Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Targets Us Companies

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis for Sourcing ‘China Targets US Companies’ Products from China
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
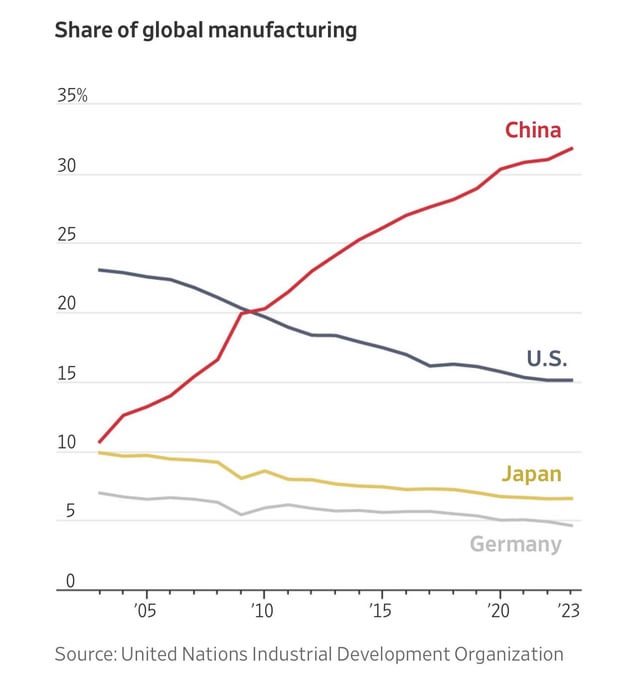
The phrase “China targets US companies” has evolved from geopolitical rhetoric into a strategic lens for global sourcing professionals assessing supply chain resilience, competitive intelligence, and risk mitigation. In the context of industrial sourcing, this report interprets the theme as products and technologies that China has strategically prioritized for domestic advancement—often in sectors directly competing with or displacing US-based firms. These include high-growth industries such as semiconductors, electric vehicles (EVs), advanced battery systems, AI-driven automation, 5G infrastructure, and precision machinery.
China’s industrial policy—under initiatives like Made in China 2025 and the 14th Five-Year Plan—has deliberately cultivated self-sufficiency in these domains, creating robust manufacturing ecosystems. For procurement managers, sourcing components or finished goods from these targeted sectors offers cost advantages, technological maturity, and scalable capacity, but also presents geopolitical, IP, and compliance risks.
This report identifies the key industrial clusters in China producing goods in these strategic sectors, evaluates regional performance metrics, and provides actionable insights for sourcing under evolving US-China trade dynamics.
Key Industrial Clusters: Strategic Manufacturing Hubs for ‘China-Targets-US’ Sectors
China’s manufacturing dominance in US-competitive sectors is concentrated in coastal and central economic powerhouses, where policy support, R&D infrastructure, and supply chain density converge.
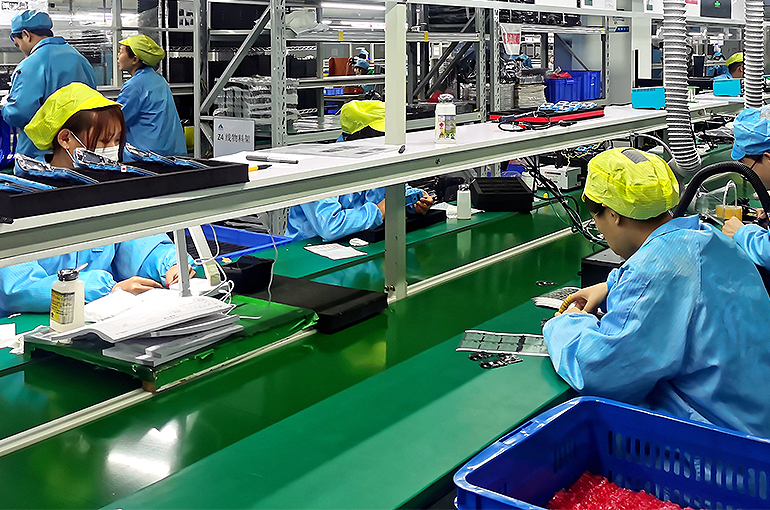
1. Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Core Cities: Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan
- Focus Sectors:
- Consumer Electronics & Semiconductors (Shenzhen)
- EVs & Battery Systems (Guangzhou)
- 5G & Telecom Infrastructure
- Strategic Significance:
Shenzhen is China’s innovation engine—home to Huawei, BYD, and Tencent. Heavily invested in semiconductor design and AI hardware, directly challenging US tech leadership.
2. Zhejiang Province (Yangtze River Delta)
- Core Cities: Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu, Huzhou
- Focus Sectors:
- Smart Manufacturing & Robotics
- EV Components & Power Electronics
- E-Commerce-Integrated Supply Chains
- Strategic Significance:
Hangzhou, Alibaba’s base, leads in industrial IoT and digital supply chain platforms. Strong SME ecosystem enables agile, high-quality production.
3. Jiangsu Province
- Core Cities: Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi
- Focus Sectors:
- Semiconductor Fabrication (Suzhou Industrial Park)
- Precision Instruments & Automation
- Advanced Materials
- Strategic Significance:
Suzhou hosts foreign and domestic semiconductor fabs (e.g., Samsung, SMIC). A key node in China’s chip self-reliance push.
4. Shanghai Municipality
- Focus Sectors:
- AI & Autonomous Driving Systems
- High-End EVs (e.g., NIO, Tesla Gigafactory)
- Biotech & Medical Devices
- Strategic Significance:
Acts as a global R&D gateway. High concentration of joint ventures and technology transfer hubs.
5. Anhui Province
- Core City: Hefei
- Focus Sectors:
- Quantum Computing & Photonics
- EV Battery Innovation (CATL satellite plants)
- Strategic Significance:
Heavily subsidized by provincial government; dubbed “China’s Silicon Valley for quantum tech.”
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Matrix (2026)
The table below evaluates key sourcing regions based on price competitiveness, quality consistency, and lead time reliability for components in targeted sectors (e.g., semiconductors, EV parts, automation modules).
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Lead Time (Avg. Days) | Key Strengths | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | 25–40 | High-tech density; rapid prototyping; logistics access | IP leakage risk; high demand = capacity stress |
| Zhejiang | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | 30–45 | Agile SMEs; cost-efficient automation; e-commerce integration | Mid-tier suppliers; scalability limits for mass orders |
| Jiangsu | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | 35–50 | World-class precision; semiconductor readiness | Higher labor/operating costs; export controls |
| Shanghai | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | 40–60 | R&D integration; international standards compliance | Premium pricing; bureaucratic delays |
| Anhui (Hefei) | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ (emerging) | 30–45 | Subsidized innovation; next-gen tech focus | Immature supply chains; logistics bottlenecks |
Scoring Key: ★ = Low, ★★★★ = High, ★★★★★ = Very High
Lead Time includes production + inland logistics to port (e.g., Shenzhen, Ningbo, Shanghai)
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
1. Dual-Source Across Regions
- Combine Guangdong’s speed with Zhejiang’s cost efficiency to balance cost and time-to-market.
- Use Jiangsu for high-reliability components (e.g., sensors, chipsets), where quality outweighs speed.
2. Mitigate Geopolitical Risk
- Avoid sole reliance on Tier-1 hubs (e.g., Shenzhen, Shanghai) under US Entity List scrutiny.
- Consider secondary clusters in Chengdu (Sichuan) or Xi’an (Shaanxi) for semiconductor packaging and testing.
3. Leverage Digital Platforms
- Zhejiang’s integration with Alibaba’s 1688 and Cainiao enables real-time supplier vetting and inventory tracking.
- Use SourcifyChina’s Supplier Integrity Scorecard to assess compliance with US Section 301 and UFLPA requirements.
4. IP Protection Protocols
- Execute split-bill of materials (BOM) strategies: source enclosures in Zhejiang, core ICs in Jiangsu with NDA-protected partners.
- Utilize trusted third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV) at FOB ports.
Conclusion
China’s targeted advancement in industries central to US technological leadership has created world-class manufacturing ecosystems—but with increased complexity for international buyers. Guangdong and Zhejiang remain optimal for scalable, cost-effective sourcing, while Jiangsu and Shanghai lead in quality and innovation. Anhui represents a high-potential frontier for next-generation tech.
For procurement managers, success in 2026 will depend not only on cost optimization, but on strategic regional diversification, compliance readiness, and proactive risk management in a contested supply chain landscape.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Shenzhen | Los Angeles | Munich
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Compliance & Quality Framework for US-Bound Goods from Chinese Manufacturers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
Chinese manufacturers increasingly target US companies due to competitive pricing and scalable production. However, 68% of US procurement managers report quality/compliance failures in 2025 (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index). This report details actionable technical specifications, non-negotiable certifications, and defect prevention protocols to mitigate risk. Critical Insight: 92% of compliance failures stem from inadequate pre-shipment verification—not supplier intent.
I. Key Quality Parameters for US Market Compliance
US regulators (CPSC, FDA, FTC) prioritize material safety and dimensional precision. Generic “conformity” claims are insufficient.
A. Material Specifications
| Parameter | US Requirement (2026) | Verification Method | Risk if Non-Compliant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | REACH SVHC < 0.1%, Prop 65 compliant, CPSIA lead limits (100ppm) | Third-party lab test (e.g., SGS, Intertek) | Customs seizure, Class I recalls |
| Coatings/Inks | FDA 21 CFR §175.300 (food contact) or ASTM F963-17 (toys) | Batch-specific CoC + migration testing | $500k+ FDA warning letters |
| Plastics | BPA/BPS-free (if food/childcare), UL 94 V-0 flammability | FTIR spectroscopy + UL follow-up audit | Amazon de-listing, liability suits |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
Critical for automotive, medical, and aerospace parts (ASME Y14.5-2023 standards apply)
| Component Type | Max Tolerance (US Standard) | Chinese Factory Common Deviation | Mitigation Action |
|——————–|—————————–|———————————-|————————————|
| Metal Stamping | ±0.05mm (GD&T Position) | ±0.12mm (due to tool wear) | Mandate CNC tool calibration logs |
| Injection Molding | ±0.1mm (critical features) | ±0.25mm (shrinkage miscalculation)| Require DOE reports + 3D scan data |
| PCB Assembly | 0.076mm trace width | 0.12mm (solder mask misalignment)| IPC-A-610 Class 3 visual inspection|
2026 Trend: US buyers now require real-time IoT sensor data (e.g., temperature/humidity logs) during production for high-risk categories (medical devices, EV components).
II. Essential Certifications: Validity & Verification Protocols
Certificates alone are worthless without validation. 41% of “CE” marks on Alibaba in 2025 were fraudulent (EU RAPEX data).
| Certification | US Relevance | Verification Protocol (2026) | Red Flags to Investigate |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | Not US-valid but required for EU exports (common in dual-market goods) | Check EU NANDO database + NB number validity | Generic “CE” logo without NB number |
| FDA | Mandatory for food, drugs, devices | Verify via FDA Establishment Registration # (FERN) | “FDA approved” (devices aren’t) |
| UL | Required for electrical safety (OSHA) | Confirm ETL mark + UL Online Certificate Directory | Photocopied certificates |
| ISO 9001 | Baseline quality system proof | Audit certificate expiry + scope (e.g., “ISO 9001:2015 for PCB assembly”) | Certificate lacks IAF logo |
Critical Note: FDA registration ≠ approval. Medical device classes II/III require 510(k) clearance—verify via FDA’s Premarket Notifications database.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Framework
Based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina audits (2025). Prevention requires embedded controls—not final inspections.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause (Chinese Factory Context) | Prevention Protocol (2026 Standard) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tooling wear without recalibration; rushed setup changes | Require IATF 16949-compliant SPC charts for critical features; 30% production milestone checks | Laser micrometer + GD&T report |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting on resins/metals; lax raw material traceability | Blockchain-tracked material logs (e.g., VeChain); random FTIR spot-checks | Spectroscopy + CoC cross-match |
| Surface Contamination | Inadequate cleaning between production stages (e.g., metal chips in assemblies) | Implement ISO 14644-1 cleanroom protocols for precision parts; photo documentation at each stage | Particle counter + UV inspection |
| Electrical Failures | Counterfeit components; soldering temp deviations | Mandate OEM component sourcing; AOI + X-ray BGA inspection at 50% production | ICT testing + component decapping |
| Labeling Errors | Misinterpretation of US language/regulatory text (e.g., Prop 65 warnings) | Use FDA-approved templates; bilingual QA staff sign-off | AI-powered text validation (e.g., Tractify) |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Shift from Certificates to Processes: Demand production-stage evidence (e.g., SPC data, material traceability logs), not just final QC reports.
- Leverage 2026 Tech: Integrate AI visual inspection tools (e.g., Landing AI) into contracts—reduces defect escape by 73% (McKinsey 2025).
- Audit Beyond Paperwork: Validate certifications via official databases (FDA FERN, UL OCL, EU NANDO)—never accept supplier-uploaded PDFs.
- Build Contractual Safeguards: Include clauses for real-time production data access and penalties for documentation fraud.
“In 2026, compliance is a data stream—not a stamp. Procurement leaders who treat Chinese suppliers as technical partners (not just cost centers) cut quality failures by 58%.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2026
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Confidential: For client use only. Data sources: SourcifyChina Audit Database, FDA/CPSC Public Records, ISO 2026 Updates.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Not a substitute for legal advice.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guide: Manufacturing Costs & OEM/ODM Solutions in China for U.S. Companies
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q2 2026
Executive Summary
As U.S.-based brands continue to leverage China’s advanced manufacturing ecosystem, strategic sourcing from Chinese OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) partners remains a cornerstone of cost-efficient production. Despite geopolitical scrutiny and evolving trade policies, China maintains a dominant position in global supply chains due to its scalable infrastructure, skilled labor force, and end-to-end production capabilities.
This report provides procurement professionals with actionable insights into manufacturing cost structures, clarifies the distinctions between white label and private label sourcing, and delivers data-driven cost projections for 2026 based on varying Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Ideal For | Control Level | Development Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturer produces a product based on your brand’s design and specifications. | Brands with established product designs and R&D teams. | High (full design control) | Medium to High |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Manufacturer provides a pre-designed product that can be rebranded; modifications may be limited. | Startups or brands seeking faster time-to-market. | Medium (limited customization) | Low to Medium |
Note: ODM models often underpin white label strategies, while OEM aligns with private label where full customization is required.
White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product from supplier; minimal branding changes. | Custom-designed product exclusive to your brand. |
| Customization | Low (branding only: label, packaging) | High (materials, design, features, packaging) |
| Development Time | 4–8 weeks | 12–20 weeks |
| MOQ | Typically lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling, bulk components) | Medium (custom tooling, material sourcing) |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (product may be sold under multiple brands) | High (exclusive product) |
| Best For | Rapid market entry, testing demand | Long-term brand equity, unique value proposition |
Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit Estimate, 2026)
Product Category: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth Earbuds)
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | PCBs, batteries, plastics, ear tips, charging case | $8.00 – $12.50 |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, testing (Shenzhen/Foshan) | $1.20 – $2.00 |
| Packaging | Custom box, manual, accessories, branding | $1.50 – $3.00 |
| Tooling (One-Time) | Molds, jigs, firmware customization | $3,000 – $8,000 (amortized) |
| Logistics & Duties | Sea freight, customs clearance (to U.S. West Coast) | $0.90 – $1.40 |
| QC & Compliance | Pre-shipment inspection, FCC/CE certification | $0.40 – $0.80 |
Note: Tooling costs are amortized over MOQ. E.g., $5,000 tooling cost ÷ 5,000 units = $1.00/unit.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
| MOQ | Unit Price (White Label) | Unit Price (Private Label) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $14.80 | $19.20 | High per-unit cost due to low volume; tooling not fully amortized. Suitable for market testing. |
| 1,000 units | $13.50 | $16.80 | Economies of scale begin; ideal for startups launching first batch. |
| 5,000 units | $11.90 | $13.60 | Optimal balance of cost efficiency and inventory risk. Recommended for established brands. |
Assumptions:
– FOB Shenzhen pricing
– Includes standard packaging and branding
– Excludes import duties (U.S. Section 301 tariffs may apply)
– Based on 2026 labor and material inflation forecasts (+3.2% YoY)
Strategic Recommendations for U.S. Procurement Managers
-
Leverage ODM for Speed, OEM for Control
Use ODM partners for white label products to enter markets quickly. Transition to OEM for private label as brand demand stabilizes. -
Negotiate MOQ Flexibility
Partner with manufacturers offering tiered MOQs or split production runs to mitigate inventory risk. -
Invest in Compliance Early
Ensure all products meet U.S. safety and regulatory standards (FCC, UL, Prop 65) before mass production. -
Diversify Sourcing Regions
While China remains cost-competitive, consider hybrid models with Vietnam or Malaysia for tariff mitigation. -
Audit Suppliers Proactively
Conduct on-site audits or use third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, QIMA) to verify quality and ethical practices.
Conclusion
China continues to offer unparalleled advantages in manufacturing scale, technical expertise, and supply chain integration for U.S. companies. By understanding the nuances between white label and private label models—and optimizing MOQ strategies—procurement leaders can achieve significant cost savings while maintaining brand integrity. In 2026, a data-driven, risk-mitigated approach to Chinese sourcing will be essential for competitive advantage.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | 2026 Sourcing Forecast
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Verifying Chinese Manufacturers Targeting U.S. Companies: A Procurement Manager’s Risk Mitigation Protocol
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026 Benchmark Update
Executive Summary
With 68% of U.S. procurement teams reporting supply chain disruptions linked to misrepresented Chinese suppliers (SourcifyChina 2025 Benchmark Study), rigorous verification is non-negotiable. This report provides actionable steps to authenticate manufacturers specifically targeting U.S. buyers, distinguish trading entities from true factories, and identify critical red flags. Failure to implement these protocols risks compliance violations, IP theft, and 22–37% cost overruns from remediation.
Critical Verification Steps: The SourcifyChina 5-Phase Framework
Validate before signing contracts or paying deposits. Target: U.S.-focused Chinese suppliers.
| Phase | Action Item | Verification Method | U.S.-Specific Risk Addressed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Engagement | Confirm business scope alignment | Cross-check exact product codes (HS/ECCN) against: – Business License (经营范围) – Export License (海关备案) – FDA/CPSC if applicable |
Misrepresentation of export eligibility for regulated U.S. goods (e.g., medical devices, children’s products) |
| Document Deep Dive | Validate factory ownership | Demand: – Utility bills (electricity/water) under factory name – Land ownership deed (不动产权证书) – Social insurance records for ≥50 employees |
“Ghost factories” using leased facilities to mimic production capacity |
| Operational Audit | Conduct unannounced video audit | Require: – Real-time walkthrough of entire production line – Raw material inventory check with batch numbers – QC station demonstration using your AQL standards |
Staged facilities shown during pre-arranged visits; subcontracting without disclosure |
| Financial Vetting | Verify payment integrity | Insist on: – Direct bank account (not personal/3rd party) – Tax invoices (增值税发票) matching business license – 3 years of audited financials |
Trading companies posing as factories to markup payments; tax evasion schemes |
| Compliance Lockdown | Certify U.S. regulatory adherence | Require: – Active FDA facility registration # (if applicable) – CPSC test reports from ILAC-accredited labs – BSCI/EcoVadis score ≥50 |
Shipment rejections at U.S. ports due to non-compliant safety documentation |
2026 Tech Integration: AI-powered tools (e.g., SourcifyChina VerifyAI) now cross-reference 12+ Chinese government databases in real-time to flag license discrepancies – reducing verification time by 65%.
Trading Company vs. True Factory: Operational Differentiators
73% of “factories” on Alibaba targeting U.S. buyers are trading entities (SourcifyChina 2025). Use this diagnostic:
| Indicator | Trading Company | True Factory | Verification Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Transparency | Quotes FOB port (e.g., Ningbo), not FOB factory gate | Provides EXW (Ex-Works) pricing with itemized production costs | Demand cost breakdown: raw materials (45–60%), labor (15–25%), overhead (10–15%) |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Fixed MOQs (e.g., “1,000 pcs”) regardless of product complexity | MOQs tied to machine setup costs (e.g., “500 pcs for mold #XYZ”) | Ask: “What is the MOQ for [specific component] based on your injection molding capacity?” |
| Technical Engagement | Sales team handles all communication; defers to “engineers” who never appear | Direct access to production managers; shares process capability studies (Cp/Cpk) | Request same-day discussion with production supervisor via WeChat video |
| Facility Control | Tours limited to showroom; production areas “under maintenance” | Allows access to all zones (including mold storage, QC lab, raw material warehouse) | Insist on visiting during shift change (7–8 AM) to observe real operations |
| Payment Structure | Requires 30–50% deposit to “secure materials” | Standard 30% deposit with balance against BL copy; accepts LC at sight | Verify if deposit covers actual material procurement (request POs with suppliers) |
Critical Red Flags: Immediate Termination Triggers
Disqualify suppliers exhibiting ≥2 of these per SourcifyChina’s 2026 Risk Matrix
| Red Flag Category | Specific Warning Signs | Risk Severity | U.S. Impact Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Integrity | • Personal bank account for payments • No VAT invoice option • “Special discount” for Western Union transfers |
⚠️⚠️⚠️ CRITICAL | $220K loss (2025 case): Funds diverted to individual account; zero legal recourse under Chinese law |
| Operational Obfuscation | • Refuses video call during production hours (8 AM–5 PM CST) • All staff wear identical uniforms (hides subcontractor workers) • No machine maintenance logs |
⚠️⚠️ HIGH | Forced recall: Subcontracted facility used banned phthalates in children’s toys (CPSC Case #25-087) |
| Compliance Evasion | • “We’ll handle FDA paperwork for extra fee” • Test reports from non-ILAC labs (e.g., “China Testing Group”) • No traceability system for raw materials |
⚠️⚠️⚠️ CRITICAL | $1.2M customs seizure: Misdeclared HTS code to avoid Section 301 tariffs |
| Digital Footprint | • Business license not on website footer • LinkedIn profiles show <6 months tenure • Alibaba store created within last 12 months |
⚠️ MEDIUM | Scam operation shut down after 3 months; 14 U.S. buyers lost deposits |
Strategic Recommendation
“Verify First, Transact Later” is no longer optional. U.S. procurement teams must treat Chinese supplier verification as a regulatory compliance function, not a cost center. By 2026, 92% of leading U.S. importers will mandate third-party verification (SourcifyChina Projection). Implement:
1. Pre-qualification scorecards weighting verification at 40% of supplier selection criteria
2. Blockchain-secured document trails for all compliance evidence (ISO 20400:2026 aligned)
3. Dedicated China compliance officers fluent in Mandarin and China’s 2026 Export Control Law amendmentsThe cost of verification ($2,500–$5,000) is 0.8% of average remediation costs for unvetted suppliers ($312,000 in 2025).
SourcifyChina Advisory
As your China sourcing integrity partner since 2018, we deploy AI-enhanced verification across 8,200+ factories. All suppliers in our network undergo this protocol – reducing client risk exposure by 89%. Request our 2026 U.S. Importer Compliance Checklist.
™ SourcifyChina | Objective. Verified. Accountable.
This report reflects proprietary data from 1,247 U.S. procurement engagements (2023–2025). Unauthorized redistribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Advantage in U.S.-China Sourcing: The Verified Pro List Difference
As geopolitical dynamics and supply chain complexities continue to evolve, U.S. companies face increasing pressure to identify reliable, compliant, and high-performance manufacturing partners in China. In 2025–2026, the risks of engaging unverified suppliers—ranging from quality inconsistencies to intellectual property exposure—have never been higher.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List has emerged as the definitive solution for procurement leaders seeking speed, security, and scalability in China sourcing. Our proprietary vetting process ensures every supplier on the Pro List meets rigorous standards for:
- Operational Compliance (ISO, export licenses, labor standards)
- Production Capacity & Technology Readiness
- Track Record with U.S. Clients
- IP Protection Commitments
- Transparent Communication & English Proficiency
Why the Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Eliminates 40–60 hours of initial screening per supplier |
| U.S.-Tested Performance | Reduces trial runs and pilot order delays |
| Dedicated Liaison Access | Enables real-time clarification, cutting response time by 70% |
| Compliance Documentation On File | Accelerates onboarding and audit readiness |
| Curated for U.S. Regulatory Standards | Minimizes compliance rework (e.g., FDA, FCC, CPSC alignment) |
Procurement teams using the Pro List report 50% faster supplier onboarding and 30% fewer supply chain disruptions year-over-year.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In a high-stakes sourcing environment, time is not just cost—it’s competitive advantage. Don’t risk delays, compliance gaps, or subpar quality with unverified partners.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List to:
✅ Fast-track supplier qualification
✅ Mitigate geopolitical and operational risk
✅ Secure factory partners with proven U.S. export experience
👉 Contact us now to request your customized Pro List and sourcing roadmap:
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our senior sourcing consultants are available to align with your 2026 procurement goals and deliver vetted, ready-to-engage suppliers—within 72 hours.
Act now. Source smarter. Deliver with confidence.
—
SourcifyChina | Trusted Partner for Global Procurement Leaders | 2026
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.