The global rice processing equipment market is witnessing robust growth, driven by rising demand for high-efficiency milling solutions and the modernization of agricultural infrastructure. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global rice milling market was valued at approximately USD 1.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5.3% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is underpinned by increasing rice consumption in Asia-Pacific, technological advancements in milling machinery, and a shift toward automated and energy-efficient systems. Combine rice mills—integrated systems that streamline husking, polishing, and grading—are gaining traction due to their ability to reduce labor costs, minimize grain breakage, and improve yield consistency. With countries like India, Vietnam, and Thailand leading rice production and export volumes, demand for reliable, high-capacity milling solutions has never been higher. Against this backdrop, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, scalability, and global reach to dominate the sector. The following list highlights the top 8 combine rice mill manufacturers shaping the future of rice processing worldwide.
Top 8 Combine Rice Mill Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Combined Rice Mill Factory and Manufacturers, Suppliers
Domain Est. 2022
Website: fotmamill.com
Key Highlights: Top Combined Rice Mill Manufacturer in China for Quality Machinery. We offer a top-notch Combined Rice Mill, perfect for those in the rice production industry….
#2 DawnAgro
Domain Est. 2023 | Founded: 1993
Website: dawnagromach.com
Key Highlights: DawnAgro, we are a professional agricultural machinery manufacturing factory founded in 1993. Professional research and development of agricultural machinery….
#3 Quality Mini Rice Mill & Combined Rice Mill Machine factory from …
Domain Est. 2023
Website: yifengagro.com
Key Highlights: China leading provider of Mini Rice Mill and Combined Rice Mill Machine, Leshan Yifeng Machinery Manufacturing Co., LTD is Combined Rice Mill Machine ……
#4 Producers Rice Mill
Domain Est. 1998
Website: producersrice.com
Key Highlights: Located in the rice capital of the world, Producers Rice Mill is logistically positioned to service customers throughout North America, Mexico and Canada….
#5 Rice Milling Machines
Domain Est. 2004
Website: fotma.com
Key Highlights: Rice Milling Machines ; 200-240 T/Day Complete Rice Parboiling And Milling Line ; 100-120TPD Complete Rice Parboiling and Milling Plant….
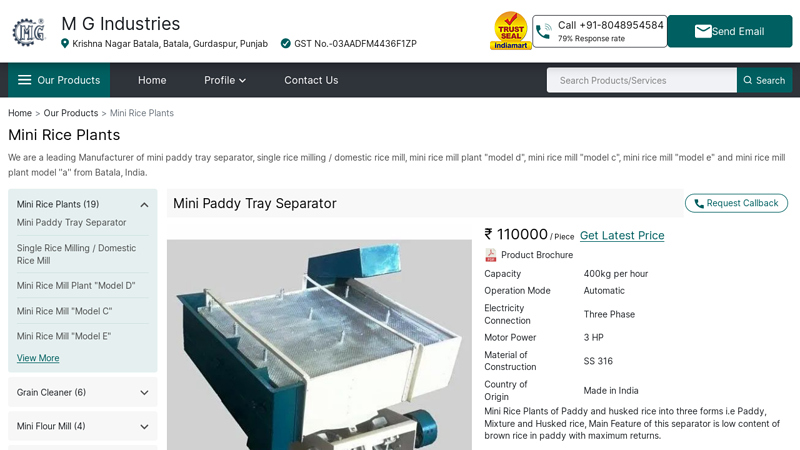
#6 Mini Rice Plants
Domain Est. 2016
Website: mg-industries.com
Key Highlights: Mini Rice Mill “Model E” · Operation Mode: Automatic · Electricity Connection: Three Phase · Material of Construction(Contact): MS · Power: 30 kwh · Brand: MG ……
#7 6w300 Combine Rice Mill Manufacturer from Raipur
Domain Est. 2021
Website: kisanmachinery.com
Key Highlights: It provides a rice milling capacity of 100–150 kilograms per hour and a grinding capacity of 20–30 kilograms per hour, ideal for small farmers, entrepreneurs, ……
#8 Top 100 Rice Mill Machinery Manufacturers in China (2025)
Domain Est. 2022
Website: ensun.io
Key Highlights: HUAYO AGRO offers a Combined Rice Mill Crusher that efficiently mills rice and crushes grains into powder, featuring excellent performance with low breakage….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Combine Rice Mill
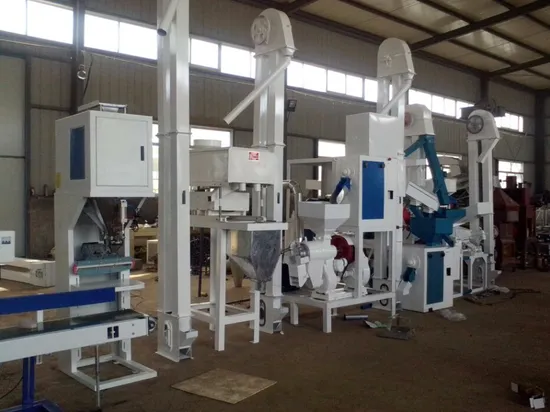

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Combine Rice Mill
The global rice processing industry is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing demand for high-quality milled rice, and increasing pressure to improve efficiency and sustainability. The Combine Rice Mill—a facility that integrates multiple stages of rice processing (pre-cleaning, dehusking, polishing, grading, and packaging) into a single streamlined system—is at the forefront of this evolution. Below are key market trends expected to shape the Combine Rice Mill sector in 2026:
-
Increased Automation and Smart Milling Technologies
By 2026, automation will be a dominant trend in combine rice mills. The integration of IoT (Internet of Things), AI-driven quality control systems, and real-time monitoring will enable mills to optimize yield, reduce grain breakage, and enhance consistency. Smart sensors will monitor moisture content, grain quality, and machine performance, allowing for predictive maintenance and remote operations—especially in large-scale commercial mills across Asia and Africa. -
Rising Demand for Compact and Modular Mills
Smallholder farmers and cooperatives in emerging markets will increasingly adopt modular combine rice mills due to their affordability, portability, and ease of installation. These systems support localized rice processing, reduce transportation costs, and minimize post-harvest losses—aligning with sustainability goals. Countries like India, Bangladesh, Nigeria, and the Philippines are expected to see widespread deployment of such units. -
Focus on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and rising energy costs will drive demand for energy-efficient combine rice mills. Manufacturers will prioritize systems that use renewable energy (solar or biomass-powered), recycle husk and bran for by-product utilization, and reduce water usage during polishing. The circular economy model—converting rice husk into fuel or construction materials—will gain traction, enhancing mill profitability. -
Growing Emphasis on Premium and Specialty Rice
With increasing consumer preference for premium rice varieties (e.g., basmati, jasmine, organic, or fortified rice), combine rice mills will adapt to handle delicate grains with minimal breakage. Advanced grading and sorting technologies (e.g., optical sorters) will become standard to ensure high purity and meet export-grade standards. This trend will be especially strong in export-oriented markets like India, Thailand, and Vietnam. -
Expansion in Africa and Southeast Asia
Africa’s rice consumption is outpacing production, leading governments and private investors to boost local milling capacity. Combine rice mills will play a key role in bridging the supply gap, supported by foreign direct investment and development initiatives. Similarly, in Southeast Asia, modernization of aging milling infrastructure will fuel demand for high-capacity, automated combine mills. -
Digital Platforms and Mill Management Software
By 2026, digital dashboards and cloud-based mill management systems will become common. These platforms will allow mill operators to track production metrics, manage inventory, and connect with buyers and suppliers through integrated agri-tech ecosystems. Blockchain may also be used to ensure traceability and build consumer trust in rice origin and quality. -
Consolidation and Economies of Scale
The market may witness consolidation among smaller players, as larger agribusinesses invest in centralized, high-throughput combine rice mills to achieve economies of scale. This trend will be supported by government policies promoting food security and value addition in rural areas.
In conclusion, the 2026 landscape for combine rice mills will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and responsiveness to evolving consumer and regulatory demands. Companies that invest in smart, scalable, and eco-friendly milling solutions will be best positioned to capture growth in both established and emerging markets.
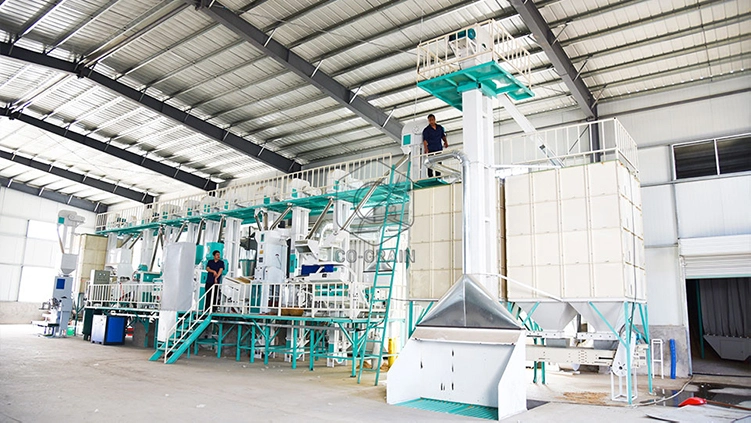

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Combined Rice Mill (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a combined rice mill—especially one that integrates multiple processing stages such as paddy cleaning, dehusking, polishing, grading, and packaging—requires careful consideration of both quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects. Overlooking these can lead to significant operational, legal, and financial risks. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Inadequate Equipment Standards
Many suppliers, particularly in competitive emerging markets, may offer lower-cost machinery that sacrifices durability, efficiency, or food safety compliance. Buyers often encounter substandard materials, inconsistent performance, or designs unsuitable for local paddy varieties. Without proper vetting, mills may require frequent maintenance, deliver inconsistent rice quality (e.g., high breakage rates), or fail to meet food safety certifications. Always request third-party quality inspections, performance test reports, and references from existing clients.
Lack of Verification for Intellectual Property Rights
Some combined rice mill designs incorporate proprietary technologies—such as energy-efficient husking systems, advanced optical sorters, or automated control units. When sourcing, especially from lesser-known manufacturers, there’s a risk of inadvertently acquiring equipment that infringes on protected patents or trademarks. This can result in legal disputes, shipment seizures, or forced decommissioning. Conduct due diligence by requesting IP documentation, verifying patent registrations, and consulting legal experts in both the supplier’s and buyer’s jurisdictions.
Misrepresentation of Automation and Technology Claims
Suppliers may overstate the level of automation, integration, or technological sophistication of their rice mills. Claims about “smart” systems, IoT connectivity, or AI-driven quality control may not be fully functional or may rely on third-party software with unclear licensing terms. This can lead to unexpected integration costs or operational limitations. Ensure technical specifications are verified through live demonstrations, software audits, and compatibility assessments before purchase.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even with high-quality equipment, long-term performance depends on reliable technical support and spare parts. Some suppliers offer attractive initial pricing but lack a local service network or stock of critical components, leading to extended downtime. Poor documentation or non-standardized parts can also complicate repairs. Confirm the supplier’s service commitments, spare parts inventory, and availability of trained technicians before finalizing the deal.
Overlooking Regulatory and Certification Compliance
Rice milling equipment must comply with food safety (e.g., FDA, EU standards), electrical safety, and environmental regulations in the destination market. Some suppliers fail to provide proper certifications (such as CE, ISO, or UL), or use non-compliant materials (e.g., non-food-grade coatings). Additionally, imported mills may use software or components subject to export controls. Verify compliance early to avoid customs delays or operational shutdowns.
Ignoring Customization and Local Adaptation Needs
A one-size-fits-all mill may not perform optimally with region-specific paddy types (e.g., aromatic or sticky rice) or local climate conditions (e.g., high humidity). Suppliers may not disclose limitations in adaptability, leading to inefficiencies or product loss. Ensure the mill can be customized for grain characteristics, capacity needs, and environmental factors—and confirm that modifications won’t void warranties or IP licenses.
Hidden Costs from Software Licensing and IP Dependencies
Modern rice mills often rely on embedded software for process control, data logging, or predictive maintenance. Some suppliers impose ongoing licensing fees, restrict software updates, or retain ownership of operational data. These hidden costs and IP dependencies can limit scalability and control. Review software licensing terms carefully and negotiate rights for modification, backup, and local hosting where possible.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—through detailed technical evaluations, legal reviews, and supplier audits—buyers can secure a high-performing, compliant, and legally sound combined rice mill that supports long-term operational success.
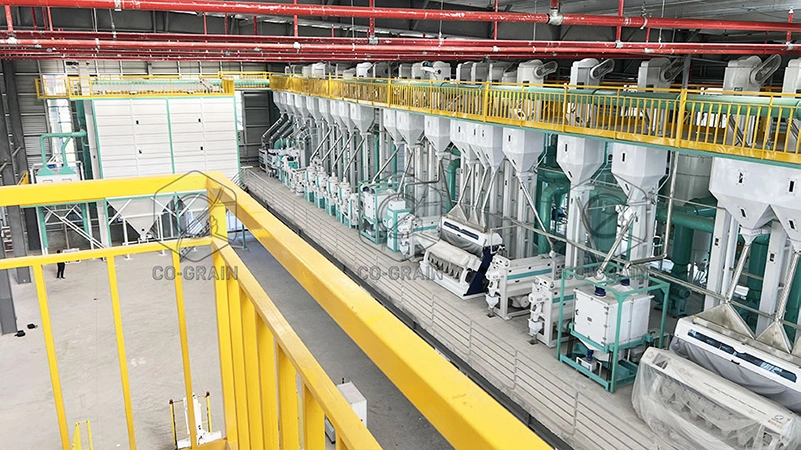

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Combine Rice Mill
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance procedures for operating a Combine Rice Mill efficiently and within regulatory standards. Adherence ensures product quality, legal operation, and supply chain reliability.
Raw Material Procurement & Incoming Logistics
Establish contracts with reliable paddy suppliers, ensuring consistent quality and traceability. Implement a standardized receiving process that includes weighing, sampling, and quality inspection (moisture content, impurities, grain damage). Maintain records of supplier details, delivery dates, and test results for traceability. Schedule deliveries to align with milling capacity and storage availability to prevent overstocking or shortages.
Storage Management for Paddy and Milled Rice
Store paddy in clean, dry, pest-free silos or warehouses with proper ventilation to control temperature and moisture (ideally below 14%). Monitor storage conditions regularly to prevent mold, insect infestation, or spoilage. Segregate paddy by variety, harvest date, and quality grade. Similarly, store milled rice in airtight, food-grade containers or bulk storage with controlled humidity to preserve freshness and prevent contamination.
Milling Operations & Internal Material Flow
Ensure all milling machinery is calibrated, maintained, and operated according to manufacturer and food safety guidelines. Implement a clear workflow from paddy cleaning, dehusking, polishing, grading, to packaging to minimize cross-contamination and physical damage. Conduct in-process quality checks at each stage. Use dedicated tools and containers for different rice grades to prevent mixing.
Packaging, Labeling & Finished Goods Handling
Package milled rice in approved food-safe materials with moisture barriers. Labels must comply with local food regulations and include product name, net weight, milling date, best-before date, batch number, mill name and address, and nutritional information where required. Store finished goods off the floor on pallets in a clean, dry area, organized by batch and date for first-expired, first-out (FEFO) inventory management.
Outbound Logistics & Distribution
Coordinate transportation using clean, covered, and pest-free vehicles. Prefer refrigerated or temperature-controlled trucks for long-distance or tropical climate deliveries to maintain rice quality. Provide shipping documentation including delivery notes, invoices, and certificates of analysis (COA) when required. Ensure timely dispatch to meet customer delivery schedules and minimize inventory holding.
Regulatory Compliance & Documentation
Register the rice mill with relevant food safety authorities (e.g., FSSAI in India, FDA in the U.S., or equivalent). Obtain necessary licenses for food processing, storage, and transportation. Maintain a Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) plan or equivalent food safety management system. Conduct regular internal audits and keep records of sanitation schedules, pest control, equipment maintenance, and staff training.
Quality Assurance & Testing Protocols
Implement a routine testing schedule for incoming paddy and finished rice, checking parameters such as moisture, broken grain percentage, chalkiness, and foreign matter. Use accredited laboratories for periodic testing of microbiological and chemical contaminants (e.g., aflatoxin, pesticide residues). Retain sample logs and test reports for a minimum of two years for compliance and traceability.
Environmental, Health & Safety (EHS) Compliance
Adhere to local environmental regulations for waste disposal, including rice husk, bran, and dust. Utilize by-products responsibly (e.g., husk for biomass fuel, bran for animal feed). Provide personal protective equipment (PPE) for workers and conduct regular safety training. Install dust control systems and fire suppression equipment in milling and storage areas to ensure workplace safety.
Recordkeeping & Traceability
Maintain comprehensive records of all operations, including procurement, production batches, quality tests, maintenance logs, and distribution. Implement a traceability system that links each batch of milled rice back to its source paddy, milling date, and delivery destination. This is critical for recalls, audits, and customer assurance.
Continuous Improvement & Regulatory Updates
Regularly review logistics efficiency and compliance standards. Stay informed about changes in food safety laws, labeling requirements, and environmental regulations. Engage in staff training and process optimization to enhance productivity, reduce waste, and ensure ongoing compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Combined Rice Mill
Sourcing a combined rice mill is a strategic decision that can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve the quality of milled rice. A combined rice mill—integrating pre-cleaning, dehusking, polishing, grading, and sorting in a single streamlined system—offers scalability and consistency, making it ideal for medium to large-scale rice processing operations.
When sourcing such equipment, it is crucial to assess key factors including production capacity, technology level, energy efficiency, ease of maintenance, after-sales support, and compliance with international quality standards. Prioritizing suppliers with proven track records, technical expertise, and reliable service networks ensures long-term operational success.
Additionally, conducting thorough market research, obtaining multiple quotations, and evaluating both local and international manufacturers can lead to cost-effective and sustainable procurement. Investing in automation and modern features such as color sorters and dust collection systems not only improves output quality but also meets increasing market demands for premium rice products.
In conclusion, sourcing a combined rice mill requires a balanced approach that considers technical specifications, budget constraints, and future growth potential. With the right partner and equipment, rice processors can achieve higher productivity, reduce post-harvest losses, and gain a competitive edge in domestic and global markets.