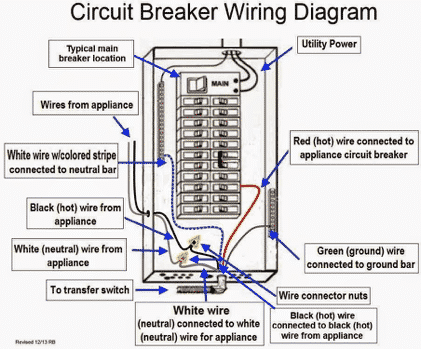
The global circuit breaker market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising electricity demand, infrastructure modernization, and the expansion of renewable energy integration. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the circuit breaker market was valued at USD 14.63 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 20.12 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% during the forecast period. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates increasing adoption of smart grid technologies and industrial automation as key catalysts, with the market expected to expand further due to stringent electrical safety regulations and urbanization in emerging economies. As demand for reliable and efficient electrical distribution systems grows, so does the need for high-quality circuit breaker box components. This has elevated the importance of leading manufacturers that innovate in thermal-magnetic protection, arc fault detection, and compact design. The following list highlights the top 10 circuit breaker box parts manufacturers shaping this evolving landscape through technological advancement, global reach, and compliance with international safety standards.
Top 10 Circuit Breaker Box Parts Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Circuit Breaker Sales
Domain Est. 1996
Website: circuitbreaker.com
Key Highlights: CBS also provides parts, support and service for circuit breakers and switchgear from the following manufacturers: General Electric | Westinghouse | Cutler ……
#2 E-T-A Engineering Technology
Domain Est. 1996
Website: e-t-a.com
Key Highlights: Our range of products includes circuit breakers, electronic circuit protectors, solid state relays, and intelligent power distribution systems….
#3 NOARK Electric
Domain Est. 2010
Website: na.noark-electric.com
Key Highlights: Explore NOARK Electric’s high-quality electrical components for industrial applications. Reliable circuit protection and motor control solutions….
#4 Circuit Breakers & Accessories
Domain Est. 1995
Website: parts.rheem.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $25 30-day returnsA circuit breaker is designed to trip if a connected electrical device is drawing more amps from the electrical circuit that it is rated for….
#5 Electrical circuit breakers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Eaton’s low and medium-voltage circuit breakers provide premium protection for overheating wires, overloads and short circuits….
#6 Standard Line of Electrical Panel
Domain Est. 1996
#7 Circuit Breakers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: se.com
Key Highlights: We have the broadest array of breakers in the industry, including Square D circuit breakers for superior circuit protection, the legendary PowerPacT molded case ……
#8 Midwest Electric Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: midwestelectric.com
Key Highlights: Midwest Electric Products is an industry leader in manufacturing quality weatherproof electrical equipment. Our product portfolio is focused on commercial and ……
#9 Federal Pacific
Domain Est. 1999
Website: federalpacific.com
Key Highlights: Switchgear. Circuit Breaker protected way feature a “Protection Assurance” feature. In the event of power loss, all VCBs can be made to open with loss of ……
#10 National Power Equipment
Domain Est. 2004
Website: npeinc.com
Key Highlights: Your source for used and remanufactured air and vacuum circuit breakers, substation switchgear, protective relays and related parts….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Circuit Breaker Box Parts
2026 Market Trends for Circuit Breaker Box Parts
The market for circuit breaker box parts is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving energy demands, and heightened safety and sustainability standards. Key trends shaping the industry include the rise of smart grid integration, increased focus on energy efficiency, regulatory shifts, and the growing impact of electrification across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Smart and Connected Components Gain Momentum
By 2026, smart circuit breaker box components—such as intelligent trip units, remote monitoring sensors, and IoT-enabled load centers—are expected to dominate new installations. These parts allow real-time energy usage tracking, predictive maintenance alerts, and remote circuit control via mobile apps or building management systems. As smart homes and energy-conscious consumers grow, demand for breakers with integrated communication capabilities (e.g., Wi-Fi, Zigbee, or cellular connectivity) will surge, enabling utilities and homeowners to optimize power distribution and respond proactively to electrical faults.
Surge in Demand for Arc Fault and Ground Fault Protection
Safety regulations are tightening globally, with codes like the National Electrical Code (NEC) mandating arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in more applications. By 2026, manufacturers will increasingly produce hybrid breakers that combine AFCI, GFCI, and surge protection into single, compact units. This integration reduces panel space requirements while enhancing fire and electrocution prevention—critical for aging infrastructure and high-density urban developments.
Electrification and Renewable Energy Integration Drive Upgrades
The expansion of electric vehicle (EV) charging stations, heat pumps, and solar photovoltaic (PV) systems is placing new demands on electrical panels. Circuit breaker box parts must support bidirectional power flow, higher amperage loads, and seamless integration with inverters and battery storage. As a result, demand for high-capacity main breakers, load management modules, and back-feed protection components will rise, particularly in residential retrofits and new green building projects.
Focus on Sustainability and Recyclable Materials
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals will push manufacturers toward sustainable materials and design. By 2026, expect greater use of recyclable metals, halogen-free insulation, and reduced-plastic housings in breaker components. Additionally, modular and field-replaceable parts will gain favor, extending product lifecycles and reducing electronic waste. Certifications like RoHS and EPDs (Environmental Product Declarations) will become standard differentiators.
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and past disruptions have prompted a shift toward regional manufacturing and inventory diversification. In 2026, leading suppliers will increasingly localize production of key breaker box parts—such as bimetallic strips, arc chutes, and solenoid mechanisms—to mitigate risks and reduce lead times. This localization trend will be especially evident in North America and Europe, where energy security and infrastructure modernization are national priorities.
Consolidation and Innovation Among Suppliers
The circuit breaker parts market will likely see further consolidation, with larger electrical equipment companies acquiring niche component innovators. Investment in R&D will focus on miniaturization, improved thermal performance, and digital twin integration for predictive analytics. Startups specializing in solid-state circuit protection and AI-driven fault detection are expected to play a disruptive role, influencing the broader component ecosystem.
In summary, the 2026 landscape for circuit breaker box parts will be defined by digitalization, safety enhancement, sustainability, and adaptability to decentralized energy systems. Stakeholders—from manufacturers to electricians—must align with these trends to meet evolving regulatory, environmental, and consumer demands.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Circuit Breaker Box Parts (Quality, IP)
Sourcing components for circuit breaker boxes—such as enclosures, breakers, busbars, and accessories—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to safety hazards, regulatory non-compliance, and legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Components
One of the most significant risks when sourcing circuit breaker box parts is compromising on quality, especially from low-cost suppliers. Substandard materials or manufacturing can lead to:
- Electrical Failures: Inadequate insulation, poor conductivity, or weak mechanical design may result in short circuits, overheating, or arcing.
- Reduced Lifespan: Low-quality components degrade faster under thermal cycling and electrical load, increasing maintenance and replacement costs.
- Safety Hazards: Non-compliant or poorly tested parts increase the risk of fire, electric shock, or equipment damage.
- Non-Compliance with Standards: Parts that don’t meet IEC, UL, or other regional safety standards cannot be legally installed and may void insurance coverage.
Tip: Always verify certifications (e.g., UL Listed, CE, CCC), request test reports, and conduct third-party inspections when sourcing from unfamiliar suppliers.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Sourcing generic or “compatible” circuit breaker parts can inadvertently lead to IP violations:
- Counterfeit Products: Some suppliers offer replicas of branded breakers or enclosures (e.g., mimicking Siemens, ABB, or Schneider designs), which may infringe on patents, trademarks, or design rights.
- Patented Designs: Components like modular breakers or interlocking mechanisms often involve protected technology. Unauthorized replication—even if functionally similar—can lead to legal action.
- Licensing Issues: Using OEM-compatible parts without proper licensing exposes buyers and integrators to liability, especially in commercial or industrial installations.
Tip: Ensure suppliers provide proof of IP clearance or licensing. Avoid parts marketed as “exact replacements” or “OEM-equivalent” unless legally authorized.
Inconsistent IP Ratings
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating is crucial for enclosures used in harsh environments. A common pitfall is assuming all enclosures meet required environmental protection levels:
- Misrepresented Ratings: Some suppliers list inflated or unverified IP ratings (e.g., claiming IP65 when the enclosure only achieves IP54).
- Poor Sealing & Gaskets: Substandard gasket materials or design flaws compromise dust and water resistance, leading to internal contamination and corrosion.
- Inadequate Testing: Lack of proper testing under real-world conditions can result in enclosure failure despite claimed IP ratings.
Tip: Request third-party test documentation (e.g., IEC 60529 certification) and verify the IP rating aligns with the installation environment (indoor, outdoor, industrial, etc.).
Lack of Traceability & Documentation
Without proper documentation, verifying part authenticity and compliance becomes nearly impossible:
- Missing Certifications: Absence of RoHS, REACH, or country-specific compliance documents can block market access.
- No Batch Traceability: In the event of a recall or failure, untraceable parts complicate root cause analysis and liability assignment.
- Incomplete Technical Data: Poorly documented dimensions, torque specs, or material composition increases installation risks.
Tip: Require full technical dossiers, material declarations, and batch tracking from suppliers before procurement.
Supply Chain Reliability & Long-Term Support
Circuit breaker systems often require decades of service. Sourcing from unreliable suppliers can lead to:
- Discontinued Parts: Inability to source replacement components years later due to supplier exit or product discontinuation.
- Inconsistent Quality Over Time: Variability between production batches affects performance and system compatibility.
- Poor After-Sales Support: Lack of technical assistance or warranty fulfillment increases downtime and repair costs.
Tip: Prioritize suppliers with proven track records, long-term product roadmaps, and local service networks.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—emphasizing certified quality, respecting IP rights, verifying IP ratings, demanding documentation, and ensuring supply chain stability—you can mitigate risks and ensure safe, compliant, and reliable electrical installations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Circuit Breaker Box Parts
Overview
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, storage, import/export, and regulatory adherence of circuit breaker box parts. These components—such as bus bars, breakers, enclosures, and mounting hardware—are essential in electrical distribution systems and are subject to strict safety, environmental, and trade regulations.
International Shipping & Customs Compliance
- Harmonized System (HS) Codes: Use accurate HS codes (e.g., 8536.30 for circuit breakers, 8537.10 for switchgear panels) to ensure proper classification and tariff application.
- Documentation Requirements: Provide commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and bills of lading. Include technical specifications for customs inspections.
- Import/Export Licenses: Verify if destination countries require special permits, especially for high-voltage components or shipments to regulated markets (e.g., EU, U.S., Middle East).
- Restricted Parties Screening: Screen all trading partners against government watchlists (e.g., OFAC, BIS) to avoid violations of export control laws.
Safety & Regulatory Standards
- UL Certification (U.S.): Ensure parts comply with UL 489 (molded-case circuit breakers) and UL 508 (industrial control equipment). UL-listed products must bear certification marks.
- CE Marking (EU): Comply with Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive. Technical files and EU Declaration of Conformity are mandatory.
- IEC Standards: Adhere to IEC 60898 (circuit breakers for overcurrent protection) and IEC 60947 (low-voltage switchgear). Widely recognized globally.
- RoHS & REACH Compliance: Confirm parts are free of restricted hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) per EU RoHS and REACH regulations.
Packaging & Handling
- Protective Packaging: Use anti-static bags, corrugated boxes with cushioning, and moisture barriers to protect sensitive electrical components.
- Labeling Requirements: Clearly label packages with part numbers, voltage ratings, weight, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile”, “Do Not Stack”), and compliance marks (UL, CE).
- Hazardous Materials: If packaging includes desiccants or adhesives, verify they meet IATA/IMDG regulations for air/sea transport.
Storage & Inventory Management
- Environmental Controls: Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments (10–30°C, <60% RH) to prevent corrosion and insulation degradation.
- Segregation: Separate live components from non-electrical parts to avoid contamination or accidental damage.
- Stock Rotation: Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) to minimize obsolescence, especially for parts with shelf-life limitations.
Transportation Requirements
- Mode Selection: Use reliable freight partners experienced in handling electrical equipment. Air freight for urgent orders; ocean freight for bulk shipments.
- Temperature Monitoring: For climate-sensitive shipments, use data loggers to record temperature and humidity.
- Insurance: Secure cargo insurance covering loss, damage, and delays, especially for high-value shipments.
End-of-Life & Environmental Compliance
- WEEE Compliance (EU): Register with national WEEE authorities and provide take-back options for end-of-life parts.
- Recycling Programs: Partner with certified e-waste recyclers to responsibly dispose of defective or obsolete components.
- Battery-Containing Parts: If any parts include batteries (e.g., alarm modules), comply with UN 38.3 testing and proper labeling for transport.
Audit & Recordkeeping
- Maintain records of certifications, test reports, shipping documents, and compliance declarations for a minimum of 10 years.
- Conduct annual internal audits to verify adherence to ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management).
Conclusion
Compliance with logistics and regulatory standards ensures the safe, legal, and efficient movement of circuit breaker box parts across global supply chains. Regular training, documentation, and partnership with certified suppliers and carriers are essential for minimizing risk and maintaining market access.
Conclusion: Sourcing Circuit Breaker Box Parts
Sourcing circuit breaker box parts requires careful consideration of safety, compliance, compatibility, and reliability. It is essential to procure components from reputable suppliers or manufacturers that meet recognized industry standards such as UL, IEC, or NEC to ensure the integrity and safety of electrical systems. Using genuine or certified parts helps prevent hazards such as electrical fires, equipment damage, or personal injury.
Additionally, understanding the specific requirements of the existing electrical system—such as voltage rating, amperage, and panel compatibility—is critical to ensure proper functionality. While cost and lead time are important factors, they should not compromise the quality and safety of the components.
In conclusion, a strategic approach that prioritizes safety, authenticity, and technical compatibility will ensure the reliable and long-term performance of circuit breaker boxes. Working with authorized distributors and consulting with qualified electricians or engineers further supports successful sourcing and installation.