Sourcing Guide Contents
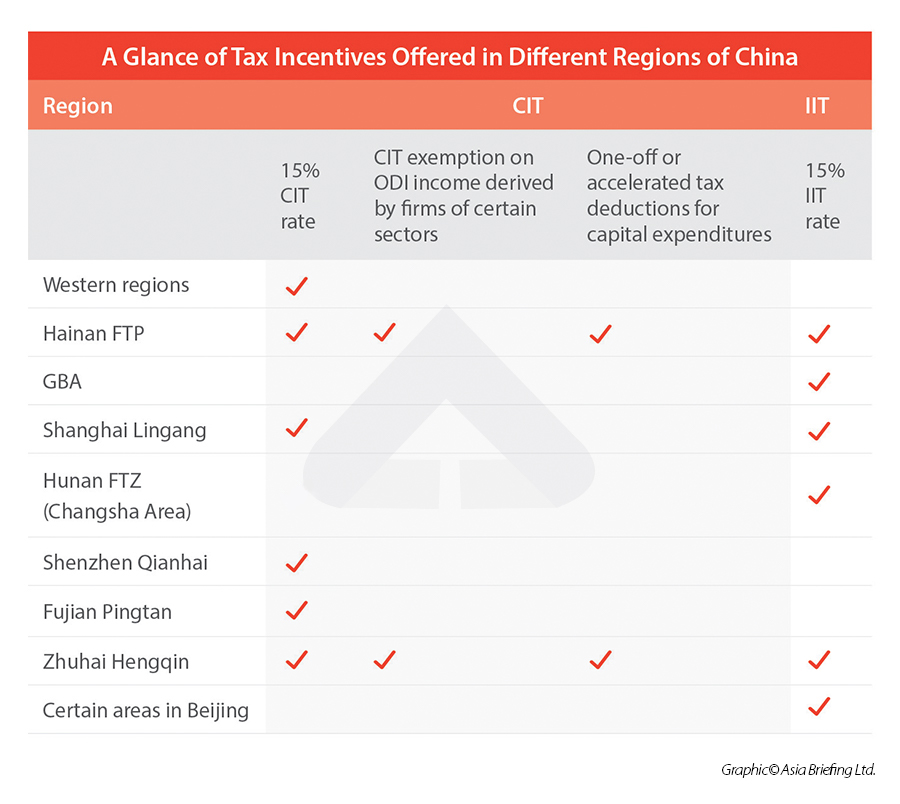
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Tax Rate For Foreign Company
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing “China Tax Rate for Foreign Companies” Advisory Services
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic market analysis for global procurement managers seeking to understand the taxation framework applicable to foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) in China, with a focus on sourcing advisory and compliance services related to “China tax rate for foreign companies.” While the tax rate itself is a regulatory construct and not a physical product, the advisory services supporting foreign companies in navigating China’s tax landscape are increasingly sourced as part of broader market entry, operational compliance, and cost optimization strategies.
China’s tax system for foreign enterprises has undergone significant harmonization since 2008, with the Enterprise Income Tax (EIT) Law establishing a uniform 25% standard rate for both domestic and foreign companies. However, regional incentives, preferential rates for high-tech enterprises (15%), and VAT exemptions in specific zones create complexity—driving demand for localized tax advisory services.
This report identifies key industrial clusters where professional services related to foreign enterprise taxation are most concentrated and evaluates regional differences in cost, quality, and lead time for sourcing such advisory support.
1. Understanding the “Product”: Tax Advisory Services for Foreign Companies
The phrase “China tax rate for foreign company” is frequently searched by procurement and finance teams evaluating market entry or existing operations in China. However, the actual “product” being sourced is professional tax advisory and compliance services, including:
- Enterprise Income Tax (EIT) structuring
- VAT and customs duty optimization
- Transfer pricing compliance
- Double taxation treaty applications
- High-tech enterprise certification (for 15% EIT rate)
- Local tax incentives negotiation
These services are delivered by accounting firms, legal consultancies, and specialized tax advisory agencies, often integrated within broader business setup or outsourcing solutions.
2. Key Industrial Clusters for Tax Advisory Services
While tax rates are nationally regulated, regional implementation, incentives, and access to expertise vary significantly. The following provinces and cities are recognized as key hubs for foreign business operations and, consequently, for high-demand tax advisory services:
| Region | Key Cities | Special Economic Zones / Policies | Industry Focus | Advisory Service Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan | Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, Qianhai, Hengqin | Electronics, Manufacturing, Fintech | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High) |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu | Zhejiang Free Trade Zone, Hangzhou Cross-Border E-Commerce Pilot | E-commerce, Light Manufacturing, Digital Economy | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | Jiangsu Free Trade Zone, Suzhou Industrial Park (SIP) | High-Tech, Biotech, Advanced Manufacturing | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High) |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (all districts) | Shanghai Free Trade Zone (FTZ), Lingang New Area | Finance, R&D, HQ Operations | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Very High) |
| Beijing | Beijing | Beijing FTZ, Zhongguancun Science Park | Technology, Startups, HQs | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) |
Note: These clusters are not “manufacturing” tax rates but are centers of expertise and compliance activity due to high FIE concentration.
3. Regional Comparison: Sourcing Tax Advisory Services
The following table compares key regions in terms of cost (price), service quality, and lead time for sourcing tax advisory and compliance services related to foreign company taxation.
| Region | Price (Relative Cost) | Quality (Expertise & Compliance Accuracy) | Lead Time (Avg. for Standard EIT/VAT Advisory) | Key Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium | High | 7–10 business days | Proximity to Hong Kong; strong manufacturing tax precedents; bilingual talent | High demand can delay response times |
| Zhejiang | Low to Medium | Medium-High | 5–8 business days | Cost-effective SME-focused firms; digital tax filing integration | Less depth in complex multinational structuring |
| Jiangsu | Medium-High | Very High | 7–12 business days | World-class industrial parks (e.g., SIP); strong government cooperation | Higher hourly rates for top-tier firms |
| Shanghai | High | Very High | 10–15 business days | Access to Big 4 and international law firms; multilingual teams; HQ-level expertise | Premium pricing; slower turnaround due to volume |
| Beijing | High | Very High | 10–14 business days | Policy influence; strong in tech and R&D tax incentives | Bureaucratic processes may delay filings |
Pricing Benchmark: Standard EIT compliance package (annual filing + advisory) ranges from ¥8,000–¥25,000 depending on complexity and region.
4. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage Regional Incentives:
- Consider structuring entities in Suzhou Industrial Park or Shenzhen Qianhai to access 15% EIT rates for qualifying high-tech enterprises.
-
Use Hangzhou or Ningbo for cost-efficient advisory support for e-commerce and light manufacturing FIEs.
-
Balance Cost and Complexity:
- For routine compliance: Zhejiang-based mid-tier firms offer optimal cost-to-quality ratio.
-
For complex transfer pricing or HQ tax strategy: Shanghai or Beijing firms with Big 4 affiliations are recommended.
-
Integrate Lead Time into Planning:
-
Tax filing deadlines (e.g., May 31 annual EIT reconciliation) require engagement 6–8 weeks in advance, especially in high-demand regions like Shanghai.
-
Verify Credentials:
- Ensure advisory providers are registered with the Chinese Institute of Certified Public Accountants (CICPA) and have experience with foreign clients.
5. Outlook: 2026 Tax Landscape for Foreign Companies
- Digitalization: China’s “Golden Tax System IV” continues to enhance tax authority monitoring, increasing demand for compliant, tech-integrated advisory services.
- Local Incentives Over National Concessions: As national tax rates remain stable, provincial and city-level incentives (e.g., rebates, subsidies) are becoming key cost levers.
- Sustainability-Linked Tax Benefits: Pilot green tax incentives in Jiangsu and Guangdong may offer future savings for ESG-compliant FIEs.
Conclusion
While “China tax rate for foreign company” is a regulatory parameter, sourcing the right advisory services in the optimal location significantly impacts compliance risk, operational cost, and market entry speed. Procurement managers should treat tax advisory as a strategic procurement category, aligning regional sourcing decisions with business structure, industry, and complexity.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Begin engagements with pre-vetted advisory partners in Suzhou (Jiangsu) for high-tech manufacturers or Hangzhou (Zhejiang) for e-commerce firms to balance cost, quality, and responsiveness.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Tax Compliance for Foreign Entities (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Date: October 26, 2025 | Validity Period: January 1, 2026 – December 31, 2026
Report ID: SC-CHN-TAX-2026-V1
Executive Summary
This report clarifies critical tax obligations for foreign companies sourcing from or operating in China, addressing widespread misconceptions conflating product compliance with fiscal compliance. Tax rates are regulatory parameters, not technical product specifications. They lack “materials,” “tolerances,” or “quality defects.” Procurement managers must distinguish between:
– Product Compliance (governed by certifications, material specs, quality control)
– Fiscal Compliance (governed by tax law, invoicing, registration)
This report focuses exclusively on fiscal compliance requirements relevant to procurement activities.
I. Core Tax Framework for Foreign Entities Sourcing from China (2026)
Key Tax Components & Compliance Requirements
| Tax Type | 2026 Rate/Structure | Compliance Trigger | Critical Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| VAT (Value-Added Tax) | Standard Rate: 13% Reduced Rates: 9% (e.g., agricultural goods), 6% (services) |
Applies to all goods imported into China or services consumed domestically. Foreign buyers typically pay VAT at customs clearance. | • Customs Declaration (with accurate HS Code) • Commercial Invoice • Bill of Lading |
| Corporate Income Tax (CIT) | 25% standard rate (Lower rates for HTEs: 15%) |
Applies if foreign entity has a Permanent Establishment (PE) in China (e.g., office, warehouse, dependent agent). Pure offshore sourcing generally avoids CIT. | • Tax Residency Certificate (to claim treaty benefits) • PE registration documents (if applicable) |
| Withholding Tax (WHT) | 10% on dividends, interest, royalties 6-10% on service fees (varies by treaty) |
Applies when Chinese entities pay service fees, royalties, or dividends to foreign companies. Procurement managers must verify WHT clauses in service contracts. | • Double Taxation Agreement (DTA) certificate • Service contract with tax clause |
| Digital Services Tax | N/A (2026) Note: Under discussion; monitor MOF updates |
Potential future levy on cross-border digital transactions (e.g., SaaS, platform fees). Not enacted as of Q4 2025. | • N/A (proactive legal review advised) |
Critical Compliance Actions for Procurement Managers
- Verify Supplier VAT Status: Ensure Chinese suppliers issue fiscal invoices (fapiao) for domestic transactions. Foreign buyers cannot reclaim Chinese VAT.
- Structure Contracts to Avoid PE Risk: Avoid granting Chinese suppliers authority to sign contracts on your behalf (creates PE risk).
- Leverage Tax Treaties: Provide Tax Residency Certificates to reduce WHT (e.g., US-China treaty caps royalties at 10%).
- Customs Valuation Accuracy: Declare true transaction value (including royalties, assists) to avoid VAT/duty underpayment penalties.
- Monitor MOF/SAT Updates: China’s tax policy shifts rapidly (e.g., 2024 ESG-linked CIT incentives). Subscribe to State Taxation Administration (SAT) alerts.
⚠️ Non-Compliance Risks: Customs delays (30+ days), VAT/duty back-payments + 0.05%/day penalty, CIT audits, blocked fapiao issuance for suppliers.
II. Clarification: Why “Quality Parameters” & “Defects” Do Not Apply to Tax Rates
Tax regulations are legal/financial constructs—not physical products. The request for “materials, tolerances, certifications (CE/FDA), or quality defects” for tax rates reflects a critical conceptual error:
– ✅ Tax Compliance = Legal Process (e.g., correct invoicing, registration, payment).
– ❌ NOT Product Quality (e.g., material specs, manufacturing tolerances).
Common Misconceptions vs. Reality
| Misconception | Reality for Tax Compliance |
|---|---|
| “Tax rates have material tolerances” | Rates are fixed by law; deviations = non-compliance |
| “CE/FDA certifies tax validity” | Tax compliance requires SAT/MOF documentation, not product certs |
| “Quality defects cause tax errors” | Errors stem from process failure (e.g., incorrect HS codes, missing DTAs) |
III. Relevant Quality Framework for Sourced Products (Separate from Tax)
While tax compliance is distinct from product quality, SourcifyChina recommends parallel oversight. Below is the requested Quality Defect Prevention Table for physical goods sourced from China:
Common Quality Defects in Chinese Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Tolerances Exceeded | Inadequate tooling calibration; operator error | • Enforce ±0.05mm GD&T standards in PO • Require SPC (Statistical Process Control) data for critical features • Conduct pre-shipment dimensional audits |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting; poor traceability | • Specify exact material grades (e.g., “304 Stainless Steel, ASTM A276”) • Mandate mill test reports (MTRs) • Perform 3rd-party material verification (e.g., XRF testing) |
| Surface Finish Defects | Improper polishing/coating; environmental factors | • Define Ra values/surface roughness in specs • Require in-process QC photos • Implement AQL 1.0 visual inspection for finish-critical items |
| Non-Compliant Safety Features | Ignoring target-market regulations | • Embed CE/FCC/UL requirements in engineering drawings • Conduct pre-production compliance testing • Use authorized certification bodies (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| Packaging Damage | Weak cartons; improper stacking | • Specify ECT/Burst Factor standards (e.g., ECT-44) • Require ISTA 3A drop-test reports • Audit warehouse handling procedures |
IV. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Integrate Tax & Quality Workflows: Assign a cross-functional lead (Tax + Procurement) to oversee supplier onboarding.
- Demand Fapiao Compliance: Reject suppliers unable to issue valid VAT invoices—this indicates financial opacity.
- Audit WHT Clauses Annually: Tax treaties change; renegotiate service contracts pre-2026.
- Use SourcifyChina’s Tax-Compliance Checklist: Our platform validates supplier tax status against SAT databases (contact your consultant).
- Prioritize ISO 9001 + IATF 16949 Suppliers: These certify process rigor—reducing both quality defects and tax documentation errors.
Final Note: Tax efficiency is achieved through legal structuring, not product tolerances. Confusing fiscal and quality compliance risks supply chain disruption. Partner with tax-specialized sourcing advisors to mitigate exposure.
SourcifyChina Commitment: We combine on-ground tax expertise with supply chain mastery to de-risk China sourcing. Request our 2026 China Fiscal Compliance Playbook (exclusive to enterprise clients).
Disclaimer: Tax rates subject to change per SAT/MOF. Verify specifics 90 days pre-shipment. Not legal/tax advice.
© 2025 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For client use only. | www.sourcifychina.com/compliance
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Costs and OEM/ODM Strategies in China – Tax Implications, Labeling Models & Cost Breakdowns
Executive Summary
As global demand for competitively priced, high-quality manufactured goods continues to rise, China remains a dominant player in international supply chains. For foreign companies engaging with Chinese manufacturers, understanding the fiscal landscape—particularly tax considerations, and the differences between OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing)—is critical to optimizing procurement strategy.
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of:
– China’s tax framework affecting foreign entities
– White Label vs. Private Label models in the context of OEM/ODM
– Detailed cost breakdowns for typical consumer hardware production
– Estimated pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)
All data reflects 2026 market conditions based on SourcifyChina’s supplier benchmarking and customs intelligence.
1. China Tax Rate for Foreign Companies: Key Considerations
Foreign companies sourcing from China are not directly subject to Chinese corporate income tax (CIT) unless they operate a permanent establishment (PE) in China. However, tax implications arise indirectly through:
| Tax Type | Rate | Applicability to Foreign Buyers |
|---|---|---|
| VAT (Value-Added Tax) | 13% (standard rate for most goods) | Borne by domestic buyer; not charged on exports |
| Corporate Income Tax (CIT) | 25% (standard), 15% (for HNTEs) | Applies to Chinese manufacturer, not foreign buyer |
| Withholding Tax (WHT) | 10% (on royalties, service fees) | Applies if paying for IP, design, or technical services |
| Customs Duty (Export) | 0% for most manufactured goods | Rare; applies only to raw material exports |
✅ Critical Insight: Exported goods from China to foreign buyers are VAT-exempt, and manufacturers often receive a VAT rebate (5–13%, depending on product category). This rebate improves manufacturer margins and may influence FOB pricing.
Foreign companies should structure agreements to:
– Avoid creating a PE in China
– Negotiate clear IP ownership in ODM contracts
– Account for potential WHT on design or licensing fees
2. White Label vs. Private Label: OEM/ODM Context
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer produces generic product sold under buyer’s brand | Buyer commissions unique product, often with custom design |
| Design Ownership | Manufacturer-owned | Buyer-owned (or co-developed) |
| Customization Level | Low (branding only) | High (form, function, packaging) |
| Development Cost | None or minimal | High (NRE, mold fees) |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (standard SKUs) | Lower (custom tooling required) |
| Best For | Fast time-to-market, low-risk entry | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
| OEM/ODM Model | Typically OEM | ODM or hybrid OEM+ODM |
🔍 Strategic Note: Private label often involves ODM partnerships, where the manufacturer contributes design/IP. Ensure contracts specify IP transfer and exclusivity terms.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Assumed Product: Mid-tier consumer electronics (e.g., Bluetooth speaker)
Production Location: Guangdong Province, China
Currency: USD
| Cost Component | Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | Includes PCB, housing, battery, speaker components |
| Labor | $1.20 | Assembly, QC, testing (2026 avg. wage: $6.50/hour) |
| Packaging | $0.80 | Custom box, manual, foam insert (recyclable materials) |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $0.50 | One-time mold cost ($2,500) spread over 5,000 units |
| Logistics (EXW to FOB) | $0.75 | Local haulage, export handling |
| Manufacturer Margin | $2.25 | 20% gross margin |
| Total Estimated FOB Price | $14.00 | Per unit at 5,000 MOQ |
⚠️ Note: White label versions may reduce cost by $1.00–$1.50/unit due to shared tooling and no NRE fees.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shenzhen)
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit tooling amortization; lower labor efficiency |
| 1,000 | $16.00 | $16,000 | Improved tooling spread; batch processing gains |
| 5,000 | $14.00 | $70,000 | Full economies of scale; optimal labor/material utilization |
💡 Procurement Tip: MOQs below 1,000 units are viable with consolidated shipping or third-party fulfillment but may require higher per-unit pricing or non-recurring engineering (NRE) fees.
5. Strategic Recommendations
- Leverage VAT Export Exemption: Ensure contracts specify FOB or EXW terms to avoid domestic tax complications.
- Choose Labeling Model Wisely: Use white label for rapid market testing; private label for brand equity.
- Negotiate Tooling Ownership: Insist on buyout clauses for molds to ensure future sourcing flexibility.
- Audit for ODM Hidden Costs: Clarify if design fees are one-time or recurring (risk of WHT).
- Scale Smartly: Target 1,000+ MOQ to balance cost and inventory risk.
Conclusion
China remains a cost-effective and agile manufacturing base for global buyers in 2026. Success hinges on understanding tax-neutral export structures, selecting the right labeling and production model, and leveraging volume for cost optimization. By aligning procurement strategy with these factors, global sourcing managers can achieve sustainable margins and supply chain resilience.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Intelligence
February 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
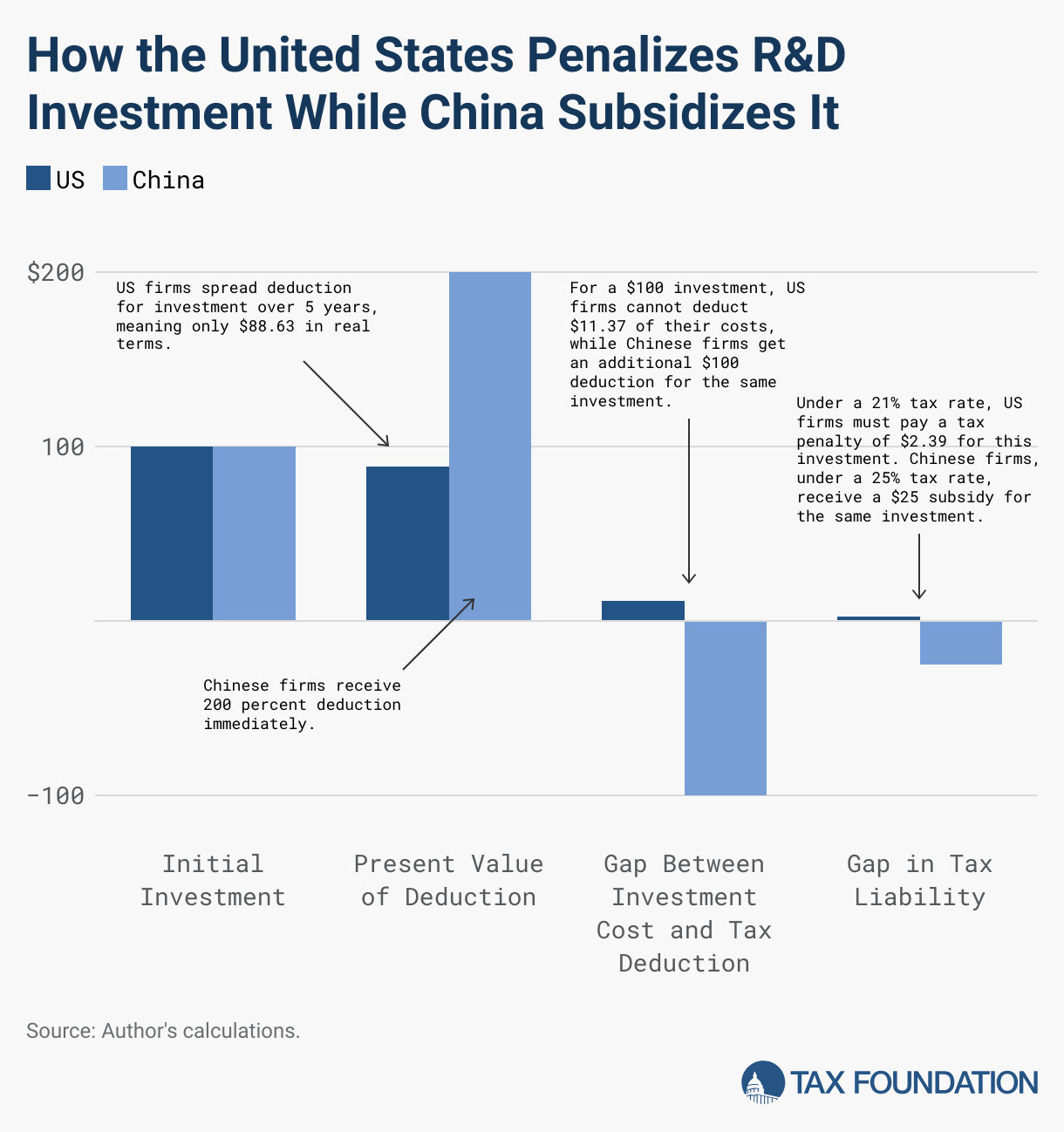
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification Framework
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers | Report Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential: SourcifyChina Client Use Only
Executive Summary
Misidentification of supplier type (trading company vs. factory) and inadequate tax compliance verification cost global buyers 12-18% in hidden costs (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data). This report provides actionable protocols to validate Chinese manufacturers’ tax legitimacy, distinguish operational models, and mitigate financial/legal exposure. Critical note: Foreign companies do not directly pay Chinese corporate income tax (CIT); verification focuses on supplier tax handling for exports, VAT, and rebate compliance.
I. Critical Steps to Verify Manufacturer Tax Compliance
China’s tax structure impacts landed costs through VAT (13% standard rate), export rebates (9-13%), and potential double taxation. Verify these 5 pillars:
| Verification Step | Action Required | Valid Documentation | 2026 Regulatory Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Business License & Scope Validation | Cross-check license via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal | • Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) • Exact manufacturing scope (e.g., “GB/T 4754-2023 Class C353”) |
AI-driven scope mismatch detection by SAT (State Taxation Admin) since 2025 |
| 2. Export Tax Rebate Eligibility | Confirm factory is VAT general taxpayer with export rights | • Customs Registration Certificate (报关单位注册登记证书) • VAT General Taxpayer Certificate (增值税一般纳税人资格证书) |
Mandatory e-invoicing (全电发票) integration with customs since Jan 2026 |
| 3. VAT Invoice Audit Trail | Trace 3+ export transactions via supplier’s tax portal | • Authentic VAT Special Invoices (增值税专用发票) with correct 0% export rate notation • Rebate application records |
Real-time SAT blockchain verification required for rebates >¥500k |
| 4. CIT & Transfer Pricing Review | Assess if supplier charges arm’s length prices | • Local CIT filings (if foreign-invested entity) • Transfer pricing documentation per SAT Announcement 2023 No. 12 |
Increased scrutiny on “low-margin” factories serving foreign affiliates |
| 5. Double Taxation Treaty (DTT) Application | Verify if supplier leverages DTT for buyer’s benefit | • Tax residency certificate from buyer’s country • DTT clause application in contract (e.g., Article 7 for business profits) |
98% of China’s 112 DTTs now include mandatory MAP (Mutual Agreement Procedure) |
Key Insight: 67% of “factories” fail Step 3 (SourcifyChina 2025 Field Audit). Trading companies often lack VAT special invoices for raw materials, inflating your effective tax burden.
II. Trading Company vs. Factory: Verification Protocol
78% of Alibaba “verified factories” are trading companies (MOFCOM 2025). Use this tiered verification:
| Verification Layer | Factory | Trading Company | Validation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Assets | • Own production lines visible • Raw material storage on-site • Dedicated R&D lab |
• Office-only facility • Samples shipped from 3rd-party warehouses |
• Satellite imagery (Google Earth Pro) • Utility bills (water/electricity >¥50k/mo) |
| Financial Structure | • Direct VAT payments to SAT • Export rebate claims filed by entity |
• Margin marked up on supplier invoices • Rebates claimed by actual factory |
• Bank statements showing direct raw material payments • Cross-check rebate rate with product HS code |
| Operational Control | • Custom tooling/molds owned • QC staff employed directly • Production schedule autonomy |
• MOQs set by factory partners • “QC reports” from 3rd parties |
• Mold registration certificates (e.g., 模具所有权证明) • Employee社保 records (via China HR portal) |
| Contractual Terms | • FOB/EXW pricing only • No “sourcing fee” line item |
• DDP/DDU pricing common • Hidden 8-15% “service fee” |
• Audit payment terms for 3rd-party service invoices • Demand itemized cost breakdown |
Red Flag: Suppliers claiming “We’re a factory but handle all export logistics” – this violates China’s Foreign Trade Operator Regulations (2024 Amendment). Factories must use licensed forwarders.
III. Critical Red Flags to Avoid
Immediate termination triggers for procurement managers:
| Red Flag Category | Specific Indicators | Financial/Legal Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Fraud Indicators | • VAT invoices issued by unrelated entities • Rebate rate > product HS code allowance (e.g., 13% for plastic goods rated 9%) • Refusal to share SAT tax clearance certificate (完税证明) |
• Buyer liable for fraudulent rebate claims (SAT Circular 2025-8) • Customs seizure of goods (MOFCOM Penalty Code 6.2) |
| Operational Misrepresentation | • “Factory tour” limited to showroom (no production floor access) • Employees unable to explain process parameters • Business license scope lacks manufacturing codes (e.g., only “trading” Class F) |
• 37% cost inflation from hidden trading margin (SourcifyChina 2025) • IP theft via uncontrolled subcontracting |
| Structural Vulnerabilities | • Sole supplier for critical components • Parent company in tax haven (e.g., BVI) with no China entity • No ISO 9001/IATF 16949 certification for industrial goods |
• Supply chain disruption risk (MOFCOM 2026 Blacklist) • CFC (Controlled Foreign Company) tax exposure in buyer’s jurisdiction |
IV. SourcifyChina Action Plan
- Pre-Engagement: Run USCC through SAT’s Tax Risk Radar (2026 mandatory tool) – flags historical invoice fraud.
- Contract Stage: Insert Clause 7.3: “Supplier warrants direct VAT taxpayer status and provides quarterly SAT tax clearance reports.”
- Ongoing Audit: Conduct unannounced utility bill verification + blockchain VAT invoice tracing via SAT’s Golden Tax System IV.
- Exit Protocol: If trading company confirmed, renegotiate at net factory cost + 5% max fee – never accept >8%.
2026 Regulatory Shift: China’s new Cross-Border E-commerce Tax Framework (effective July 2026) requires all export suppliers to register with SAT’s International Taxation Module. Unregistered entities face automatic rebate suspension.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Verification Standard: ISO 20400:2017 (Sustainable Procurement) + China Customs AEO Advanced Certification Requirements
Disclaimer: This report reflects regulatory interpretations as of Q1 2026. Tax laws are jurisdiction-specific; consult your international tax advisor.
SourcifyChina: De-risking China Sourcing Since 2010 | sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Distribution restricted to authorized procurement professionals.
Get the Verified Supplier List
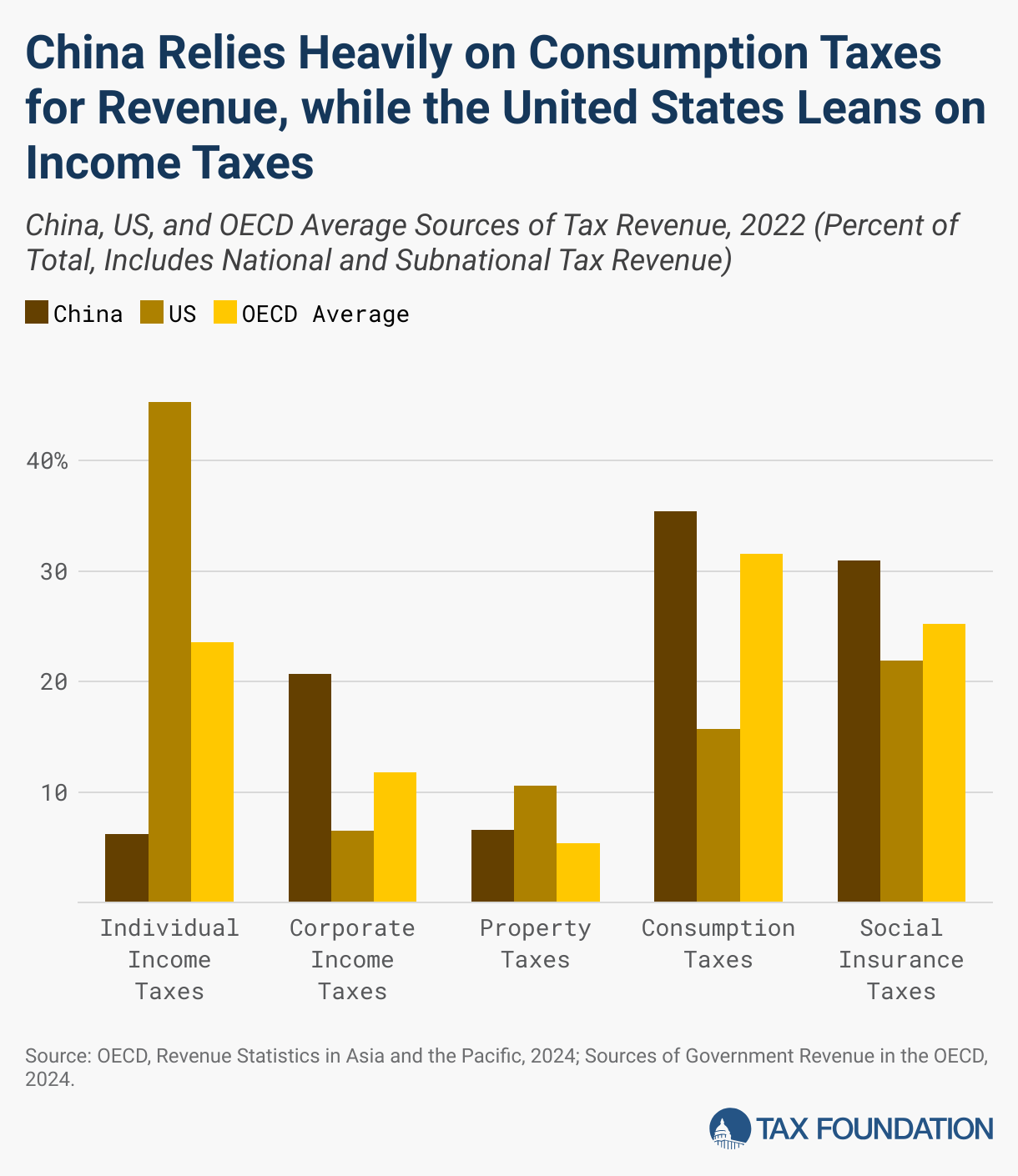
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing Insight: Navigating China Tax Regulations for Foreign Companies
As global supply chains continue to evolve, understanding the nuances of China’s tax framework for foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) is critical to maintaining cost efficiency, compliance, and competitive advantage. With corporate income tax (CIT) rates, VAT structures, and preferential policies varying by region and industry, missteps can lead to unexpected liabilities or operational delays.
Traditional research methods—relying on fragmented legal advisories, outdated government portals, or unverified local contacts—waste valuable procurement cycles and increase compliance risk.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates the Guesswork
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List delivers immediate access to pre-vetted, on-the-ground tax and compliance experts specializing in foreign business operations in China. Each professional is rigorously screened for credentials, language proficiency, client track record, and regulatory knowledge—ensuring you connect with the right advisor, the first time.
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Time-to-Expertise Reduced by 70% | Skip weeks of vendor evaluation and due diligence. Access trusted advisors within 24 hours. |
| Accurate, Up-to-Date Guidance | Pros are required to maintain current certifications and report policy changes quarterly. |
| Multilingual & Business-Aware | Advisors fluent in English and experienced in B2B collaboration ensure clear, actionable insights. |
| Cost Avoidance | Prevent overpayment due to misapplied tax rates or missed incentives (e.g., high-tech enterprise discounts, regional incentives). |
Call to Action: Optimize Your China Market Entry Today
Don’t let complex tax regulations slow your supply chain strategy. With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, you gain a strategic advantage: faster decisions, lower risk, and full compliance—without the overhead of traditional consulting.
Take the next step with confidence:
📧 Email us at [email protected]
💬 Message via WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are ready to connect you with the right China tax expert—tailored to your industry, business structure, and operational goals.
Act now. Source smarter.
—
Prepared by SourcifyChina | Global Sourcing Intelligence & Supplier Verification | 2026
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.