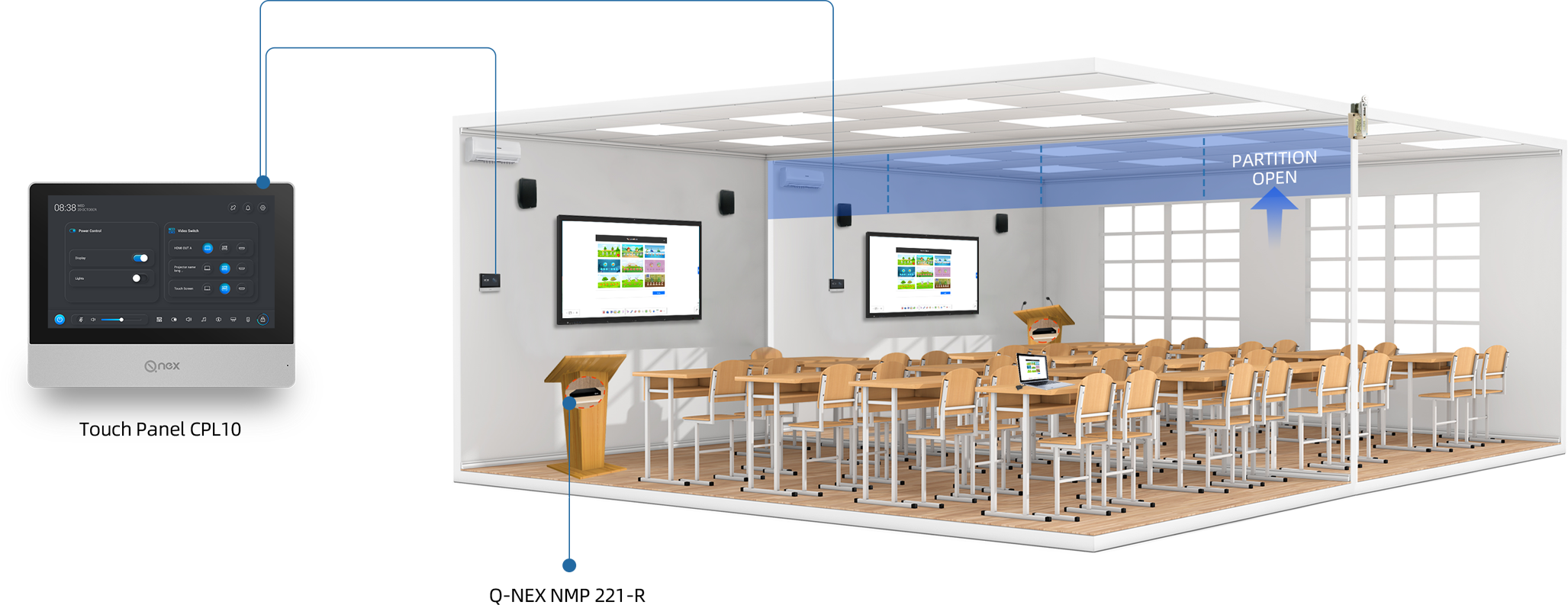
The global classroom amplification system market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing investments in educational infrastructure and the rising emphasis on inclusive learning environments. According to Grand View Research, the global public address and voice alarm system market—encompassing classroom amplification—was valued at USD 4.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further reinforced by Mordor Intelligence, which highlights a rising demand for audio enhancement technologies in K–12 and higher education institutions to improve speech intelligibility, support students with hearing challenges, and optimize classroom acoustics. As schools worldwide adopt technology to bridge learning gaps, the need for reliable, high-performance classroom amplification systems has become a strategic priority. In this evolving landscape, leading manufacturers are innovating to deliver scalable, user-friendly, and integrated audio solutions tailored to modern educational settings. Against this backdrop, we examine the top 10 classroom amplification system manufacturers shaping the future of auditory learning.
Top 10 Classroom Amplification System Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
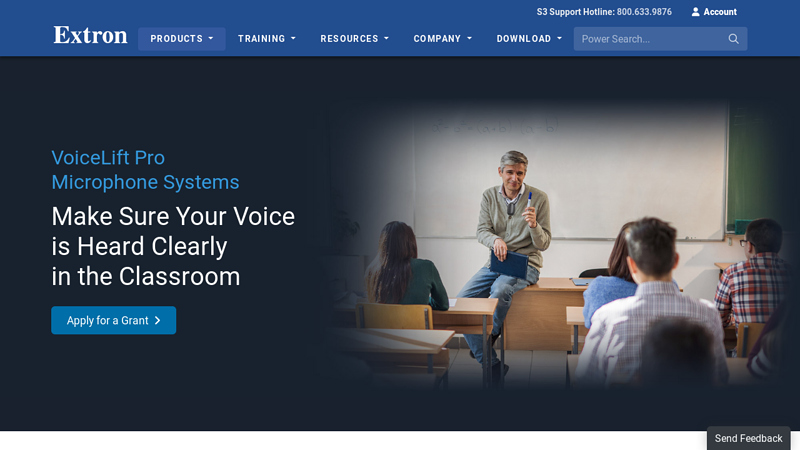
#1 Voice Amplification for Instructors
Domain Est. 1995
Website: extron.com
Key Highlights: The VoiceLift Pro microphone system allows instructors to be heard by amplifying their natural speaking voice and distributing it throughout the room….
#2
Domain Est. 1995
Website: bogen.com
Key Highlights: The Bogen brand continues to focus on telephone paging systems, commercial audio, and sophisticated communications systems for education and commercial markets….
#3 Anchor Audio
Domain Est. 1995
Website: anchoraudio.com
Key Highlights: Shop Anchor Audio’s portable PA systems—battery-powered, Bluetooth-enabled, lightweight, and self-contained. Easy setup sound solutions for any event….
#4 About Meyer Sound
Domain Est. 1995
Website: meyersound.com
Key Highlights: Meyer Sound is the global leader and innovator in self‑powered loudspeaker systems, active acoustics, spatial sound mixing, and sound system design ……
#5 ASHLY AUDIO
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ashly.com
Key Highlights: Ashly Audio designs and builds innovative audio systems for churches, restaurants, hotels, schools, courtrooms, health clubs and conference ……
#6 Biamp
Domain Est. 1996
Website: biamp.com
Key Highlights: Biamp is a leading provider of professional AV equipment well-suited for a variety of applications, including conferencing, paging, and video….
#7 Classroom Audio Systems
Domain Est. 1999
Website: teachlogic.com
Key Highlights: All TeachLogic classroom audio systems increase voice clarity to support better learning outcomes. The features vary based on what you need to connect to….
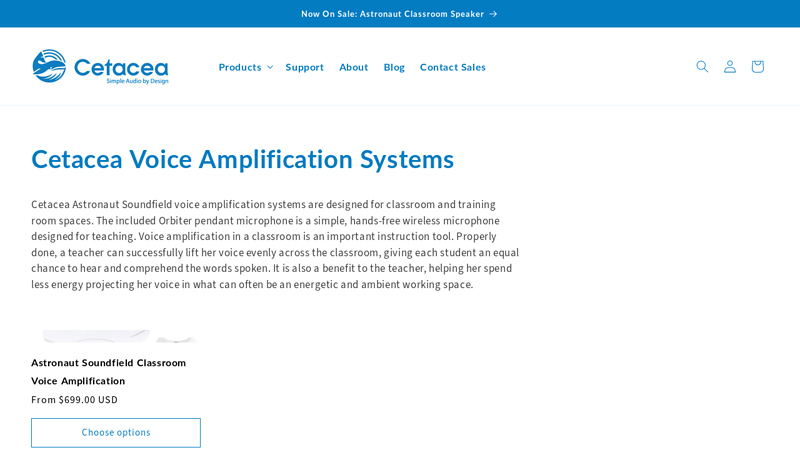
#8 Cetacea Voice Amplification Systems
Domain Est. 2001
Website: cetaceasound.com
Key Highlights: Cetacea Astronaut Soundfield is a complete all-in-one classroom voice and multimedia amplification system. Includes the Orbiter wireless pendant microphone….
#9 Professional Audio Systems: Paging, PA System & More
Domain Est. 2007
Website: atlasied.com
Key Highlights: AtlasIED provides audio solutions that enhance communication in commercial spaces. Explore our range of amplifiers, paging & VOIP systems, speakers & more….
#10 Classroom Amplification, Lightspeed
Domain Est. 2017
Website: remcsave.org
Key Highlights: Networked classroom amplifcation audio system with web console software, life safety interface, one Clearmike microphone with battery pack….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Classroom Amplification System

2026 Market Trends for Classroom Amplification Systems
The global classroom amplification system market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in educational technology, increased focus on inclusive learning environments, and growing investments in modernizing school infrastructure. These systems, designed to enhance speech clarity and ensure equitable auditory access for all students, are becoming integral components of 21st-century classrooms. This analysis explores key market trends expected to shape the classroom amplification system landscape in 2026.
Rising Demand for Inclusive and Accessible Education
One of the primary drivers of market growth is the global emphasis on inclusive education. Governments and educational institutions are increasingly adopting policies to support students with hearing impairments, auditory processing disorders, and attention-related challenges. Classroom amplification systems—particularly personal and soundfield systems—help level the auditory playing field, ensuring that every student, regardless of seating position or auditory ability, can clearly hear the instructor. By 2026, compliance with accessibility regulations such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and similar frameworks worldwide will continue to propel adoption across K–12 and higher education sectors.
Integration with Smart Classroom Ecosystems
Classroom amplification systems are no longer standalone audio devices. By 2026, seamless integration with smart classroom technologies—such as interactive whiteboards, learning management systems (LMS), and voice-activated assistants—will become standard. Manufacturers are developing amplification systems with IoT capabilities, enabling remote monitoring, usage analytics, and over-the-air software updates. This interconnectedness allows educators and administrators to optimize audio performance and gather data on classroom engagement and acoustical effectiveness.
Expansion of Wireless and Portable Solutions
Wireless technology will dominate the 2026 market, replacing older wired systems due to their flexibility and ease of installation. Portable and rechargeable teacher microphones with Bluetooth connectivity, noise-canceling features, and long battery life are becoming preferred choices. Moreover, multi-device compatibility—supporting smartphones, tablets, and laptops—enables teachers to stream instructional content directly through the amplification system, enhancing multimedia teaching capabilities.
Growth in Emerging Markets
While North America and Western Europe currently lead in market penetration, the fastest growth is expected in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa. Increasing government initiatives to improve education quality, coupled with urbanization and infrastructure development, are driving demand in these regions. Countries like India, Brazil, and South Africa are investing in digital classrooms, creating new opportunities for amplification system providers. By 2026, localized manufacturing and affordable product tiers will likely emerge to cater to cost-sensitive educational markets.
Focus on Acoustic Optimization and Health
There is growing recognition of the impact of classroom acoustics on student learning outcomes and teacher vocal health. Poor acoustics contribute to teacher voice strain and student fatigue. In response, schools are adopting comprehensive acoustic solutions that combine amplification with sound-absorbing materials and room design improvements. By 2026, holistic acoustic management—supported by AI-driven noise analysis tools—will become a key consideration in classroom design, further boosting demand for intelligent amplification systems.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The market is expected to see increased competition among established players (e.g., FrontRow, Lightspeed Technologies, Audio Enhancement) and emerging tech companies. Innovation will focus on AI-powered features such as adaptive volume control, speech enhancement algorithms, and real-time feedback on speech intelligibility. Additionally, cloud-based management platforms will allow district-wide deployment and monitoring, appealing to large educational institutions seeking scalability and cost-efficiency.
Conclusion
By 2026, the classroom amplification system market will be characterized by technological sophistication, integration with broader educational ecosystems, and a strong emphasis on inclusivity and acoustic wellness. As schools worldwide strive to create equitable and effective learning environments, amplification systems will evolve from niche audio tools into essential components of modern education infrastructure. Stakeholders—including manufacturers, educators, and policymakers—must collaborate to ensure these technologies are accessible, user-friendly, and aligned with pedagogical goals.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Classroom Amplification System (Quality and IP Considerations)
When selecting a classroom amplification system, institutions often focus on price and basic functionality, overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects. These oversights can lead to poor performance, compliance risks, and long-term costs. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Audio Quality and System Reliability
Many schools opt for low-cost systems without thoroughly evaluating audio clarity, speaker coverage, or microphone performance. Poor-quality amplification can result in distorted sound, feedback, or uneven volume distribution—negatively impacting student comprehension, especially for those with hearing difficulties. Additionally, unreliable hardware may lead to frequent maintenance, increased downtime, and higher total cost of ownership.
Ignoring Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
Classroom amplification systems must integrate seamlessly with existing audiovisual setups, such as smartboards, projectors, and PA systems. Choosing a system without assessing compatibility—especially regarding input/output standards, cabling, and control protocols—can lead to integration challenges, reduced functionality, and the need for costly adapters or upgrades.
Underestimating Installation and Calibration Requirements
Even high-quality systems perform poorly if not installed and calibrated correctly. Some vendors provide minimal setup support, assuming plug-and-play functionality. However, improper microphone placement, speaker alignment, or volume calibration can compromise speech intelligibility and overall effectiveness. Schools may lack in-house technical expertise, leading to suboptimal deployment.
Neglecting Intellectual Property and Software Licensing
Modern amplification systems often include proprietary software for configuration, remote management, and firmware updates. Failing to verify proper IP ownership, software licensing terms, and update policies can expose institutions to legal risks. Unauthorized or unlicensed software use may violate copyright laws, and lack of vendor support for updates can leave systems vulnerable to obsolescence or security flaws.
Assuming All IP-Enabled Systems Are Secure
Many newer amplification systems connect to school networks (IP-based), enabling centralized management and monitoring. However, IP connectivity introduces cybersecurity risks. Systems without secure boot, encrypted communication, or regular security patches may become entry points for network breaches. Procurement decisions should include a review of the manufacturer’s cybersecurity practices and compliance with data protection standards.
Overlooking Future-Proofing and Scalability
Choosing a system based solely on current needs without considering future growth can result in costly replacements. Systems lacking scalability, modular upgrades, or support for emerging standards (e.g., audio over IP protocols) may become obsolete quickly. Additionally, proprietary technologies with closed ecosystems can lock schools into a single vendor, limiting flexibility and increasing long-term costs.
Failing to Verify Vendor Support and Warranty Terms
Long-term performance depends on reliable technical support and warranty coverage. Some vendors offer limited support or exclude software-related issues from warranties. Without clear service-level agreements (SLAs) and accessible customer support, schools may face delays in resolving issues, impacting classroom continuity.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—prioritizing quality components, ensuring IP compliance, and evaluating long-term sustainability—schools can deploy classroom amplification systems that enhance learning outcomes and deliver lasting value.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Classroom Amplification System
Introduction
This guide outlines the logistics and compliance requirements for the procurement, deployment, and use of Classroom Amplification Systems (CAS) in educational environments. These systems enhance speech intelligibility for students and support inclusive learning, particularly for those with hearing impairments, auditory processing challenges, or attention difficulties. Adherence to logistical procedures and regulatory standards ensures effective implementation and legal compliance.
Regulatory Compliance
Accessibility Standards
All Classroom Amplification Systems must comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act. These laws require that educational institutions provide equal access to learning for students with disabilities. Amplification systems are considered auxiliary aids and must be provided when necessary to ensure effective communication.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Regulations
Wireless amplification systems must operate within designated frequency bands approved by the FCC. Devices using UHF, 2.4 GHz, or other wireless technologies must be certified and must not interfere with licensed communication services. Schools must ensure that equipment is FCC-compliant and that proper licensing (if required) is obtained.
State and Local Education Requirements
Some states have specific regulations regarding assistive listening technologies in classrooms. Districts must consult state education department guidelines and special education mandates to ensure alignment with local policies, including Individualized Education Program (IEP) and 504 Plan implementation.
Procurement and Inventory Management
Vendor Selection
Procurement must involve vetting vendors for compliance with ADA, FCC, and educational technology standards. Preferred vendors should offer equipment with warranties, technical support, and compatibility with existing classroom technology (e.g., interactive whiteboards, public address systems).
Purchase Approval Process
All purchases of amplification systems require approval from the district’s special education department and technology team. A documented justification, such as student IEP recommendations or audiologist evaluations, must support each purchase.
Asset Tracking
Each system must be assigned a unique asset tag and logged in the district’s inventory management system. Records should include serial numbers, location (school and classroom), assigned user (teacher or student), and maintenance history.
Installation and Configuration
Site Assessment
Prior to installation, conduct an acoustic evaluation of the classroom to determine optimal speaker placement, microphone type (e.g., lapel, pendant), and system configuration. Consider room size, background noise, and student seating arrangements.
Professional Installation
Installation must be performed or supervised by qualified technical personnel to ensure proper functionality and safety. Systems should be securely mounted, cabling concealed, and wireless frequencies coordinated to prevent interference.
User Training
Teachers and support staff must receive training on:
– Daily operation (power on/off, volume control)
– Microphone use and care
– Troubleshooting common issues
– Reporting malfunctions
Training records must be maintained in personnel files.
Maintenance and Support
Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Implement a routine maintenance plan, including:
– Monthly inspection of batteries and charging stations
– Quarterly cleaning of microphones and speakers
– Biannual system performance testing
Repair and Replacement Protocol
Defective units must be reported immediately to the school technology coordinator. A loaner unit should be available during repairs. Systems beyond repair must be replaced following the district’s procurement process.
Software and Firmware Updates
Ensure that all digital amplification systems receive regular software and firmware updates from the manufacturer to maintain security, functionality, and compliance.
Data Privacy and Security
Audio Transmission Security
For wireless systems, ensure that audio signals are encrypted to prevent eavesdropping. Systems should use secure pairing protocols (e.g., Bluetooth with encryption) and avoid open transmission on public frequencies.
Student Privacy
Amplification systems should not be used to record classroom sessions unless permitted under FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act) and with proper consent. Any recording must be securely stored and only accessible to authorized personnel.
Usage Policies
Authorized Users
Amplification systems are assigned for use by specific teachers or students as documented in IEPs or 504 Plans. Unauthorized use or relocation of equipment is prohibited.
Daily Operation Guidelines
Teachers must:
– Turn on the system at the start of class
– Wear the microphone appropriately (e.g., 6–8 inches from mouth)
– Monitor volume levels to avoid feedback or excessive noise
– Turn off the system when not in use to conserve battery
Monitoring and Evaluation
The special education department should conduct annual reviews to assess the effectiveness of amplification systems. Feedback from teachers, students, and audiologists should be collected and used to improve deployment practices.
Disposal and Decommissioning
End-of-Life Procedures
When systems are retired, they must be decommissioned in accordance with district IT asset disposal policies. Data storage components (if any) must be securely wiped or destroyed.
Environmental Compliance
Dispose of batteries and electronic components in compliance with local, state, and federal environmental regulations (e.g., EPA guidelines for electronic waste).
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management of Classroom Amplification Systems ensures equitable access to education, regulatory adherence, and long-term sustainability. Schools and districts must establish clear policies, provide ongoing training, and maintain accurate documentation to support effective implementation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, sourcing a classroom amplification system is a strategic investment in enhancing the teaching and learning environment. These systems significantly improve speech intelligibility, ensuring that all students—including those with hearing impairments, language delays, or attention difficulties—can clearly hear the instructor, regardless of their seating position. By reducing teacher vocal strain and promoting greater student engagement and focus, amplification systems contribute to a more inclusive, equitable, and effective classroom experience.
When selecting a system, key considerations such as ease of use, sound quality, scalability, compatibility with existing technology, and budget must be carefully evaluated. Wireless portability, microphone flexibility, and integration with multimedia tools further enhance usability across various classroom settings.
Ultimately, implementing a well-chosen classroom amplification system supports better academic outcomes, fosters inclusivity, and empowers educators—making it a valuable component of modern educational infrastructure. Proper planning, stakeholder input, and ongoing training will ensure successful adoption and long-term benefits for both teachers and students.