The global cold shrink tubing market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand across industries such as electrical, telecommunications, automotive, and renewable energy. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 1.27 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by the rising need for reliable cable insulation solutions, particularly in harsh environments where traditional heat-shrink alternatives may be impractical. Additionally, increasing infrastructure investments and the global push toward energy efficiency are further accelerating adoption. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, scalability, and product durability to capture significant market share. Based on market presence, product portfolio breadth, and technological advancement, the following seven companies represent the forefront of the cold shrink manufacturing industry.
Top 7 Cold Shrink Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
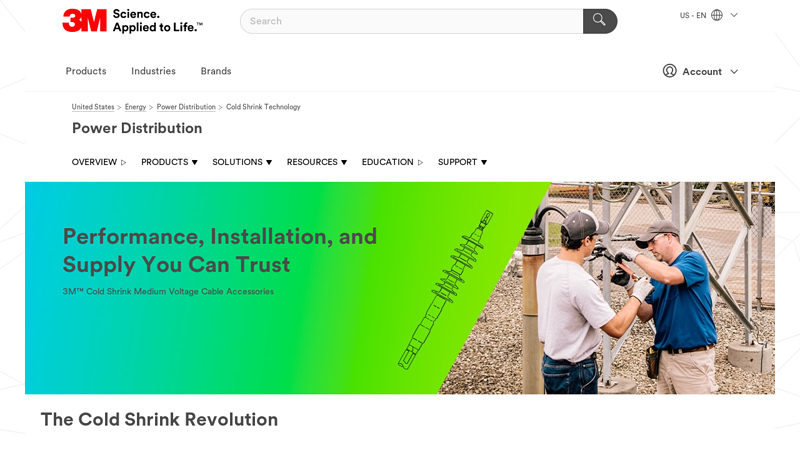
#1 3M Cold Shrink Products
Domain Est. 1988
Website: 3m.com
Key Highlights: The Cold Shrink Revolution. For over 60 years, professional electrical workers have trusted 3M for innovative solutions that enhance safety and productivity….
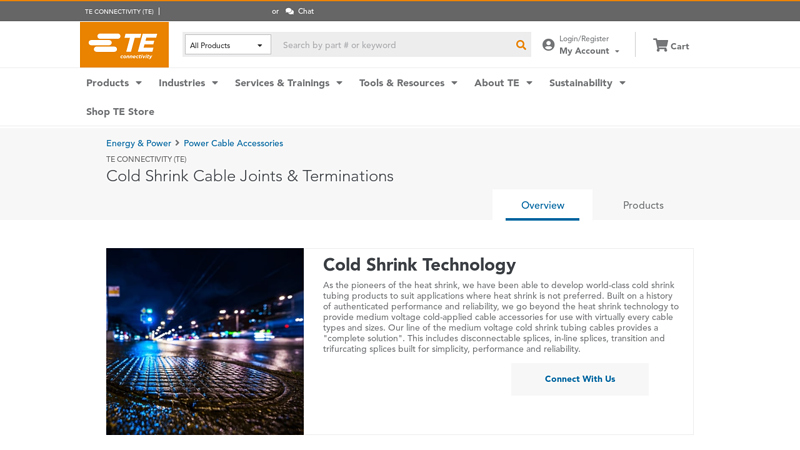
#2 Cold Shrink Cable Joints and Terminations
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: Search our portfolio of Cold Shrink Cable Accessories Models & Products and select your specifications. You can now buy select products directly on TE.com….
#3 DSG
Domain Est. 2000
Website: dsgcanusa.com
Key Highlights: DSG-Canusa has been developing and producing high-quality heat shrink tubing, cold-applied accessories and heat shrink equipment for over 50 years….
#4 Gala Thermo Shrink PVT. LTD
Domain Est. 2001
Website: galathermo.com
Key Highlights: Range of products like Heat Shrink, Cable Joints, Cable Terminations, cable end sealing caps, Spreader caps, heat shrink end caps, heat shrink tubes, heat ……
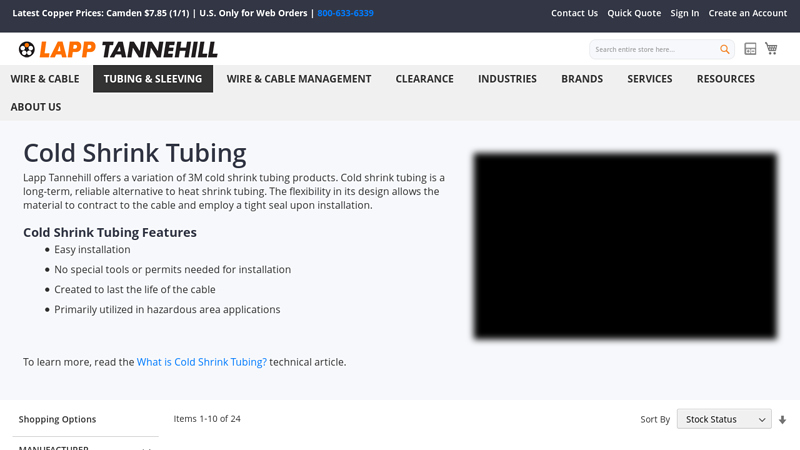
#5 Cold Shrink Tubing
Domain Est. 2007
Website: lapptannehill.com
Key Highlights: 5-day deliveryLapp Tannehill offers a variation of 3M cold shrink tubing products. Cold shrink tubing is a long-term, reliable alternative to heat shrink tubing….
#6 Heat Shrink Tubing
Domain Est. 2012
Website: idealind.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsIDEAL® Heat Shrink is easy to install underground splice kits to help save time and money. Protects cable during storage with watertight ……
#7 3M Cold Shrink Products
Website: 3mnz.co.nz
Key Highlights: The Cold Shrink Revolution. For over 60 years, professional electrical workers have trusted 3M for innovative solutions that enhance safety and productivity….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cold Shrink

H2 2026 Market Trends for Cold Shrink
Based on current technological trajectories, industry demands, and macroeconomic factors, the Cold Shrink market in the second half of 2026 is expected to be shaped by several key trends:
-
Accelerated Demand in Renewable Energy & EV Infrastructure:
- Solar & Wind: Continued global push for decarbonization will drive massive investments in solar and wind farms. Cold shrink terminations and connectors are essential for reliable cable management in harsh outdoor environments (UV, moisture, temperature swings). H2 2026 will see peak installation cycles for projects approved earlier, significantly boosting demand for high-performance, long-life cold shrink solutions, particularly for medium-voltage (MV) applications.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): The rapid expansion of EV charging networks (DC fast charging, depot charging for fleets) requires robust, safe cable connections. Cold shrink components offer quick, reliable, and insulated joints/terminations for charging station cabling and power distribution within depots. Demand for specialized, compact, and heat-resistant cold shrink kits tailored for EV infrastructure will surge.
-
Focus on Enhanced Performance & Durability:
- Material Innovation: Expect wider adoption of advanced silicone rubber and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) formulations offering superior resistance to extreme temperatures (-60°C to +135°C+), UV degradation, ozone, and chemical exposure. This is critical for reliability in renewable energy, industrial, and transportation applications.
- Sealing & Moisture Protection: Heightened emphasis on IP68/IP69K rated sealing performance, especially for subsea connectors, offshore wind, and harsh industrial environments. Integrated gel seals within cold shrink components will become more common.
- Fire Performance: Increased demand for cold shrink products with enhanced fire resistance (low smoke, zero halogen – LSZH/LS0H) and flame retardancy (e.g., meeting IEC 60332-3) for applications in tunnels, public buildings, and transportation.
-
Digitalization & Supply Chain Optimization:
- Predictive Maintenance & IoT: While not embedded in the shrink itself, cold shrink installations in critical infrastructure (grid, data centers) will increasingly be monitored via external IoT sensors. Data on temperature, humidity, and partial discharge at termination points will drive demand for predictable and reliable components like cold shrink, reinforcing its value proposition for maintenance teams.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Lessons learned from recent disruptions will lead to more localized manufacturing and strategic raw material sourcing. Leading suppliers will prioritize supply chain transparency and resilience, potentially impacting sourcing decisions for end-users in H2 2026. “Just-in-case” inventory strategies may persist.
-
Sustainability & Regulatory Pressure:
- Circular Economy: Growing focus on the end-of-life management of cable accessories. Suppliers will face increasing pressure to develop more recyclable materials or take-back schemes. Products with longer service life inherently support sustainability goals.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stricter environmental regulations (e.g., evolving RoHS, REACH) will drive the phase-out of certain additives and promote the use of environmentally friendly materials in cold shrink production. Compliance will be a non-negotiable market entry requirement.
-
Market Consolidation & Competitive Dynamics:
- Consolidation: The competitive landscape may see further consolidation as larger players acquire niche technology providers (e.g., specialized material science firms) to enhance their product portfolios and compete globally.
- Competition from Alternatives: While cold shrink offers significant advantages (speed, reliability, no heat source), competition from advanced heat shrink (requiring less heat, faster recovery) and prefabricated solutions (plug-in connectors) will persist. Suppliers will need to clearly articulate cold shrink’s unique value proposition (safety, suitability for confined spaces, performance consistency).
In summary, H2 2026 will position the Cold Shrink market as a critical enabler of the global energy transition and electrification. Growth will be primarily driven by renewables and EV infrastructure, with intense focus on performance, durability, and sustainability. Suppliers excelling in material innovation, supply chain reliability, and meeting stringent environmental and safety standards will be best positioned to capture market share during this period of significant infrastructure build-out.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cold Shrink (Quality, IP)
Sourcing cold shrink tubing—especially for critical applications in electrical, telecom, or industrial sectors—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failures, safety hazards, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Inconsistent Performance
Low-cost cold shrink tubing may use substandard elastomeric materials that degrade rapidly under environmental stress (UV, moisture, temperature extremes). This can result in cracking, loss of sealing integrity, or electrical insulation failure. Always verify compliance with relevant standards (e.g., UL, IEC, RoHS) and request test reports for shrinkage ratio, dielectric strength, and long-term durability.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Many suppliers, particularly from unverified sources, fail to provide proper documentation such as material traceability, batch testing, or third-party certifications. Without these, it’s impossible to ensure consistency or validate performance claims, increasing the risk of non-compliance in regulated industries.
Counterfeit or Non-Genuine Products
The cold shrink market sees frequent counterfeiting, especially of well-known brands. Fake products often mimic packaging and branding but use inferior materials. Sourcing through unauthorized distributors or gray market channels heightens this risk. Always procure through authorized channels and verify supplier authenticity.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Some manufacturers produce cold shrink designs that closely mimic patented technologies from leading brands (e.g., specific adhesive systems, core removal mechanisms, or stress control geometries). Using such products—even unknowingly—can expose your company to IP litigation. Conduct due diligence on supplier design origins and avoid “look-alike” products without proper licensing.
Inadequate Technical Support and Customization
Low-cost suppliers may lack engineering expertise to support application-specific requirements such as custom sizing, voltage ratings, or environmental resistance. This can lead to improper product selection and field failures. Choose suppliers who offer technical collaboration and application validation.
Hidden Costs from Field Failures
While upfront pricing may be attractive, poor quality or IP-infringing cold shrink products can result in costly field repairs, downtime, warranty claims, or safety incidents. These hidden costs often far exceed initial savings, making due diligence essential.
To mitigate these risks, prioritize suppliers with strong quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), transparent supply chains, IP compliance, and a track record in your industry. Conduct audits, request samples, and validate performance before bulk procurement.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cold Shrink Tubing
Overview of Cold Shrink Tubing
Cold shrink tubing is a pre-expanded elastomeric sleeve used primarily in electrical and industrial applications for insulation, environmental protection, and mechanical safeguarding of cables and connections. Unlike heat shrink tubing, it requires no heat source for installation—instead, it retracts upon removal of a removable core, conforming tightly to the underlying component. Due to its critical safety and performance role, proper logistics handling and compliance with regulatory standards are essential.
Storage & Handling Requirements
Cold shrink tubing is sensitive to environmental conditions and physical stress. To maintain its integrity prior to installation:
– Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight, UV exposure, and extreme temperatures (recommended range: 10°C to 30°C / 50°F to 86°F).
– Protect from ozone sources (e.g., electric motors, welding equipment) and chemical vapors, which can degrade elastomeric materials.
– Keep in original packaging until ready for use to prevent dust, moisture, or mechanical damage.
– Avoid stacking heavy items on packaged products to prevent deformation.
– Handle with clean, dry gloves to avoid contamination of the inner surface.
Transportation Guidelines
Ensure safe and compliant transport of cold shrink tubing across supply chains:
– Use climate-controlled vehicles when transporting in extreme climates.
– Secure packaging to prevent shifting during transit; use cushioning materials to minimize shock and vibration.
– Label packages as “Fragile” and “Protect from Sunlight” to alert handlers.
– Maintain traceability through batch/lot numbers, especially for compliance documentation.
– Comply with IATA, IMDG, or other relevant transport regulations if shipping internationally—even though cold shrink tubing is typically non-hazardous, packaging materials may have specific requirements.
Regulatory & Industry Compliance
Cold shrink tubing must meet various international and industry-specific standards depending on the application:
– UL / cUL Listing: Required for use in North American electrical installations; verify product is listed under UL 224 or UL 62 for insulation.
– RoHS Compliance: Ensure materials are free of restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium, PBDEs), especially for electronics and EU markets.
– REACH (EU): Confirm compliance with SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) regulations.
– CE Marking: Mandatory for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards.
– Flame Ratings: Products used in tunnels, mass transit, or confined spaces may require low-smoke zero-halogen (LSZH) properties compliant with IEEE 1202, IEC 60332, or EN 45545-2.
– ATEX / IECEx: For use in explosive atmospheres, verify certification for hazardous locations.
Documentation & Traceability
Maintain thorough documentation throughout the logistics chain:
– Retain Certificates of Conformance (CoC), Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS), and test reports from manufacturers.
– Ensure each shipment includes lot numbers and expiration dates (if applicable) for traceability.
– Keep records of compliance certifications (UL, CE, RoHS, etc.) accessible for audit purposes.
– For aerospace, rail, or military applications, adhere to additional traceability standards such as AS9100, IRIS, or MIL-STD.
Shelf Life & Expiry Management
Cold shrink materials may degrade over time, affecting performance:
– Follow manufacturer-recommended shelf life (typically 2–5 years when stored properly).
– Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to prevent use of expired products.
– Inspect tubing before use for signs of cracking, tackiness, or loss of elasticity—discard if compromised.
– Clearly label packages with manufacturing and expiration dates.
Installation & End-User Compliance
Ensure end-users apply cold shrink tubing according to manufacturer instructions:
– Verify compatibility with cable diameter, voltage class, and environmental conditions.
– Train personnel on proper installation techniques to avoid air entrapment or misalignment.
– Document installations where required (e.g., in regulated industries) for quality assurance and audits.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
Address end-of-life and sustainability aspects:
– Cold shrink tubing is typically not recyclable due to composite materials; dispose of in accordance with local waste regulations.
– Encourage responsible sourcing by selecting suppliers with environmental management systems (e.g., ISO 14001).
– Minimize packaging waste through optimized logistics and reusable shipping containers where possible.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for cold shrink tubing ensures product reliability, safety, and regulatory adherence. From correct storage and transport to full documentation and standards compliance, every step in the supply chain plays a role in maintaining performance integrity. Always consult manufacturer specifications and applicable regulations based on regional and application-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cold Shrink Tubing:
Sourcing cold shrink tubing requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and technical compatibility. After evaluating suppliers, materials, performance specifications, and certifications, it is evident that selecting the right cold shrink solution is critical for ensuring long-term insulation, environmental protection, and electrical safety in cable termination and splicing applications.
Key considerations such as material composition (e.g., silicone rubber or EPDM), shrink ratio, temperature and weather resistance, and compliance with international standards (e.g., UL, CSA, IEC) must guide the sourcing decision. Partnering with reputable manufacturers or suppliers who offer consistent product quality, technical support, and timely delivery helps mitigate project risks and downtime.
Furthermore, total cost of ownership—not just unit price—should be evaluated, taking into account ease of installation, durability, and lifecycle performance. In conclusion, successful sourcing of cold shrink tubing involves a comprehensive assessment of technical requirements and supply chain reliability, ultimately supporting safer, more efficient, and sustainable electrical installations.