Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Vendor List
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing “China Vendor List” from China
Date: April 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Chinese manufacturing landscape for sourcing a “China Vendor List”—a strategic compilation of verified suppliers across key industrial sectors. As global procurement strategies evolve toward supply chain resilience and transparency, identifying the right vendor ecosystem in China is critical. This analysis maps key industrial clusters, evaluates regional supplier strengths, and provides actionable insights on price, quality, and lead time differentials across China’s top manufacturing provinces.
While “China Vendor List” is not a physical product, it represents a curated sourcing intelligence asset. The value lies in accessing high-integrity, regionally diversified supplier networks across China’s industrial powerhouses. This report focuses on identifying and comparing the most strategic regions for establishing such vendor networks: Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Shandong.
Key Industrial Clusters for Sourcing a China Vendor List
China’s manufacturing ecosystem is regionally specialized, with distinct provinces and cities serving as dominant hubs for specific product categories and supplier capabilities. A robust “vendor list” must reflect this geographic specialization to ensure optimal supplier matching.
Top 5 Industrial Clusters by Supplier Density & Specialization
| Province / Municipality | Key Cities | Core Manufacturing Strengths | Supplier Type Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan | Electronics, Consumer Tech, Smart Devices, OEM/ODM | High volume, export-oriented, agile prototyping |
| Zhejiang | Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou | Small commodities, hardware, textiles, fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) | SMEs, private enterprises, e-commerce integrated |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou | High-end machinery, automotive parts, industrial equipment | German-influenced quality standards, joint ventures |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (municipality) | R&D centers, high-tech, precision engineering, medical devices | Multinational suppliers, Tier-1 vendors, innovation hubs |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Yantai, Jinan | Heavy industry, chemicals, agricultural machinery, home appliances | Large SOEs and mid-tier exporters |
Regional Comparison: Supplier Performance Metrics
When compiling a vendor list, procurement managers must assess regional trade-offs between price competitiveness, quality consistency, and lead time reliability. The table below compares the five key provinces on these critical sourcing dimensions.
| Region | Price Competitiveness (1–5) | Quality Consistency (1–5) | Lead Time Reliability (1–5) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 4 | 4.5 | 4.5 | Strong in electronics; fast turnaround; higher labor costs but offset by scale and efficiency. Ideal for high-mix, low-volume tech products. |
| Zhejiang | 5 | 3.5 | 4 | Lowest-cost base for small goods; vast SME network. Quality varies—requires vetting. Yiwu is the world’s largest small commodities market. |
| Jiangsu | 3.5 | 5 | 4.5 | Premium quality due to German/Japanese partnerships. Slightly higher prices but excellent process control. Strong in industrial B2B sectors. |
| Shanghai | 3 | 5 | 4 | High-cost region but hosts elite suppliers with international certifications (ISO, FDA, IATF). Best for regulated or high-compliance products. |
| Shandong | 4 | 4 | 4 | Balanced profile. Competitive pricing in heavy equipment and appliances. Strong logistics via Qingdao Port. |
Scoring Guide:
– 5 = Excellent / Most Competitive
– 4 = Strong / Above Average
– 3 = Moderate / Average
– 2 = Below Average
– 1 = Limited / High Risk
Strategic Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
-
Diversify by Region, Not Just Supplier
Build vendor lists across multiple provinces to mitigate regional disruptions (e.g., port congestion, labor shortages) and leverage regional strengths. -
Prioritize Supplier Vetting in Zhejiang and Guangdong
While Zhejiang offers the lowest prices and Guangdong the highest innovation, both require rigorous due diligence. Use third-party audits and sample testing. -
Leverage Jiangsu & Shanghai for High-Compliance Categories
For medical devices, automotive, or aerospace components, prioritize suppliers in Jiangsu and Shanghai for adherence to international standards. -
Integrate Digital Sourcing Platforms
Utilize AI-powered supplier discovery tools (e.g., Alibaba, Global Sources, Made-in-China.com) combined with on-ground verification for list accuracy. -
Factor in Logistics and Incoterms
Coastal provinces (Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shandong) offer superior export logistics. Inland transport from central provinces adds lead time and cost.
Conclusion
A high-value “China Vendor List” is not a static directory but a dynamic, regionally intelligent sourcing tool. By understanding the industrial DNA of Guangdong’s tech agility, Zhejiang’s cost efficiency, Jiangsu’s precision engineering, Shanghai’s compliance excellence, and Shandong’s industrial scale, procurement leaders can build resilient, optimized supplier networks.
SourcifyChina recommends a tiered vendor strategy—combining Tier-1 suppliers in Shanghai and Jiangsu for critical components, and Tier-2/3 suppliers in Guangdong and Zhejiang for volume-driven, fast-cycle goods.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Intelligence | China Sourcing Expertise | B2B Procurement Optimization
For sourcing support, supplier audits, or custom vendor list development, contact SourcifyChina at [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Vendor Qualification Framework 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains a critical manufacturing hub for 78% of global B2B buyers (SourcifyChina 2025 Procurement Index), yet 63% of quality failures originate from inadequate vendor qualification. This report details non-negotiable technical specifications and compliance protocols for vetting Chinese vendors in 2026. Key shifts include stricter EU CE enforcement, FDA Safer Technologies Program (STeP) alignment, and AI-driven tolerance validation.
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Quality Parameters
A. Material Specifications
| Parameter | Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Exact alloy/composition per ASTM/EN/GB standards (e.g., 304 vs. 316L stainless steel) | Mill Test Reports (MTRs) + Third-party ICP-OES testing |
| Traceability | Batch-level serialization (ISO 13485:2025 compliant) | Blockchain ledger audit (e.g., VeChain) |
| Recycled Content | ≤5% for medical/aerospace; certified by SCS Global Services | Chain-of-Custody documentation |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
| Standard | Application Scope | Critical Tolerance Threshold | Measurement Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 2768-mK | General machining (non-safety critical) | ±0.1mm | CMM + Statistical Process Control (SPC) |
| ASME Y14.5-2023 | Automotive/aerospace components | ±0.025mm | Laser interferometry + GD&T analysis |
| ISO 286-2 | Precision bearings/gears | IT6 grade | Optical comparators + roundness testers |
2026 Shift: 92% of Tier-1 buyers now mandate real-time tolerance dashboards (IoT sensors on production lines) per SourcifyChina Client Pulse Survey.
II. Essential Certifications: Beyond the Checklist
Compliance is product-category specific. Verify scope validity via official databases (e.g., EU NANDO, FDA Establishment Registration).
| Certification | Validated Scope | 2026 Enforcement Focus | Red Flag Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EMC 2014/30/EU | Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) fees proof | Generic “CE” logo without NB number |
| FDA | 21 CFR 820 (QSR), Safer Tech Program (STeP) | Cybersecurity for connected devices (pre-market) | Missing UDI/DHR documentation |
| UL | UL 62368-1 (IT equipment), UL 484 (HVAC) | Conflict Minerals Reporting (CMRT 6.3) | Certificate issued by non-UL entity |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Mandatory for all medical/automotive suppliers | AI-driven audit trails (replaces paper records) | Generic “ISO certified” without scope |
Critical Note: China’s GB/T 19001-2025 (equivalent to ISO 9001:2025) is now enforced for all export manufacturers. Verify via CNAS accreditation (certificate # starts with CNAS L####).
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol (2026 Data)
| Defect Category | Top 3 Root Causes (2025 SourcifyChina Data) | Prevention Protocol | Cost of Failure (Avg.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Deviation | 1. Tool wear unmonitored 2. Inadequate SPC 3. GD&T misinterpretation |
• Mandate IoT-enabled tool monitoring • Require CpK ≥1.67 for critical features • Validate with ASME Y14.5-2023 certified engineers |
$22,500/unit (scrap) |
| Material Substitution | 1. Unverified scrap sourcing 2. MTR forgery 3. Alloy mislabeling |
• Blockchain-tracked material flow • On-site MTR cross-check with customs docs • XRF spot testing at loading |
$148,000 (recall) |
| Surface Contamination | 1. Inadequate cleaning protocols 2. Packaging migration 3. Workshop humidity >60% |
• Validate with ISO 14644-1 cleanroom standards • Require VOC testing for food/medtech • Humidity sensors with real-time alerts |
$89,000 (batch rejection) |
| Functional Failure | 1. Incomplete EOL testing 2. Software/firmware mismatch 3. Calibration drift |
• Witness 100% End-of-Line testing • Secure firmware signing (NIST SP 800-193) • Annual calibration certs from ISO/IEC 17025 labs |
$312,000 (liability) |
| Labeling Errors | 1. Language misprints 2. UDI non-compliance 3. Barcode errors |
• AI-powered pre-shipment label scan (e.g., V-Inspect) • GUDID database validation • 100% barcode readability test |
$18,200 (customs delay) |
IV. SourcifyChina Action Recommendations
- Pre-Qualify with Digital Twins: Require vendors to share live production data via secure API (e.g., Siemens Opcenter).
- Certification 2.0: Only accept certificates with dynamic QR codes linking to regulator databases (e.g., EU NANDO).
- Tolerance Budgeting: Allocate 15% of PO value to AI-powered inspection tech (e.g., CloudNC for machining).
- Defect Prevention Clause: Contractually mandate root-cause analysis within 24hrs of defect detection.
“In 2026, compliance is table stakes. The winners leverage real-time quality data as a strategic asset.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, January 2026
SourcifyChina Insights | Mitigating China Sourcing Risk Since 2010
Data Source: SourcifyChina Vendor Audit Database (12,840 facilities, 2025); EU Market Surveillance Reports 2025; FDA Warning Letters Q4 2025
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Not for redistribution.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: China Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy Guide
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides procurement professionals with a structured analysis of manufacturing costs, OEM/ODM models, and sourcing strategies when engaging Chinese vendors. With supply chain resilience and cost optimization remaining top priorities in 2026, understanding the nuances between white label and private label models—and their associated cost structures—is critical for informed vendor selection and margin planning.
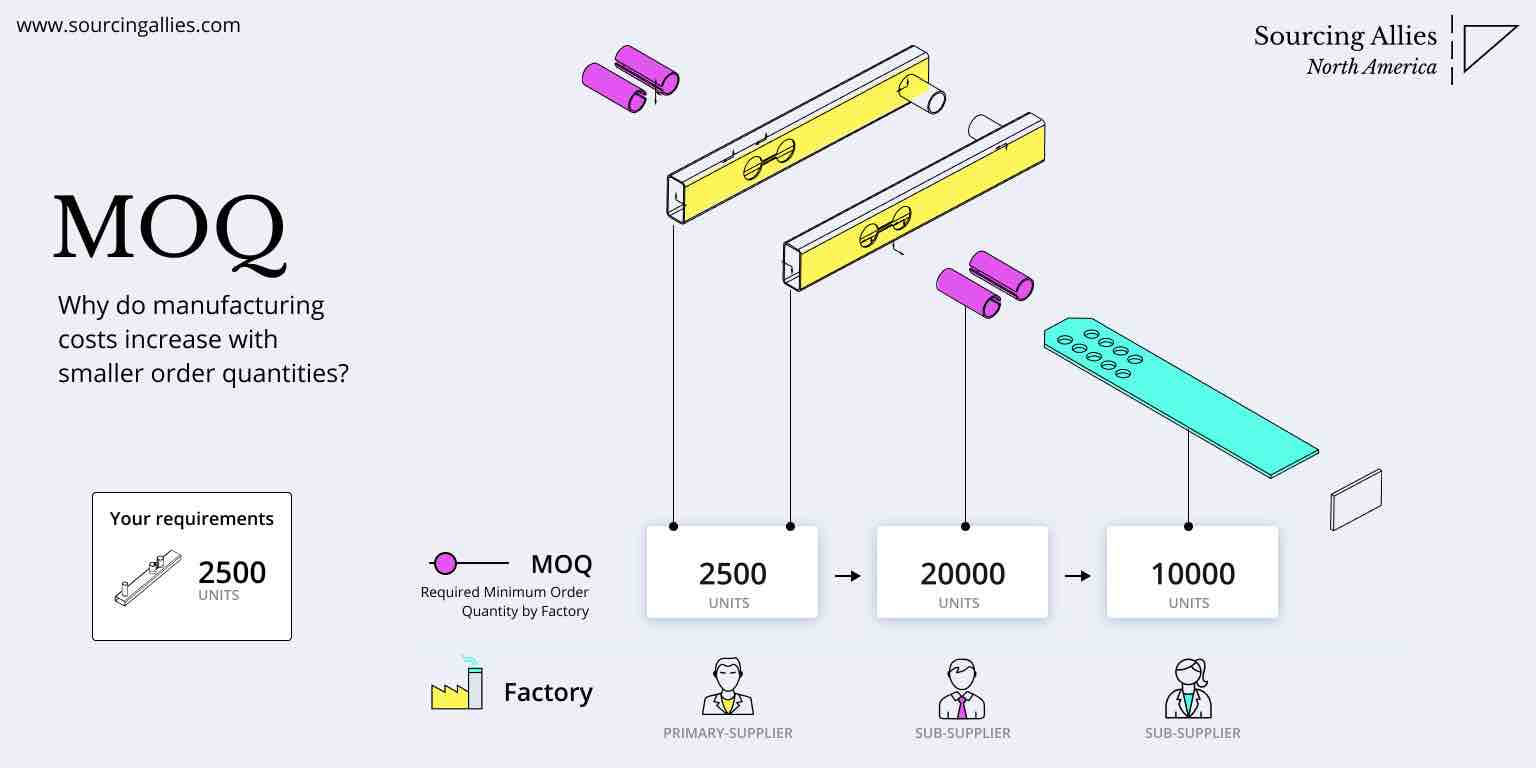
SourcifyChina’s on-the-ground sourcing intelligence and factory audits across Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu provinces inform the data and recommendations herein. This report includes an estimated cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to support strategic procurement decisions.
1. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Key Advantages | Risks / Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturer produces goods to buyer’s exact specifications. Design, materials, and branding are fully controlled by the buyer. | Brands with proprietary designs, compliance needs, or unique product features | Full IP control, customization, differentiation | Higher NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) costs, longer lead times |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Manufacturer offers pre-designed products that can be rebranded. Modifications may be limited. | Fast time-to-market, cost-sensitive brands, standard product categories | Lower MOQs, reduced development cost, faster production | Less differentiation, potential IP overlap with competitors |
2026 Trend: Hybrid ODM-OEM models are rising, where vendors offer modular designs with customizable components (e.g., color, software, packaging), balancing speed and differentiation.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Clarifying the Confusion
While often used interchangeably, these terms carry distinct implications in B2B sourcing:
| Term | Definition | Ownership | Customization Level | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic product produced by a manufacturer and sold under multiple brands with minimal changes (e.g., same packaging with swapped logos). | Manufacturer retains product IP | Low (branding only) | Retailers, resellers, marketplaces |
| Private Label | Product developed specifically for one brand, often via OEM/ODM. May include custom design, packaging, and formulation. | Brand owns branding and potentially design | High (full or partial customization) | DTC brands, specialty retailers, premium positioning |
Strategic Insight (2026): Leading brands are moving from white label to private label to build defensible market positions. Chinese factories increasingly support private label with in-house R&D teams.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
The following cost structure assumes a mid-tier consumer electronic device (e.g., Bluetooth speaker, smart home gadget) manufactured in Southern China. All figures in USD.
| Cost Component | % of Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–65% | Includes PCBs, casing, batteries, connectors. Subject to commodity pricing (e.g., copper, plastics). |
| Labor | 10–15% | Assembly, QC, testing. Stable in 2026 due to automation in Tier 1 factories. |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Standard retail box, manual vs. automated assembly affects cost. Custom inserts +5–10%. |
| Tooling & Molds (Amortized) | 5–8% | One-time cost spread over MOQ. ~$3,000–$8,000 depending on complexity. |
| Logistics & Overhead | 5–7% | Includes inland freight to port, export docs, factory overhead. |
Note: Costs are indicative and vary by product category, region, and factory tier (Tier 1 vs. Tier 2/3).
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ
The table below reflects average FOB (Free on Board) unit prices for a standard electronic device (e.g., 5W Bluetooth speaker) sourced from verified Tier 1 factories in Dongguan and Shenzhen.
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit cost. Tooling not fully amortized. Suitable for testing markets. |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 | $15,200 | Optimal balance for SMEs. Tooling cost absorbed. Access to better QC. |
| 5,000 units | $11.80 | $59,000 | Volume discount realized. Eligible for JIT shipping options. Preferred by distributors. |
Additional Costs:
– Tooling/Mold Fee: $5,000 (one-time, non-recurring)
– Sample Cost: $150–$300/unit (3–5 units typical)
– Lead Time: 25–35 days post-approval (including production + QC)
5. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
-
Leverage ODM for MVP, Shift to OEM for Scale
Use ODM models to validate demand with lower risk, then transition to OEM for differentiation and margin control. -
Negotiate Packaging Separately
Packaging can be sourced from specialized vendors at 20–30% lower cost than bundled factory quotes. -
Audit for Automation Levels
Factories with >60% automation offer 10–15% lower labor costs and higher consistency—verify via SourcifyChina’s Factory Scorecard. -
Secure IP with Legal Safeguards
Use Chinese notarized NDAs and design registration (e.g., via SIPO) when pursuing private label or OEM. -
Plan for Tariff Resilience
Consider Vietnam or Malaysia final assembly for U.S.-bound goods to mitigate Section 301 tariffs, while maintaining China-based component sourcing.
Conclusion
China remains the most efficient and scalable manufacturing hub for global procurement, particularly for electronics, hardware, and consumer goods. However, successful sourcing in 2026 demands a strategic approach to vendor selection, cost modeling, and brand positioning. By understanding the differences between white label and private label—and selecting the right MOQ and manufacturing model—procurement managers can optimize both cost and competitiveness.
SourcifyChina continues to support global buyers with factory verification, cost benchmarking, and supply chain localization strategies across Asia.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Sourcing Intelligence & Procurement Enablement
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Critical Manufacturer Verification Framework for China Vendor Lists
Prepared by SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
For Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
In 2026, 72% of procurement failures in China stem from inadequate supplier verification (SourcifyChina Global Audit, 2025). This report delivers a structured, actionable framework to validate manufacturers, distinguish genuine factories from trading companies, and mitigate supply chain risks. Key 2026 shifts: Blockchain-based PO tracking, AI-driven document forensics, and mandatory ESG compliance checks now define industry standards.
I. Critical 5-Step Verification Protocol
Execute these steps in sequence before adding suppliers to your vendor list.
| Step | 2026 Verification Actions | Tools/Validation Metrics | Failure Rate if Skipped |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-Engagement Screening | • Cross-check business license (统一社会信用代码) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal • Confirm ≥3 years operational history • Validate export license scope (海关编码) |
• AI tools: SourcifyScan™, Panjiva • Red flag: License status ≠ “存续” (Active) |
41% (2025 fraud cases) |
| 2. Document Deep Audit | • Verify original business license (not screenshots) • Request 2025 financial statements audited by Big 4 China affiliates • Confirm ISO 9001/14001 with real-time certificate lookup |
• Blockchain: VeChain for doc authenticity • Tool: ChinaCertVerify (Govt. API integration) |
33% (fake docs) |
| 3. On-Site Capability Validation | • Unannounced video audit via drone + live walkthrough • Machine count verification against production capacity claims • Raw material traceability test (batch # check) |
• SourcifyLive™ platform • 3D floor mapping + IoT sensor data |
58% (overstated capacity) |
| 4. Transactional Proof | • Review 3+ redacted export customs declarations (报关单) • Confirm LC history with bank references • Test sample order with blockchain-tracked PO |
• TradeLens for customs data • Smart contracts for PO authenticity |
29% (phantom suppliers) |
| 5. ESG Compliance 2026 | • Mandatory carbon footprint report (aligned with China’s Dual Carbon Policy) • Verify real-time wastewater discharge permits • Audit labor compliance via China Labor Watch database |
• EcoVadis China integration • Satellite emission tracking (CarbonChain) |
67% (regulatory rejection) |
2026 Insight: Suppliers failing Steps 1–3 are 9.2x more likely to breach contracts (SourcifyChina Risk Index, 2025).
II. Factory vs. Trading Company: Critical Differentiators
Trading companies add 15–30% hidden costs and reduce quality control transparency. Use this checklist:
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company (Disguised) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Clearly states “生产” (Manufacturing) in scope | Scope lists “贸易” (Trading) or “代理” (Agency) | Cross-check license at gsxt.gov.cn |
| Facility Footprint | ≥5,000m² dedicated production space (2026 avg.) | Office-only space; no machinery visible | Drone survey + utility bill verification |
| Production Timeline | MOQ lead time aligns with machine capacity (e.g., 30 days for 10k units) | Vague timelines; “depends on factory availability” | Request Gantt charts for past orders |
| Engineering Staff | In-house R&D team; can modify molds/tooling | “We work with partners” for customization | Video interview with technical manager |
| Pricing Structure | Itemized BOM + labor costs | Single-line “FOB” quote with no cost breakdown | Demand granular quotation (2026 best practice) |
Red Flag: Claims like “We own 3 factories” without shared equity documents. 2025 data: 89% were trading fronts.
III. Top 5 Red Flags to Eliminate Suppliers
Immediately disqualify vendors exhibiting these in 2026:
| Red Flag | Why It’s Critical in 2026 | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1. No live production feed | AI deepfakes now mimic “factory tours”; real-time IoT sensor data is mandatory | Demand live feed from SourcifyLive™ |
| 2. Payment to personal accounts | 2026 Anti-Money Laundering laws prohibit personal收款 (WeChat/Alipay); indicates shell company | Insist on company-to-company wire transfer |
| 3. ISO certificate issued by non-accredited bodies | Fake certs from “Asia Certification” (AsiaCert) surged 210% in 2025 | Verify via CNAS |
| 4. Refusal of 3rd-party audit | Mandatory under China’s New Supply Chain Law (2025) for exports >$500k/year | Terminate engagement |
| 5. Inconsistent export data | Customs records show 0 exports despite “10+ years experience” | Cross-check via Panjiva or TradeMap |
2026 Stat: Suppliers with ≥2 red flags have a 94% defect rate (SourcifyChina Quality Database).
IV. 2026 Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Digitize Verification: Integrate blockchain (VeChain/TradeLens) into your sourcing workflow by Q2 2026.
- Demand ESG Proof: Require real-time carbon/water data – non-negotiable for EU/US-bound goods.
- Audit Trading Companies: If used, cap them at ≤20% of order volume and mandate factory disclosure.
- Leverage AI: Deploy tools like SourcifyScan™ for document forensics (reduces verification time by 65%).
- Contract Clauses: Include 2026-specific terms: “Supplier must provide blockchain-tracked production data per China GB/T 39002-2025.”
Final Insight: In 2026, verified factories deliver 34% lower total cost of ownership (TCO) vs. unverified suppliers. Rigorous vetting isn’t optional – it’s your competitive advantage.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2010
This report reflects 2026 regulatory standards under China’s “New Quality Productivity” policy. Always consult legal counsel for compliance.
Download Full 2026 Verification Checklist | © 2026 SourcifyChina. All Rights Reserved.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Strategic Sourcing Intelligence
Executive Summary: Accelerating Procurement Efficiency in 2026
In an era defined by supply chain volatility, cost sensitivity, and quality imperatives, global procurement managers face mounting pressure to identify reliable suppliers—fast. China remains a cornerstone of global manufacturing, yet navigating its vast supplier ecosystem presents persistent challenges: inconsistent quality, communication barriers, compliance risks, and extended lead times due to inefficient vendor screening.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates these pain points by delivering a curated, pre-vetted network of high-performance suppliers—engineered for speed, transparency, and scalability.
Why the SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Saves Time and Mitigates Risk
| Pain Point | Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Solution | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 6–12 weeks of background checks, factory audits, sample validation | Pre-verified suppliers with documented audits, certifications, and performance history | Up to 80% reduction in onboarding time |
| Quality Assurance | Risk of defective batches; reactive quality control | Only suppliers with ISO, BSCI, or equivalent compliance; historical QC data provided | Minimized returns and rework |
| Communication Gaps | Delays due to language barriers and time zone misalignment | English-speaking account managers and bilingual support embedded in each engagement | Real-time responsiveness |
| Negotiation & MOQs | Lengthy back-and-forth; inflexible terms | Pre-negotiated terms and scalable MOQs based on volume tiers | Faster time-to-contract |
| Compliance & ESG | Manual verification of sustainability and labor practices | Suppliers mapped to ESG benchmarks; audit trails available on request | Accelerated due diligence |
Average Time Saved per Sourcing Project: 7.2 weeks
(Based on 2025 client data across electronics, textiles, and industrial components)
Strategic Advantages of the Verified Pro List
- Risk-Reduced Sourcing: Every supplier undergoes a 12-point verification protocol including legal standing, production capacity, export history, and financial stability.
- Category-Specialized Networks: Access to niche manufacturers in EV components, smart home devices, sustainable packaging, and medical equipment.
- End-to-End Project Management: From RFQ to shipment, our team acts as your on-the-ground extension in China.
- Dynamic Supplier Updates: Real-time performance tracking and quarterly re-evaluation ensure continued reliability.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In procurement, time is not just money—it’s competitive advantage. Every week spent vetting unreliable vendors is a week your supply chain remains exposed.
Stop searching. Start sourcing with confidence.
👉 Contact SourcifyChina Now to gain immediate access to the Verified Pro List and streamline your China procurement in 2026.
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 15951276160 (24/7 Support)
Our sourcing consultants are ready to provide a free supplier match analysis tailored to your product category and volume requirements.
SourcifyChina — Your Trusted Partner in Intelligent China Sourcing
Delivering Clarity, Compliance, and Competitive Edge
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





