The global autoclave market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand for sterilization equipment across healthcare, pharmaceutical, and research sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global autoclave market size was valued at USD 1.23 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is largely fueled by increasing regulatory compliance requirements, advancements in sterilization technologies, and the expanding biopharmaceutical industry. Within this landscape, Class B autoclaves—known for their ability to achieve vacuum-assisted air removal and sterilize porous and packaged loads—are increasingly favored in medical and dental facilities for their versatility and adherence to stringent EN 13060 standards. As demand for high-performance sterilization solutions rises, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in the Class B segment, offering innovative, reliable, and compliant equipment that meets evolving industry needs.
Top 4 Class B Autoclave Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Autoclave Manufacturer from China
Domain Est. 2013
Website: zealway.us
Key Highlights: ZEALWAY produces high-end sterilizing autoclaves from quality materials to support different applications while guaranteeing end-user safety….
#2 EN 13060 Class B Tabletop Autoclaves
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tuttnauer.com
Key Highlights: Class B autoclaves are great space-savers built for high performance. They are microwave-sized autoclaves that fit easily on the counters of busy clinics ……
#3 Autoclave Enbio S (Medical Class B) 2025
Website: sterimax.us
Key Highlights: The Enbio S is an ultra-fast professional medical autoclave that ensures complete sterilization in record time — tools are sterile in just 7 minutes….
#4 Find the best class B autoclaves and much more at B
Domain Est. 2012
Website: b-autoclave.com
Key Highlights: Are you looking for a class B autoclave? B-autoclave is the autoclave specialist. You can also find ultrasonic cleaners and accessories with us….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Class B Autoclave

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Class B Autoclaves
The Class B autoclave market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by intensified regulatory demands, technological advancements, and shifting healthcare priorities. Key trends shaping this landscape include:
-
Regulatory Harmonization & Stricter Enforcement: Global regulatory bodies (FDA, EMA, MHRA) are expected to further align standards (e.g., EN 13060, ISO 17665) and enforce compliance more rigorously. The emphasis on traceability and validation will push demand for autoclaves with integrated electronic records, audit trails, and seamless connectivity to hospital information systems (HIS), making standalone units less viable.
-
Integration of IoT and Smart Technology: By 2026, connectivity will be standard. Class B autoclaves will increasingly feature IoT capabilities for real-time remote monitoring, predictive maintenance alerts, automated cycle reporting, and cloud-based data management. This enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and provides crucial data for quality assurance and regulatory audits.
-
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: Environmental regulations and cost pressures will drive demand for autoclaves with significantly lower water and energy consumption. Expect advancements in vacuum pump efficiency, faster cycle times, improved insulation, and water recycling systems. “Green” certifications will become a key differentiator.
-
Focus on User Experience and Workflow Optimization: Manufacturers will prioritize intuitive touchscreen interfaces, simplified loading/unloading (e.g., ergonomic chamber design, automatic door operation), and faster overall processing times to reduce staff burden and increase throughput in high-volume settings like central sterile supply departments (CSSDs).
-
Growth in Dental and Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs): The expansion of outpatient care and specialized dental practices will be a major growth driver. Compact, highly reliable, and easy-to-validate Class B autoclaves tailored for these smaller, high-compliance environments will see increased demand, often featuring simplified validation protocols.
-
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization: Post-pandemic lessons will continue to influence procurement. Healthcare facilities and governments may prioritize suppliers with robust, geographically diversified supply chains and local service networks to mitigate disruption risks, potentially favoring established regional players or those investing in local manufacturing/assembly.
-
Advanced Materials Compatibility: As medical devices incorporate more complex materials (polymers, composites, electronics), autoclave cycles and chamber designs will need to ensure effective sterilization without damaging sensitive components, requiring more sophisticated cycle programming and monitoring.
In conclusion, the 2026 Class B autoclave market will be characterized by smarter, more connected, and sustainable devices operating within a framework of heightened regulatory scrutiny. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to innovate in connectivity, efficiency, and usability while ensuring uncompromising safety and compliance.
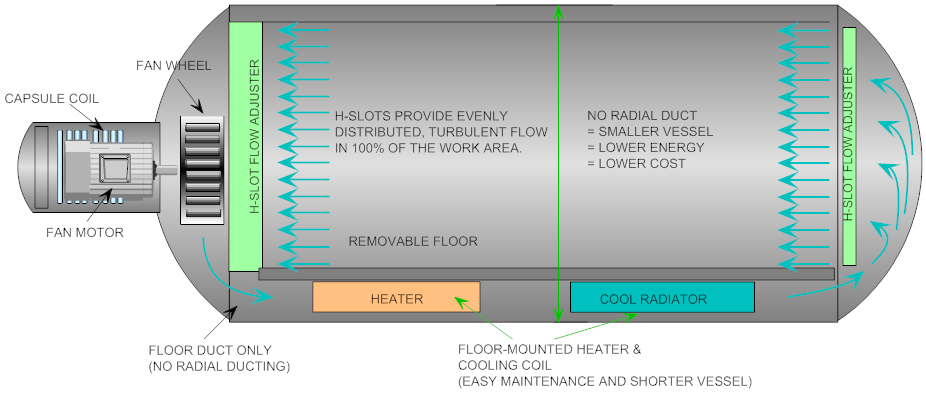
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Class B Autoclaves: Quality and IP Considerations
Sourcing a Class B autoclave—a high-performance sterilization device critical in dental, medical, and laboratory settings—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects. Overlooking these factors can lead to equipment failure, regulatory non-compliance, legal disputes, or compromised patient safety.
1. Compromising on Build Quality and Certification
One of the most frequent pitfalls is prioritizing cost over quality, resulting in substandard equipment.
- Lack of Compliance with Standards: Class B autoclaves must comply with international standards such as ISO 13485 (quality management) and EN 13060 (specific to small steam sterilizers). Sourcing units without valid CE marking or FDA 510(k) clearance in applicable markets can lead to regulatory rejection and operational shutdowns.
- Poor Material Construction: Low-quality stainless steel chambers or subpar door seals degrade quickly under repeated high-pressure steam cycles, increasing maintenance costs and risking sterilization failure.
- Inadequate Validation Documentation: Reputable suppliers provide full validation packages (IQ/OQ/PQ). Accepting units without these documents makes it difficult to prove compliance during audits.
2. Overlooking Software and Firmware Integrity
Modern Class B autoclaves rely on proprietary software for cycle control, data logging, and compliance reporting. This introduces IP and functionality risks.
- Unauthorized Software Replicas or Clones: Some suppliers may use reverse-engineered or pirated firmware. This not only violates IP rights but also poses cybersecurity risks and unreliable performance.
- Lack of Software Updates and Support: Sourcing from manufacturers who do not provide regular firmware updates may leave equipment vulnerable to bugs or non-compliance with evolving regulatory requirements.
- Proprietary Data Lock-In: Some vendors use closed systems that prevent data export in standard formats, making integration with electronic health records (EHR) or audit systems difficult—an indirect IP-related usability issue.
3. Infringing on Patented Technologies
Class B autoclave designs often include patented innovations in chamber dynamics, air removal (e.g., vacuum pulses), or energy efficiency.
- Risk of IP Litigation: Purchasing a device that incorporates patented technology without proper licensing exposes the buyer or distributor to legal action, especially in markets with strong IP enforcement (e.g., the EU or U.S.).
- Use of Counterfeit or “Grey Market” Units: These units may mimic branded designs and infringe on design patents or trademarks. While cheaper, they typically lack genuine IP licensing and fail safety inspections.
4. Insufficient Due Diligence on Suppliers
Failing to vet suppliers thoroughly increases exposure to both quality and IP risks.
- Unverified Manufacturing Origins: Some suppliers rebrand equipment from uncertified factories, masking the true origin and bypassing IP protections. This can lead to counterfeit claims or import bans.
- Absence of IP Documentation: Reputable manufacturers provide evidence of IP ownership or licensing for key technologies. A lack of transparency here is a red flag.
- Weak After-Sales and Legal Support: If a quality or IP issue arises post-purchase, suppliers without strong legal and technical infrastructure may be unable to resolve the matter, leaving the buyer liable.
5. Misunderstanding Regional Regulatory and IP Frameworks
Different regions have varying requirements for medical device approval and IP enforcement.
- Assuming Global Compliance: A device certified in one region (e.g., CE-marked in Europe) may not meet FDA or Health Canada requirements. Similarly, IP protection is territorial—patents valid in one country may not apply elsewhere.
- Import Restrictions Due to IP Conflicts: Customs authorities in some countries can seize shipments suspected of IP infringement, even if the buyer was unaware, causing delays and financial loss.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Verify Certifications: Ensure the autoclave has up-to-date regulatory approvals for your target market.
- Request IP Documentation: Ask suppliers for proof of patent ownership, licensing agreements, or freedom-to-operate opinions.
- Conduct Factory Audits or Third-Party Inspections: Especially when sourcing from new or offshore suppliers.
- Use Reputable Distributors: Partner with authorized dealers who provide warranties and support.
- Include IP Indemnity Clauses in Contracts: Require suppliers to assume liability for IP infringement claims.
By addressing both quality and intellectual property concerns proactively, organizations can ensure they source reliable, compliant, and legally defensible Class B autoclaves.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Class B Autoclave
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the installation, operation, and maintenance of a Class B autoclave, ensuring adherence to international and regional standards, particularly within medical, dental, and laboratory environments.
H2: Regulatory Framework & Standards
Class B autoclaves are subject to strict regulatory oversight due to their critical role in sterilizing complex medical devices, including hollow and porous loads. Compliance is mandatory for patient safety and legal operation.
- ISO 13485: Applies to quality management systems for medical devices; essential for manufacturers and users in regulated environments.
- EN 13060:2014+A1:2018: The European standard defining requirements, test methods, and performance criteria for small steam sterilizers, including Class B equipment.
- FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration): Classifies steam sterilizers as Class II medical devices; 510(k) clearance may be required depending on use and jurisdiction.
- Health Canada & TGA (Australia): Require compliance with recognized standards and may require device licensing.
- CDC Guidelines (U.S.) & HTM 01-06 (UK): Provide operational best practices for dental and healthcare settings, endorsing Class B autoclaves for all types of reusable instruments, including those with lumens.
H2: Installation Logistics
Proper installation is critical for performance, safety, and compliance.
- Site Preparation:
- Ensure adequate space for operation, maintenance, and ventilation (minimum 10 cm clearance on all sides).
- Verify floor load capacity (autoclaves are heavy when filled with water and instruments).
-
Provide a level, stable surface.
-
Utilities:
- Water Supply: Requires purified or distilled water (preferably via a reverse osmosis system) to prevent limescale buildup. Connection to a closed-loop water system is ideal.
- Drainage: Must be connected to a proper waste line capable of handling high-temperature condensate. Air gap or backflow preventer is recommended.
- Electrical Supply: Confirm voltage and amperage compatibility (typically 208–240 V, single-phase). Use a dedicated circuit with proper grounding.
-
Steam Supply (if applicable): Most Class B units are tabletop and generate steam internally; verify if external steam is needed.
-
Ventilation: Ensure room has adequate air exchange to manage heat and moisture release during operation.
H2: Operational Compliance
Daily operation must be documented and validated to meet regulatory expectations.
- Cycle Selection: Use manufacturer-recommended cycles for specific load types (solid, porous, hollow instruments). Class B autoclaves employ fractional or full vacuum air removal for effective steam penetration.
- Loading Practices:
- Avoid overloading; follow manufacturer’s loading diagrams.
- Use validated sterilization containers and pouches.
- Separate textile and metal loads as per guidelines.
- Process Monitoring:
- Use Class 5 (integrating) or Class 6 (simulating) chemical indicators in every load.
- Maintain detailed sterilization logs (date, cycle, load contents, operator, chemical indicator results).
- Biological Monitoring (Spore Testing):
- Conduct weekly (minimum) spore tests using Geobacillus stearothermophilus.
- Retain records for a minimum of 3–5 years (per facility policy and regulation).
H2: Maintenance & Validation
Regular maintenance ensures equipment longevity and consistent sterilization efficacy.
- Routine Maintenance:
- Daily: Clean chamber and door seal; check water level.
- Weekly: Descale chamber and tubing (using approved descaling agents).
- Monthly: Inspect door gasket, filters, and safety valves.
-
Annually: Comprehensive service by qualified technician.
-
Performance Qualification (PQ):
- Conduct initial and periodic (typically every 12 months) validation including:
- Temperature mapping (thermocouples in worst-case locations).
- Vacuum integrity test.
- Leak rate test.
- Bowie-Dick test (daily or per cycle type, as per HTM 01-06).
- Document all tests and retain reports.
H2: Training & Documentation
Personnel must be trained and records meticulously maintained.
- Staff Training:
- All operators must be trained on safe operation, cycle selection, loading, and emergency procedures.
-
Training records must be kept and updated annually.
-
Documentation Requirements:
- Equipment manual and service history.
- Sterilization logs.
- Spore test results and corrective actions.
- Validation reports (IQ/OQ/PQ).
- Maintenance records.
- Staff training records.
H2: Decommissioning & Disposal
At end-of-life, ensure environmentally and legally compliant disposal.
- Decontaminate the unit according to local biohazard regulations.
- Recycle components where possible (metals, electronics).
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU and equivalent standards elsewhere.
- Retain equipment history file for audit purposes.
Note: Always consult local regulatory authorities and the autoclave manufacturer’s instructions for use (IFU) to ensure full compliance. Regulations may vary by country and healthcare setting.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Class B Autoclave:
In conclusion, sourcing a Class B autoclave is a critical decision that directly impacts the safety, efficiency, and compliance of sterile processing operations, particularly in dental and medical settings. Class B autoclaves offer the highest level of sterilization performance due to their ability to effectively sterilize all types of loads, including packaged and porous materials, through the use of a vacuum phase. When sourcing such equipment, it is essential to consider factors such as regulatory compliance (e.g., CE marking, ISO standards), chamber size, cycle times, ease of use, maintenance requirements, and manufacturer reputation.
Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership—beyond the initial purchase price—to include service contracts, consumables, and energy efficiency ensures long-term value. Engaging with trusted suppliers, verifying technical specifications, and conducting due diligence on after-sales support will contribute to a successful procurement outcome.
Ultimately, investing in a high-quality Class B autoclave underscores a commitment to patient safety, regulatory adherence, and operational excellence in healthcare delivery.