The global carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) or cellulose gum market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, and personal care. According to Grand View Research, the global CMC market was valued at USD 780.3 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by CMC’s versatile functionality as a thickening, stabilizing, and suspending agent, alongside increasing consumer preference for clean-label and plant-based additives. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects steady expansion in the market, supported by advancements in green chemistry and the shift toward bio-based polymers in industrial applications. With Asia Pacific emerging as a key production and consumption hub, particularly in China and India, the competitive landscape is evolving as manufacturers scale innovation and sustainability efforts. In this dynamic environment, the following nine companies stand out as leading CMC cellulose gum manufacturers, combining production capacity, global reach, and technological expertise to meet growing market demands.
Top 9 Cmc Cellulose Gum Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 CMC (Carboxymethyl Cellulose) Supplier
Domain Est. 1999
Website: blendtek.com
Key Highlights: Blendtek is a high quality distributor of cellulose gum (CMC) and other Gums & Hydrocolloids for food manufacturers in North America….
#2 blanose™ cellulose gum
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ashland.com
Key Highlights: Blanose™ cellulose gum, or sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), from Ashland is widely used as a cost-effective thickener and stabilizer in food and ……
#3 Your Reliable Cellulose Gum Supplier
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ifpc.com
Key Highlights: As a trusted supplier, IFPC provides high-quality bulk cellulose gum designed for consistency, performance, and scalability in food manufacturing….
#4 Sodium CMC – Carboxymethyl Cellulose
Domain Est. 1998
Website: aepcolloids.com
Key Highlights: As a Cellulose Gum supplier, we provide Cellulose Gum (also known as sodium carboxymethyl cellulose) that’s used primarily as a stabilizer for processing of ……
#5 CMC
Domain Est. 2001
Website: colonygums.com
Key Highlights: Cellulose Gum is a powerful cost-effective cold water-soluble thickening hydrocolloid. The size of the cellulose polymers influences some of the rheological ……
#6 Jining Fortune Biotech Co.,Ltd.
Domain Est. 2013
Website: sdfrchem.com
Key Highlights: Fortune Biotech is an industry leader in the production field of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), with over 40 years’ experience….
#7 Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose(CMC) For Food Grade
Domain Est. 2016
Website: s-cmcs.com
Key Highlights: YUYU® CMC(Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose) can play many kinds of functions in food fields, with thickening, suspension, emulsification, stability, shape, film, ……
#8 Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)
Domain Est. 2017 | Founded: 1944
Website: nouryon.com
Key Highlights: We have been producing CMC/cellulose gum since 1944 under well-recognized brands to deliver tailored solutions with many benefits for a wide range of industries ……
#9 Cellulose Gum Ingredients Distributor
Domain Est. 2022
Website: tilleydistribution.com
Key Highlights: Cellulosics provide exciting results in a plethora of food applications. Source CMC, MC, and HPMC cellulose gum ingredients with Tilley Distribution today….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cmc Cellulose Gum

H2: Market Trends for CMC (Carboxymethyl Cellulose) Gum in 2026
The global CMC (Carboxymethyl Cellulose) gum market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by its widespread applications across multiple industries and ongoing innovations in sustainable and functional materials. Key trends shaping the market include expanding demand in the food and beverage sector, rising use in pharmaceutical formulations, increasing adoption in eco-friendly products, and regional growth dynamics.
-
Rising Demand in Food and Beverage Industry
CMC gum continues to serve as a vital thickening, stabilizing, and emulsifying agent in processed foods. By 2026, the growing consumer preference for convenience foods, plant-based alternatives, and extended shelf-life products is expected to boost CMC consumption. Its role in dairy alternatives (such as almond and oat milk), low-fat products, and gluten-free formulations supports its relevance in clean-label and health-conscious markets. -
Expansion in Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Applications
In the pharmaceutical sector, CMC is increasingly used as a binder, disintegrant, and viscosity enhancer in tablets, syrups, and topical formulations. The trend toward advanced drug delivery systems and oral care products—such as toothpastes and mouthwashes—will further drive demand. In personal care, CMC’s non-irritating and film-forming properties make it ideal for lotions, creams, and hair care products, especially in natural and hypoallergenic formulations. -
Shift Toward Sustainable and Biodegradable Materials
With increasing regulatory pressure and consumer demand for environmentally responsible products, CMC’s biodegradability and non-toxic profile position it as a preferred alternative to synthetic thickeners. The push for green chemistry in industrial applications—such as textiles, paper, and detergents—is accelerating adoption. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to invest in bio-based and sustainably sourced CMC production to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals. -
Technological Advancements and Customization
Innovation in derivatization techniques allows for tailored CMC grades with specific viscosity, solubility, and stability profiles. This customization supports niche applications in oil drilling fluids, ceramics, and 3D printing materials. Companies are focusing on R&D to develop high-purity, low-substitution CMC for sensitive applications in electronics and biomedical devices. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate CMC market growth by 2026, led by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and expanding food processing sectors in China, India, and Southeast Asia. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand due to stringent food safety regulations and high adoption in pharmaceuticals. Latin America and Africa present emerging opportunities, particularly in personal care and agricultural formulations. -
Supply Chain and Raw Material Challenges
The reliance on cellulose (primarily from wood pulp and cotton linters) exposes the CMC market to fluctuations in raw material prices and supply chain disruptions. By 2026, leading producers are anticipated to vertically integrate or secure long-term contracts with pulp suppliers. Additionally, interest in alternative feedstocks, such as agricultural waste, may rise to enhance sustainability and reduce costs.
In conclusion, the CMC gum market in 2026 will be characterized by robust demand across end-use industries, innovation in product functionality, and a strong emphasis on sustainability. Companies that prioritize eco-friendly production, product differentiation, and strategic regional expansion are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.
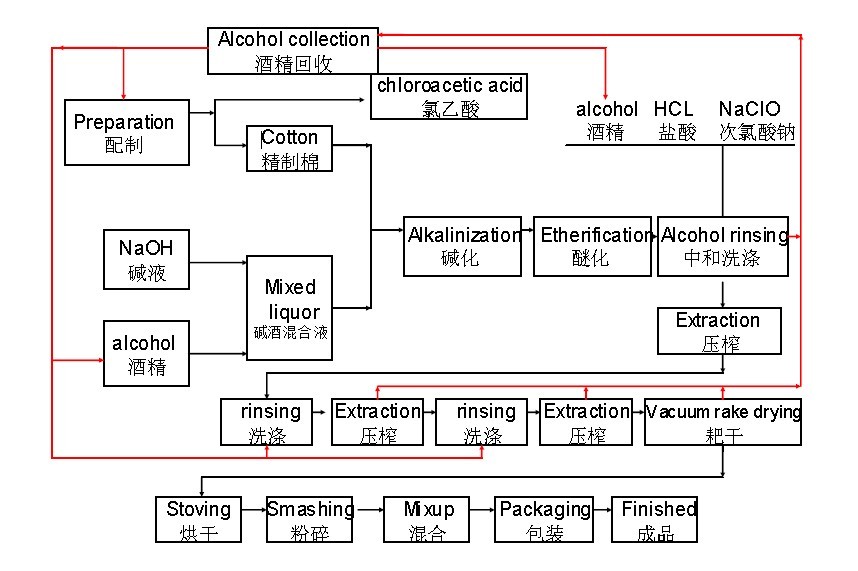
Common Pitfalls Sourcing CMC Cellulose Gum (Quality & IP)
Sourcing Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) Gum effectively requires careful attention to both technical specifications and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these areas can lead to product failures, supply chain disruptions, regulatory issues, and legal risks. Below are the most common pitfalls in both quality and IP domains.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Specification Clarity
Failing to define precise technical parameters such as degree of substitution (DS), viscosity grade, pH range, moisture content, and particle size leads to batch inconsistencies. Suppliers may deliver off-spec material that impacts performance in end applications like food, pharmaceuticals, or industrial processes.
2. Unverified Purity and Contaminants
CMC may contain impurities like heavy metals, residual solvents, or microbial contaminants. Sourcing without requiring and validating Certificates of Analysis (CoA) or third-party testing exposes users to health, safety, and compliance risks—especially in regulated industries.
3. Misalignment with Application Requirements
CMC grades vary significantly in functionality (e.g., thickening, stabilizing, film-forming). Selecting a grade unsuitable for the intended use (e.g., using a low-viscosity CMC in a high-thickening application) results in poor performance and reformulation costs.
4. Inconsistent Batch-to-Batch Quality
Some suppliers lack robust quality control systems. Without stringent process validation and supplier audits, performance variability across batches can disrupt manufacturing and compromise product consistency.
5. Poor Solubility or Dispersion Characteristics
CMC may form lumps or gels prematurely if not properly dispersed. Sourcing a grade with inappropriate particle size or substitution pattern can lead to processing issues, especially in cold water applications.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Infringement of Patented CMC Grades or Processes
Certain CMC formulations or manufacturing methods are protected by patents. Sourcing from suppliers using patented technologies without proper licensing can expose the buyer to infringement claims, even if unintentional.
2. Lack of Freedom-to-Operate (FTO) Analysis
Companies often fail to conduct FTO assessments before incorporating CMC into new products. This oversight risks costly litigation or forced product reformulations, particularly in competitive markets like pharmaceuticals or specialty foods.
3. Ambiguous or Inadequate Supplier IP Warranties
Procurement agreements that lack clear IP indemnification clauses leave buyers vulnerable. If a supplier delivers CMC that infringes third-party IP, the buyer may bear legal and financial liability without recourse.
4. Use of Proprietary Grades Without Authorization
Some suppliers offer “custom” or branded CMC grades protected by trade secrets or patents. Using such grades without permission—even if purchased legitimately—may violate usage restrictions specified in the supplier’s terms.
5. Insufficient Documentation for Regulatory Submissions
In regulated industries, traceability and IP transparency are critical. Failure to obtain complete documentation (e.g., DMFs, Letters of Access) from the CMC supplier can delay regulatory approvals or result in non-compliance.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, buyers should implement rigorous supplier qualification, define detailed technical and regulatory specifications, conduct IP due diligence, and secure appropriate contractual protections. Proactive management of both quality and IP aspects ensures reliable supply, regulatory compliance, and protection against legal exposure.
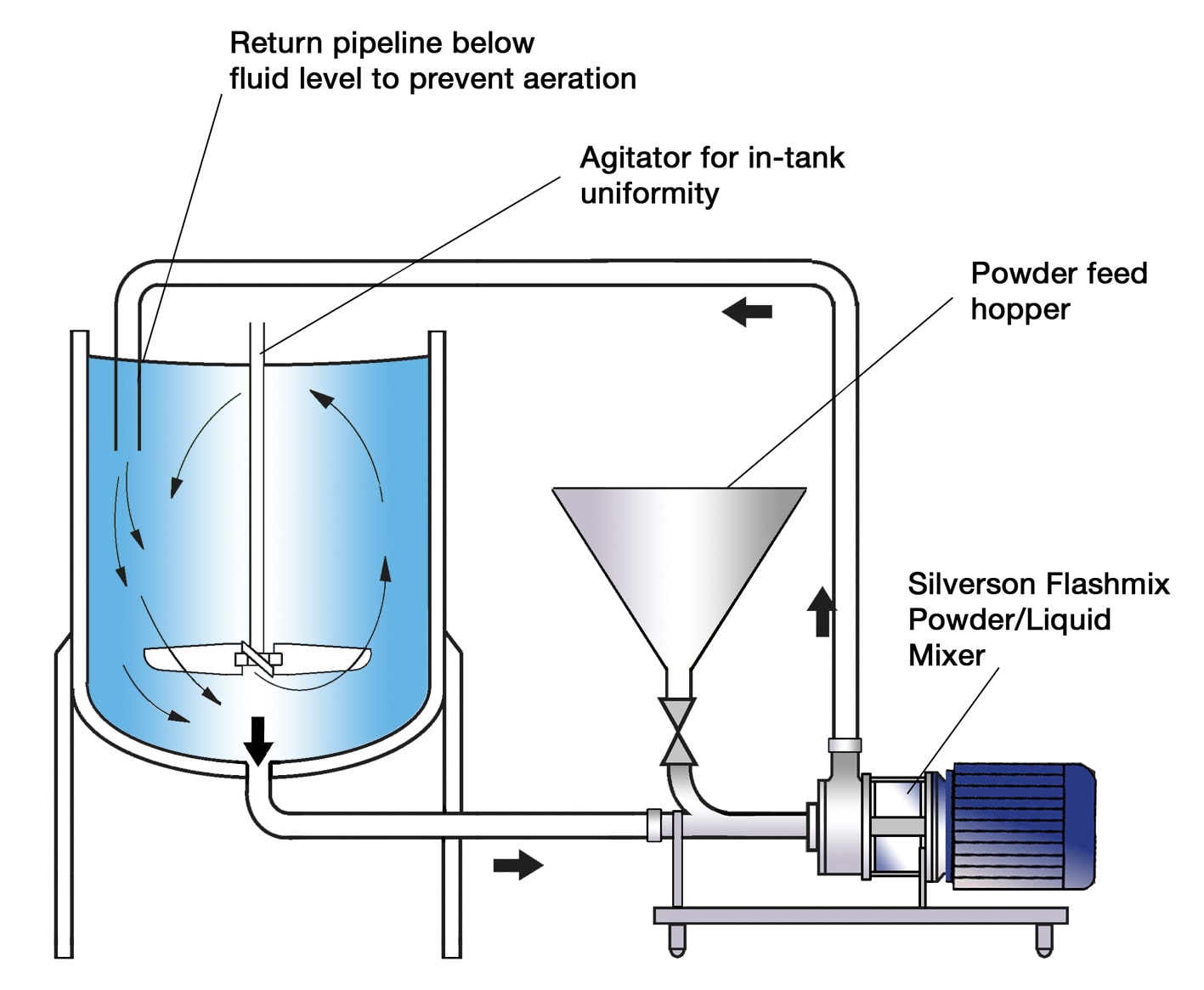
Logistics & Compliance Guide for CMC (Carboxymethyl Cellulose) Gum
Overview and Key Considerations
Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) Gum is a water-soluble cellulose derivative widely used as a thickener, stabilizer, and emulsifier in food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and industrial applications. Proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure product quality, safety, and adherence to international standards. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance requirements for the storage, transportation, and documentation of CMC Gum.
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
CMC Gum is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. FDA and approved for use in food (21 CFR 172.874) and pharmaceutical applications (USP-NF). In the EU, it is listed as E466 under Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008. Documentation must include:
– Certificate of Analysis (CoA) with specifications for viscosity, degree of substitution (DS), pH, and microbial limits
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) compliant with GHS and regional regulations (e.g., REACH in the EU, OSHA HazCom in the U.S.)
– Declaration of non-GMO status (if applicable)
– Kosher, Halal, or organic certifications where required
– Import/export documentation, including commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
CMC Gum is typically supplied in multi-wall paper bags with polyethylene liners (e.g., 25 kg bags) or in bulk containers. Packaging must:
– Be moisture-resistant to prevent clumping or degradation
– Include proper labeling per GHS and target market regulations, indicating product name, CAS number (9004-32-4), net weight, batch number, and manufacturer details
– Display handling symbols (e.g., “Keep Dry,” “Protect from Moisture”)
– Comply with food-grade packaging standards when intended for food or pharmaceutical use
Storage Conditions
To maintain product integrity, CMC Gum must be stored in a:
– Dry, cool, and well-ventilated area
– Temperature range of 15–25°C (59–77°F)
– Environment with relative humidity below 65%
– Location away from direct sunlight, heat sources, and strong oxidizing agents
Bags should be kept off the floor on pallets and rotated using the FIFO (First In, First Out) method.
Transportation Guidelines
During transit, CMC Gum must be protected from:
– Moisture (e.g., wet containers, rain exposure)
– Contamination (e.g., proximity to hazardous chemicals or strong odors)
– Physical damage (e.g., punctures, compression)
Use covered, clean, and dry transport vehicles. For international shipments, comply with IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or ADR (road) regulations when applicable. Although CMC Gum is non-hazardous under normal conditions, classification per UN transport regulations should be confirmed via SDS.
Customs and Import Compliance
Importers must verify:
– Tariff classification (e.g., HS Code 3912.31 or 3912.39 depending on form and purity)
– Import permits or notifications required by destination country
– Labeling compliance with local language and regulatory requirements
– Adherence to food additive or chemical control laws (e.g., FDA prior notice for U.S. food imports, EU REACH registration for industrial volumes)
Quality Control and Traceability
Maintain full traceability through:
– Batch-specific documentation
– Regular audits of supplier compliance
– In-process checks for moisture content and microbial contamination upon receipt
– Record retention for minimum of 3–5 years, per regulatory requirements
Environmental and Safety Handling
CMC Gum is non-toxic and biodegradable but may cause mild irritation if inhaled as dust. Handling facilities should:
– Use local exhaust ventilation in areas with high dust generation
– Provide PPE such as gloves and dust masks
– Follow SDS recommendations for spill response (e.g., vacuuming, avoiding water dispersion)
– Dispose of waste per local environmental regulations
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for CMC Gum ensures product safety, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction. Coordination between suppliers, logistics partners, and regulatory bodies is critical—especially when shipping across international borders. Always consult the latest regional regulations and update protocols accordingly.
Conclusion for Sourcing CMC (Carboxymethyl Cellulose) Cellulose Gum
In conclusion, sourcing CMC (Carboxymethyl Cellulose) cellulose gum requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, regulatory compliance, and supply chain reliability. CMC is a versatile additive widely used in food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and industrial applications due to its thickening, stabilizing, and emulsifying properties. When selecting a supplier, it is essential to evaluate factors such as product specifications (degree of substitution, viscosity, purity), certifications (e.g., food-grade, Kosher, Halal, ISO, HACCP), and adherence to international standards.
Establishing long-term relationships with reputable manufacturers—particularly those with proven track records in consistency and scalability—can enhance supply security and product performance. Additionally, considering sustainability practices and the origin of raw materials may align with corporate social responsibility goals and growing market demand for eco-friendly ingredients.
Ultimately, successful sourcing of CMC cellulose gum hinges on thorough due diligence, technical evaluation, and ongoing collaboration with suppliers to ensure that the chosen product meets both application-specific requirements and broader business objectives.