The global cold casting market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for lightweight, cost-effective manufacturing solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the metal casting market—which includes cold casting technologies—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.2% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that advancements in resin-based casting materials and rising adoption of rapid prototyping are accelerating market expansion, with the global casting market valued at USD 147.8 billion in 2022 and expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.1% through 2030. As manufacturers seek sustainable and energy-efficient alternatives to traditional high-temperature casting, cold casting has emerged as a preferred method due to its lower energy consumption, reduced emissions, and design flexibility. This shift has fostered a competitive landscape of innovators leading the charge in material science and precision manufacturing—here are the top 8 cold casting manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 8 Cold Casting Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Uni Abex Alloy Products Limited
Domain Est. 2001
Website: uniabex.com
Key Highlights: Uni Abex Alloy Products Limited is a pioneer and leading manufacturer & exporter of Centrifugal and Static Castings in Heat, Corrosion and Wear Resistant ……
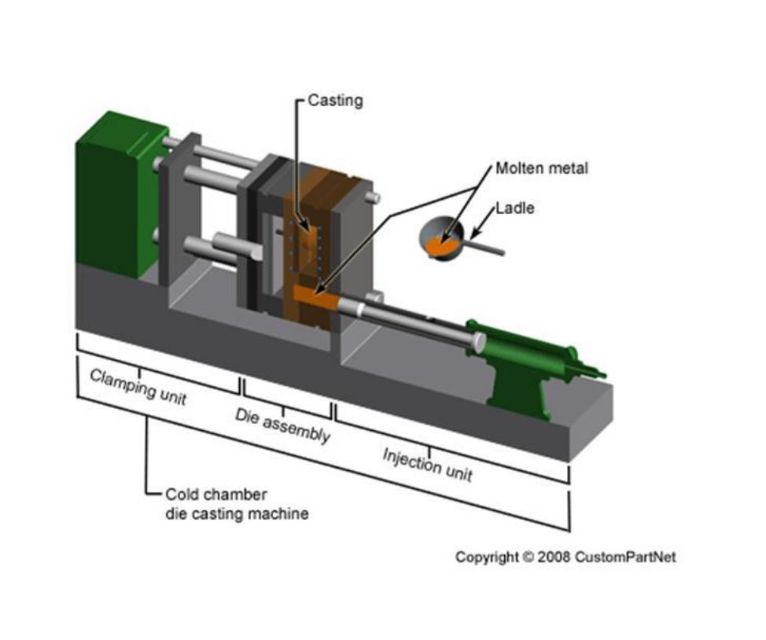
#2 Cold Chamber Die Casting Services
Domain Est. 1995
Website: dynacast.com
Key Highlights: Our cold chamber die casting process is ideal for aluminum and magnesium parts requiring high strength and superior finish….
#3 Mineral casting
Domain Est. 1996
Website: schneeberger.com
Key Highlights: Mineral casting by SCHNEEBERGER provides durable and precise components. All steps in the manufacturing process are subject to strict quality criteria….
#4 Cold Chamber Die Casting
Domain Est. 1996
Website: phbcorp.com
Key Highlights: Cold chamber die casting is a process that is ideal for metals with higher melting points and corrosive properties, such as aluminum, brass, and copper alloys….
#5 Huntsman Corporation Enriching Lives Through Innovation …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: huntsman.com
Key Highlights: We have an extensive portfolio of hot and cold cast elastomers, hot casting machines and TPU elastomers and develop solutions to meet specific needs. View ……
#6 Advanced Cold
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ha-international.com
Key Highlights: HAI offers a comprehensive portfolio of cold box technologies suited to fulfill the most demanding requirements in the industry….
#7 investment casting, die casting, hot forging, cold forging, stainless …
Domain Est. 2006
Website: forcebeyond.com
Key Highlights: ForceBeyond offers superior quality die castings, investment castings, super duplex stainless steel castings, hot forgings, cold forgings, ……
#8 Cold Casting Metal Powder
Domain Est. 2017
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cold Casting
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cold Casting
The cold casting market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in materials science, increasing demand for sustainable manufacturing, and the growing adoption of alternative metal finishing techniques across various industries. Cold casting—also known as cold metal casting or faux metal casting—utilizes metal powders (such as bronze, aluminum, copper, or iron) suspended in resin binders to create metal-like objects at ambient temperatures, offering a cost-effective and energy-efficient alternative to traditional foundry casting.
-
Rising Demand in Art, Decor, and Architectural Applications
By 2026, the art and architectural sectors are expected to remain primary drivers of cold casting adoption. Artists, sculptors, and interior designers increasingly favor cold casting for its versatility, fine detail reproduction, and lower production costs compared to hot metal casting. The ability to replicate intricate designs with a genuine metallic finish makes cold casting ideal for decorative fixtures, signage, furniture accents, and heritage restoration projects. -
Expansion in Industrial Prototyping and Small-Scale Manufacturing
Cold casting is gaining traction in rapid prototyping and small-batch manufacturing, particularly in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. As companies seek lightweight, durable, and aesthetically pleasing components without the high energy costs of traditional metallurgy, cold-cast parts offer a compelling solution. By 2026, advancements in hybrid resins and nano-reinforced metal powders are expected to enhance mechanical properties, broadening applications in functional prototypes and end-use parts. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Production
Environmental concerns are shaping manufacturing preferences, and cold casting aligns well with green manufacturing initiatives. The process consumes less energy than traditional smelting and casting, produces fewer emissions, and often incorporates recycled metal powders. Regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals will likely accelerate adoption in eco-conscious markets, particularly in Europe and North America. -
Technological Innovations in Materials and Processes
Ongoing R&D is expected to improve the density, strength, and surface finish of cold-cast products. By 2026, next-generation formulations combining high-loading metal powders with advanced epoxy or UV-curable resins will enable parts with near-solid metal characteristics. Additionally, integration with 3D printing—such as binder jetting or resin-based additive manufacturing—will expand design freedom and enable complex geometries previously unattainable with conventional casting. -
Growth in Emerging Markets
Developing regions in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are projected to witness increased investment in cold casting technologies due to rising urbanization, infrastructure development, and local manufacturing capabilities. Countries like India, Vietnam, and Mexico are becoming hubs for decorative metalwork and industrial tooling, where cold casting provides an accessible entry point for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). -
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The cold casting market is expected to see greater consolidation, with material suppliers, equipment manufacturers, and service providers forming strategic partnerships. Companies offering turnkey cold casting solutions—including resins, metal powders, molds, and finishing systems—will gain competitive advantage. Digital platforms for design sharing and decentralized production may further democratize access to cold casting technologies.
Conclusion
By 2026, the cold casting market will be characterized by innovation, diversification, and sustainability. As industries seek efficient, scalable, and environmentally responsible alternatives to traditional metalworking, cold casting is positioned to capture growing market share across artistic, industrial, and architectural domains. Continued material development and integration with digital fabrication will solidify its role as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Cold Casting (Quality, IP)
Sourcing cold casting components—where metal powders are mixed with resins and molded without high-temperature melting—can offer cost and design advantages, but it also introduces specific risks related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls is critical for successful procurement.
Quality Inconsistencies and Material Deficiencies
One of the most frequent challenges in cold casting is inconsistent quality across batches. Since cold cast parts rely on the proper ratio of metal powder to resin and precise curing processes, even minor deviations in supplier manufacturing can lead to weak structural integrity, poor surface finish, or inaccurate dimensions. Suppliers may use lower-grade metal powders or suboptimal resins to cut costs, resulting in parts that lack the desired metallic appearance or mechanical strength. Additionally, improper curing or mixing can introduce air bubbles, shrinkage, or delamination, compromising product reliability.
Lack of Standardized Testing and Certification
Many cold casting suppliers, especially smaller or overseas vendors, may not adhere to recognized quality standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM) or provide comprehensive material test reports. Without standardized testing for hardness, density, or wear resistance, buyers have little objective data to assess suitability for intended applications. This absence of certification increases the risk of field failures, especially in functional or load-bearing components.
Inadequate Process Control and Traceability
Cold casting requires tight process control during mixing, mold filling, degassing, and curing. Unreliable suppliers may lack the equipment or protocols to maintain consistency, leading to variable outcomes. Moreover, poor traceability—such as undocumented batches or unmarked raw materials—makes it difficult to investigate defects or initiate recalls, posing risks for compliance and customer satisfaction.
Intellectual Property Exposure
When sourcing cold cast parts, especially custom designs, there is significant risk of IP theft. Sharing detailed CAD files, molds, or material specifications with suppliers—particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement—can lead to unauthorized replication or resale of your designs. Some suppliers may reverse-engineer prototypes or produce knock-offs for competing clients without legal repercussions.
Insufficient Legal Protections and Agreements
Many sourcing arrangements fail to include robust IP clauses in contracts. Without clearly defined ownership rights, non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), and restrictions on mold usage, companies leave themselves vulnerable. Suppliers may claim partial ownership of tooling or use proprietary designs for other customers, undermining competitive advantage.
Dependency on Proprietary Material Formulations
Some cold casting suppliers use proprietary resin-metal blends that are not fully disclosed. While this may offer performance benefits, it creates dependency and limits the ability to switch suppliers or verify material compliance. If the formulation changes without notice, it can affect part quality and long-term supply chain stability.
Poor Communication and Technical Misalignment
Misunderstandings about technical requirements—such as surface finish, tolerance levels, or environmental resistance—can result in non-conforming parts. Suppliers may interpret specifications differently or lack the technical expertise to advise on design for manufacturability (DFM), leading to costly revisions or rejected shipments.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, require material certifications, enforce strong IP protections, and maintain clear technical documentation. Pilot runs, third-party inspections, and ongoing quality audits are essential to ensure both product integrity and IP security when sourcing cold casting components.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cold Casting
Cold casting is a manufacturing process that combines metal powders (such as bronze, aluminum, or iron) with a binding resin (typically epoxy or polyester) to create a final product that resembles solid metal. While it avoids high temperatures associated with traditional foundry methods, proper logistics and compliance procedures are essential to ensure safety, quality, and regulatory adherence. This guide outlines critical aspects for handling, storing, transporting, and complying with regulations related to cold casting operations.
Material Handling & Storage
Cold casting involves handling fine metal powders and reactive resins, which present unique hazards. Proper procedures must be followed:
- Metal Powders: Store metal powders in sealed, non-reactive containers away from moisture, heat, and ignition sources. Many metal powders (e.g., aluminum, magnesium) are flammable and may pose explosion risks in dust form. Use grounded containers and tools to prevent static discharge.
- Resin Systems: Store resins and hardeners in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and incompatible materials. Follow manufacturer-recommended shelf life and temperature ranges. Clearly label all containers.
- Segregation: Keep flammable powders and reactive chemicals separated from oxidizers and acids. Use designated storage cabinets with spill containment trays.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Worker safety is paramount during cold casting operations. Required PPE includes:
- Respiratory Protection: Use NIOSH-approved respirators with P100 filters when handling dry metal powders or during mixing to prevent inhalation of fine particulates.
- Gloves: Wear chemically resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile or neoprene) when handling resins and hardeners to prevent skin contact and dermatitis.
- Eye Protection: Use safety goggles or face shields to protect against splashes during resin mixing and pouring.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves, aprons, and closed-toe shoes to minimize exposure to chemicals and dust.
Ventilation & Workspace Safety
Cold casting should be conducted in a controlled environment to reduce exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and airborne particulates:
- Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV): Use fume hoods or downdraft tables when mixing resins or handling powders to capture VOCs and dust at the source.
- General Ventilation: Ensure adequate room ventilation with fresh air exchange to maintain safe air quality.
- Dust Control: Use HEPA-filtered vacuum systems (never dry sweep) to clean up metal dust. Regularly inspect and maintain ventilation systems.
Waste Management & Disposal
Waste materials from cold casting, such as contaminated rags, leftover mix, and used molds, must be handled according to environmental regulations:
- Hazardous Waste Classification: Determine whether waste (e.g., uncured resin, solvent-cleaned materials) is hazardous under RCRA (Resource Conservation and Recovery Act) or local regulations.
- Labeling & Storage: Store waste in clearly labeled, compatible, and leak-proof containers in a designated hazardous waste area.
- Disposal: Use licensed hazardous waste disposal contractors. Never pour resins, solvents, or metal powders down drains or into regular trash.
Transportation & Shipping
When shipping cold casting materials or finished products, comply with DOT (Department of Transportation) and IATA regulations as applicable:
- Resins and Hardeners: Classified as flammable or corrosive liquids depending on formulation. Package in UN-certified containers with proper hazard labels (e.g., Class 3 Flammable Liquid).
- Metal Powders: Finely divided metals may be classified as flammable solids (UN 1309 or similar). Prevent dust generation and static during transit.
- Finished Products: Non-hazardous once fully cured, but documentation should confirm completion of curing process to avoid classification issues.
Regulatory Compliance
Cold casting operations must comply with various federal, state, and local regulations:
- OSHA Standards: Adhere to Hazard Communication (HazCom) Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200), requiring Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and employee training for all chemicals used.
- EPA Regulations: Comply with air emission standards for VOCs and proper hazardous waste disposal under RCRA.
- NFPA Guidelines: Follow NFPA 484 (Standard for Combustible Metals) for handling and storage of metal powders.
- REACH & RoHS (for Export): If exporting to the EU, ensure materials comply with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives.
Emergency Preparedness
Have response plans in place for potential incidents:
- Spill Kits: Maintain chemical-specific spill kits (absorbents, neutralizers, PPE) near work areas.
- Fire Response: Use Class D extinguishers for metal fires; standard ABC extinguishers may not be effective. Keep sand or dry powder extinguishers accessible.
- First Aid: Provide eyewash stations and emergency showers within 10 seconds’ travel from work areas. Train personnel in first aid procedures for chemical exposure.
Recordkeeping & Training
Maintain documentation to demonstrate compliance and ensure operational safety:
- SDS Management: Keep up-to-date Safety Data Sheets for all chemicals, readily accessible to employees.
- Training Records: Document employee training on chemical handling, PPE use, emergency procedures, and regulatory compliance.
- Inspection Logs: Regularly inspect storage areas, ventilation systems, and safety equipment; log results and corrective actions.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance guide, cold casting operations can maintain a safe working environment, minimize environmental impact, and remain in compliance with applicable regulations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cold Casting:
In conclusion, sourcing cold casting as a manufacturing or artistic production method offers a compelling combination of cost-efficiency, design flexibility, and material versatility. Unlike traditional hot casting techniques, cold casting eliminates the need for high temperatures and complex foundry setups, making it accessible for smaller operations, prototyping, and custom fabrication. By utilizing resins combined with metallic powders such as bronze, copper, or aluminum, cold casting effectively replicates the aesthetic and weight of solid metal at a fraction of the cost and energy expenditure.
Moreover, the process allows for intricate detailing and rapid production, making it ideal for art sculptures, architectural elements, jewelry, and industrial prototypes. When sourcing materials and partners for cold casting, it is essential to prioritize the quality of resins and metal powders, as well as collaborate with reliable suppliers and skilled artisans to ensure consistent and durable results.
Overall, cold casting stands out as a sustainable and innovative alternative in metal replication, bridging the gap between traditional craftsmanship and modern manufacturing demands. With careful sourcing and process control, it presents a valuable solution for businesses and artists seeking efficiency, realism, and scalability.