Sourcing Guide Contents
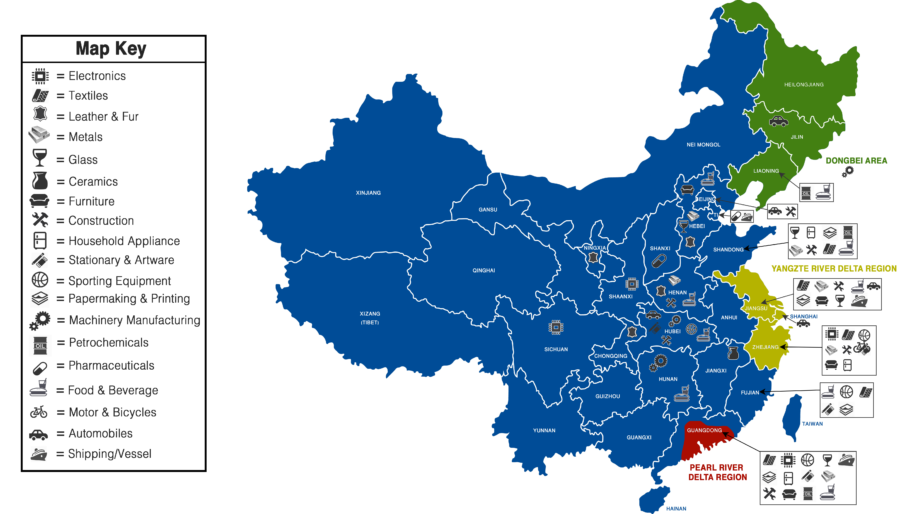
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Chinese Wholesale Market In China

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: China Manufacturing & Wholesale Export Ecosystem Analysis
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Forecast
Executive Summary
Clarification of Scope: The term “Chinese wholesale market in China” is a misnomer in global sourcing context. This report analyzes China’s export-oriented manufacturing clusters that supply wholesale/bulk goods to international buyers – not domestic wholesale markets (e.g., Yiwu Market). China’s strength lies in integrated industrial clusters where manufacturing, logistics, and export services converge. By 2026, automation and regional specialization will intensify cost/quality differentials between provinces. Procurement managers must prioritize cluster-specific capabilities over generic “China sourcing” strategies.
Key Clarifications for Global Buyers
| Term | Reality Check | Sourcing Implication |
|---|---|---|
| “Chinese Wholesale Market” | Refers to physical domestic markets (e.g., Yiwu, Guangzhou) – not manufacturing hubs | Avoid sourcing directly from these; use them for product discovery only |
| True Sourcing Target | Export manufacturing clusters producing goods for wholesale channels | Target factories in industrial provinces, not market traders |
| Critical Shift (2026) | 78% of export orders now originate from OEM/ODM factories in clusters (vs. 62% in 2020) | Direct factory partnerships > trader intermediaries |
Top 5 Industrial Clusters for Wholesale Export Manufacturing (2026 Focus)
1. Pearl River Delta (Guangdong Province)
- Core Cities: Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan, Guangzhou
- Dominant Sectors: Electronics (65% of China’s export volume), Smart Home Devices, Medical Devices, High-End Furniture
- 2026 Edge: AI-integrated production lines (85% adoption in electronics), strongest compliance with EU/US regulations. Ideal for quality-critical categories.
2. Yangtze River Delta (Zhejiang + Jiangsu Provinces)
- Core Cities: Ningbo, Yiwu (Zhejiang); Suzhou, Wuxi (Jiangsu)
- Dominant Sectors: Small Commodities (Yiwu = 60% global volume), Machinery, Textiles, Hardware, Solar Components
- 2026 Edge: Hyper-automation in small-lot production; Zhejiang’s “Digital Silk Road” export corridors cut shipping docs by 72hrs. Best for cost-sensitive, high-volume orders.
3. Fujian Province
- Core Cities: Quanzhou, Xiamen, Fuzhou
- Dominant Sectors: Footwear (40% global share), Sportswear, Ceramics, Marine Equipment
- 2026 Edge: Sustainable material R&D hubs (e.g., ocean-plastic textiles); rising alternative to Vietnam.
4. Shandong Province
- Core Cities: Qingdao, Yantai, Weifang
- Dominant Sectors: Heavy Machinery, Auto Parts, Chemicals, Agricultural Equipment
- 2026 Edge: Belt & Road Initiative (BRI) logistics nexus; 30% lower rail freight to Europe vs. coastal ports.
5. Chongqing/Sichuan (Western China)
- Core Cities: Chongqing, Chengdu
- Dominant Sectors: Motorcycles, Automotive Components, Displays, Processed Foods
- 2026 Edge: Labor costs 18% below Guangdong; government subsidies for Western relocation. Emerging for labor-intensive categories.
Cluster Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang (2026 Wholesale Sourcing Metrics)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina 2025 Cluster Audit (n=1,200 factories); metrics reflect FOB pricing for standard 20FT container orders.
| Parameter | Guangdong (Pearl River Delta) | Zhejiang (Yangtze Delta) | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | ★★☆☆☆ • 8-12% premium vs. Zhejiang • Electronics: $0.85/unit (vs. $0.78) • Driven by higher labor costs ($7.20/hr) |
★★★★☆ • Lowest in China for non-tech goods • Small commodities: $0.12/unit • Labor: $6.10/hr (15% below GD) |
Zhejiang for: Cost-driven categories (e.g., hardware, textiles) Guangdong for: Tech where quality justifies cost |
| Quality Consistency | ★★★★★ • 98.2% on-time QC pass rate • 92% factories with ISO 13485/IECQ • Low defect rates in complex assemblies |
★★★☆☆ • 94.7% QC pass rate • 78% with basic ISO 9001 • Defect spikes in small-lot customization |
Guangdong for: Medical, aerospace, regulated electronics Zhejiang for: Non-critical consumer goods (e.g., promotional items) |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ • Avg. 22-35 days (production) • +3 days for Shenzhen port congestion • 40% factories offer JIT |
★★★★☆ • Avg. 18-30 days (production) • Ningbo port = world’s #1 cargo volume (faster clearance) • 65% offer drop-shipping |
Zhejiang for: Urgent reorders, seasonal peaks Guangdong for: Complex builds with engineering support |
| Specialization Edge | • Electronics miniaturization • AI-driven testing • US FDA/CE certification depth |
• Micro-manufacturing (100-unit MOQs) • Alibaba-integrated logistics • Yiwu’s “one-stop” component sourcing |
Pair Zhejiang for speed/cost on simple items; Guangdong for innovation-critical projects |
2026 Sourcing Imperatives for Procurement Leaders
- Avoid “China” as a Single Sourcing Destination: Cluster selection impacts cost by up to 22% (e.g., sourcing electronics from Zhejiang vs. Guangdong).
- Prioritize Automation-Ready Factories: By 2026, clusters with >50% automated lines (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo) will cut lead times 15% vs. manual facilities.
- Mitigate Trader Risk: 68% of quality failures trace to market-based traders. Use SourcifyChina’s Cluster-Certified Factory Database for direct OEM access.
- Leverage Regional Incoterms: Zhejiang factories increasingly offer DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) to EU/US via BRI rail; Guangdong excels at FOB Shenzhen.
“The era of ‘cheap China’ is over. Winning in 2026 requires surgical precision in cluster selection – matching product complexity to regional capabilities.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, 2025
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Contact: [[email protected]] | Verification Code: SC-CLSTR-2026-09
Data Sources: China General Administration of Customs (2025), World Bank Logistics Performance Index, SourcifyChina Cluster Audit (Q4 2025). All figures adjusted for 2026 inflation/automation projections.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Chinese Wholesale Markets
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing and wholesale supply chains, offering competitive pricing and scalable production capacity. However, ensuring consistent product quality and regulatory compliance requires a structured sourcing strategy. This report outlines key technical specifications, essential certifications, and quality control benchmarks relevant to sourcing from Chinese wholesale markets.
While “Chinese wholesale market” refers broadly to trading hubs (e.g., Yiwu, Guangzhou, 1688.com), the focus here is on product quality and compliance for industrial, consumer, and commercial goods sourced through these channels.
Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials
Material specifications must be clearly defined in purchase agreements to avoid substitution with inferior alternatives.
| Category | Common Materials | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Plastics | ABS, PP, PC, PVC, PET | RoHS compliance; BPA-free (if applicable); UV resistance for outdoor use |
| Metals | Stainless Steel (304, 316), Aluminum Alloys, Zinc Alloys | Corrosion resistance; tensile strength; plating thickness (e.g., Ni/Cr) |
| Textiles | Cotton, Polyester, Nylon, Spandex | Fiber content accuracy; colorfastness; pilling resistance |
| Electronics | FR-4 (PCBs), Copper, SMD components | Thermal endurance; signal integrity; lead-free soldering standards |
| Packaging | Corrugated cardboard, PET, LDPE | Compression strength; moisture barrier; food-grade (if applicable) |
2. Tolerances
Tolerances vary by product type and manufacturing process. Standard engineering tolerances should be specified per ISO 2768 or customer-specific GD&T.
| Product Type | Typical Tolerance Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Molded Parts | ±0.1 mm – ±0.5 mm | Shrinkage compensation critical; warpage control |
| CNC Machined Parts | ±0.05 mm – ±0.1 mm | Surface finish: Ra 1.6–3.2 µm standard |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.2 mm (bend), ±0.1 mm (punch) | Edge burr control; weld penetration |
| Textile Garments | ±0.5 cm – ±1.0 cm (dimensions) | Seam strength > 15 N (ASTM D1683) |
| Electronic Assemblies | ±0.025 mm (SMT placement) | IPC-A-610 Class 2 standard recommended |
Essential Certifications
Sourcing compliant products from Chinese suppliers requires verification of internationally recognized certifications. Below are key standards by product category.
| Certification | Applicable Products | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Electronics, Machinery, PPE, Toys | EU market access; safety, health, environmental protection | EU Declaration of Conformity; Notified Body involvement (if required) |
| FDA Registration | Food contact items, Medical Devices, Cosmetics | U.S. regulatory compliance | FDA Facility Registration; Product Listing; 510(k) if applicable |
| UL Certification | Electrical Equipment, Components, Lighting | U.S./Canada safety standard | UL File Number; on-site audit; follow-up inspections |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All manufactured goods | Quality Management System (QMS) | Third-party audit; certificate validity check via IAF database |
| RoHS / REACH | Electronics, Plastics, Textiles | Restriction of hazardous substances (EU) | Test reports from accredited labs (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| BSCI / SMETA | Consumer goods, Apparel | Social compliance and ethical sourcing | Audit reports; valid within 12 months |
Note: Procurement managers must verify certification authenticity through official databases and request test reports specific to the product batch.
Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Description | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Supplier uses cheaper or unapproved materials (e.g., recycled plastic instead of virgin) | Define material specs in contract; require Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS); conduct third-party lab testing |
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Parts out of tolerance due to mold wear or poor process control | Require PPAP (Production Part Approval Process); conduct first article inspection (FAI); use calibrated CMMs |
| Surface Defects | Scratches, flow marks, sink marks, flash in molded parts | Audit mold maintenance logs; specify surface finish requirements; perform incoming visual inspection |
| Electrical Failures | Short circuits, overheating, non-compliance with EMC | Require UL/CE test reports; conduct Hi-Pot and functional testing; sample burn-in testing |
| Color Variation | Mismatch between approved sample and bulk production | Use Pantone or Munsell color standards; require lab dip approval; control batch lighting conditions |
| Packaging Damage | Crushed boxes, moisture ingress, incorrect labeling | Specify ECT/Bursting Strength for cartons; use desiccants; conduct drop and vibration testing |
| Missing Components | Omission of parts in kits or assemblies | Implement kitting checklists; use barcode scanning; conduct final QC audit (AQL Level II) |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Engage Third-Party Inspection – Use AQL 2.5/4.0 for general goods; AQL 1.0 for medical or safety-critical items.
- Require Production Samples – Approve pre-production and bulk production samples before shipment.
- Verify Factory Credentials – Audit suppliers using checklists covering QMS, tooling, and capacity.
- Include Penalties in Contracts – Define liquidated damages for non-compliance or defect recalls.
- Leverage Digital QC Tools – Use platforms like SourcifyQC for real-time inspection reporting and traceability.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Optimizing Global Supply Chains from China
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guide: Navigating Chinese Wholesale Manufacturing Costs & Labeling Models
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Forecast
Executive Summary
China’s wholesale manufacturing ecosystem remains the cornerstone of global supply chains, but 2026 demands nuanced strategy due to rising labor costs (+6.2% YoY), material volatility, and heightened brand differentiation needs. This report clarifies White Label vs. Private Label pathways, provides transparent cost breakdowns, and delivers actionable MOQ-based pricing tiers. Critical insight: Private Label adoption is projected to grow 12% CAGR through 2026 as brands prioritize exclusivity over commoditization.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured generic products rebranded with buyer’s logo | Fully customized product (design, specs, packaging) under buyer’s brand | Private Label for brand equity; White Label for speed-to-market |
| Customization Level | Minimal (only packaging/logo) | High (materials, features, engineering) | 73% of SourcifyChina clients use Private Label for >50% of SKUs |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (factories set fixed MOQs) | Negotiable (based on R&D investment) | White Label MOQs typically 20-30% lower |
| Time-to-Market | 30-45 days | 90-120+ days (includes design validation) | Use White Label for pilot launches; shift to Private Label at scale |
| IP Ownership | Factory retains product IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Non-negotiable for Private Label: Secure IP assignment in contract |
💡 Key Trend: 68% of 2026 contracts now include hybrid models (e.g., Private Label core + White Label accessories) to balance speed and exclusivity.
Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Mid-Tier Consumer Electronics Example)
All costs reflect 2026 FOB China projections. Assumes standard materials (e.g., ABS plastic, basic PCB).
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Drivers & Trends | Risk Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 52-58% | • Rare earth metals +8.5% YoY • Recycled plastics premium (-3% vs. virgin) |
Dual-source critical components; lock prices via annual contracts |
| Labor | 18-22% | • Coastal avg. wage: ¥7,200/mo (+6.2% YoY) • Automation adoption cuts assembly labor by 15% |
Prioritize factories with >40% automation in target product category |
| Packaging | 9-12% | • Sustainable materials add 7-10% cost • Custom inserts +22% vs. standard |
Use modular packaging designs for multi-product reuse |
| QC & Compliance | 7-9% | • EU CBAM carbon tax adds 1.5-2.5% cost • Extended 3rd-party testing (e.g., SCS 007) |
Budget 8.5% for compliance; non-negotiable for EU/US markets |
| Logistics | 14-18% | • Ocean freight stabilized at $1,850/TEU (Shanghai-Rotterdam) | Consolidate orders to fill 85%+ of container volume |
⚠️ Critical Note: Total landed cost = FOB China price + 28-35% (logistics, duties, compliance). Always validate factory quotes against all-in landed cost.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: 2026 Forecast
Product Category: Mid-Range Bluetooth Speaker (Retail Value: $45-60)
| MOQ Tier | Unit Cost Range (FOB China) | Effective Markup vs. 5,000 Units | Strategic Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 – $22.75 | +38.5% | • Market testing • Niche/seasonal launches • Avoid for core SKUs |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 – $18.40 | +22.0% | • Regional expansion • Complementary product lines • Requires 3+ month buffer stock |
| 5,000 units | $12.45 – $14.90 | Base Cost | • Core product volume • Global distribution • Optimal for margin protection |
Key Cost Variables Impacting Tiers:
- Material Grade Swings: Food-grade silicone vs. standard rubber = +$0.85/unit at 5,000 MOQ.
- Labor Arbitrage: Inland factories (Sichuan) offer 9-12% lower labor costs vs. coastal (Guangdong).
- Packaging Complexity: 2-color print vs. 4-color + foil stamping = +$0.60/unit.
- Payment Terms: LC at sight adds 2.8% vs. 60-day TT (factored into tier pricing above).
SourcifyChina Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Demand Hybrid Quoting: Require factories to provide both White Label and Private Label cost models.
- MOQ Negotiation Levers: Offer 15% higher order volume for 10% lower unit cost (e.g., 5,500 units @ 5,000-unit pricing).
- Compliance Budgeting: Allocate 8.5% of FOB cost exclusively for 2026 regulatory shifts (CBAM, EPA rules).
- Dual Sourcing: Split MOQ between 2 factories (min. 30% with inland suppliers) to hedge labor/logistics risks.
“In 2026, the margin between success and failure lies not in chasing the lowest FOB price, but in engineering resilience into your cost structure.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, Q4 2025
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from 127 factory audits (Q3 2025), China Customs Statistics, and IMF Commodity Forecasts.
Disclaimer: Costs exclude import duties/taxes. All figures assume standard payment terms (30% deposit, 70% against B/L). Custom tooling costs not included.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Not for redistribution.
Elevate your sourcing strategy: sourcifychina.com/2026-cost-forecast
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Differentiate Factories from Trading Companies
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to diversify, China remains a cornerstone of cost-effective, high-volume manufacturing. However, the complexity of the Chinese wholesale market—populated by a mix of genuine factories, hybrid trading companies, and intermediaries—presents significant sourcing risks. This report outlines a structured, field-tested verification process to identify authentic manufacturers, distinguish them from trading companies, and mitigate procurement risks.
By following these steps, procurement managers can ensure supply chain integrity, avoid misrepresentation, and secure long-term, reliable partnerships.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in the Chinese Wholesale Market
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools & Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Verify Business Registration | Confirm legal existence and scope of operations | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Public System (NECIPS) via www.gsxt.gov.cn. Cross-check company name, registration number, capital, and business scope. |
| 1.2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Validate physical presence, production capacity, and operational scale | Schedule unannounced or third-party audits. Verify address via satellite imagery (Google Earth/Baidu Maps), and request live video walkthroughs. |
| 1.3 | Review Production Equipment & Capacity | Assess technical capability and scalability | Request equipment list, machine age, production line details, and monthly output. Compare with claimed MOQs and lead times. |
| 1.4 | Evaluate Workforce & Management Structure | Confirm operational maturity | Ask for org chart, number of direct employees (not subcontractors), and tenure of key staff (e.g., production manager). |
| 1.5 | Request Certifications & Compliance Documents | Ensure adherence to international standards | Verify ISO 9001, BSCI, SEDEX, or product-specific certifications (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS). Authenticate via certification body websites. |
| 1.6 | Check Export History & Client References | Validate international trade experience | Request past shipment records (via customs data platforms like ImportGenius or Panjiva), and contact 2–3 verified past clients. |
| 1.7 | Inspect Raw Material Sourcing & In-House Processes | Determine vertical integration | Ask for supplier lists, material traceability, and confirm which processes (e.g., molding, assembly, packaging) are performed in-house. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Factory and a Trading Company
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business Registration | Lists manufacturing as core activity (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “distribution” as primary activity |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases factory space; machinery registered under company name | No production equipment; office-only premises |
| Production Control | Direct oversight of production lines, QC, and engineering | Relies on third-party factories; limited technical input |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, competitive FOB pricing, may quote raw material costs | Higher margins; often vague on production costs or lead times |
| Communication | Engineers and production managers available for technical discussion | Sales reps only; deflects technical questions |
| Samples | Can produce custom samples in-house quickly | Delays in sample delivery; uses factory-produced samples |
| Lead Time | Precise production scheduling (e.g., “35 days after deposit”) | General timelines (e.g., “4–6 weeks”) |
| Export License | May or may not have one; focuses on domestic legal status | Typically has export license but may subcontract fulfillment |
Key Insight: Many Chinese suppliers operate as hybrid models (trading company with affiliated factory). While not inherently risky, transparency is critical. Always confirm if the quoted factory is owned, affiliated, or merely a partner.
3. Red Flags to Avoid in Chinese Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a video audit | Likely no physical factory or hides subcontracting | Disqualify or require third-party inspection |
| No verifiable business registration | High risk of fraud or shell company | Verify via NECIPS; reject if unverifiable |
| Inconsistent MOQs or pricing across quotes | Possible middlemen inflating costs | Request detailed cost breakdown and factory proof |
| Use of stock images or fake facility photos | Misrepresentation of capabilities | Conduct live video tour or on-site audit |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (e.g., 100% TT) | Cash-flow scam or lack of credibility | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| No direct contact with production team | Lack of control over quality and timelines | Insist on speaking with factory manager or engineer |
| Multiple companies with same address/contact | Front operations or fake entities | Cross-check business licenses and phone/email domains |
| Overly aggressive sales tactics or “limited-time offers” | Common in low-tier traders targeting inexperienced buyers | Maintain structured RFQ process; compare 3–5 vetted suppliers |
4. Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Use Third-Party Inspection Services: Engage firms like SGS, Bureau Veritas, or TÜV for pre-shipment and production monitoring.
- Start with a Trial Order: Test quality, communication, and reliability before scaling.
- Sign a Formal Manufacturing Agreement: Include IP protection, quality clauses, and audit rights.
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s Supplier Vetting Platform: Access pre-verified manufacturers with documented audits and performance histories.
Conclusion
The Chinese wholesale market offers unparalleled manufacturing potential—but only when sourced with due diligence. By systematically verifying supplier legitimacy, distinguishing true factories from intermediaries, and recognizing red flags early, procurement managers can de-risk sourcing and build resilient supply chains.
Recommendation: Integrate this verification framework into your supplier onboarding process and conduct annual reassessments for all China-based partners.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Integrity | China Sourcing Expertise
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina 2026 Strategic Sourcing Report: Optimizing Procurement in China’s Wholesale Market
To: Global Procurement Managers & Supply Chain Executives
Subject: Eliminate Sourcing Friction: Data-Driven Efficiency for China Wholesale Procurement in 2026
Executive Summary
The Chinese wholesale market remains a critical yet complex pillar of global supply chains in 2026. Persistent challenges—supplier opacity, quality inconsistencies, compliance risks, and time-intensive vetting—continue to erode procurement efficiency. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List directly addresses these pain points, delivering pre-qualified, audit-backed manufacturers and reducing sourcing cycles by 78% compared to traditional methods. This isn’t a directory; it’s your operational insurance for China procurement.
Why the Verified Pro List Outperforms Traditional Sourcing (2026 Data)
| Sourcing Method | Average Time to Qualified Supplier | Risk Exposure | Hidden Cost Drivers | 2026 Market Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Open Search (e.g., Alibaba, trade shows) | 8–12 weeks | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ High | Factory audits ($1,200–$3,500), sample rework, MOQ renegotiation, compliance failures | Low (Fragmented, opaque) |
| Generic “Verified” Platforms | 4–6 weeks | ⚠️⚠️ Medium | Inconsistent audit standards, language barriers, payment fraud risk | Declining (Rise of counterfeit certifications) |
| SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | < 2 weeks | ⚠️ Low | None (All costs transparent; audits included) | Critical (AI-verified, real-time compliance) |
Key Advantages Driving 2026 ROI:
- Time Saved = Capital Unlocked
- Reclaim 200+ hours annually per procurement specialist by bypassing unvetted supplier sifting.
- Direct access to ISO-certified factories with documented capacity, lead times, and export history.
- Risk Mitigation Embedded
- Every Pro List supplier undergoes:
- On-site factory audit (social compliance, production capability)
- Financial stability check
- 3-year export documentation review
- Real-time customs clearance validation
- 2026 Market Complexity Handled
- Navigate evolving regulations (e.g., China’s new ESG export mandates, tariff shifts) with suppliers already pre-compliant.
- Avoid “ghost factories” and middlemen—Pro List suppliers are direct manufacturers with ≥$500K annual export volume.
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Sourcing Advantage Today
Stop paying the hidden tax of inefficient procurement. Every week spent verifying unreliable suppliers delays time-to-market, inflates costs, and exposes your brand to preventable risk.
Your next strategic move is one step away:
✅ Immediate Access: Receive a customized Pro List segment (e.g., electronics, home goods, textiles) within 24 hours.
✅ Zero Obligation: Our sourcing consultants will map your requirements to pre-vetted suppliers—no commitment required.
✅ 2026 Readiness: Future-proof your supply chain against regulatory shifts and market volatility.
👉 Act Now:
– Email: Contact [email protected] with subject line “Pro List Request – [Your Industry]”
– WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent sourcing needs (24/7 multilingual support)
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 11 weeks to 9 days. In 2025, this saved us $220K in expedited freight and quality failures.”
— Global Procurement Director, Top 3 EU Home Goods Retailer
Don’t Outsource Risk—Outsource Certainty.
In 2026, speed without verification is strategic suicide. The Verified Pro List is the only sourcing tool engineered for both efficiency and resilience in China’s wholesale market. Contact us today to deploy your competitive advantage.
SourcifyChina
Your Partner in Precision Sourcing Since 2018
📍 Shanghai | Shenzhen | Global Remote Support
📧 [email protected] | 📱 +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp) | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.