The global closed-cell foam blocks market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, and industrial insulation sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global foam insulation market was valued at USD 46.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030, with closed-cell foam playing a pivotal role due to its superior thermal resistance, moisture barrier properties, and structural durability. Key growth drivers include stricter energy efficiency regulations, increasing infrastructure spending, and the shift toward lightweight, high-performance materials in manufacturing. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders through innovation, scalability, and material consistency. Below are the top 10 closed-cell foam blocks manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Closed Cell Foam Blocks Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Polyethylene Foam
Domain Est. 2000
Website: foambymail.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $75 21-day returnsFoam Factory, Inc. is your source for a wide range of cost-effective closed-cell polyethylene foam products! From sheets in a variety of formul…
#2 Plastazote® Closed
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zotefoams.com
Key Highlights: Explore Plastazote® closed-cell polyethylene foams—lightweight, durable, and versatile materials ideal for medical, packaging, and industrial applications….
#3 Worldwide Foam
Domain Est. 2008
Website: worldwidefoam.com
Key Highlights: We offer one-day lead time from our seven strategic locations while providing the widest ranges of closed cell cross-linked polyethylene foam….
#4 Closed Cell Foam Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: insulfab.net
Key Highlights: Closed cell foam and sponge rubber products have been used for gasketing, cushioning, insulating, and padding applications for years….
#5 High Density, Closed
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sealedair.com
Key Highlights: Rolled or planked, polyethylene foam for packaging and specialty uses. High strength-to-weight ratio, reusable, and often recyclable….
#6 Hibco Foam Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hibco.com
Key Highlights: Closed cell foam available in 1.5, 1.8, 2.2, 4, 6, 9 lbs./cu. ft. densities … Hibco Foam Plastics is a premier supplier of quality engineered foam plastics….
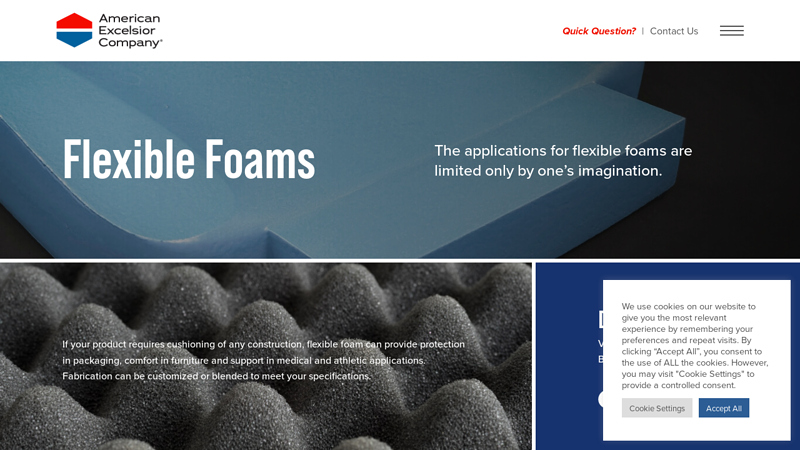
#7 Flexible Foams
Domain Est. 1999
Website: americanexcelsior.com
Key Highlights: Flexible foam can provide protection in packaging, comfort in furniture and support in medical and athletic applications….
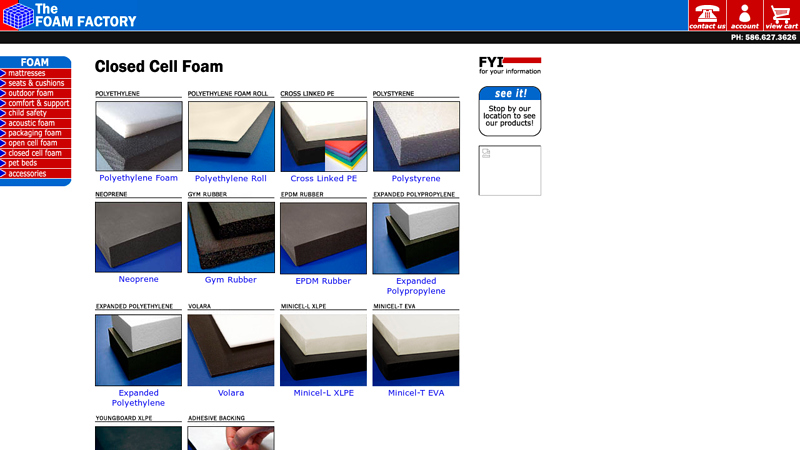
#8 closed
Domain Est. 2001
Website: thefoamfactory.com
Key Highlights: Polyethylene foam is a strong, resilient closed-cell foam. Ideally suited as the material or part of a material required in products requiring a shock ……
#9 XPE Foam
Domain Est. 2001
Website: schmitzfoam.com
Key Highlights: We offer RoFoam®, a lightweight, flexible and incredibly durable closed-cell polyethylene foam. designed for a wide range of applications….
#10 New England Foam Products
Domain Est. 2002
Website: newenglandfoam.com
Key Highlights: New England Foam supplies Open-Cell and Closed-Cell Foam including: Polyurethane, Filters, Furniture, Polyester, Polyether, Polyethylene, Crosslinked, Expanded ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Closed Cell Foam Blocks
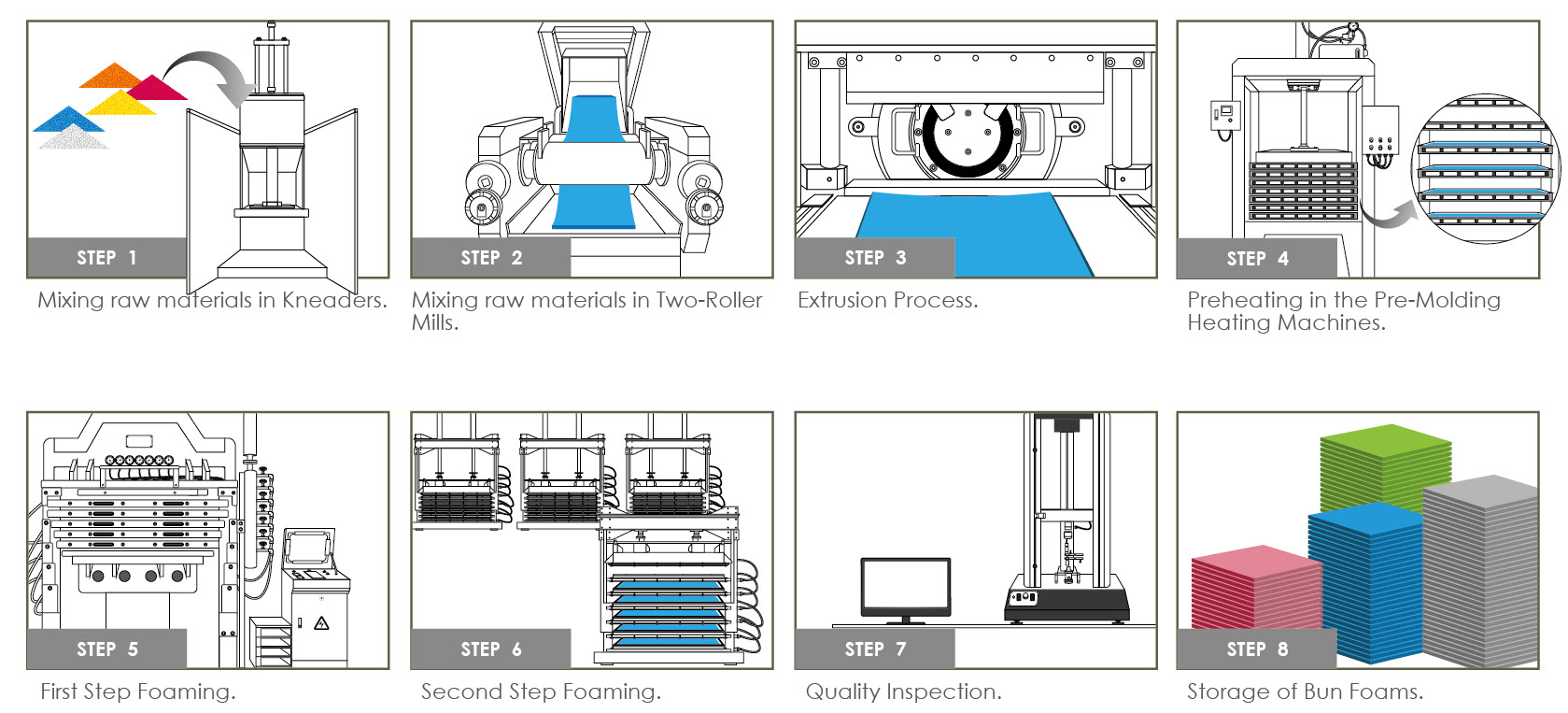
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Closed Cell Foam Blocks
The global market for closed cell foam blocks is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by a confluence of technological advancements, shifting regulatory landscapes, and evolving end-user demands. Key trends shaping this trajectory include:
1. Accelerated Growth in Construction & Insulation: The dominant driver remains the global push for energy efficiency and sustainable building practices. Stringent building codes (e.g., tightening insulation requirements in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific) are mandating higher-performance insulation. Closed cell foam blocks, renowned for their superior R-value per inch, exceptional moisture resistance, air barrier capabilities, and durability, are increasingly favored over traditional materials (like fiberglass or open-cell foam) in both new construction and retrofitting projects (especially foundations, basements, below-grade applications, and roofing). The trend towards net-zero energy buildings will further amplify demand.
2. Rising Emphasis on Sustainability & Environmental Compliance: Environmental regulations are fundamentally reshaping the industry. The phase-down of high Global Warming Potential (GWP) blowing agents (like HFCs) under initiatives such as the Kigali Amendment and EU F-Gas regulations is accelerating. By 2026, the market will see a dominant shift towards closed cell foams utilizing next-generation, ultra-low-GWP blowing agents (e.g., hydrofluoroolefins – HFOs, hydrocarbons like pentane, or CO2). Manufacturers investing in sustainable formulations and transparent Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) will gain a competitive edge. Recyclability and end-of-life management will also become more critical considerations.
3. Technological Innovation & Performance Enhancement: Competition will drive innovation focused on improving core properties:
* Higher R-Values: Development of formulations and manufacturing processes to achieve even greater thermal resistance per inch.
* Enhanced Fire Performance: Advancements in fire retardant technologies to meet increasingly stringent fire safety codes without compromising other properties.
* Improved Sustainability: Research into bio-based raw materials (e.g., polyols derived from vegetable oils) and formulations designed for easier recycling.
* Customization: Growth in demand for blocks with specific densities, compressive strengths, or surface treatments tailored to niche applications (e.g., specialized industrial insulation, cryogenics).
4. Geographic Expansion & Regional Dynamics: While North America and Europe remain mature markets with steady growth driven by regulations, significant expansion is expected in:
* Asia-Pacific: Rapid urbanization, infrastructure development (especially in China, India, and Southeast Asia), and increasing adoption of international building standards will fuel substantial demand.
* Emerging Markets: Growing awareness of energy efficiency benefits will open new opportunities in regions like Latin America and the Middle East, particularly for industrial and commercial applications.
5. Supply Chain Resilience & Raw Material Volatility: The industry will continue to navigate challenges related to the cost and availability of petrochemical-based raw materials (polyols, isocyanates) and specialized blowing agents. The geopolitical landscape and energy prices will remain key factors. By 2026, leading players will prioritize supply chain diversification, long-term contracts, and potentially increased vertical integration to mitigate risks and ensure stable production.
6. Consolidation and Competitive Intensification: The market is likely to see continued consolidation as larger players acquire specialized manufacturers to broaden product portfolios and geographic reach. Competition will intensify, not just on price, but increasingly on value propositions like technical support, sustainability credentials, product performance consistency, and integrated system solutions.
In summary, the 2026 closed cell foam block market will be characterized by robust growth in core insulation applications, a decisive shift towards environmentally sustainable production, significant technological advancements enhancing performance, and expanding opportunities in developing regions, all within a context of ongoing supply chain management challenges and competitive pressure.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Closed Cell Foam Blocks: Quality and IP Concerns
Sourcing closed cell foam blocks—used in applications ranging from insulation and buoyancy to packaging and gaskets—can present significant challenges related to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to product failures, safety risks, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key areas to watch:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Material Properties
Closed cell foam performance depends on consistent density, cell structure, compressive strength, and thermal resistance. Suppliers, especially lower-tier or offshore manufacturers, may deliver batches with variable specifications due to inconsistent production processes or substandard raw materials. This inconsistency can compromise product performance in critical applications like marine buoyancy or HVAC insulation. -
Poor Compression Set and Long-Term Durability
A common failure is sourcing foam that degrades under sustained load or environmental exposure. Low-quality foams may exhibit poor compression set resistance, leading to loss of shape and insulating capability over time. Buyers must verify long-term performance data and request accelerated aging tests. -
Inadequate Environmental Resistance
Not all closed cell foams are equally resistant to UV, moisture, chemicals, or temperature extremes. Sourcing foam without proper validation for the intended environment (e.g., outdoor use, marine applications) can result in premature degradation. Ensure material certifications (e.g., ASTM, UL) match application requirements. -
Off-Gassing and Compliance Issues
Some foams emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or fail to meet fire safety standards (e.g., flame spread, smoke density). This is especially critical in building, transportation, or medical applications. Always confirm compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., LEED, RoHS, REACH, FMVSS). -
Misrepresentation of Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate performance claims (e.g., R-value, density, lifespan) without third-party testing. Relying solely on datasheets without independent verification or samples increases the risk of receiving subpar material.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
-
Unauthorized Production of Proprietary Foam Formulations
Some suppliers may reverse-engineer or copy patented foam chemistries or manufacturing processes. Purchasing such materials—even unknowingly—can expose your company to IP infringement claims, especially if the foam is used in commercial products. -
Lack of IP Clarity in Custom Formulations
When working with suppliers to develop custom foam solutions, ownership of the resulting formulation or process may be ambiguous. Without a clear contractual agreement, the supplier might retain rights or resell the same formulation to competitors. -
Use of Counterfeit or Grey-Market Materials
Some suppliers source foam blocks from unauthorized channels, selling branded or patented foam without licensing. These “grey market” products may appear identical but lack quality controls and expose buyers to legal liability for IP violations. -
Inadequate Supplier Due Diligence
Failing to audit a supplier’s IP compliance—such as verifying licenses for patented technologies (e.g., specific blowing agents or polymer blends)—can result in downstream liability. Ensure suppliers can demonstrate legal rights to produce and sell the foam. -
Weak Contractual Protections
Purchase agreements that omit IP warranties, indemnification clauses, or confidentiality terms leave buyers vulnerable. Always include language that holds the supplier accountable for IP infringement and protects any jointly developed innovations.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Require material test reports (MTRs) and conduct independent lab testing on samples.
- Audit suppliers for quality systems (e.g., ISO 9001) and IP compliance.
- Use NDAs and IP assignment clauses in development agreements.
- Verify regulatory certifications relevant to your application.
- Work with reputable, transparent suppliers who disclose material origins and IP status.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP risks, companies can ensure reliable performance and legal safety in their closed cell foam supply chain.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Closed Cell Foam Blocks
Overview
Closed Cell Foam Blocks are lightweight, durable, and widely used in insulation, packaging, marine applications, and construction due to their moisture resistance and structural integrity. Proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure safe handling, transportation, and adherence to international and local standards.
Packaging & Handling
Closed cell foam blocks are susceptible to physical damage and environmental exposure if not properly packaged and handled.
- Protective Wrapping: Use moisture-resistant polyethylene (PE) film or shrink wrap to prevent water absorption and contamination.
- Palletization: Secure foam blocks on wooden or plastic pallets using stretch film or strapping to prevent shifting during transit.
- Stacking: Limit stack height to prevent compression damage—typically no more than 2–3 layers unless specified by the manufacturer.
- Handling Equipment: Use forklifts or pallet jacks with smooth tines; avoid sharp edges that could puncture foam.
- Storage Conditions: Store indoors in a dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight, extreme heat, or open flames.
Transportation Requirements
Transport methods must preserve material integrity and comply with carrier and regulatory standards.
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, rail, air, and sea freight. Consider volume-to-weight ratio (low density) to optimize space utilization.
- Containerization: For ocean freight, use dry van containers. Ensure blocks are tightly secured to prevent movement.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Avoid prolonged exposure to temperatures above 70°C (158°F), which may cause deformation.
- Hazard Classification: Most closed cell foams are non-hazardous (UN3082, Environmentally Hazardous Substance, if applicable). Confirm with Safety Data Sheet (SDS).
- Labeling: Mark packages with handling labels (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) and product identification.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance ensures legal import/export and safe use across jurisdictions.
- REACH (EU): Confirm that foam constituents (e.g., blowing agents like HFCs or HFOs) are registered under REACH.
- RoHS (EU): Verify absence of restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) if used in electrical/electronic applications.
- VOC Emissions (USA/CA): Comply with EPA and CARB regulations for volatile organic compound emissions, especially for indoor insulation.
- Fire Safety Standards:
- ASTM E84 / UL 723: Surface burning characteristics (flame spread and smoke development).
- FM Approval or UL 1715: For commercial insulation applications.
- Country-specific fire codes (e.g., EN 13501-1 in Europe for reaction to fire classification).
- Customs Documentation: Provide accurate HS Code (typically 3921.12 or 3921.90 for plastic sheets/plates in cellular form), commercial invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin.
- TSCA (USA): Ensure compliance with Toxic Substances Control Act, particularly for chemical components.
Environmental & Safety Considerations
Sustainability and worker safety are key in foam logistics.
- Recyclability: Confirm recyclability codes (e.g., #6 PS or #7 Other) and local recycling capabilities.
- Waste Disposal: Follow local regulations for non-hazardous industrial waste; incineration must comply with air emission standards.
- SDS Availability: Maintain updated Safety Data Sheets for transport and workplace safety (OSHA HazCom).
- PPE for Handling: Recommend gloves and safety glasses to prevent skin irritation from dust during cutting.
Import/Export Restrictions
Certain regions impose specific rules on foam materials.
- Blowing Agents: Foams using high-GWP (Global Warming Potential) blowing agents (e.g., HFC-134a) may be restricted under the Kigali Amendment or EU F-Gas Regulation.
- Biocidal Treatments: If foam includes fungicides or antimicrobials, compliance with EU BPR or US EPA regulations is required.
- Phytosanitary Rules: Wooden pallets must comply with ISPM 15 (heat treatment or fumigation certification).
Documentation Checklist
Ensure the following documents accompany shipments:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading/Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
– Test Reports (Fire, VOC, REACH/RoHS compliance)
– ISPM 15 Certificate (if using wood packaging)
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for closed cell foam blocks require attention to packaging integrity, transportation conditions, regulatory standards, and documentation. Proactive verification of chemical compliance, fire ratings, and environmental regulations ensures smooth global distribution and end-user safety. Always consult manufacturers and regulatory authorities for product-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Closed Cell Foam Blocks
After a thorough evaluation of suppliers, material specifications, cost considerations, and performance requirements, sourcing closed-cell foam blocks has proven to be a strategic decision for applications requiring thermal insulation, moisture resistance, durability, and structural integrity. The closed-cell foam’s superior properties—such as low water absorption, high compressive strength, and excellent insulating capabilities—make it well-suited for use in construction, marine, automotive, and industrial applications.
Multiple reputable suppliers offer consistent quality and customization options in terms of density, thickness, and size, enabling alignment with project-specific needs. Competitive pricing, combined with favorable lead times and reliable logistics, further supports long-term sourcing viability. Additionally, evaluating environmental impact and compliance with industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) ensures that the selected foam meets both performance and sustainability goals.
In conclusion, establishing a reliable supply chain for closed-cell foam blocks enhances product performance, reduces maintenance costs, and supports operational efficiency. Moving forward, maintaining strong supplier relationships and ongoing quality monitoring will be key to ensuring continued success in material performance and project outcomes.