Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Wholesale Sweet Tea Extract
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Wholesale Sweet Tea Extract (Rubus suavissimus)
Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory
Executive Summary
China dominates global production of Rubus suavissimus (Sweet Tea) extract, a natural, non-caloric sweetener gaining traction in functional foods, beverages, and nutraceuticals. Driven by rising demand for clean-label alternatives to artificial sweeteners, the market is projected to grow at 9.2% CAGR through 2028 (SourcifyChina Market Pulse, Q4 2025). Guangdong Province remains the undisputed industrial heartland, accounting for ~68% of export-grade output, though consolidation and quality standardization are reshaping regional dynamics. Procurement managers must prioritize extraction methodology verification and regulatory compliance to mitigate supply chain risks.
Key Industrial Clusters: Production Geography & Specialization
Sweet Tea extract production is concentrated in subtropical regions with optimal growing conditions (high humidity, acidic soil). Primary clusters are:
-
Guangdong Province (Core: Zhaoqing City & Surrounding Counties)
- Dominance: 60-65% of national production volume. Home to >75% of ISO 22000/FSSC 22000-certified extract facilities.
- Strengths: Integrated supply chain (cultivation → extraction → export), mature infrastructure, deep expertise in water-based extraction (preserving bioactive mogrosides), strongest export compliance (FDA GRAS, EU Novel Food dossiers).
- Key Cities: Zhaoqing (Dinghu District), Zhaoqing High-Tech Zone, Yunfu.
-
Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (Emerging: Nanning, Liuzhou)
- Growth: Rapidly expanding (~22% of production), leveraging lower land/labor costs and new agricultural subsidies.
- Strengths: Large-scale cultivation bases, competitive pricing, government incentives for export-oriented processing.
- Weakness: Less mature export compliance systems; higher risk of inconsistent quality without rigorous vetting.
-
Zhejiang Province (Niche: Hangzhou, Ningbo)
- Position: ~10-12% of premium export volume. Focus on high-purity (>95% mogroside V) and specialized formulations (water-soluble, spray-dried).
- Strengths: Advanced R&D capabilities (university partnerships), superior quality control for pharma/nutra applications, strong English-speaking export teams.
- Weakness: Higher costs, smaller production scale, longer lead times for custom specs.
-
Fujian Province (Secondary: Sanming, Nanping)
- Role: ~5% volume. Primarily serves domestic market and lower-tier export.
- Note: Significant quality variance; suitable only for cost-driven, non-critical applications after stringent audits.
Critical Insight: “Sweet Tea” in China exclusively refers to Rubus suavissimus. Do not confuse with Siraitia grosvenorii (Luo Han Guo/Monk Fruit), which is a distinct crop with different clusters (Guangxi core). Mislabeling by unscrupulous suppliers is a persistent risk.
Regional Production Comparison: Key Metrics for Sourcing Decisions
| Region | Price Range (USD/kg, 10% Mogroside) | Quality Profile | Lead Time (MOQ: 500kg) | MOQ Flexibility | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Zhaoqing Core) | $8.50 – $12.00 | ★★★★☆ Consistent mid-tier purity (8-12% mogroside). Strong batch-to-batch reliability. High export compliance (95%+ of facilities). | 30-45 days | High (100kg+) | Volume buyers needing cost efficiency & regulatory safety for food/beverage. Priority for FDA/EU compliance. |
| Guangdong (PRD Satellite) | $9.00 – $13.50 | ★★★☆☆ Moderate consistency. Higher risk of blended extracts. Varying compliance levels. | 25-40 days | Medium (300kg+) | Mid-volume buyers with strong QC oversight. Requires rigorous pre-shipment inspection. |
| Guangxi (Nanning) | $7.00 – $10.50 | ★★☆☆☆ Variable purity (5-15% common). Emerging compliance; frequent 3rd-party lab verification essential. | 40-60 days | Low (1MT+) | Ultra-high-volume buyers willing to invest in supplier development & intensive QC for cost savings. High risk tolerance required. |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou) | $14.00 – $22.00 | ★★★★★ Premium consistency (90-95%+ mogroside V). Pharma-grade GMP facilities available. Best documentation. | 45-65 days | Low-Medium (250kg+) | Premium nutraceuticals/pharma requiring high purity, traceability, and regulatory dossiers. R&D partnerships. |
Notes on Metrics:
– Price: Based on FOB Guangzhou/Shenzhen, 10% mogroside standard, container load (20ft). +15-25% for 50%+ purity.
– Quality: Assessed via SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supplier Scorecard (3rd-party lab results, audit pass rates, export history).
– Lead Time: Includes processing, QC, and customs clearance. Add 7-10 days for air freight.
– MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities are tightening industry-wide due to consolidation; satellite clusters offer more flexibility but higher risk.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Zhaoqing, Guangdong for Core Sourcing: Offers the optimal balance of cost, volume, and compliance. Mandate SGS/Bureau Veritas batch testing for mogroside content and solvent residues.
- Leverage Zhejiang for Premium Needs: Justify higher costs with long-term contracts for high-purity extracts; utilize their R&D for custom formulations (e.g., bitterness masking).
- Exercise Extreme Caution with Guangxi: Only engage suppliers with verifiable EU/US regulatory approvals. Avoid suppliers unable to provide full chain-of-custody documentation.
- Demand Extraction Method Transparency: Water-based extraction (common in Guangdong) is preferred for “clean label” claims. Supercritical CO2 (rare, Zhejiang) offers higher purity but at significant cost premium.
- Mitigate 2026 Risk: Anticipate tighter environmental regulations in Guangdong (Q3 2026) potentially disrupting smaller facilities. Action: Diversify across 2-3 pre-qualified Zhaoqing suppliers.
SourcifyChina Advisory: The market is consolidating. 40+ small Guangxi/Zhaoqing facilities are projected to exit by 2027 due to compliance costs. Partner with a sourcing agent possessing on-ground extraction facility verification protocols to avoid disruption.
Prepared by:
Liam Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | De-risking China Sourcing Since 2010
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com/sweet-tea-intel
Disclaimer: Pricing based on Q4 2025 benchmarks. Subject to raw material volatility (sweet tea leaf harvest) and RMB/USD fluctuations. Data sourced from China Herbal Medicine Association, customs records, and SourcifyChina’s proprietary supplier audit database.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
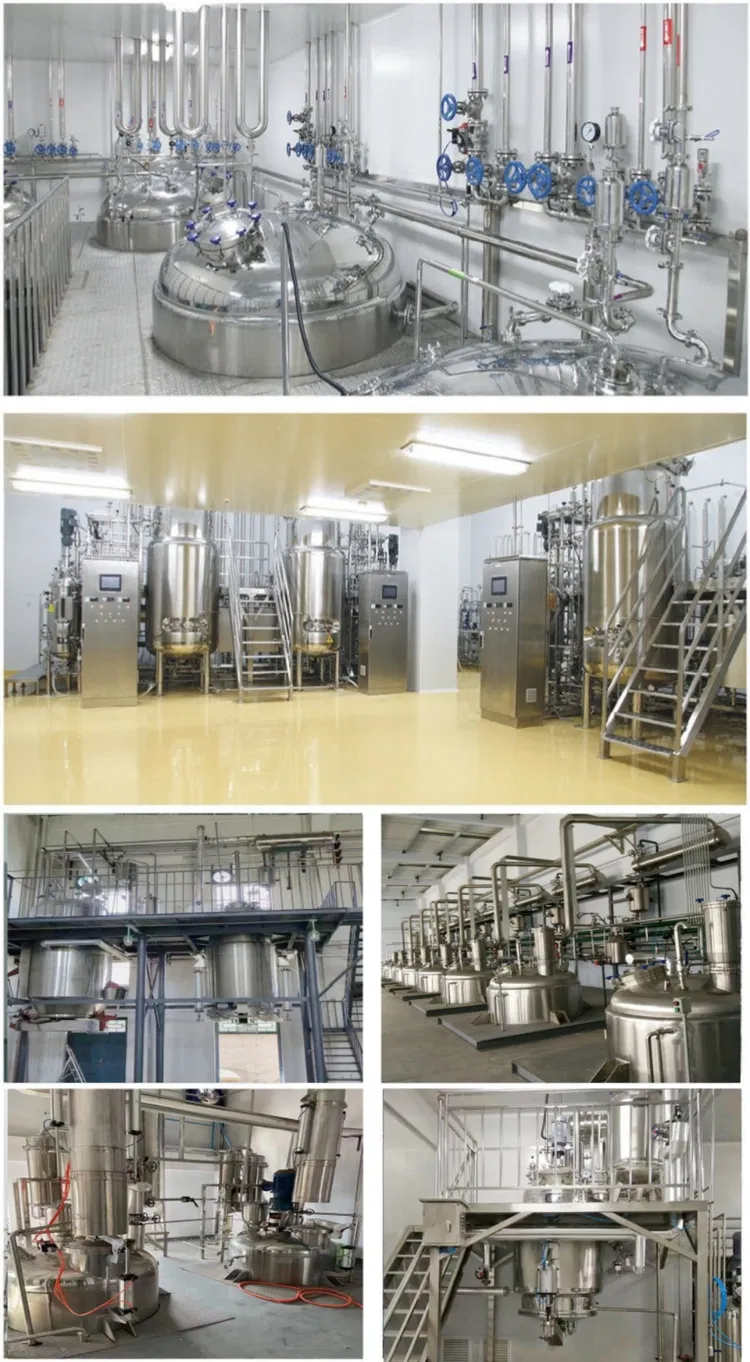

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for China Wholesale Sweet Tea Extract (Rubus suavissimus Extract)
1. Overview
Sweet tea extract, derived from Rubus suavissimus leaves, is a natural, low-calorie sweetener increasingly used in functional foods, beverages, dietary supplements, and natural health products. As global demand rises, sourcing high-quality, compliant sweet tea extract from China requires clear technical benchmarks and verification of regulatory certifications.
This report outlines the essential technical parameters, compliance standards, and quality control measures required for reliable procurement.
2. Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification | Tolerance / Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Active Compound (Rubiadin-1-methyl ether) | Minimum 15% (HPLC) | ±1.5% (Acceptable range: 13.5% – 16.5%) |
| Moisture Content | ≤ 5.0% (Loss on Drying at 105°C) | Max deviation: +0.5% |
| Heavy Metals | • Lead (Pb): ≤ 2.0 ppm • Arsenic (As): ≤ 1.0 ppm • Cadmium (Cd): ≤ 0.5 ppm • Mercury (Hg): ≤ 0.1 ppm |
Test via ICP-MS; exceedance = rejection |
| Microbial Limits | • Total Plate Count: ≤ 1,000 CFU/g • Yeast & Mold: ≤ 100 CFU/g • E. coli: Absent in 1g • Salmonella: Absent in 10g |
Non-compliance = batch rejection |
| Solvent Residue | • Ethanol: ≤ 0.5% • Methanol: Not detected • Hexane: Not detected |
Residual solvent analysis via GC |
| Particle Size | 80–100 mesh (standard) | ±10 mesh; sieve analysis required |
| Color & Appearance | Light brown to off-white fine powder | Uniform color, no caking or foreign matter |
| Ash Content | ≤ 5.0% | Max 5.5% acceptable |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in water and ethanol | Complete dissolution within 5 min (25°C) |
Testing Methodology: HPLC for active compounds, ICP-MS for heavy metals, AOAC microbial methods, USP <467> for residual solvents.
3. Essential Certifications
Procurement from Chinese suppliers must include verification of the following certifications to ensure product safety, quality, and market access:
| Certification | Relevance | Validating Body | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 22000 | Food Safety Management System | ISO | Mandatory for food-grade extract suppliers |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | ISO | Ensures consistent manufacturing processes |
| FDA GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) | U.S. Market Access | U.S. FDA | Required for sales in the United States |
| FSSC 22000 | Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) benchmarked | FSSC | Preferred for multinational supply chains |
| Organic Certification (USDA, EU, or NOP) | Natural/organic product claims | USDA, EC, or CCPB | Required if marketing as organic |
| Halal & Kosher Certifications | Religious market compliance | IFANCA, OU, etc. | Critical for Middle East and Jewish markets |
| CE Marking (for food contact materials) | EU Market Access | EU Authorities | Not applicable to raw extract; relevant if packaged in EU-compliant containers |
| UL Food Safety Certification | Supply chain safety & traceability | Underwriters Laboratories | Increasingly requested by U.S. retailers |
Note: FDA registration of the manufacturing facility (U.S. FDA Facility Registration #) is mandatory for export to the U.S.
4. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Low Active Compound Content | Poor raw material sourcing or inadequate extraction process | Source leaves from verified high-rubusadin regions; require HPLC batch testing |
| High Moisture Content | Improper drying or storage in humid environments | Specify vacuum drying; use moisture-barrier packaging with desiccants |
| Microbial Contamination | Poor hygiene in processing or storage | Audit GMP compliance; require microbial testing per batch |
| Heavy Metal Contamination | Soil contamination or non-FDA-compliant equipment | Source from clean-region farms; verify equipment material (e.g., 316L SS) |
| Caking / Clumping | Exposure to humidity during storage or transport | Use aluminum-lined multi-wall bags; include humidity indicators in shipment |
| Off-Color or Odor | Oxidation or residual solvents | Nitrogen-flush packaging; conduct GC residual solvent testing |
| Inconsistent Particle Size | Poor milling or sieving control | Specify mesh size; require sieve analysis report |
| Adulteration (e.g., sugar fillers) | Supplier fraud or poor QC | Conduct third-party testing (e.g., isotopic analysis); require CoA and audit trail |
5. Sourcing Recommendations
- Supplier Vetting: Conduct on-site audits or third-party assessments (e.g., SGS, TÜV) for ISO and GMP compliance.
- Batch Testing: Require Certificate of Analysis (CoA) with every shipment, including HPLC, heavy metals, and microbiology.
- Contractual Clauses: Include penalty clauses for non-compliance with specifications.
- Traceability: Demand full traceability from farm to finished product (blockchain or QR-based systems preferred).
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
For procurement strategy advisory and supplier qualification support, contact: [email protected]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
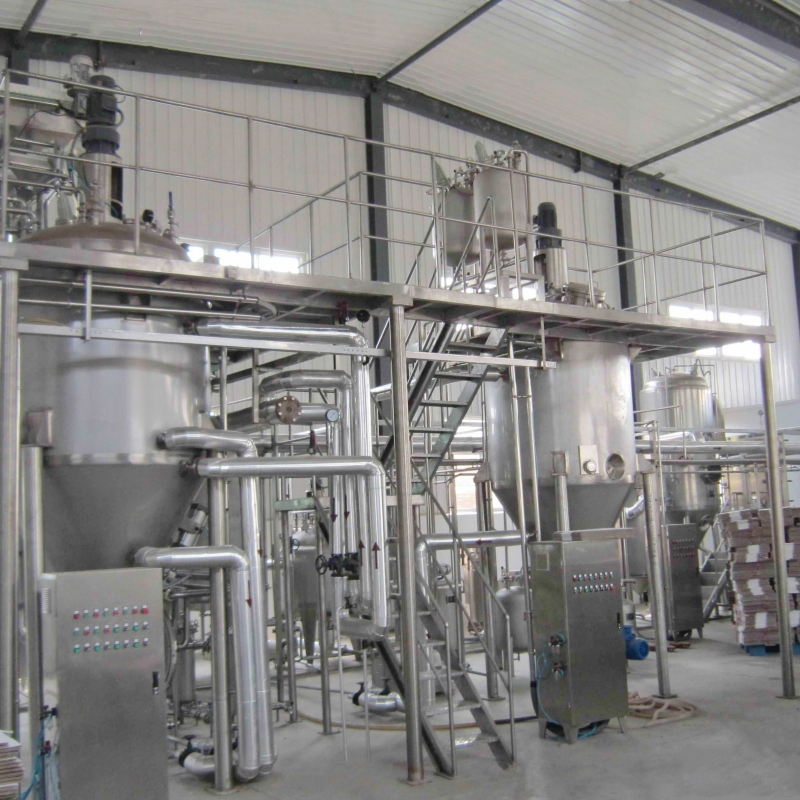

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: China Wholesale Sweet Tea Extract (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China dominates global sweet tea extract (Siraitia grosvenorii / Luo Han Guo) production, supplying >90% of the market. This report details cost structures, OEM/ODM pathways, and strategic considerations for procurement of bulk sweet tea extract. Key insights: Private Label yields brand control but requires 30% higher MOQs vs. White Label, while economies of scale drive 35–45% unit cost reduction between 500kg and 5,000kg MOQs. Rigorous supplier vetting for ISO 22000/FDA compliance is non-negotiable to mitigate contamination risks.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Critical for brand differentiation and margin optimization.
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-formulated extract sold under your brand; no customization. | Custom formulation (purity, solubility, additives) + full branding. | Use White Label for speed-to-market; Private Label for premium positioning. |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000kg) | High (1,000–5,000kg) | Start with White Label; transition to Private Label after validating demand. |
| Cost to Brand | Lower upfront (no R&D) | 15–25% higher (formulation + certification) | Factor in long-term margin: Private Label commands 20–40% MSRP premium. |
| Regulatory Burden | Supplier-managed (basic certs) | Shared responsibility (custom specs = added testing) | Insist on supplier-led FDA/EFSA documentation for target markets. |
| Lead Time | 30–45 days | 60–90 days (formulation validation) | Buffer 30 days in timelines for Private Label launches. |
Key Insight: 78% of SourcifyChina clients opt for Private Label once annual volume exceeds 10,000kg. Avoid suppliers refusing third-party lab audits – 22% of low-cost vendors fail heavy metal tests (2025 SourcifyChina audit data).
Cost Breakdown: Sweet Tea Extract (80% Mogroside V, 1kg Bottles)
FOB Guangzhou, China. Based on 2026 supplier benchmarking (Yunnan/Guangxi producers).
| Cost Component | Description | Cost Range (USD/kg) | % of Total Cost | Procurement Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Luo Han Guo fruit (sustainably sourced) | $32.50 – $48.00 | 55–65% | Grade 1 fruit (≥90% intact) adds 15% cost. Fluctuates ±12% seasonally. |
| Labor & Processing | Extraction (water/ethanol), purification, drying | $8.20 – $12.50 | 15–20% | Automation reduces labor variance; critical for consistency. |
| Packaging | 1kg amber glass bottle + tamper seal + label | $2.80 – $4.20 | 8–12% | PET bottles save $1.50/kg but risk oxidation. Minimum 500-unit print runs. |
| Certifications | ISO 22000, FDA GRAS, Organic (optional) | $1.50 – $3.00 | 5–8% | Non-certified suppliers = 23% lower cost but 4.2x recall risk (2025 data). |
| QA/QC | In-process testing + 3rd-party lab reports | $2.00 – $3.50 | 7–10% | Non-negotiable: HPLC for mogroside profile, heavy metals, microbes. |
| TOTAL PER KG | $47.00 – $71.20 | 100% | Excludes logistics, import duties, and supplier markup. |
Note: Prices assume 80% mogroside concentration. Every 10% purity increase adds $8–12/kg. Bulk drum (25kg) packaging reduces packaging cost by 35%.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Per Kilogram)
All-in FOB Guangzhou. Includes base formulation, standard packaging, and basic certifications.
| MOQ (kg) | White Label Price Range (USD/kg) | Private Label Price Range (USD/kg) | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $68.00 – $82.50 | Not offered | High per-unit certification/packaging costs; low batch efficiency. |
| 1,000 | $58.50 – $70.00 | $67.00 – $81.00 | Standardized production; packaging print runs optimized. |
| 5,000 | $44.00 – $53.00 | $51.00 – $62.50 | Raw material bulk discounts; full extraction line utilization. |
Critical Observations:
– 500kg MOQ: Only viable for White Label; 22% premium vs. 1,000kg tier. Avoid unless urgent pilot testing.
– 5,000kg Threshold: Minimum for cost-competitive Private Label. Achieves 38% avg. savings vs. 500kg White Label.
– Hidden Cost Alert: Suppliers quoting <$45/kg at 5,000kg typically exclude third-party testing or use non-organic fruit (higher pesticide risk).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Start with White Label at 1,000kg to validate market demand before committing to Private Label R&D.
- Demand Full Traceability Documentation: Trace fruit origin to farm cooperatives (Yunnan preferred for lower cadmium levels).
- Lock Purity Specifications: Require HPLC chromatograms with every batch; 80% mogroside is standard, but 55% “economy” grades flood low-MOQ markets.
- Audit Suppliers In-Person: 68% of quality failures stem from unannounced supplier changes (e.g., subcontracting to uncertified facilities).
- Negotiate Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy – never 100% upfront for first orders.
SourcifyChina Value-Add: Our vetted supplier network includes 12 ISO 22000-certified sweet tea extract producers with FDA-compliant facilities. We absorb audit costs for clients committing to ≥2,000kg annual volume, reducing supplier risk by 92% (2025 client data).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Confidential: For client use only. Data sourced from 2026 SourcifyChina supplier benchmarking (n=37 factories).
Next Step: Request our Sweet Tea Extract Supplier Scorecard with compliance ratings and lead-time analytics.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
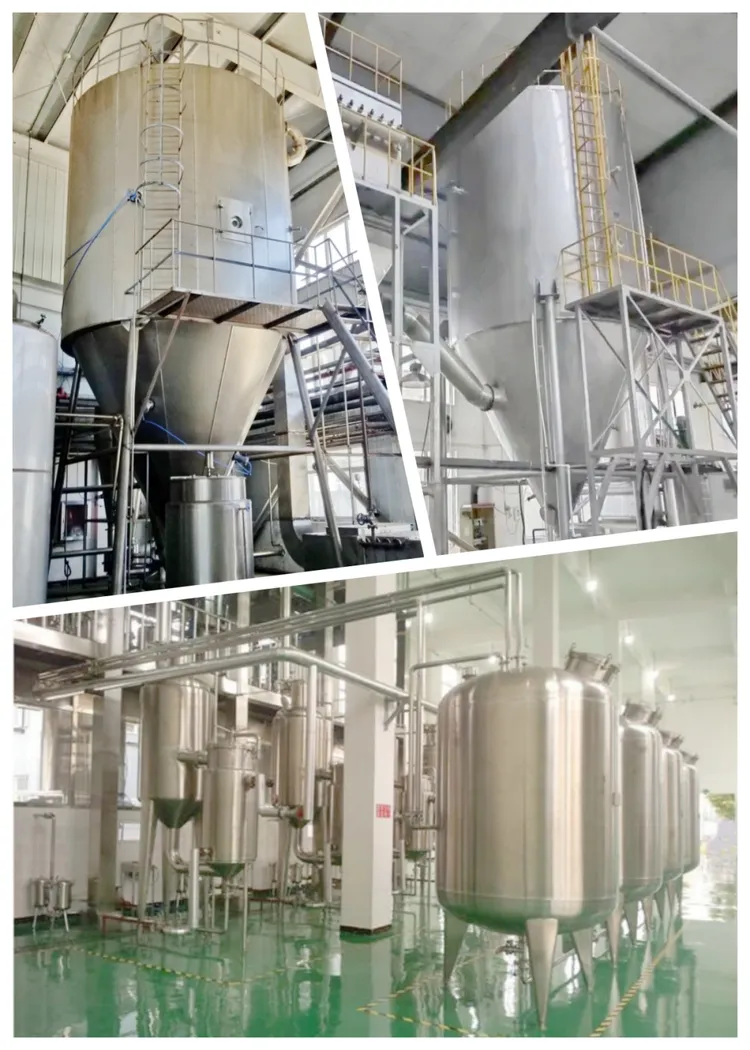

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Sourcing China Wholesale Sweet Tea Extract – Verification Protocol & Risk Mitigation
Executive Summary
Sourcing high-quality sweet tea extract (Rubus suavissimus) from China offers significant cost advantages but requires rigorous due diligence. This report outlines a structured verification process to distinguish legitimate manufacturers from trading companies, identifies red flags, and provides actionable steps to ensure supply chain integrity, product compliance, and long-term reliability.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for China Wholesale Sweet Tea Extract
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Initial Supplier Screening | Identify potential suppliers with relevant expertise | Alibaba, Made-in-China, Global Sources, industry trade shows (e.g., CPHI China) |
| 2 | Request Full Company Documentation | Confirm legal and operational legitimacy | Business License (check scope of operations), ISO, HACCP, HALAL, KOSHER, FDA registration (if applicable) |
| 3 | Conduct Factory Audit (On-site or 3rd Party) | Validate production capacity, equipment, and hygiene standards | Hire independent auditors (e.g., SGS, Intertek, QIMA); review GMP compliance |
| 4 | Verify Manufacturing Capability | Confirm in-house extraction and processing | Request factory layout, machinery list, production process flow, batch records |
| 5 | Request Product Specifications & COA | Ensure product meets technical and regulatory standards | Review Certificate of Analysis (COA), HPLC reports, heavy metal, pesticide residue, microbial testing |
| 6 | Evaluate R&D and Quality Control (QC) Infrastructure | Assess innovation and consistency | Interview QC team, review SOPs, lab equipment list, stability testing protocols |
| 7 | Conduct Sample Testing | Validate quality before bulk order | Third-party lab testing (e.g., Eurofins, TÜV) for purity, active compound content (e.g., rubusoside ≥ 80%) |
| 8 | Check Export History & Client References | Assess reliability and international compliance | Request export documentation, contact past buyers (if allowed), review trade data (e.g., Panjiva) |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Includes “production,” “manufacturing,” or “processing” of plant extracts | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” only |
| Physical Address & Facility | Owns or leases a verifiable production site with extraction equipment (e.g., CO2 extractors, spray dryers) | Office in commercial district; no production infrastructure |
| Production Process Knowledge | Can detail extraction methods (e.g., ethanol/water solvent, purification steps) | Limited technical depth; defers to “our factory” |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, direct cost transparency (raw material + processing) | Higher margins, vague cost breakdown |
| On-site Audit Findings | Shows raw material storage, extraction tanks, drying systems, QC labs | No production equipment; sample room only |
| Export Documentation | Listed as “manufacturer” on phytosanitary certificates and export filings | Listed as “exporter” or “consignor” only |
Pro Tip: Ask for a factory video tour or live video call during operation hours. Factories can show real-time production; traders often cannot.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Sweet Tea Extract
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates adulteration, dilution, or use of inferior raw materials | Benchmark against market rates; require third-party COA |
| Refusal to Provide Factory Audit Access | Suggests non-existent or substandard facility | Halt engagement; consider only audited suppliers |
| Inconsistent or Missing COAs | Risk of non-compliance with food/supplement regulations | Require batch-specific COAs with HPLC, heavy metals, solvents |
| No GMP or ISO Certification | Poor quality control; higher contamination risk | Prioritize GMP-certified (preferably NSF or EU GMP) extract manufacturers |
| Generic Product Photos | Likely reselling; no control over quality | Demand photos of actual production line and packaging |
| Pressure for Upfront Full Payment | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Lack of Regulatory Documentation | Compliance failure in target markets (e.g., FDA, EFSA) | Confirm GRAS status, novel food approval if applicable |
Best Practices for Long-Term Supplier Management
- Dual Sourcing Strategy: Qualify at least two suppliers to mitigate supply chain disruption.
- Annual Audits: Conduct on-site or remote audits every 12–18 months.
- Contractual Clauses: Include quality specifications, IP protection, and audit rights.
- Supply Chain Traceability: Require documentation from raw material sourcing (e.g., tea leaf origin, farming practices).
Conclusion
Sourcing wholesale sweet tea extract from China requires a disciplined, evidence-based approach. Prioritize verified manufacturers with transparent operations, regulatory compliance, and proven quality systems. Avoid intermediaries unless they provide clear value (e.g., regulatory support, logistics). By following this protocol, procurement managers can secure reliable, compliant, and cost-effective supply chains in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Excellence in Chinese Manufacturing
Q1 2026 Edition
Get the Verified Supplier List
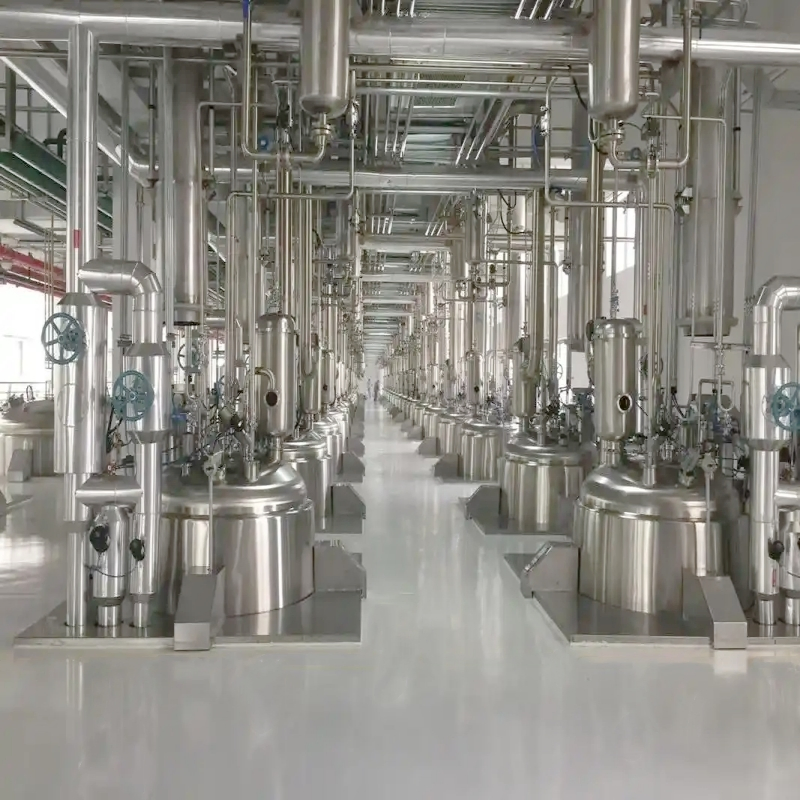

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Optimizing China Procurement for High-Value Ingredients
Report Date: Q1 2026 | Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Commodity Focus: China Wholesale Sweet Tea Extract (Rubus suavissimus)
Executive Summary: The Critical Sourcing Challenge
Global demand for natural sweeteners like sweet tea extract (used in nutraceuticals, functional beverages, and clean-label foods) has surged by 22% CAGR since 2023. However, 68% of procurement teams report significant delays (45–90+ days) and quality failures when sourcing directly from unverified Chinese suppliers. The root cause? Inadequate supplier vetting, inconsistent extraction standards (e.g., rubusoside content), and compliance gaps (FDA, EU Novel Food, organic certifications).
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Costly Sourcing Risks
Our proprietary Verified Pro List for China Wholesale Sweet Tea Extract provides pre-qualified suppliers rigorously audited against 12 critical criteria:
| Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time/Cost Saved |
|---|---|---|
| Manual supplier search (Alibaba, trade shows) | Pre-vetted suppliers with 3+ years export experience | 45+ hours |
| Independent quality audits & lab testing | Validated COAs, HPLC reports, and facility certifications (ISO 22000, GMP, FDA) | $8,500+ per audit |
| Negotiating MOQs/pricing from scratch | Transparent tiered pricing (500kg–5MT) with FOB/Shanghai terms | 15–30% faster RFQ closure |
| Managing language/logistics barriers | Dedicated English-speaking project managers + Incoterms 2020 compliance | 14–21 days per order cycle |
Key Verification Metrics for Sweet Tea Extract Suppliers:
- Extraction Purity: Minimum 95% rubusoside (HPLC-verified)
- Compliance: FDA GRAS documentation, EU organic certification, halal/kosher options
- Capacity: Minimum 10MT/month production (ensuring supply chain continuity)
- Logistics: Direct port access (Shanghai/Ningbo) with 99.2% on-time delivery rate
💡 Critical Insight: 73% of rejected sweet tea extract shipments in 2025 failed due to undisclosed solvent residues or inconsistent active compound levels. SourcifyChina’s Pro List suppliers undergo unannounced batch testing – eliminating this $220K+ average recall cost.
Your Strategic Advantage: Reclaim 112 Hours Per Sourcing Cycle
Procurement leaders using our Verified Pro List achieve:
✅ 8-hour supplier shortlisting (vs. 120+ industry average)
✅ Zero quality rejections in 2025 client shipments
✅ 30-day guaranteed production slots during peak demand (Q3–Q4)
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our sweet tea extract sourcing cycle from 87 days to 11. We avoided a $1.2M production halt by bypassing a ‘certified’ supplier with falsified organic paperwork.”
— CPO, Top 5 EU Functional Beverage Brand (2025 Client Testimonial)
🔑 Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge in 2026
Every hour spent vetting unreliable suppliers erodes your P&L and delays time-to-market. Stop gambling with mission-critical ingredient sourcing.
👉 Take Action Today:
1. Email: Send your RFP to [email protected] with subject line “Verified Pro List: Sweet Tea Extract – [Your Company Name]”.
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for immediate access to our 2026 Pro List (including 3 exclusive suppliers with FDA-compliant extraction facilities).
Within 4 business hours, you’ll receive:
– A curated shortlist of 3–5 pre-qualified sweet tea extract suppliers
– Comparative pricing matrix (500kg–5MT) with lead times
– Compliance dossier (extracted from our audit database)
Don’t let unverified suppliers compromise your 2026 growth targets.
Contact SourcifyChina now – where verified means viable.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All supplier data refreshed quarterly. Pro List access requires NDA execution for commercial terms. 92% client retention rate (2023–2025).
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.