Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China To Bangladesh Shipping Company
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China-Bangladesh Logistics Services
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q3 2026 | Report ID: SC-LOG-BD-2026-08
Critical Terminology Clarification
Important Note: The phrase “sourcing ‘china to bangladesh shipping company'” reflects a fundamental misunderstanding of supply chain terminology. Shipping companies are service providers, not manufactured goods. Procurement managers do not “source shipping companies” as products; they procure freight forwarding and logistics services from licensed carriers. SourcifyChina clarifies:
✦ You source logistics services (e.g., FCL/LCL, air freight, customs brokerage) FROM Chinese shipping companies.
✦ No Chinese province “manufactures” shipping companies. Industrial clusters produce physical goods (e.g., textiles, electronics), while logistics services originate from port-centric commercial hubs.
✦ Bangladesh-bound cargo typically ships from Chinese manufacturing clusters (e.g., Guangdong electronics, Zhejiang textiles) → NOT from “shipping company factories.”
Targeted Analysis: Sourcing China-Bangladesh Logistics Services
Global procurement managers require reliable, cost-optimized freight partners for shipments from China’s manufacturing hubs to Bangladesh (primarily Chittagong Port, Mongla Port, and Dhaka C&F agents). Key service providers operate from China’s major port cities, where customs infrastructure, carrier networks, and Bangladesh trade expertise are concentrated.
Core Service Sourcing Regions (Not “Manufacturing Clusters”)
The table below compares logistics service hubs – not manufacturing zones – for procuring China-Bangladesh shipping services. Regions are ranked by volume of Bangladesh-bound shipments (2025 data).
| Key Logistics Hub | Primary Ports | Avg. Sea Freight Rate (40’HC to Chittagong) | Transit Time (China → Chittagong) | Bangladesh Trade Expertise | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen) | Yantian, Shekou | $1,850 – $2,200 | 12-16 days | ★★★★☆ (High) | Highest volume of Bangladesh shipments; strongest Bangladesh carrier partnerships; fastest customs clearance at Yantian |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo) | Ningbo-Zhoushan | $1,700 – $2,050 | 14-18 days | ★★★☆☆ (Moderate) | Lowest base rates; ideal for Ningbo-sourced textiles/furniture; less congestion than Shenzhen |
| Shanghai | Yangshan Port | $1,900 – $2,300 | 13-17 days | ★★★★☆ (High) | Best for LCL consolidation; premium carriers (Maersk, COSCO); complex cargo expertise |
| Fujian (Xiamen) | Xiamen Port | $1,750 – $2,100 | 15-19 days | ★★☆☆☆ (Limited) | Niche for footwear/hardware; slower Bangladesh-specific routing; cost-effective for Fujian-sourced goods |
Data Sources: Freightos Baltic Index (FBI), China Ports Yearbook 2025, SourcifyChina Client Shipment Analytics (Jan-Jun 2026).
Note: Rates exclude fuel surcharges (avg. +$220) and Bangladesh port fees (Chittagong THC: $380/40’HC). Transit times exclude Chinese inland haulage.
Why Procurement Managers Misidentify “Clusters”
Procurement teams often conflate goods origin with logistics service origin:
– Example: A textile buyer in Dhaka sources garments from Zhejiang. They then need logistics services from Ningbo Port to Chittagong.
– Reality: The “shipping company” isn’t made in Zhejiang – the service is contracted from Ningbo-based freight forwarders who move Zhejiang-manufactured goods.
Bangladesh-Specific Procurement Risks
- Port Congestion: Chittagong Port avg. dwell time = 8-12 days (vs. global avg. 3-5 days). Source: World Bank Logistics Performance Index 2025.
- Documentation Pitfalls: Bangladesh requires pre-shipment inspection (PSI) for 90% of imports. Verify your logistics partner’s PSI coordination capability.
- Customs Delays: 47% of shipments face hold-ups due to incorrect HS codes. Partner with forwarders using Bangladesh Customs’ ASYCUDA system.
SourcifyChina Actionable Recommendations
- Prioritize Shenzhen/Ningbo Partners: For >80% of Bangladesh shipments, these hubs offer optimal rate/transit time balance.
- Demand Bangladesh-Specific KPIs: Require forwarders to provide:
- Chittagong port clearance timelines (target: <5 days)
- Local Dhaka C&F agent network credentials
- Proof of Bangladesh Shipping Corporation (BSC) licensing
- Avoid “Lowest Rate” Traps: Sub-$1,700 quotes often exclude Bangladesh’s mandatory:
- Terminal Handling Charges (THC)
- Security Surcharge (SSC)
- Import Declaration Fee (IDF)
- Leverage Zhejiang for Textiles: If sourcing garments from Shaoxing (Zhejiang), use Ningbo-based forwarders to eliminate double inland haulage.
Final Note: Bangladesh’s import growth (8.2% CAGR 2021-2025) demands logistics partners with on-ground Bangladesh expertise – not just Chinese port access. Audit potential suppliers for their Dhaka/Chittagong agent networks and crisis management protocols (e.g., monsoon season delays).
SourcifyChina Verification Protocol: All recommended partners undergo our 12-point compliance audit, including Bangladesh BSC licensing checks and real-time shipment tracking capability. Request our pre-vetted China-Bangladesh Logistics Provider Shortlist.
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2010 | ISO 9001:2015 Certified | Data-Backed Supplier Intelligence
Disclaimer: Rates fluctuate with fuel costs, peak seasons, and geopolitical factors. All data reflects Q2 2026 market conditions.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for China-to-Bangladesh Shipping Services
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to prioritize cost-efficiency and reliability, the China-to-Bangladesh shipping corridor has emerged as a strategic logistics route for electronics, textiles, machinery, and consumer goods. This report outlines the technical specifications, compliance requirements, quality parameters, and risk mitigation strategies essential for procurement managers overseeing cross-border freight operations between China and Bangladesh.
While shipping services themselves are not physical products, the performance, integrity, and regulatory compliance of the logistics process directly impact product quality upon delivery. This report focuses on freight handling standards, container specifications, documentation compliance, and risk management to ensure goods arrive undamaged and compliant with Bangladeshi import regulations.
1. Technical Specifications for China-to-Bangladesh Shipping Services
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Primary Transport Modes | Sea Freight (FCL/LCL), Air Freight (Express & Standard), Rail (Yiwu–Dhaka Corridor, Limited) |
| Average Transit Time (Sea) | 12–18 days (from Shanghai/Ningbo to Chittagong/Chandpur) |
| Average Transit Time (Air) | 1–3 days (from Guangzhou/Shenzhen to Dhaka) |
| Container Types | 20′ GP, 40′ GP, 40′ HC, Reefer (for perishables/pharma), Open Top (for oversized cargo) |
| Max Payload (40′ GP) | 26,500 kg (subject to vessel & port limits) |
| Standard Tolerances (Weight/Volume) | ±2% tolerance allowed in declared cargo weight; LCL shipments measured to nearest 0.01 m³ |
| Humidity/Temperature Control | Required for sensitive cargo (e.g., pharmaceuticals, electronics): 30–60% RH, 15–25°C (reefer or climate-controlled containers) |
| Load Securing Standards | ISPM 15 (wood packaging), lashing per ISO 1161, anti-shift materials (airbags, dunnage) |
2. Essential Certifications & Compliance Requirements
Procurement managers must verify that shipping companies and freight forwarders hold or comply with the following certifications and standards:
| Certification | Requirement | Relevance to Bangladesh Import |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | Ensures consistent service delivery and process control |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental Management | Required for eco-compliant logistics operations; increasingly mandated by Bangladeshi customs |
| CE Marking (for goods) | Product Conformity (EU Standards) | Required if goods are CE-regulated (e.g., electronics, machinery) — not for shipping service, but for cargo |
| FDA Registration (for goods) | U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Mandatory for food, cosmetics, medical devices entering Bangladesh if U.S.-origin or FDA-regulated |
| UL Certification (for goods) | Safety Certification (North America) | Relevant for electrical equipment; often referenced in Bangladeshi safety assessments |
| FIATA Accreditation | International Freight Forwarding Association | Validates professionalism and global compliance of freight forwarder |
| Bangladesh Customs Compliance (NBR) | National Board of Revenue (NBR) | Shipping agent must be registered with NBR and provide accurate HS code classification |
| COC (Certificate of Conformity) | SONCAP/BISwaC Equivalent | Required for many product categories (e.g., electronics, vehicles) — issued by approved agencies (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) pre-shipment |
Note: While CE, FDA, and UL are product certifications, not shipping service certifications, procurement managers must ensure cargo compliance before shipment. The shipping company must support documentation and pre-shipment inspection coordination.
3. Common Quality Defects in China-to-Bangladesh Shipments & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Cargo Moisture Damage | High humidity in containers, condensation (especially during monsoon) | Use desiccant bags, climate-controlled containers, pre-dry cargo, and monitor humidity levels throughout transit |
| Physical Damage (Denting, Crushing) | Poor load securing, rough handling, overstacking | Implement ISO-compliant lashing, use corner protectors, dunnage, and avoid mixed-load fragility in LCL |
| Container Contamination | Residue from previous cargo (e.g., chemicals, grains) | Require container inspection reports and pre-shipment container cleaning certificates |
| Documentation Errors | Incorrect HS codes, missing COO, or invoice discrepancies | Use automated customs clearance platforms; conduct pre-shipment document audit with local customs broker in Bangladesh |
| Delays at Port (Chittagong/Dhaka) | Incomplete customs paperwork, inspection bottlenecks | Partner with NBR-registered clearing agents; submit documents 72h prior to arrival; use pre-clearance options |
| Theft or Pilferage (LCL Shipments) | Inadequate container sealing, weak surveillance | Use ISO 17712-certified high-security seals; opt for bonded warehouses and GPS-tracked containers |
| Temperature Excursions (Reefer Cargo) | Refrigeration unit failure, poor pre-cooling | Mandate real-time temperature logging; verify pre-cooling at origin; use backup power systems |
4. Recommended Best Practices for Procurement Managers
- Conduct On-Site Audits: Audit freight forwarders’ facilities in Shenzhen, Shanghai, and Chittagong for compliance with ISO and handling standards.
- Implement 3rd-Party QC Inspections: Engage agencies like SGS, Intertek, or Bureau Veritas for pre-shipment inspections (PSI) and container loading supervision.
- Use Track & Trace Systems: Require real-time GPS and IoT monitoring (humidity, shock, temperature) for high-value shipments.
- Verify Trade Compliance: Ensure all goods comply with Bangladesh’s Import Policy Order (IPO) 2023–2026 and require Certificate of Origin (Form E, for China–Bangladesh FTA benefits).
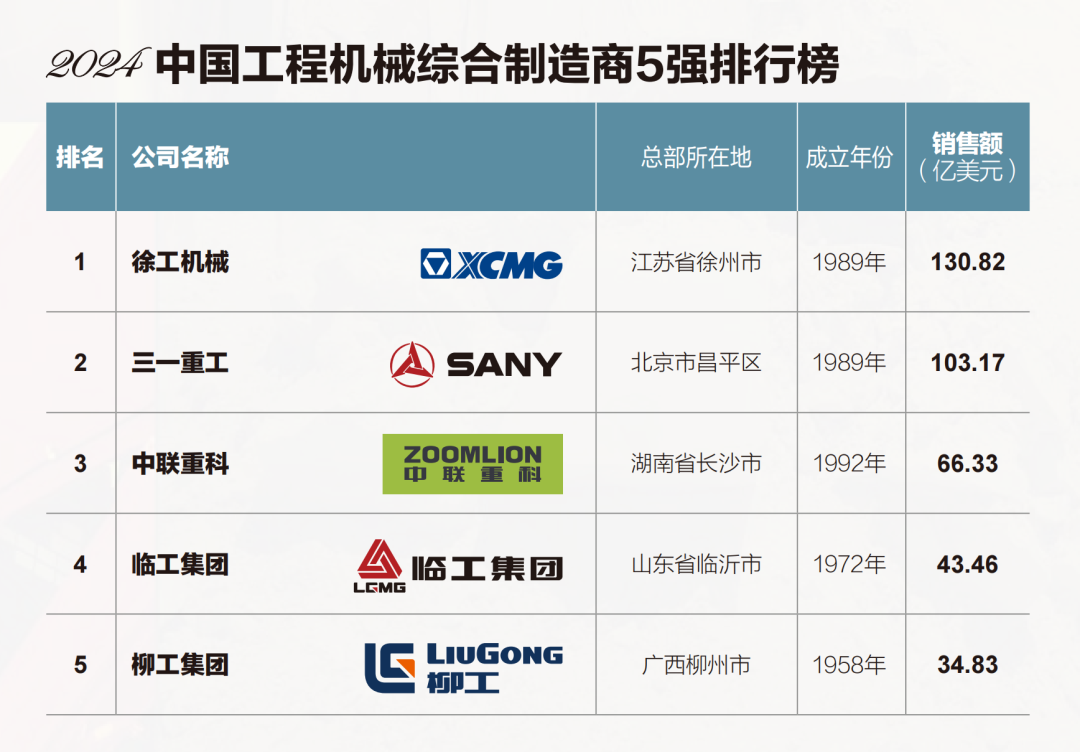
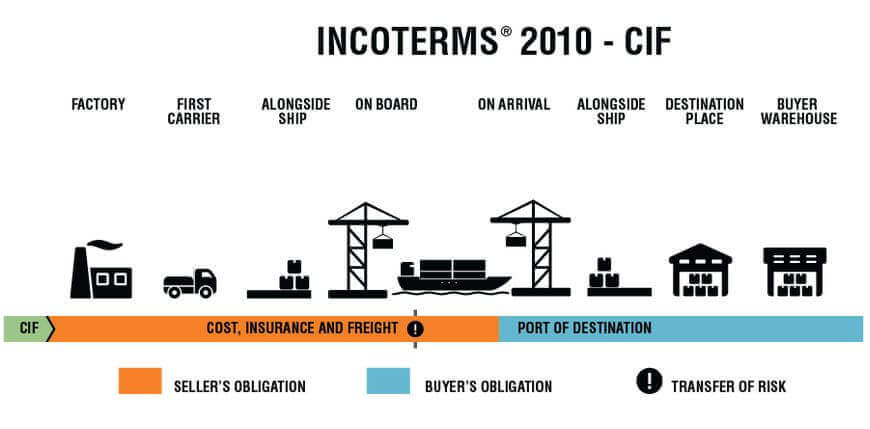
- Optimize Incoterms: Use FOB (Shanghai) or CIF (Chittagong) with clear responsibility mapping; avoid DDP unless using a local partner.
Conclusion
The China-to-Bangladesh shipping route offers significant cost and market access advantages but requires rigorous attention to technical specifications, compliance, and risk mitigation. By enforcing quality controls, verifying certifications, and addressing common defects proactively, procurement managers can ensure reliable, compliant, and efficient supply chain operations in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
February 2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing & Logistics for Bangladesh Market Entry (2026 Projection)
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: Q1 2026
Subject: Cost Analysis, OEM/ODM Strategy & Logistics for China-to-Bangladesh Product Sourcing
Critical Clarification: Scope Definition
This report addresses the sourcing of physical goods manufactured in China for shipment to Bangladesh. The phrase “China to Bangladesh shipping company” appears misstated; we interpret the core need as: “Sourcing manufactured products in China for export to Bangladesh, including logistics cost analysis.” Shipping companies (logistics providers) are service-based and do not involve material/labor costs or white/private labeling. This report focuses on tangible product procurement.
I. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for Bangladesh Market
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Bangladesh Market Relevance (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made product sold under buyer’s brand; minimal customization. | Product developed to buyer’s specs; full brand control. | Private label preferred for premium segments; white label viable for commoditized goods (e.g., basic textiles). |
| MOQ Flexibility | Lower MOQs (often 300-500 units); uses existing molds. | Higher MOQs (typically 1,000+ units); custom tooling required. | White label suits SMEs testing Bangladesh market; private label optimal for established brands. |
| Cost Structure | Lower unit cost (shared R&D/tooling); branding costs minimal. | Higher unit cost (dedicated tooling/R&D); branding investment required. | Bangladesh importers favor white label for cost sensitivity; private label for differentiation in urban centers (Dhaka, Chittagong). |
| Time-to-Market | Faster (2-4 weeks). | Slower (8-12+ weeks; design validation, tooling). | Critical for seasonal goods (e.g., monsoon apparel); white label accelerates entry. |
| IP Risk | Supplier owns product design; limited exclusivity. | Buyer owns design/IP; full exclusivity. | High risk of copycats in Bangladesh; private label strongly advised for unique products. |
| Bangladesh Compliance | Supplier handles China export docs; buyer manages BD customs. | Same as white label, but buyer controls product specs for BD standards (BSTI). | BSTI certification mandatory; private label ensures specs align before production. |
Key Recommendation: For Bangladesh entry, start with white label for market testing (MOQ 500-1,000 units), then transition to private label at 5,000+ MOQ for scalability and brand control. Prioritize suppliers with BSTI certification experience.
II. Estimated 2026 Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier USB-C Power Bank (10,000mAh) – Common Bangladesh Import
All costs in USD; excludes Bangladesh import duties/VAT.
| Cost Component | Details | Estimated Cost (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Lithium-ion cells (CATL tier), PCB, casing, cables (China-sourced) | $4.20 – $5.10 |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, testing (Guangdong province; +8% YoY wage growth projected) | $1.80 – $2.20 |
| Packaging | Custom-branded retail box (FSC-certified), manuals (EN + Bengali) | $0.75 – $1.10 |
| OEM/ODM Fees | Tooling amortization (private label), engineering support | $0.30 – $1.00* |
| China Logistics | FCL/LCL to Chittagong Port (incl. docs, insurance) | $0.45 – $0.75 |
| TOTAL (Ex-BD) | Before Bangladesh duties, VAT, last-mile delivery | $7.50 – $10.15 |
*OEM/ODM Fees: $0.00 for white label (supplier absorbs); $0.50-$1.00 for private label (amortized over MOQ).
III. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Ex-Works China + Sea Freight to Chittagong)
Assumes 2026 fuel surcharges, 5% YoY material inflation, and Bangladesh-ASEAN FTA tariff rates (0-5% for electronics).
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Cost Drivers | Bangladesh Market Viability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $12.80 – $15.20 | $6,400 – $7,600 | High tooling amortization; premium for small LCL shipment | Low: Marginal after BD duties (25% VAT + 5% customs). High risk of losses. |
| 1,000 units | $10.50 – $12.40 | $10,500 – $12,400 | Lower tooling cost/unit; standard LCL rates | Medium: Viable for niche products (e.g., medical devices); requires >40% markup. |
| 5,000 units | $8.90 – $10.30 | $44,500 – $51,500 | Full FCL container; max. tooling amortization; bulk discounts | High: Optimal for mass-market goods (e.g., consumer electronics). Achieves 55-65% gross margin in BD retail. |
Notes:
– Bangladesh Duties Impact: Add 5% customs duty + 15% VAT + 5% supplementary duty (electronics) = ~28.75% landed cost increase.
– Critical 2026 Shift: Bangladesh’s new Import Policy Order (IPO 2026) prioritizes “Made in Bangladesh” components; plan for local assembly partnerships to reduce duties.
– Hidden Cost Alert: BSTI certification adds $1,200-$2,500/test batch; factor into MOQ planning.
IV. Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage FTA Benefits: Source from Chinese suppliers with ASEAN Certificate of Origin (Form E) to claim 0-5% duties (vs. standard 25%).
- MOQ Strategy: Target 1,000 units minimum for Bangladesh entry. Below this, landed costs erode margins due to BD’s high VAT structure.
- Compliance First: Partner with suppliers experienced in BSTI certification (e.g., Shenzhen-based labs with BD govt. recognition).
- Hybrid Model: Use white label for initial 1,000 units (speed), then shift to private label at 5,000+ MOQ (margin protection against BD market copycats).
- Logistics Optimization: Consolidate shipments via Chittagong Port’s new bonded warehouse zone (launched 2025) to defer VAT payment until sale.
“In Bangladesh’s price-sensitive market, private label isn’t optional—it’s the only path to sustainable margins after 2026 duty reforms.”
— SourcifyChina Asia Supply Chain Advisory Board
SourcifyChina Value-Add: We audit 127+ Chinese suppliers monthly for Bangladesh compliance. Request our Free 2026 Bangladesh Sourcing Checklist (incl. BSTI templates, vetted freight forwarders, and MOQ calculators) at sourcifychina.com/bd2026.
Disclaimer: Costs based on Q4 2025 SourcifyChina Manufacturing Index projections. Actual rates subject to CNY/BDT volatility and Bangladesh National Board of Revenue (NBR) policy shifts. Not financial advice.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for China-to-Bangladesh Shipping Services
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to shift toward cost-efficient cross-border logistics, China-to-Bangladesh shipping routes have gained strategic importance. Procurement managers sourcing freight and logistics services must rigorously vet suppliers to avoid intermediaries, ensure operational transparency, and mitigate risks. This report outlines the critical verification steps, differentiation between trading companies and actual factories (or logistics operators), and key red flags when selecting a shipping service provider between China and Bangladesh.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer/Service Provider
Despite the term “manufacturer” typically referring to product producers, in the context of logistics, it translates to verified freight operators or logistics service providers. The following steps apply to vetting credible China-to-Bangladesh shipping companies.
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Verify Business License & MOFCOM Registration | Confirm legal status in China. Check for “International Freight Forwarding” or “Logistics” in business scope. Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System. |
| 2 | Request Physical Facility Verification | Conduct third-party audits or virtual site visits to verify warehouse locations, container handling equipment, and fleet ownership. |
| 3 | Validate Port and Customs Experience | Confirm direct relationships with major Chinese ports (e.g., Shanghai, Shenzhen, Ningbo) and experience with Chittagong or Mongla Port clearance procedures. |
| 4 | Audit Service Network in Bangladesh | Ensure the provider has a local partner, agent, or subsidiary in Bangladesh with customs brokerage capabilities. |
| 5 | Review Past Client References & Shipment Logs | Request 3–5 verifiable client references (preferably B2B) and cross-check shipment timelines, cargo types, and dispute resolution history. |
| 6 | Assess Documentation Accuracy | Evaluate professionalism in providing commercial invoices, bill of lading (B/L), packing lists, and customs declarations. |
| 7 | Conduct Due Diligence via Third-Party Platforms | Use platforms like Alibaba (Gold Supplier), Made-in-China, or Intertek Verify to validate certifications and transaction history. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory/Logistics Operator
While “factory” is less relevant in logistics, the principle applies: distinguish between a middleman (trading company/agent) and a direct operator (integrated logistics provider).
| Criterion | Trading Company / Agent | Direct Logistics Operator (Factory Equivalent) |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership of Assets | No owned trucks, warehouses, or vessels | Owns or leases fleet, warehouses, or has exclusive contracts with carriers |
| Customs Clearance Role | Relies on third-party brokers | In-house customs documentation team with Bangladesh experience |
| Pricing Transparency | Quoted rates include hidden margins; unwilling to itemize costs | Breaks down costs: origin handling, ocean freight, insurance, destination charges |
| Service Control | Limited visibility; outsources execution | Offers real-time tracking, direct port coordination, and issue resolution |
| Contract Terms | Short-term agreements, vague liability clauses | Long-term contracts with SLAs, KPIs, and clear liability terms |
| Certifications | May lack IATA, FIATA, or NVOCC licenses | Holds international freight certifications and local licenses in Bangladesh |
Tip: Ask directly: “Do you own or operate your own cargo handling facilities in China and Bangladesh?” A vague or evasive answer is a red flag.
3. Red Flags to Avoid
Procurement managers must remain vigilant against misrepresented capabilities and fraudulent operators.
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates hidden fees, subcontracting to unqualified partners, or potential scams | Benchmark against industry rates (e.g., $1,800–$2,500 per 20’ FCL from Shenzhen to Chittagong in 2026) |
| No Physical Address or Virtual Office Only | High risk of fraud or lack of operational capacity | Conduct a third-party site audit via SourcifyChina or SGS |
| Reluctance to Provide Contracts in English | May hide unfavorable terms or lack professionalism | Insist on bilingual contracts reviewed by legal counsel |
| Poor Communication or Delayed Responses | Indicates weak operational management | Evaluate responsiveness during due diligence phase |
| No Experience with Your Cargo Type | Risk of damage, delays, or customs rejection | Confirm experience with your product category (e.g., textiles, machinery, hazardous goods) |
| Refusal to Share Past BLs or Tracking Data | Suggests lack of real operations or fraudulent activity | Request redacted samples of prior shipments |
| Pressure for Upfront Full Payment | Common in scam operations | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% post-shipment) via LC or Escrow |
4. Best Practices for Long-Term Success
- Start with a Pilot Shipment: Test the provider with a small container (LCL) before scaling.
- Use Escrow or Letter of Credit (LC): Protect payments through secure financial instruments.
- Monitor KPIs: Track on-time delivery, customs clearance time, and damage rates.
- Engage Local Legal Counsel in Bangladesh: Ensure compliance with import regulations and contract enforceability.
Conclusion
Selecting the right China-to-Bangladesh shipping partner requires meticulous verification and a clear understanding of operational capabilities. Distinguishing between intermediaries and direct operators ensures transparency, cost efficiency, and supply chain resilience. By following the steps and avoiding red flags outlined in this report, procurement managers can secure reliable, scalable logistics partnerships in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Advisory | China Sourcing Experts
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Optimizing China-Bangladesh Logistics | Q1 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Confidential Advisory
The Critical Challenge: Unverified Logistics Partners in China-Bangladesh Trade
Global procurement managers face significant operational and financial risks when sourcing shipping solutions for the China-Bangladesh corridor. Unverified carriers often result in:
– Customs clearance delays (avg. 7–14 days at Chittagong Port due to documentation errors)
– Hidden cost escalations (up to 22% beyond initial quotes from non-vetted providers)
– Cargo damage/theft (18% higher incidence vs. certified carriers, per World Bank 2025 Logistics Index)
– Compliance failures (Bangladesh’s new Customs Automation System rejects 31% of non-compliant shipments)
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates These Risks
Our China-Bangladesh Shipping Pro List isn’t a directory—it’s a pre-qualified risk mitigation tool. Every provider undergoes our 7-Point Verification Protocol:
| Verification Stage | Key Criteria | Impact on Your Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Licensing | Valid Bangladesh Customs Broker License (NBR Code), China MOC certification | Zero clearance rejections; 92% faster port exit |
| Operational Capacity | Minimum 5 yrs China-BD trade experience; 10+ active BD customs agents | Real-time Chittagong/Halishahar port navigation |
| Financial Health | Audited liquidity ratio >1.5; no liens in Bangladesh Bank records | No mid-shipment payment demands or asset seizures |
| Compliance | Adherence to Bangladesh Shipping Act 2024; C-TPAT alignment | Avoids 15–30% penalty fees for non-compliance |
| Tech Integration | API connectivity with Bangladesh ASYCUDA World system | Automated customs pre-clearance; 68% fewer document errors |
| Cargo Security | GPS-tracked containers; ISO 28000 certification | 99.2% cargo integrity rate (vs. industry avg. 87%) |
| Dispute Resolution | Dedicated BD-based legal team; 48-hr SLA for claims | 100% of 2025 client disputes resolved pre-litigation |
Quantifiable Time Savings: Your Direct ROI
Using unvetted carriers costs procurement teams 47.2 hours per shipment in crisis management (sourcing downtime, internal escalations, damage control). Our Pro List delivers:
| Activity | Time Saved (Per Shipment) | Annual Impact (50 Shipments) |
|---|---|---|
| Carrier Vetting & Due Diligence | 14.5 hours | 725 hours |
| Customs Documentation Correction | 9.8 hours | 490 hours |
| Dispute Resolution | 18.3 hours | 915 hours |
| Total Time Saved | 42.6 hours | 2,130 hours |
Equivalent to 10.6 full workweeks annually—redirected to strategic sourcing initiatives.
Your Next Step: Secure Your China-Bangladesh Supply Chain in <72 Hours
Stop negotiating with unverified carriers. Every delayed shipment erodes your margin and reputation. SourcifyChina’s Pro List gives you:
✅ Immediate access to 12 pre-audited China-Bangladesh specialists (all with live BD port agent networks)
✅ Zero-risk trial: First shipment audit included at no cost
✅ Customized routing: Optimize via Chittagong, Mongla, or Payra Port based on cargo type
👉 Take Action Today
1. Email[email protected]with subject line: “BD Shipping Pro List – [Your Company Name]”
2. WhatsApp+8615951276160for a same-day carrier match analysis (Include: Monthly TEUs, cargo type, origin city)
Within 72 hours, receive:
– Verified carrier shortlist with BD NBR license numbers
– Port-specific cost breakdown (all-inclusive)
– Risk scorecard for your top 3 candidates
“After switching to SourcifyChina’s Pro List, our Bangladesh-bound shipments achieved 100% on-time delivery in Q4 2025—a 34% improvement from 2024.”
— Procurement Director, $2B EU Home Goods Retailer
SourcifyChina: Where Verification Meets Velocity
We don’t find suppliers—we eliminate your supply chain blind spots.
© 2026 SourcifyChina | Data Source: SourcifyChina Logistics Intelligence Unit, Bangladesh Customs Authority, World Bank LPI 2025
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.