The global coffee husk market is gaining momentum as sustainability and circular economy practices take center stage in the food and beverage industry. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global coffee by-products market—driven by increased utilization of coffee husks, silverskin, and pulp—is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2023 to 2028. With rising demand for upcycled ingredients in functional foods, natural flavorings, and eco-friendly packaging, coffee husks are emerging as a valuable co-product in coffee processing. As global coffee production exceeds 10 million metric tons annually, even a small fraction of husk yield represents a substantial resource stream. This growing economic and environmental relevance has positioned key manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, turning agricultural waste into high-value outputs. Below, we highlight the top seven coffee husk manufacturers leading this transformation—companies that are not only scaling production but also pioneering sustainable applications in food, cosmetics, and renewable materials.
Top 7 Coffee Husks Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Find Verified Coffee Husk Suppliers, Manufacturers and Wholesalers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: go4worldbusiness.com
Key Highlights: Buy premium Coffee Husk in bulk from verified wholesale suppliers and manufacturers. Best prices, bulk discounts, trusted deals at go4WorldBusiness.com….
#2 Exporter
Domain Est. 2022
Website: weandourco.com
Key Highlights: Trusted coffee husk manufacturer, supplier, and exporter offering high quality coffee husk products for various industries….
#3 Brown Coffee Husk from Salem
Domain Est. 2012
Website: venusmodifiedstarch.com
Key Highlights: Brown Coffee Husk · Packaging Size: 25 Kg · Brand: Venus Strach · Packaging Type: PP Bag · Country of Origin: Made in India · Moisture: 10-15 % · Ash: 6-7 %….
#4 Huskee
Domain Est. 2017
Website: huskee.co
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50 14-day returnsHuskeeTech. Our unique eco-composite polymer made from coffee husk that forms the basis of our HuskeeOriginal cups, saucers and lids….
#5 Coffee Husk Products
Domain Est. 2019
Website: perk.eco
Key Highlights: Our luxurious, extra-thick, high loft products are made from materials that were previously bound for land-fill. Our fabrics are rescued offcuts and roll ends….
#6 Coffee Husk Charcoal Making Machine
Domain Est. 2013
Website: bestongroup.com
Key Highlights: It transforms coffee husks into biochar/charcoal for carbon removal and sustainable fuel resource. Pyrolysis-Based Coffee Husk Charcoal Making Machine for ……
#7 Buy & Sell Coffee Husk
Domain Est. 2019
Website: buyofuel.com
Key Highlights: Connect with leading suppliers and buyers of coffee husk. Discover the best prices and high-quality biofuels on our curated platform for efficient ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Coffee Husks

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Coffee Husks – Growth, Innovation, and Sustainability Driving Value
By 2026, the market for coffee husks (the outer skin or pericarp removed from coffee beans during processing) is poised for significant transformation, shifting from a low-value byproduct to a high-potential resource across multiple industries. Driven by sustainability imperatives, circular economy models, and technological innovation, this niche market is expected to experience robust growth and diversification.
Rising Demand for Sustainable & Circular Solutions
The primary driver reshaping the coffee husk market is the global push toward sustainability. With over 15 million tons of coffee produced annually, generating millions of tons of husk waste, the environmental burden of disposal (often through burning or landfilling) is increasingly untenable. By 2026, regulatory pressures and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) commitments will compel coffee producers, processors, and retailers to adopt zero-waste strategies. Coffee husks present a prime opportunity for valorization—turning waste into value. This shift is fostering partnerships between coffee farms, agritech startups, and waste management firms to establish efficient collection and processing systems, particularly in key producing regions like Brazil, Vietnam, and Colombia.
Expansion into High-Value Applications
While traditional uses of coffee husks (e.g., compost, low-grade fuel) persist, 2026 will see accelerated innovation in high-value applications, significantly boosting market value:
-
Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals: Coffee husks are rich in dietary fiber, antioxidants (especially chlorogenic acids), and polyphenols. By 2026, expect increased commercialization of husk-derived ingredients in health bars, dietary supplements, and functional beverages. Regulatory approvals for food-grade processing will expand market access, particularly in North America and Europe.
-
Natural Ingredients in Cosmetics and Personal Care: The antioxidant and exfoliating properties of coffee husks make them attractive for skincare products. Major cosmetic brands are likely to launch husk-based scrubs, masks, and anti-aging formulations, appealing to the clean beauty and upcycled ingredients trend.
-
Biodegradable Materials and Packaging: Startups are developing coffee husk composites for bioplastics, planters, and packaging materials. As plastic bans tighten globally, husk-based alternatives offer a compostable solution, gaining traction in eco-conscious consumer markets.
-
Animal Feed and Agriculture: Processed husks serve as low-cost, fiber-rich feed supplements or soil conditioners. In developing markets, this application will grow due to cost-effectiveness and waste reduction benefits.
Technological Advancements and Supply Chain Scaling
Efficient valorization hinges on scalable processing technologies. By 2026, expect wider adoption of:
– Drying and milling innovations to preserve bioactive compounds.
– Extraction techniques (e.g., green solvents, supercritical CO₂) for isolating high-purity extracts.
– Blockchain traceability to ensure sustainable sourcing and quality control from farm to final product.
These technologies will reduce processing costs and improve product consistency, making coffee husk derivatives more competitive.
Regional Market Dynamics
- Latin America & Africa: As major coffee producers, these regions will lead in husk collection and primary processing. Local entrepreneurship and foreign investment will drive infrastructure development.
- Asia-Pacific: High innovation potential, especially in countries like India and Indonesia, with growing domestic demand for sustainable products.
- North America & Europe: Serve as key markets for premium husk-based consumer goods, supported by strong regulatory frameworks and consumer willingness to pay for sustainable options.
Challenges Ahead
Despite positive momentum, challenges remain:
– Seasonal and geographic variability in husk supply.
– Lack of standardized quality metrics for husk-derived products.
– High initial investment in processing infrastructure.
– Consumer awareness and acceptance of upcycled ingredients.
Conclusion
By 2026, the coffee husk market will emerge as a dynamic segment within the broader agricultural waste valorization industry. Valued not just for waste reduction but for its economic and environmental benefits, coffee husks will increasingly feature in sustainable supply chains. Companies that invest early in technology, partnerships, and branding around upcycled coffee husk products are likely to capture significant market share, turning a once-discarded byproduct into a cornerstone of circular innovation.
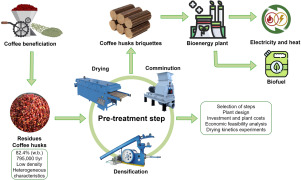
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Coffee Husks: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Inconsistent Quality and Contamination Risks
One of the most frequent challenges in sourcing coffee husks is ensuring consistent quality. Coffee husks, also known as coffee cherry skins or cascara, can vary significantly in moisture content, color, aroma, and microbial load depending on processing methods, drying conditions, and geographic origin. Poor drying or storage practices can lead to mold growth, mycotoxin contamination, or off-flavors, making the material unsuitable for food, cosmetic, or nutraceutical applications. Sourcing from unreliable suppliers without standardized quality controls increases the risk of receiving inconsistent or substandard batches.
Lack of Traceability and Supply Chain Transparency
Many suppliers, especially smallholder aggregators or intermediaries, may lack robust traceability systems. Without clear information on the coffee variety, farm origin, processing date, and handling practices, it becomes difficult to verify claims about sustainability, organic certification, or food safety. This opacity increases the risk of adulteration or mislabeling and can jeopardize compliance with regulatory standards in target markets.
Intellectual Property and Bio-Prospecting Risks
As interest in upcycled coffee byproducts grows, so do intellectual property (IP) concerns. Companies developing proprietary extraction methods, formulations, or health claims based on coffee husks may face challenges in protecting their innovations. Additionally, sourcing husks from regions with traditional knowledge about cascara use—such as in Ethiopia or Latin America—can lead to bio-prospecting disputes if benefit-sharing agreements are not in place. Failure to address IP and ethical sourcing considerations may result in legal challenges or reputational damage.
Regulatory and Certification Compliance Gaps
Coffee husks intended for human consumption or cosmetic use must meet specific regulatory standards, such as FDA, EFSA, or local food safety regulations. However, not all suppliers are aware of or compliant with these requirements. Sourcing husks without proper certifications (e.g., organic, Fair Trade, food-grade processing) can expose buyers to regulatory risks, import restrictions, or product recall liabilities.
Seasonal Availability and Supply Instability
Coffee production is inherently seasonal, leading to fluctuating availability of husks. Suppliers may lack adequate storage infrastructure to maintain quality over time, resulting in supply gaps or degraded material during off-seasons. Relying on a single source without contingency planning can disrupt production schedules and increase procurement costs.
Overlooking Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Practices
While coffee husks are a byproduct, their collection and processing can still have social and environmental impacts. Unethical labor practices, lack of fair compensation for farmers, or environmentally harmful processing methods (e.g., excessive water use or chemical treatments) may contradict a buyer’s sustainability commitments. Failing to audit suppliers on these aspects can undermine ESG goals and brand integrity.
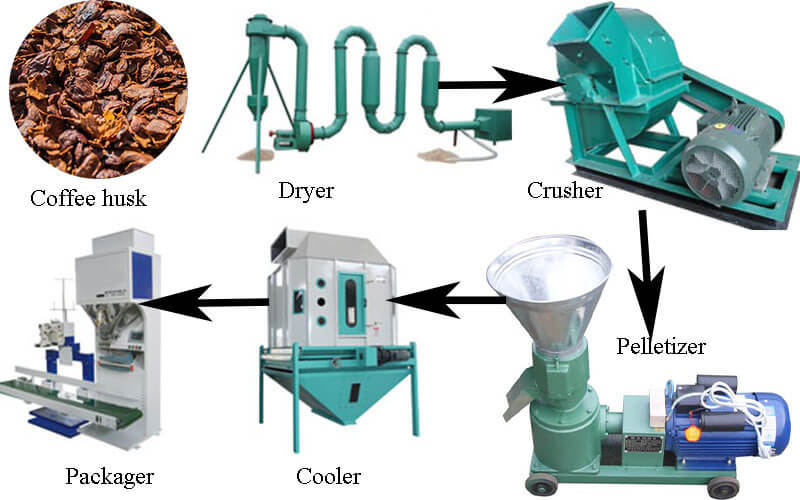
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Coffee Husks
Overview of Coffee Husks
Coffee husks, also known as coffee cherry husks or cascara, are the dried outer layers of the coffee cherry removed during the wet or dry milling process. Once considered a byproduct, they are increasingly used for tea, dietary supplements, animal feed, and bioenergy. Proper logistics and compliance are essential to ensure quality, safety, and legal adherence across international supply chains.
Classification & HS Code
Accurate classification is critical for customs clearance and tariff determination.
– Recommended HS Code: 1212.99 (Other plants and parts of plants used primarily in herbal beverages, not elsewhere specified)
– Alternative Codes:
– 2303.10 – Residues of coffee (when used for animal feed)
– 1214.90 – Other fodder plants (if classified as livestock feed)
Note: HS code may vary by country. Verify with local customs authorities.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance varies by destination country and intended use (food, feed, agricultural input, etc.).
Food-Grade Use (e.g., Cascara Tea)
- FDA (USA): Must comply with food safety regulations under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA). Registration with FDA, adherence to GMPs, and potential prior notice for imported food.
- EU Regulations:
- Classified as a Novel Food if marketed for human consumption; requires pre-market authorization (Regulation (EU) 2015/2283).
- Comply with Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 (General Food Law) and hygiene standards (EC) No 852/2004.
- Labeling: Must include allergen information, origin, preparation instructions, and nutritional facts where applicable.
Animal Feed Use
- EU: Subject to Feed Hygiene Regulation (EC) No 183/2005 and listing in the EU Register of Feed Materials.
- USA: Regulated by AAFCO and FDA Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM). Requires safety data and compliance with animal food GMPs.
Phytosanitary Requirements
- ISPM 15: If shipped in wooden packaging, must comply with ISPM 15 (heat treatment or fumigation and stamping).
- Phytosanitary Certificate: Often required for agricultural products to certify freedom from pests and diseases. Issued by the national plant protection organization (e.g., USDA APHIS, SENASAG).
Packaging & Storage
- Moisture Control: Maintain moisture below 12% to prevent mold growth. Use moisture-barrier bags (e.g., poly-lined jute or woven polypropylene).
- Storage Conditions: Store in dry, cool, ventilated areas away from direct sunlight and contaminants.
- Bulk vs. Bagged:
- Bulk: Suitable for industrial use; requires sealed containers to prevent contamination.
- Bagged: 25–60 kg bags recommended for ease of handling and international shipping.
Transportation & Logistics
- Mode of Transport:
- Sea freight: Most cost-effective for large volumes; use containerized shipping (20’ or 40’ dry containers).
- Air freight: For high-value or time-sensitive food-grade cascara.
- Fumigation: May be required for certain destinations; declare any treatments used.
- Cold Chain: Not required unless specified, but temperature-controlled shipping may be beneficial in tropical climates.
Documentation Requirements
Essential documents for international trade:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading (or Air Waybill)
– Certificate of Origin
– Phytosanitary Certificate (if required)
– Health Certificate (for food/feed use)
– Organic Certification (if applicable)
– Novel Food Authorization (for EU food use)
Sustainability & Traceability
- Certifications: Consider Fair Trade, Organic, or Rainforest Alliance to meet buyer expectations and compliance standards.
- Traceability: Maintain batch-level tracking from farm to export to ensure recall readiness and transparency.
Risk Management
- Contamination Risks: Test for mycotoxins (aflatoxins, ochratoxins), heavy metals, and pesticide residues.
- Quality Control: Conduct pre-shipment inspections and lab testing per ISO or AOAC standards.
- Insurance: Secure cargo insurance covering loss, damage, and spoilage.
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for coffee husks depend on proper classification, adherence to destination-specific regulations, careful packaging, and thorough documentation. Engage with local authorities and certified laboratories to ensure your product meets all legal and safety requirements across the supply chain.
In conclusion, sourcing coffee husks presents a sustainable and economically viable opportunity across various industries, including agriculture, renewable energy, and natural product manufacturing. As a byproduct of coffee processing, coffee husks are abundantly available in coffee-producing regions, making them a readily accessible resource. Their utilization supports circular economy principles by transforming waste into valuable products such as organic fertilizers, biofuels, and biodegradable packaging materials. However, successful sourcing requires establishing transparent supply chains, ensuring consistent quality, and supporting ethical practices that benefit local farmers and communities. With increasing global interest in sustainability and waste reduction, investing in the responsible sourcing of coffee husks not only addresses environmental challenges but also opens doors for innovation and shared economic growth.