The global closed-cell polyurethane foam market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across construction, automotive, and refrigeration industries for high-performance insulation materials. According to Grand View Research, the global rigid polyurethane foam market—of which closed-cell polyurethane is a dominant segment—was valued at USD 27.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by stringent energy efficiency regulations, rising urbanization, and the superior thermal performance and durability of closed-cell formulations compared to alternative insulation materials. As manufacturers continue to innovate in response to sustainability mandates and evolving end-user requirements, a select group of industry leaders has emerged. Based on production capacity, geographic reach, technological innovation, and market presence, here are the top 9 closed-cell polyurethane manufacturers shaping the future of the industry.
Top 9 Closed Cell Polyurethane Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 General Plastics
Domain Est. 1996
Website: generalplastics.com
Key Highlights: General Plastics is certified and equipped to offer polyurethane foam solutions, providing part design support and design production from start to finish….
#2 SWD Urethane
Domain Est. 1996
Website: swdurethane.com
Key Highlights: Working our way from being contractors, to distributors, to full-scale manufacturers, we’ve honed our spray foam expertise from the inside out….
#3 Spray Foam Insulation
Domain Est. 1992
Website: dow.com
Key Highlights: A low-viscosity, functional polyether polyol for high and low-density rigid polyurethane foams. It can be used alone or with other polyols and flame retardants….
#4 BASF SPF: Spray Foam Insulation & Roofing
Domain Est. 1995
Website: spf.basf.com
Key Highlights: BASF manufactures both closed-cell and open-cell spray polyurethane foam products for residential and commercial construction….
#5 Genyk USA
Domain Est. 2012
Website: genyk.com
Key Highlights: Closed-Cell Spray Foam. Maximize your yield with our cutting-edge closed-cell spray foam. Efficient, durable, and perfect for superior thermal performance in ……
#6 Accufoam
Domain Est. 2014
Website: accufoam.com
Key Highlights: High-performance spray foam insulation made in America. Accufoam delivers industry-leading open and closed cell systems engineered for superior efficiency, ……
#7
Domain Est. 2016
Website: upcfoam.com
Key Highlights: We’re proud to be family-owned and to offer a range of high-performing, American-made polyurethane spray foam products, all manufactured in one of our ISO 9001 ……
#8 Closed Cell
Domain Est. 2018
Website: carlislesfi.com
Key Highlights: Closed Cell is a two-component, medium-density, one-to-one-by-volume spray-applied polyurethane foam. To produce Closed Cell, requires the use of an “A” ……
#9 World
Domain Est. 2020
Website: huntsmanbuildingsolutions.com
Key Highlights: Huntsman Building Solutions offers a range of high performing polyurethane spray foam products designed to suit your needs – no matter the size or scale….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Closed Cell Polyurethane
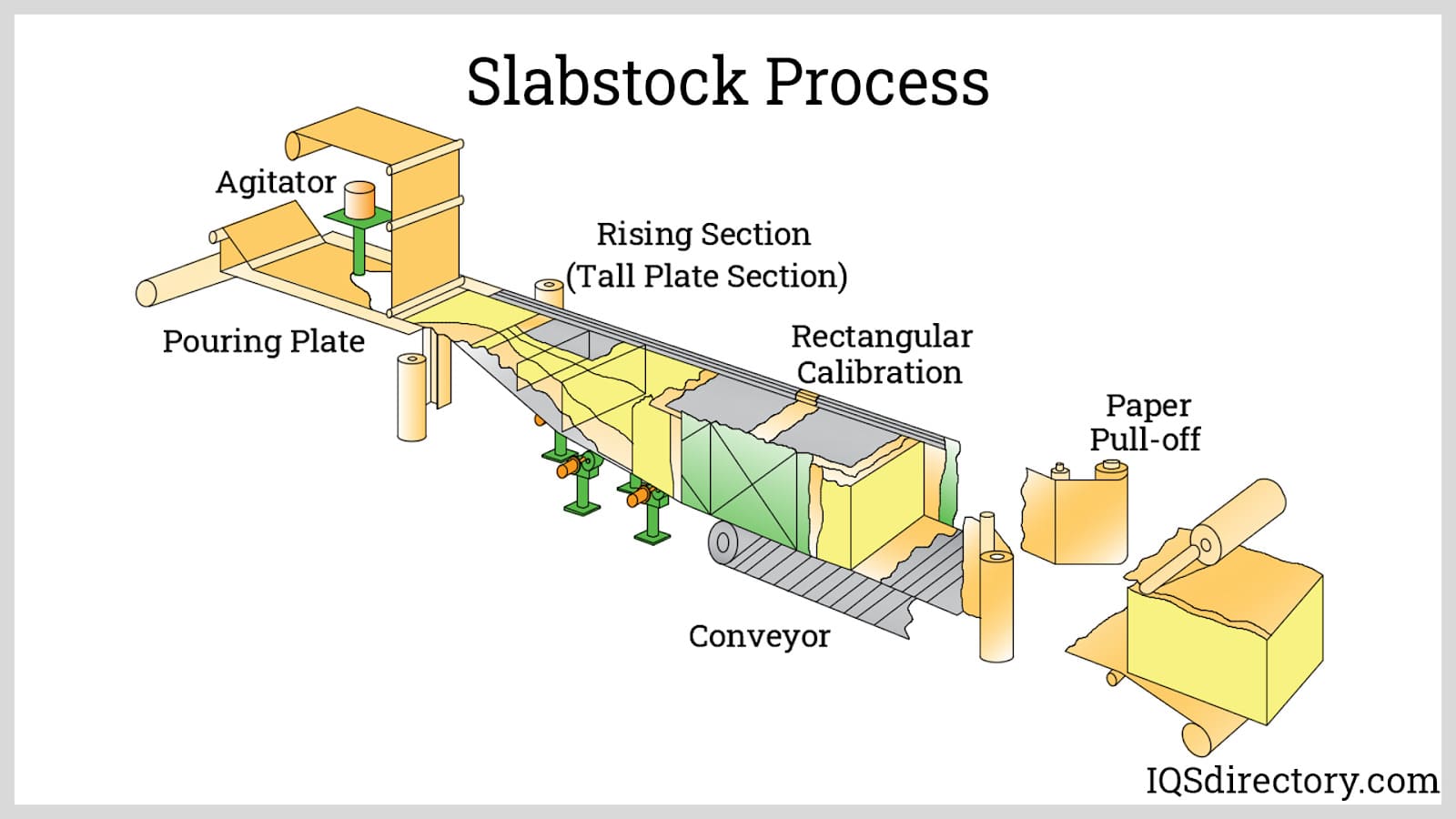
H2: Projected Market Trends for Closed-Cell Polyurethane in 2026
By 2026, the global closed-cell polyurethane (ccPU) market is expected to experience robust growth, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, refrigeration, and industrial sectors. Key trends shaping the market include increasing emphasis on energy efficiency, advancements in insulation materials, and stringent environmental regulations. Below are the major market dynamics anticipated to influence the closed-cell polyurethane landscape:
-
Growth in Construction Insulation Demand
The construction industry remains the largest consumer of closed-cell polyurethane, particularly for spray foam insulation and panel laminates. With global building codes tightening around thermal performance and carbon emissions, ccPU’s high R-value per inch and air-sealing properties make it a preferred solution. Urbanization in emerging economies and government-led green building initiatives in regions like Europe and North America are expected to sustain demand. -
Automotive Lightweighting and Thermal Management
In the automotive sector, closed-cell polyurethane is increasingly used in structural components, underbody coatings, and battery enclosures for electric vehicles (EVs). As automakers prioritize weight reduction and thermal insulation to improve fuel efficiency and battery safety, demand for ccPU foams is projected to rise. Innovations in flame-retardant and sound-dampening ccPU formulations will further support adoption. -
Shift Toward Sustainable and Low-GWP Blowing Agents
Environmental regulations—such as the EU’s F-Gas Regulation and the U.S. EPA’s AIM Act—are accelerating the transition from high-global warming potential (GWP) blowing agents like HFCs to low-GWP alternatives such as hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) and hydrocarbons. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to widely adopt next-generation blowing agents, improving the environmental profile of ccPU without compromising performance. -
Expansion of Cold Chain Infrastructure
The growing need for temperature-controlled logistics in pharmaceuticals and perishable goods is boosting demand for insulated refrigerated trucks, containers, and cold storage facilities—all of which rely heavily on ccPU. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is expected to see significant investment in cold chain infrastructure, driving regional market growth. -
Technological Innovations and Material Enhancements
Ongoing R&D is focused on improving the fire resistance, moisture resistance, and long-term thermal stability of closed-cell polyurethane. Bio-based polyols and recyclable formulations are also gaining traction, aligning with circular economy goals. By 2026, commercialization of partially bio-based ccPU products is expected to expand, appealing to sustainability-conscious industries. -
Regional Market Dynamics
North America and Europe will maintain strong market shares due to mature construction markets and regulatory support for energy-efficient materials. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region, led by industrial expansion in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Local production capacity and raw material availability will be key competitive factors.
In summary, the closed-cell polyurethane market in 2026 will be shaped by sustainability mandates, technological innovation, and increasing demand for high-performance insulation. Companies that invest in eco-friendly formulations, diversify applications, and align with regional regulatory frameworks are likely to capture significant market share.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Closed Cell Polyurethane: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing closed-cell polyurethane (CCPU) requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, supply chain disruptions, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Specification
Failing to define precise technical requirements—such as density, closed-cell content (>90%), thermal conductivity (k-value), compressive strength, moisture absorption, and fire resistance—can result in substandard materials. Suppliers may meet basic industry standards but still deliver products unsuitable for your specific application, especially in demanding environments like insulation or marine seals.
Inconsistent Batch-to-Batch Performance
CCPU properties can vary significantly between production runs due to differences in raw materials, catalysts, or processing conditions. Without a robust quality assurance program—including third-party testing and lot traceability—sourcing from inconsistent suppliers risks system failures, such as insulation breakdown or loss of structural integrity.
Unverified Supplier Credentials
Engaging suppliers without proper certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, UL, ASTM/EN compliance) increases the risk of receiving non-conforming or counterfeit products. Some suppliers may repackage lower-grade foam or use recycled content without disclosure, compromising performance and safety.
Overlooking Environmental and Aging Factors
CCPU exposed to UV radiation, extreme temperatures, or chemicals may degrade over time. Sourcing without long-term durability data (e.g., accelerated aging tests) or resistance profiles can lead to premature product failure, especially in outdoor or industrial applications.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Use of Proprietary Formulations Without Licensing
Many high-performance CCPU formulations are protected by patents or trade secrets (e.g., specific catalyst systems, blowing agents, or polymer blends). Sourcing from suppliers using such IP without proper licensing exposes your company to infringement claims, especially if the end product is sold in regulated markets like the EU or U.S.
Lack of IP Clarity in Custom Development
When co-developing a custom foam formulation, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can result in disputes. Suppliers may claim rights to innovations, restricting your freedom to manufacture or source elsewhere. Always secure written agreements specifying IP ownership, usage rights, and confidentiality.
Counterfeit or Grey Market Materials
Unauthorized replication of branded or patented foams (e.g., certain spray foam or insulation products) is common in some regions. Sourcing from unverified channels may introduce counterfeit materials that mimic appearance but fail performance and compliance standards—and may expose your business to liability for IP infringement.
Insufficient Due Diligence on Supplier IP Compliance
Some manufacturers, especially in low-cost regions, may use patented technologies without authorization. Relying on such suppliers—even unknowingly—can lead to supply chain seizures, legal action, or reputational harm. Conduct IP audits or require suppliers to certify freedom-to-operate (FTO).
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks:
– Define detailed technical and compliance specifications.
– Audit suppliers and require test reports (e.g., ASTM D2856, D1622).
– Conduct pilot trials before full-scale sourcing.
– Include IP clauses in supplier contracts.
– Perform IP landscape analysis before selecting a formulation.
– Use authorized distributors or direct partnerships with IP holders.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns, companies can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and legal protection in their CCPU supply chains.
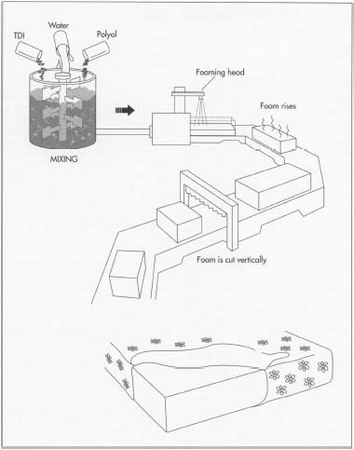
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Closed Cell Polyurethane
Overview of Closed Cell Polyurethane
Closed cell polyurethane is a rigid foam material widely used for insulation, packaging, and structural applications due to its high thermal resistance, low moisture absorption, and excellent strength-to-density ratio. It is typically manufactured using isocyanates and polyols, often with blowing agents that may have environmental and safety implications. Safe handling, transportation, and regulatory compliance are essential throughout its supply chain.
Regulatory Classification and Identification
Closed cell polyurethane in its final, cured form is generally considered stable and non-hazardous. However, uncured components (e.g., isocyanates, polyols, catalysts) are often classified as hazardous substances. Key regulatory frameworks include:
- GHS (Globally Harmonized System): Prepolymer components may carry hazard classifications such as H317 (May cause allergic skin reaction), H334 (May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled), and H411 (Toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects).
- OSHA (U.S.): Isocyanates are regulated under OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1000 as hazardous air pollutants; permissible exposure limits (PELs) apply.
- REACH (EU): Pre-manufacture notification and registration of chemical substances required; certain blowing agents (e.g., HFCs) are restricted under F-gas regulations.
- TSCA (U.S.): All chemical substances, including polyurethane components, must be reviewed and comply with EPA guidelines.
Ensure Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are available and up to date for all chemical components used in production.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Final Product (Cured Foam): Typically non-hazardous; labeled with product name, manufacturer details, batch number, and handling instructions.
- Uncured Components (Resins, Blends): Must be packaged in UN-certified containers resistant to chemical degradation. Label containers with GHS-compliant labels, including:
- Product identifier
- Signal word (e.g., “Danger”)
- Hazard statements and pictograms
- Precautionary statements
- Supplier information
- Blowing Agents: If containing regulated substances (e.g., HFCs, hydrocarbons), special pressure-resistant packaging and flammable labeling may be required.
Transportation Guidelines
- Road (ADR – Europe / DOT – U.S.):
- Cured polyurethane: Generally non-regulated as a hazardous material.
- Uncured components: May be classified as Class 3 (Flammable Liquids), Class 6.1 (Toxic), or Class 8 (Corrosive), depending on formulation.
- Transport vehicles must display appropriate placards if hazardous materials exceed threshold quantities.
- Maritime (IMDG Code):
- Ship hazardous components in accordance with packing groups and stowage provisions. Declare using correct UN numbers (e.g., UN 1866 for polymeric substances, monomers, when hazardous).
- Air (IATA):
- Strict regulations apply; many isocyanate-containing mixtures are forbidden or limited on passenger aircraft.
- Use IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) for classification, packaging, marking, and documentation.
Use only approved packaging and ensure proper segregation from incompatible materials (e.g., oxidizers, acids).
Storage Considerations
- Store raw materials (especially isocyanates) in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from heat, moisture, and direct sunlight.
- Keep containers tightly sealed to prevent moisture ingress, which can degrade reactivity and generate CO₂.
- Segregate flammable or reactive components from oxidizers and incompatible chemicals.
- Implement secondary containment for liquid storage to prevent environmental contamination.
- Follow a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to prevent aging and degradation.
Occupational Health and Safety
- Exposure Controls: Install local exhaust ventilation in processing areas. Use closed systems where possible.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Required when handling uncured components:
- Chemical-resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile, butyl rubber)
- Safety goggles or face shield
- Respiratory protection (e.g., NIOSH-approved respirator with organic vapor cartridges, especially for spray applications)
- Protective clothing to prevent skin contact
- Training: Provide worker training on chemical hazards, emergency procedures, and proper use of PPE per OSHA HAZCOM and EU CLP regulations.
Environmental Compliance
- Emissions Control: Monitor and control emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and isocyanates during production. Use abatement technologies (e.g., thermal oxidizers) if necessary.
- Blowing Agents: Transition toward low-GWP (Global Warming Potential) alternatives (e.g., HFOs, water-blown systems) to comply with Kigali Amendment and EU F-gas regulations.
- Waste Management: Dispose of uncured resin waste, contaminated materials, and empty containers as hazardous waste per local regulations (e.g., RCRA in the U.S.). Recycle cured foam scrap where possible.
- Spill Response: Maintain spill kits for chemical components. Contain spills immediately, avoid runoff, and decontaminate using approved protocols.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
- Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for all chemical inputs.
- Keep records of:
- Chemical inventories
- Employee training and exposure monitoring
- Transportation manifests (for hazardous shipments)
- Waste disposal receipts
- Regulatory permits and compliance audits
- Ensure SDS and labels are provided in the official language(s) of the destination country for international shipments.
International Trade Considerations
- Verify customs classification (HS Codes) — commonly 3901–3913 for plastics and polymer-based foams.
- Comply with import/export restrictions on precursor chemicals (e.g., isocyanates may be controlled under chemical weapons conventions in some jurisdictions).
- Monitor changes in environmental regulations (e.g., EU Green Deal, U.S. EPA SNAP program) affecting acceptable blowing agents and formulations.
Emergency Response
- In case of fire: Use dry chemical, CO₂, or water spray. Combustion may release toxic gases (e.g., HCN, NOₓ, isocyanates).
- Skin contact with uncured resin: Wash immediately with soap and water; seek medical attention for persistent irritation.
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical help if breathing difficulties occur.
- Ensure emergency numbers and spill response procedures are posted in work areas.
Conclusion
Safe and compliant logistics for closed cell polyurethane require attention to the hazardous nature of its precursors, proper classification, packaging, and transport, as well as adherence to health, safety, and environmental regulations globally. Regular training, documentation, and proactive risk management are key to ensuring operational continuity and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Closed-Cell Polyurethane
In conclusion, sourcing closed-cell polyurethane requires a strategic approach that balances performance requirements, cost-efficiency, sustainability, and supply chain reliability. This high-performance material offers exceptional thermal insulation, moisture resistance, compressive strength, and durability, making it ideal for demanding applications in construction, refrigeration, marine, and industrial sectors.
When selecting a supplier, it is essential to prioritize quality certifications, material consistency, and technical support to ensure the product meets industry standards and project-specific needs. Evaluating suppliers based on manufacturing capabilities, environmental practices, and geographic proximity can further optimize lead times and reduce logistical costs.
Additionally, ongoing market trends—such as increasing demand for low-global-warming-potential (GWP) blowing agents and recyclable formulations—highlight the importance of partnering with forward-thinking suppliers committed to sustainability and regulatory compliance.
Overall, a well-informed sourcing strategy for closed-cell polyurethane not only enhances product performance and longevity but also supports cost-effective, environmentally responsible operations across the value chain.