eur.), but critical parameters like HLB value, fatty acid profile, free fatty acid content, moisture, peroxide value, or residual solvents can vary significantly between batches or suppliers. This variability directly impacts emulsion stability, texture, and shelf-life.
* Risk: Formulation instability (e.g., phase separation, graininess, poor texture), inconsistent product performance, shortened shelf-life, and potential safety issues (e.g., rancidity).
* Mitigation: Define strict, product-specific specifications beyond generic standards. Require Certificates of Analysis (CoA) for every batch with data on key performance indicators (KPIs). Conduct incoming quality control (QC) testing, especially for critical parameters.
2. Undeclared or Unverified Raw Material Sources (Traceability)
* Problem: The source of the base material (e.g., soy, sunflower, palm) significantly impacts the emulsifier’s properties, allergen profile, and sustainability credentials. Suppliers may not provide transparent or verifiable traceability.
* Risk: Unintended allergen contamination (e.g., undeclared soy in a “non-soy” product), exposure to GMOs despite claims, inability to meet sustainability commitments (e.g., RSPO-certified palm oil), and reputational damage.
* Mitigation: Demand full traceability documentation (e.g., supplier declarations, certificates of origin, sustainability certifications). Audit suppliers, especially for high-risk materials. Verify claims (e.g., Non-GMO Project verification, allergen-free status) through independent testing if necessary.
3. Inadequate Microbiological Control and Contaminant Risk
* Problem: Emulsifiers, especially natural ones like lecithin, can be susceptible to microbial growth (bacteria, yeast, mold) or contamination with heavy metals, pesticides, or mycotoxins if sourced from poorly controlled agricultural or processing environments.
* Risk: Product spoilage, safety hazards (pathogens, toxins), regulatory non-compliance (e.g., exceeding limits for lead, cadmium, aflatoxins), and recalls.
* Mitigation: Specify strict microbiological limits (Total Plate Count, Yeast & Mold, pathogens like Salmonella, E. coli) and contaminant limits (heavy metals, pesticides, mycotoxins) in the specification. Ensure the supplier has robust GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) and HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) systems. Review their supplier qualification and testing protocols.
4. Stability and Shelf-Life Miscalculation
* Problem: Emulsifiers can degrade over time (oxidation, hydrolysis), especially if stored improperly (heat, light, moisture). Suppliers may provide optimistic shelf-life estimates not validated under real-world conditions.
* Risk: Loss of emulsifying efficiency during storage, leading to failed formulations, inconsistent product quality, and waste.
* Mitigation: Require stability data (real-time and accelerated) from the supplier under defined storage conditions. Implement FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory management. Monitor incoming material age and condition. Conduct periodic stability testing on stored inventory.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Infringement of Patented Formulations, Processes, or Uses
* Problem: While the base emulsifier (e.g., Polysorbate 80) might be generic, specific forms (e.g., highly purified grades, specific isomer ratios), manufacturing processes (e.g., enzymatic modification), or approved applications (e.g., specific drug delivery systems, unique food applications) may be protected by active patents.
* Risk: Legal action (injunctions, damages) from the patent holder, forced reformulation, product recalls, and significant financial and reputational damage. Sourcing a “common” emulsifier doesn’t guarantee freedom to operate.
* Mitigation: Conduct thorough Freedom-to-Operate (FTO) analysis before finalizing sourcing and formulation. This involves patent landscape searches focused on the specific emulsifier grade, its manufacturing process, and the intended application. Consult with IP counsel. Ensure the supplier warrants they are not infringing third-party IP in their supply.
2. Trade Secret Misappropriation via Reverse Engineering
* Problem: Attempting to replicate a competitor’s successful product by analyzing its emulsifier system and sourcing identical components risks infringing on trade secrets if the specific combination, ratio, or processing method is confidential and not reverse-engineerable from public information.
* Risk: Costly litigation for misappropriation of trade secrets, even if the individual emulsifiers are generic.
* Mitigation: Focus innovation on developing novel formulations or processes rather than direct copying. Ensure R&D practices respect confidentiality obligations. Legal review of reverse engineering activities is crucial.
3. Ambiguous or Inadequate IP Clauses in Supply Agreements
* Problem: Standard supply contracts may lack clear terms regarding IP ownership of custom formulations developed using the supplier’s emulsifier, liability for IP infringement by the supplied material, or the supplier’s obligations regarding their own IP rights.
* Risk: Disputes over ownership of new product developments, unexpected liability for infringement claims, inability to use the material in planned applications.
* Mitigation: Negotiate clear IP clauses in supply agreements. Define ownership of jointly developed IP. Require supplier indemnification against third-party IP infringement claims related to their supplied emulsifier. Clarify permitted uses.
4. Sourcing from Suppliers with Questionable IP Practices
* Problem: A supplier might offer a very low price on a specialized emulsifier grade, potentially indicating they are using a patented process or formulation without a license.
* Risk: Becoming an “infringer by supply” if you use their material, exposing your company to liability even if you were unaware of the infringement.
* Mitigation: Perform due diligence on suppliers, especially for specialized or unusually priced materials. Assess their reputation and technical capabilities. Consider requesting assurances regarding their IP compliance (though this has limits). Prefer established, reputable suppliers with transparent operations.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls through stringent specifications, robust supplier qualification, thorough due diligence, and clear contractual agreements, companies can mitigate risks and ensure a reliable, compliant, and legally sound supply of common emulsifiers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Common Emulsifiers
Overview
Emulsifiers are essential additives used across food, pharmaceutical, personal care, and industrial sectors to stabilize mixtures of immiscible liquids (e.g., oil and water). Common emulsifiers include lecithin, mono- and diglycerides, polysorbates, sorbitan esters, and sodium stearoyl lactylate. Ensuring safe and compliant logistics for these substances is critical due to their widespread use and regulatory scrutiny.
Classification and Handling
Emulsifiers are typically classified as non-hazardous chemicals under transport regulations when in solid or non-flammable liquid form. However, proper classification under systems such as GHS (Globally Harmonized System) and transport regulations (e.g., ADR, IMDG, IATA) must be verified per product specification.
- Solid emulsifiers (e.g., powdered lecithin, SSL): Generally non-hazardous; handle as general cargo.
- Liquid emulsifiers (e.g., liquid mono-diglycerides, polysorbate 80): May require evaluation for flash point and classification. Most are non-flammable but should be stored away from heat sources.
- Packaging: Use sealed, moisture-resistant containers (e.g., multi-wall paper bags, HDPE drums, or food-grade totes). Avoid contamination with incompatible substances.
Storage Requirements
- Temperature Control: Store in a cool, dry place (typically 15–25°C). Some liquid emulsifiers may require protection from freezing or excessive heat (check MSDS).
- Humidity: Keep relative humidity below 65% to prevent caking or degradation (especially for hygroscopic emulsifiers like polysorbates).
- Segregation: Store away from strong oxidizers, acids, and bases. Food-grade emulsifiers must be segregated from non-food chemicals to prevent cross-contamination.
- Shelf Life: Most emulsifiers have a shelf life of 12–24 months; rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out).
Transportation
- Domestic (e.g., US, EU): Generally transported as non-hazardous goods via road or rail. Use clean, dry, and pest-free vehicles.
- International (Air & Sea):
- IATA (Air): Most emulsifiers are not restricted, but verify UN number and packing group. Liquid forms may require leak-proof packaging.
- IMDG (Sea): Typically shipped as general cargo. Documentation must include accurate product name, quantity, and hazard classification (if applicable).
- Labeling: Packages must display proper identification, net weight, batch number, and handling instructions (e.g., “Keep Dry,” “Protect from Sunlight”).
Regulatory Compliance
Emulsifiers are subject to stringent regulatory frameworks depending on application and region.
Food-Grade Emulsifiers
- United States (FDA): Must comply with 21 CFR regulations; listed as GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) or approved food additives. Ensure suppliers provide FDA-compliant documentation (e.g., Letter of Guarantee, COA).
- European Union (EFSA): Regulated under Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008. Must be authorized for specific food categories with defined maximum levels (e.g., E471, E435).
- Other Regions: Check local standards (e.g., FSSAI in India, Health Canada, ANVISA in Brazil).
Non-Food Applications (Cosmetics, Pharma)
- Cosmetics (EU/UK): Comply with Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009; emulsifiers must be listed in Annex IV/V and undergo safety assessments.
- Pharmaceuticals: Must meet pharmacopoeial standards (e.g., USP, Ph. Eur.) and be manufactured under GMP conditions.
Labeling and Documentation
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Required under GHS and REACH (EU), OSHA HazCom (US). Must be up to date and available to handlers.
- Certificates of Analysis (COA): Essential for quality verification; include assay, impurities, microbial limits, and compliance statements.
- Allergen & GMO Declarations: For lecithin (often from soy), declare allergens and GMO status per regional rules (e.g., EU GMO labeling, FALCPA in US).
Import/Export Considerations
- Customs Classification: Use correct HS codes (e.g., 1520.00 for lecithin, 3402.20 for synthetic emulsifying agents).
- Import Permits: Some countries require prior notification or approval for food additives (e.g., Saudi Arabia SFDA, China NHC).
- REACH (EU): Non-EU manufacturers must appoint an Only Representative (OR) or work through an EU importer to register substances.
- TSCA (US): Confirm emulsifiers are listed on the TSCA Inventory.
Best Practices for Compliance & Safety
- Audit suppliers regularly for regulatory compliance and quality control.
- Train logistics staff on handling, spill response, and emergency procedures.
- Maintain traceability through batch tracking and documentation retention (minimum 5 years).
- Use third-party labs to verify incoming shipments for purity and contaminants.
Conclusion
Safe and compliant logistics of common emulsifiers require a thorough understanding of chemical properties, transport regulations, and regional compliance frameworks. Implementing robust quality control, proper documentation, and supplier oversight ensures uninterrupted supply and regulatory adherence across global markets.
In conclusion, sourcing common emulsifiers requires a balanced consideration of functionality, regulatory compliance, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Widely used emulsifiers such as lecithin, mono- and diglycerides, polysorbates, and sorbitan esters each offer specific advantages depending on the application—be it in food, cosmetics, or pharmaceuticals. Natural emulsifiers like lecithin and plant-based gums are increasingly favored due to growing consumer demand for clean-label products, while synthetic options remain vital for their consistent performance and stability in complex formulations. When sourcing, it is essential to evaluate supplier reliability, raw material origin, allergen considerations, and adherence to food safety standards such as FDA, EFSA, or ISO certifications. Ultimately, selecting the right emulsifier and supplier involves aligning technical requirements with market trends and sustainability goals to ensure both product quality and consumer trust.