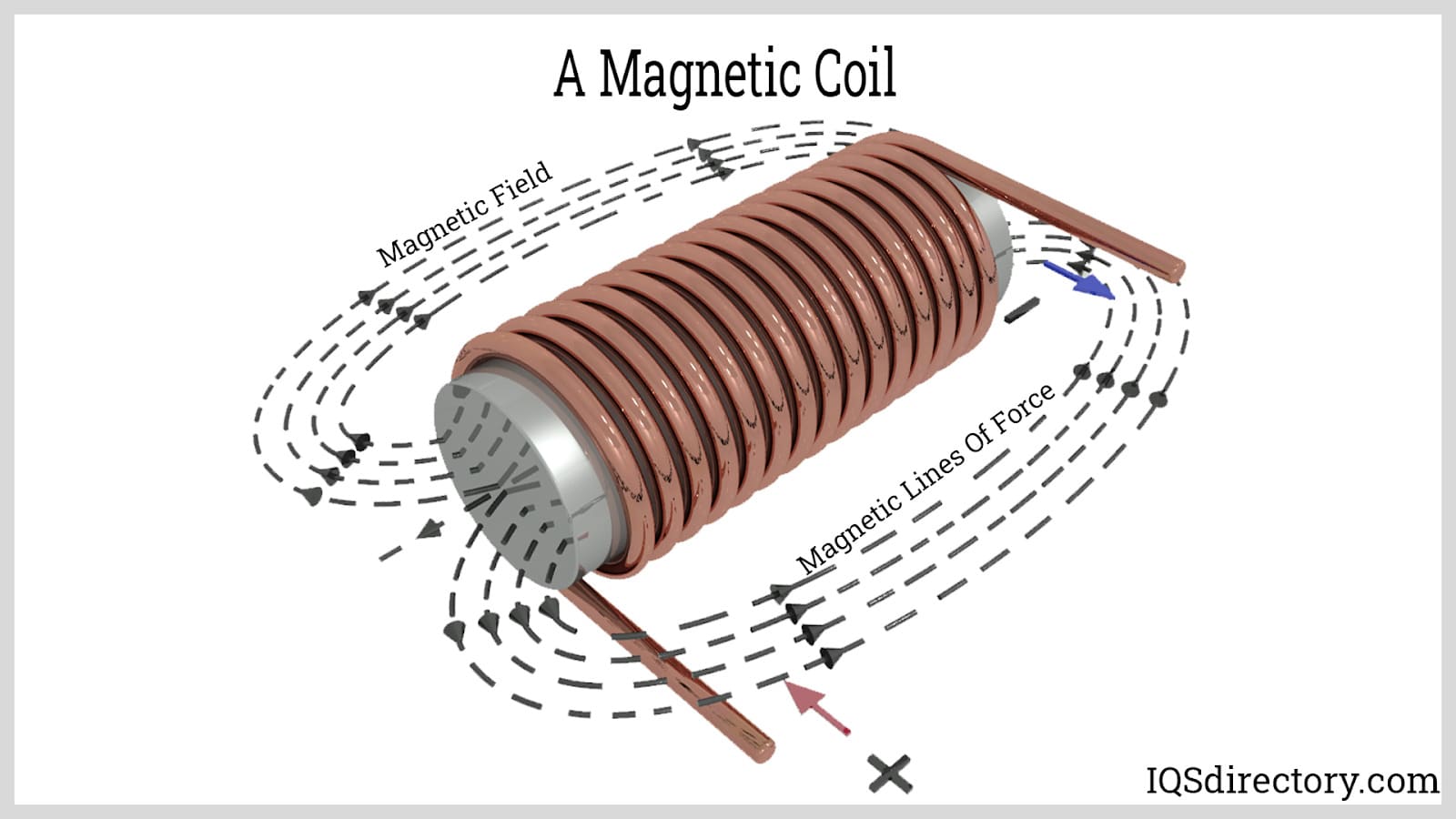
The global market for electromagnetic components, including coils and magnets, has experienced significant growth driven by rising demand across industries such as automotive, renewable energy, consumer electronics, and industrial automation. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global magnet market was valued at USD 30.42 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.5% through 2028, fueled by increasing adoption of electric vehicles and wind power generation. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global electric motor market—which relies heavily on precision coils and high-performance magnets—will expand at a CAGR of 6.9% from 2023 to 2030, underpinned by energy efficiency regulations and automation trends. As technological advancements continue to drive innovation in power systems and motion control, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in producing high-quality coils and magnetic components. These companies stand at the forefront of scaling production, advancing materials science, and meeting the evolving demands of next-generation applications. Below are the top 10 coil and magnet manufacturers shaping the future of this dynamic market.
Top 10 Coil And Magnet Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Arnold Magnetic Technologies
Domain Est. 2001
Website: arnoldmagnetics.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading magnet manufacturer of high-quality permanent magnets, magnetic assemblies, precision thin metals, flexible composites, and electromagnets….
#2 Magnetic Coil Mfg. Co.
Domain Est. 2005 | Founded: 1945
Website: magcoil.com
Key Highlights: Magnetic Coil Manufacturing Company, Inc. was founded in 1945 and is a producer of high quality transformer and coil products. Magnetic Coil will be ……
#3 Coilcraft: Magnetic Components Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1995
Website: coilcraft.com
Key Highlights: Coilcraft is a global magnetic components manufacturer specializing in inductors and transformers – proudly serving a number of industries….
#4 Custom Electromagnets & Coils
Domain Est. 2000
Website: stangenes.com
Key Highlights: Stangenes Industries simulates, designs, manufactures, and tests a variety of AC, DC, and pulsed electromagnets. These range from high-precision DC focusing ……
#5 Electromagnetic Coil Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: badgermagnetics.com
Key Highlights: Badger Magnetics is an industry leading electromagnetic coil manufacturer of high quality, custom designed and wound electromagnetic products….
#6 Magnetic Coil Suppliers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: electriccoils.net
Key Highlights: We manufacture coils for a variety of industries; winding wire gauges from 4-58 AWG. We are ISO 9001-2015 certified, ITAR registered and DFARS Compliant….
#7 Manufacturer of magnetic coils
Domain Est. 2013
Website: magnecoil.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in custom manufacture of coils for electromagnets. Our services span the entire process, from drawing to final production….
#8 Electromagnets and Coils
Domain Est. 1995
Website: gmw.com
Key Highlights: GMW designs and manufactures a wide array of copper electromagnets with fields over 5T. We offer both DC and AC electromagnets….
#9 Gowanda Electronics
Domain Est. 1995
Website: gowanda.com
Key Highlights: Gowanda Electronics: Precision-engineered electronic components & inductors for demanding applications. Quality solutions for critical designs….
#10 Prem Magnetics
Domain Est. 2000
Website: premmagnetics.com
Key Highlights: Prem Magnetics designs and manufactures power transformers, inductors, and coils. Our products are 100% tested. Shop now or request a custom solution….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Coil And Magnet
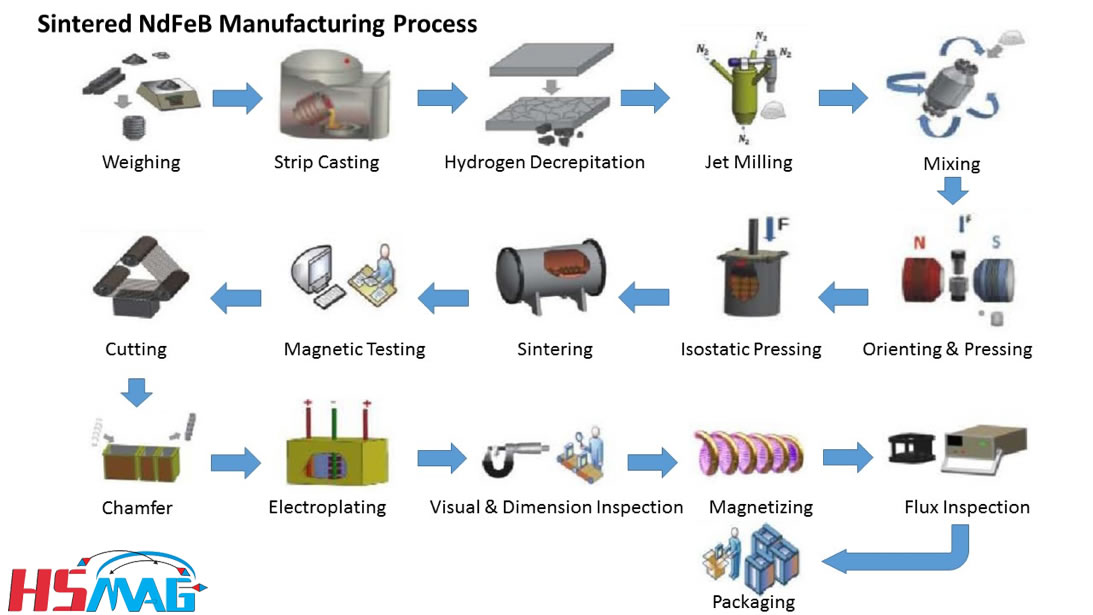
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Coil and Magnet Technologies
The coil and magnet market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by escalating demand in electrification, renewable energy, and advanced electronics. Key trends shaping the industry include:
1. Accelerated Demand from Electric Vehicles (EVs) and E-Mobility
The global push toward carbon neutrality continues to fuel exponential growth in EV production. By 2026, every major automaker is expected to expand its EV lineup, directly increasing demand for high-performance magnets (especially neodymium-iron-boron, or NdFeB) and precision wire coils used in electric motors, sensors, and charging systems. Innovations in axial flux motors and wireless charging will further amplify coil and magnet requirements.
2. Expansion in Renewable Energy Infrastructure
Wind turbines—particularly offshore installations—rely heavily on permanent magnet generators. As global wind energy capacity grows to meet climate targets, demand for high-efficiency rare-earth magnets will rise steadily. Additionally, solar inverters and energy storage systems increasingly use advanced coils for power conversion, supporting market expansion.
3. Supply Chain Diversification and Critical Minerals Strategy
Geopolitical tensions and supply concentration (especially in rare earth elements from China) are compelling manufacturers to diversify sourcing. By 2026, expect increased investment in recycling technologies, alternative magnet chemistries (e.g., ferrite hybrids, Mn-Al-C), and regional production hubs in North America and Europe to mitigate supply risks.
4. Advancements in Miniaturization and High-Frequency Applications
Consumer electronics, 5G infrastructure, and IoT devices demand smaller, more efficient coils and magnets. Innovations in thin-film magnets, micro-coils, and high-frequency ferrite materials will gain traction, enabling compact designs for wearables, smartphones, and medical devices.
5. Growth in Industrial Automation and Robotics
The rise of smart factories and collaborative robots (cobots) is increasing the need for precision actuators, servo motors, and magnetic sensors—all reliant on advanced coil and magnet systems. Energy-efficient motor designs using optimized magnetic circuits will be a key focus.
6. Sustainability and Regulatory Pressure
Environmental regulations, including EU’s EcoDesign Directive and U.S. efficiency standards, are pushing manufacturers toward higher-efficiency motors (IE4, IE5). This shift favors the use of premium magnets and advanced coil winding techniques to reduce energy losses. Sustainable manufacturing practices and end-of-life recyclability will become competitive differentiators.
7. Integration with AI and Predictive Maintenance
Smart coils embedded with sensors and enabled by AI analytics will allow real-time monitoring of motor health and performance. This trend, particularly in industrial and transportation sectors, will drive demand for intelligent magnetic components capable of data transmission and self-diagnostics.
In summary, the 2026 coil and magnet market will be defined by technological innovation, supply chain resilience, and alignment with global decarbonization goals. Companies investing in material science, automation, and sustainable practices are best positioned to lead this evolving landscape.
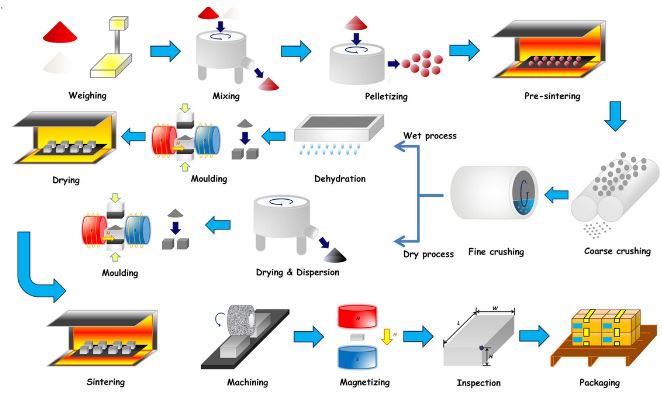
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Coils and Magnets (Quality, IP)
Sourcing high-performance coils and magnets involves significant technical and legal considerations. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to product failures, supply chain disruptions, and costly legal disputes. Below are common pitfalls to avoid.
Inadequate Quality Verification and Testing
One of the most frequent missteps is relying solely on supplier-provided specifications without independent validation. Coils and magnets are sensitive to manufacturing variances—such as winding consistency, core material purity, or magnet grade—that directly affect performance, thermal stability, and longevity. Without rigorous incoming inspection and third-party testing (e.g., for magnetic flux, resistance, inductance, or temperature derating), substandard components may enter production, causing field failures or reliability issues.
Lack of Traceability and Material Certification
High-reliability applications (e.g., medical, aerospace, automotive) demand full traceability of materials and manufacturing processes. Sourcing coils or magnets without proper documentation—such as material test reports (MTRs), RoHS/REACH compliance, or lot traceability—exposes companies to compliance risks. In magnetic materials, for instance, the source and processing of rare-earth elements (e.g., neodymium, dysprosium) significantly impact performance and regulatory standing.
Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Using coils or magnets that incorporate patented designs—such as specific winding patterns, core geometries, or magnetization techniques—without proper licensing can result in IP litigation. Some suppliers may offer “compatible” or “equivalent” components that inadvertently infringe on existing patents. Conducting IP due diligence, including freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses and supplier warranties, is essential to mitigate legal exposure.
Dependency on Proprietary or Non-Standard Components
Some suppliers offer custom coils or magnets with unique form factors or performance claims tied to proprietary technology. While attractive for differentiation, this can create long-term supply chain vulnerability. If the supplier discontinues the product or raises prices, redesigning or qualifying alternatives may be costly and time-consuming, especially if the original design lacks standardization or proper documentation.
Insufficient Attention to Environmental and Operational Durability
Coils and magnets degrade under environmental stress—moisture, temperature extremes, vibration, or corrosive atmospheres. Sourcing components without verified environmental ratings (e.g., IP67 sealing, thermal class insulation) or accelerated life testing data can lead to premature failure in end-use conditions. For example, uncoated sintered neodymium magnets may corrode rapidly in humid environments unless properly plated.
Poor Supplier Qualification and Long-Term Viability
Partnering with underqualified or financially unstable suppliers increases the risk of inconsistent quality and supply interruptions. Assessing a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949), and financial health is crucial. A low-cost magnet supplier might cut corners on sintering or coating processes, leading to inconsistent magnetic properties or mechanical brittleness.
Failure to Secure IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When commissioning custom coils or magnets, companies often assume they own the resulting design. However, without clear contractual agreements, IP rights may remain with the supplier. This can prevent in-house manufacturing, block future sourcing from alternative vendors, or lead to unexpected royalty demands. Always ensure design transfer agreements and IP assignment clauses are in place.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires a proactive sourcing strategy that balances cost, performance, compliance, and legal safety. Robust supplier audits, detailed technical specs, and strong contractual safeguards are essential for reliable and defensible component procurement.
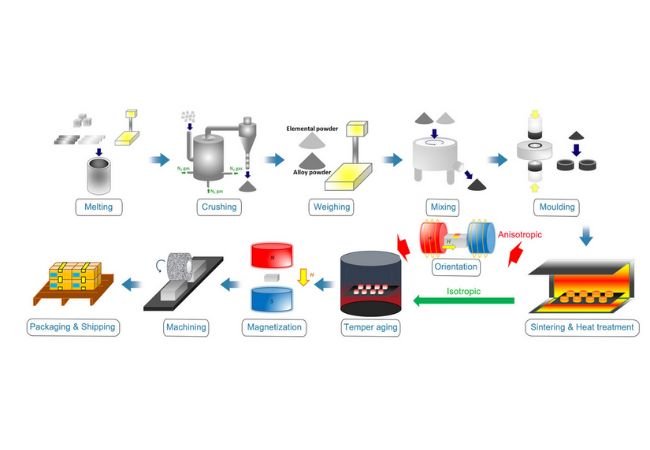
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Coil and Magnet
Overview of Coil and Magnet Shipments
Coils and magnets are essential components in various industries, including electronics, automotive, energy, and aerospace. Due to their physical properties—such as weight, size, magnetic fields, and potential for corrosion—shipping these items requires strict adherence to logistics and regulatory compliance standards to ensure safety, efficiency, and legal conformity.
Packaging Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit and to mitigate risks associated with magnetic interference.
– Use sturdy, shock-resistant containers made of wood or reinforced cardboard.
– Secure coils with bracing, blocking, and cushioning to prevent movement.
– For magnets, employ non-magnetic packaging materials to avoid unintended attraction.
– Seal packages against moisture, especially for ferrous materials prone to rust.
– Clearly label packages with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Keep Dry.”
Magnetic Field Regulations (IMO & IATA)
Strong magnets are classified as Dangerous Goods due to their potential to interfere with navigation and communication systems.
– Determine magnetic field strength using a gauss meter at a distance of 2.1 meters (7 feet) from the package.
– If the field strength exceeds 0.159 A/m (0.002 Gauss), the shipment is regulated under IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (Class 9 – Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods) and IMO IMDG Code.
– Complete a Dangerous Goods Declaration and use approved Class 9 labels when required.
– Exemptions may apply for shipped magnets with field strength below the threshold—documentation must confirm compliance.
Export Controls and Trade Compliance
Coils and magnets may be subject to export control regulations due to potential dual-use applications (civilian and military).
– Verify if the product falls under export control lists such as the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL) or EU Dual-Use Regulation.
– Obtain necessary export licenses for restricted destinations or end-uses.
– Screen customers and end-users against denied party lists (e.g., OFAC, BIS Denied Persons List).
– Maintain accurate records of export transactions for audit and compliance purposes.
Transportation Modes and Considerations
Different transport methods present unique challenges for coils and magnets:
– Air Freight: Most stringent magnetic field restrictions; requires Class 9 classification and airline approval.
– Ocean Freight: Subject to IMDG Code; requires proper container stowage and separation from sensitive equipment.
– Road & Rail: Ensure load stability; use low-bed trailers for oversized coils; secure magnets to prevent shifting.
– Use cranes or forklifts with adequate capacity during loading/unloading; follow site-specific safety protocols.
Customs Documentation and Classification
Accurate documentation ensures smooth clearance at borders.
– Assign correct HS (Harmonized System) codes—e.g., 8505.11 for permanent magnets, 8505.20 for electromagnets.
– Provide commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
– Include technical specifications (e.g., material type, dimensions, magnetic strength) to support classification.
– Declare any applicable exemptions or preferential trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, GSP).
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Handle materials in accordance with workplace safety and environmental regulations.
– Comply with OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent local safety standards for manual handling and lifting.
– Use personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling heavy or sharp-edged coils.
– Follow REACH and RoHS regulations if shipping to the EU—ensure no restricted substances are present.
– Dispose of packaging materials responsibly; recycle where possible.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Maintain product integrity throughout the supply chain.
– Implement a traceability system (e.g., barcodes or RFID) for batch tracking.
– Conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify packaging and labeling accuracy.
– Retain shipping records, test reports, and compliance certificates for a minimum of five years.
Incident Reporting and Contingency Planning
Prepare for potential logistics disruptions or compliance issues.
– Establish procedures for reporting damaged shipments or magnetic interference incidents.
– Train staff on emergency response for dangerous goods incidents.
– Maintain insurance coverage for high-value or hazardous shipments.
– Develop alternate routing plans for geopolitical or regulatory delays.
Conclusion
Shipping coils and magnets demands a comprehensive approach integrating logistics best practices with strict regulatory compliance. By adhering to packaging standards, magnetic field regulations, export controls, and documentation requirements, businesses can ensure safe, efficient, and legally compliant global distribution. Regular training and audits are recommended to maintain continuous improvement in logistics operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Coil and Magnet:
After a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers, technical specifications, cost considerations, and reliability factors, it is evident that a strategic approach to sourcing coils and magnets is essential for ensuring product performance, consistency, and cost-efficiency. Based on the analysis, sourcing from reputable suppliers with proven expertise in electromagnetic components—offering high-quality materials, stringent quality control, and scalability—is recommended.
The decision should balance performance requirements (such as magnetic strength, coil resistance, and thermal stability) with lead times, pricing, and long-term supply chain resilience. Where applicable, dual sourcing or establishing partnerships with suppliers capable of customization and technical support will mitigate risks and support future scalability.
In conclusion, prioritizing quality, reliability, and supplier collaboration in the sourcing process will directly contribute to the overall efficiency and success of the end application, whether in motors, sensors, transformers, or other electromagnetic systems.