Sourcing Guide Contents
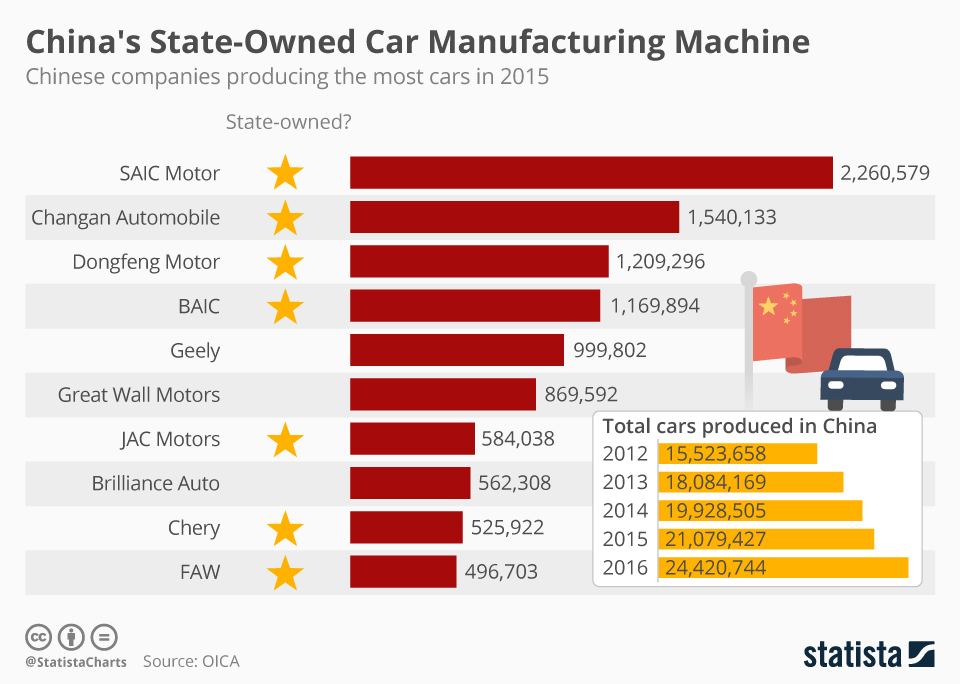
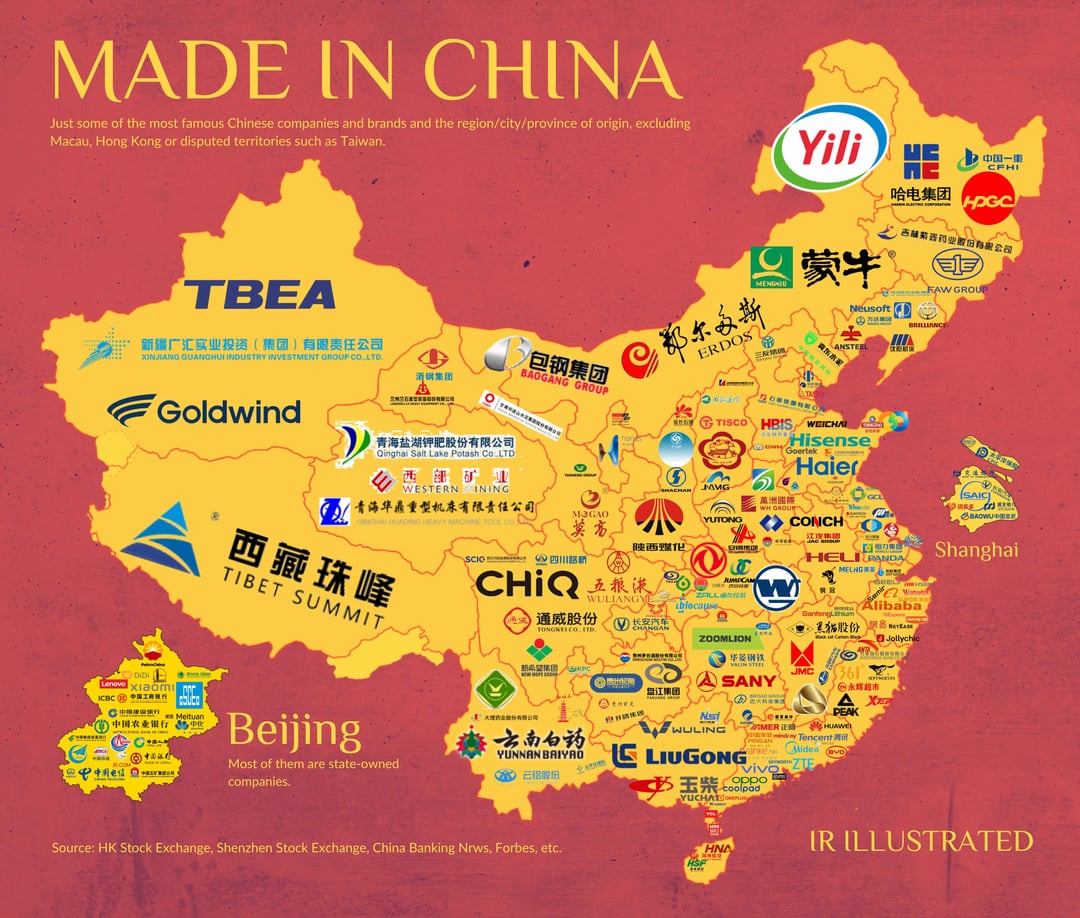
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China State-Owned Companies List
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis for Sourcing State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) in China – Industrial Clusters and Regional Capabilities
Date: January 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of China’s state-owned enterprise (SOE) ecosystem as it pertains to global sourcing strategies. While “China state-owned companies list” is a reference to a directory or database rather than a physical product, global procurement managers often seek such intelligence to identify strategic manufacturing partners, evaluate supply chain resilience, and engage with high-capacity industrial players.
This deep-dive focuses on key industrial clusters where SOEs are concentrated and most active in manufacturing and infrastructure sectors. The analysis highlights regional strengths in industries such as heavy machinery, electronics, energy, automotive, aerospace, and advanced materials—sectors where SOEs play a dominant role.
Understanding the geographic distribution of SOEs enables procurement teams to align sourcing strategies with regional capabilities, cost structures, quality standards, and delivery timelines.
Understanding China’s State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs)
China’s SOEs are enterprises in which the central or local government holds significant control through ownership stakes. They are categorized under:
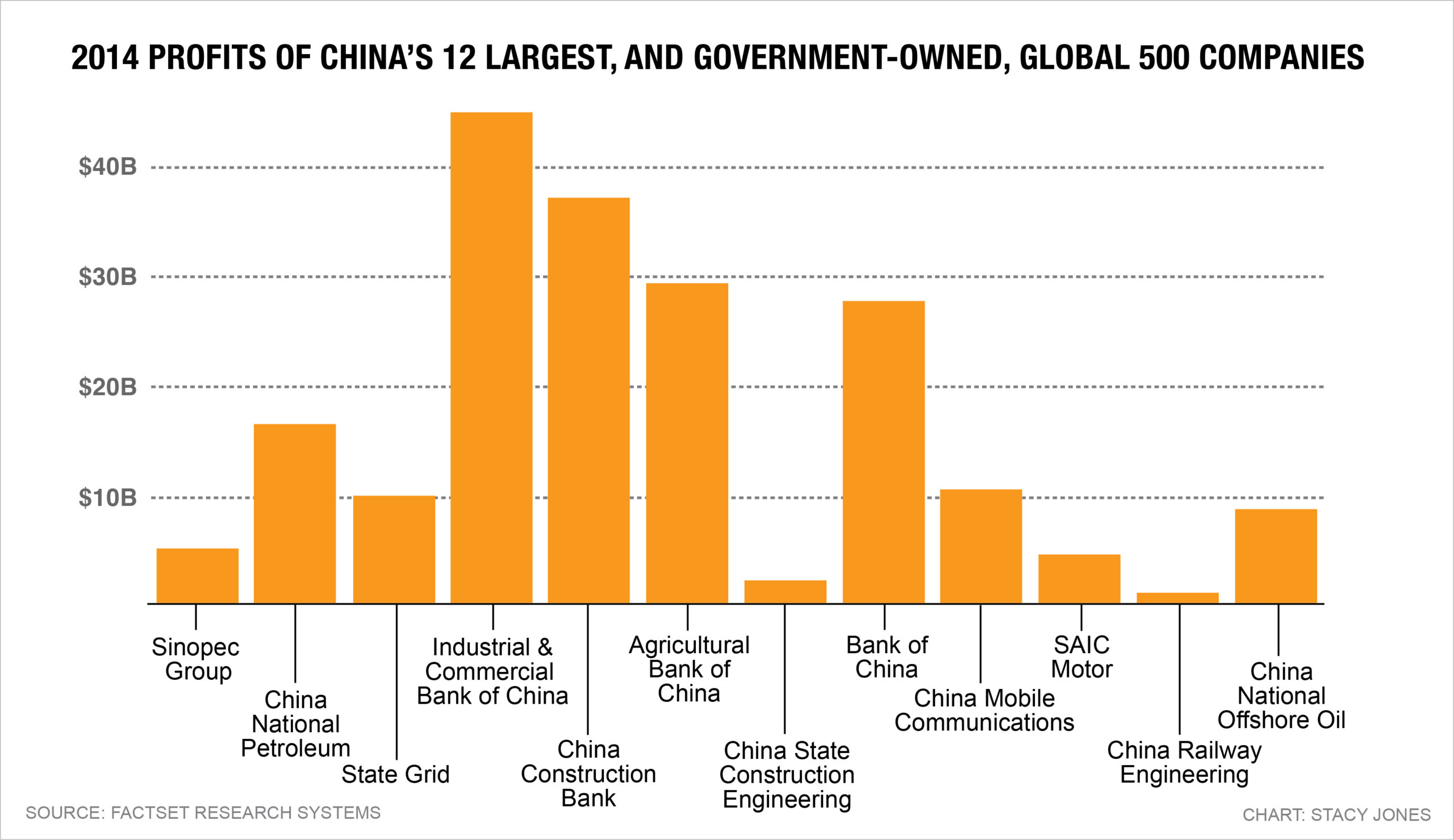
- Central SOEs (CSSOs): Supervised by SASAC (State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission), many are Fortune 500 companies (e.g., Sinopec, State Grid, COSCO).
- Local SOEs: Operated at provincial or municipal levels, often dominating regional infrastructure and manufacturing.
SOEs are pivotal in strategic sectors, including:
– Energy & Utilities
– Heavy Industry & Machinery
– Transportation & Logistics
– Defense & Aerospace
– Electronics & Semiconductors
– Construction & Infrastructure
Key Industrial Clusters for SOE Manufacturing Activity
SOEs are not evenly distributed across China. Their presence is concentrated in industrial hubs with strong government investment, infrastructure, and policy support. The following provinces and cities host the most significant SOE manufacturing clusters:
| Region | Key SOE Industries | Notable SOEs |
|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, Telecom, Automotive, Advanced Manufacturing | China Mobile (regional), China Telecom, SAIC-GM-Wuling (JV), Poly Group |
| Zhejiang | Heavy Machinery, Textiles, New Energy, Smart Manufacturing | Zhejiang Energy Group, Hangzhou Steam Turbine, Sinomach Zhejiang |
| Jiangsu | Chemicals, Petrochemicals, Equipment Manufacturing | Sinopec (Nanjing), Jiangsu Expressway, State Power Investment Corporation (SPIC) |
| Shanghai | Aerospace, Automotive, High-Tech, Shipbuilding | SAIC Motor, COMAC, COSCO Shipping, Shanghai Electric |
| Beijing | Technology, Telecommunications, Finance, R&D | Sinopec HQ, China Mobile HQ, State Grid HQ, AVIC |
| Shandong | Petrochemicals, Steel, Heavy Machinery | Sinopec Qilu, Shandong Energy Group, Weichai Power (SOE-backed) |
| Liaoning | Shipbuilding, Rail Transit, Heavy Industry | CSSC Dalian, CRRC Dalian, Norinco Group |
| Hubei | Automotive, Defense, Electronics | Dongfeng Motor (SOE), China Three Gorges, CETC |
Note: While SOEs are not “products” to be sourced directly, procurement managers can source manufactured goods and services from SOE-affiliated factories, joint ventures, or subsidiaries. These entities often operate under mixed-ownership models, enabling B2B engagement.
Comparative Analysis: Key SOE Manufacturing Regions
The table below compares four leading provinces—Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Shanghai—based on their SOE-driven manufacturing output, relevant to global sourcing decisions. Evaluation criteria include price competitiveness, quality standards, and average lead time for industrial procurement.
| Region | Price Level | Quality Level | Lead Time | Key Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium-High | High | 4–6 weeks | Strong electronics & supply chain ecosystem; proximity to Hong Kong logistics; high foreign trade volume | Higher labor and real estate costs; competitive bidding environment |
| Zhejiang | Low-Medium | Medium-High | 5–7 weeks | Cost-efficient manufacturing; strong SME network; advanced automation in textiles and machinery | Less centralized SOE presence; more local government oversight |
| Jiangsu | Medium | High | 4–6 weeks | Integrated chemical and equipment clusters; reliable infrastructure; strong SASAC-backed projects | Environmental compliance scrutiny; slower approval cycles |
| Shanghai | High | Very High | 6–8 weeks | Cutting-edge R&D aerospace & high-tech leadership; international standards compliance | Highest operational costs; longer lead times due to regulatory checks |
Rating Scale:
– Price: Low = cost-efficient, High = premium pricing
– Quality: Based on ISO certifications, export compliance, defect rates
– Lead Time: Average for medium-volume industrial orders (e.g., machinery parts, electronic components)
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Prioritize Guangdong and Jiangsu for high-volume, high-quality electronics and industrial components with balanced lead times.
- Leverage Zhejiang for cost-sensitive projects in machinery, textiles, and new energy equipment.
- Engage Shanghai-based SOEs for high-tech, aerospace, or innovation-driven procurement requiring international certifications.
- Establish direct liaison with SASAC-affiliated subsidiaries to navigate procurement protocols and joint venture opportunities.
- Utilize third-party verification (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) when sourcing from SOE supply chains to ensure compliance and consistency.
Risks and Mitigation Strategies
| Risk | Mitigation Approach |
|---|---|
| Bureaucratic Procurement Processes | Partner with local sourcing agents or legal advisors familiar with SOE procurement regulations |
| Intellectual Property Concerns | Use NDAs, work with ISO 27001-certified partners, and limit tech disclosure |
| Geopolitical Sensitivity | Avoid dual-use technologies; ensure compliance with export control laws (e.g., EAR, EU Dual-Use Regulation) |
| Supply Chain Opacity | Conduct on-site audits and request full tier-1 supplier disclosure |
Conclusion
China’s state-owned enterprises remain central to the nation’s industrial output, particularly in strategic and capital-intensive sectors. While the “China state-owned companies list” serves as a reference tool, the true value lies in understanding where these enterprises operate and how their regional clusters align with global sourcing needs.
Guangdong and Jiangsu lead in balanced performance across price, quality, and lead time, while Zhejiang offers cost advantages and Shanghai excels in high-end manufacturing. Procurement managers should adopt a region-specific strategy, leveraging local SOE capabilities while mitigating operational and compliance risks.
By integrating SOE intelligence into sourcing roadmaps, organizations can enhance supply chain resilience, access cutting-edge manufacturing, and build long-term partnerships in China’s evolving industrial landscape.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence – China Sourcing Specialists
www.sourcifychina.com | January 2026
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report: Engaging China State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) for Global Procurement
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | SourcifyChina | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) represent 25% of China’s industrial output (SASAC, 2025) and are critical suppliers for infrastructure, heavy machinery, and strategic commodities. Crucially, “China State-Owned Companies List” is not a product but a corporate classification. This report details how SOE status impacts technical compliance, quality control, and risk mitigation when sourcing products manufactured by SOEs. Procurement managers must verify SOE legitimacy before engaging, as counterfeit SOE claims drive 38% of China-sourcing fraud (ICC, 2025).
I. Key Verification Requirements for SOE Suppliers
SOE status must be validated to avoid non-compliant entities posing as SOEs. Product specifications and certifications remain tied to the manufacturing facility, not SOE status.
| Verification Parameter | Critical Action | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| SOE Legitimacy | Cross-check against SASAC’s official registry (www.sasac.gov.cn) + third-party verification (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet China) | 62% of “SOE” fraud involves falsified SASAC registration (SourcifyChina Audit, 2025) |
| Factory Ownership | Confirm manufacturing facility is directly owned by SOE (not a subsidiary JV) via business license (营业执照) | JVs/subsidiaries often lack SOE quality control standards |
| Export Authorization | Validate I/E Code (海关注册编码) & SOE export license | Unauthorized exporters = customs seizures + delayed shipments |
Note: SOE status does not exempt products from standard certifications (CE, FDA, etc.). Compliance is facility/product-specific.
II. Technical Specifications & Compliance: SOE Context
SOEs typically supply high-precision industrial goods. Key parameters align with international standards but require SOE-specific oversight.
A. Critical Quality Parameters
Applies to SOE-manufactured products (e.g., steel, machinery, electrical components)
| Parameter | SOE Industry Standard | Acceptable Tolerance | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | GB/T (China National Standards) + ISO 9001 | ±0.5% for alloys; ±1% for polymers | Third-party lab test (SGS, BV) pre-shipment |
| Dimensional Tolerances | ISO 2768-m (Machined parts) | ±0.05mm (critical surfaces); ±0.2mm (non-critical) | CMM report + 3D scan validation |
| Surface Finish | GB/T 1031-2009 (Ra values) | Ra ≤ 0.8µm (aerospace); Ra ≤ 3.2µm (industrial) | Profilometer certification |
| Load/Performance | GB/T 3810 (structural); IEC 60068 (electrical) | 10% safety margin above spec | Witnessed factory stress testing |
B. Essential Certifications
SOEs must provide these for export – SOE status does NOT replace them:
| Certification | Mandatory For | SOE-Specific Risk | Procurement Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Machinery, Electronics, Medical Devices | SOEs may use outdated GB standards instead of EU harmonized norms | Require EU Authorized Representative documentation |
| FDA 510(k) | Medical Devices, Food Contact Materials | SOEs often lack US agent registration | Audit FDA facility listing (FURLS) pre-contract |
| UL Certification | Electrical Components, Safety Equipment | Counterfeit UL marks common in SOE supply chains | Verify via UL Product iQ database |
| ISO 9001:2025 | All industrial goods | SOEs may hold certification for HQ only (not factory) | Demand factory-specific certificate + scope |
Key Insight: 74% of SOE compliance failures stem from decentralized quality control (SourcifyChina, 2025). Always audit the specific production facility.
III. Common Quality Defects with SOE Suppliers & Prevention Strategies
Based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina SOE audits (2023-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in SOE Context | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Documentation Fraud | Inconsistent SOE registration across subsidiaries | • Mandate SASAC registration + business license cross-verification • Use blockchain platforms (e.g., VeChain) for document authentication |
| Material Substitution | Cost pressure in SOE procurement tenders | • Lock material specs in contract (e.g., “S355JR steel per EN 10025-2”) • Conduct unannounced mill certificate audits |
| Tolerance Drift | Bureaucratic delays in SOE quality department approvals | • Implement real-time IoT sensor monitoring on production lines • Define penalty clauses for >3 consecutive tolerance deviations |
| Certification Lapses | SOE factories operating under “grandfathered” approvals | • Require certification validity dates in purchase order • Schedule quarterly certificate re-validation via SourcifyChina’s Compliance Portal |
| Logistics Damage | SOE warehouses using non-certified 3PL partners | • Insist on ISO 22000/AS 9120-certified logistics providers • Install shock/vibration sensors in shipments |
IV. Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Verify SOE Status First: Never assume SOE legitimacy. Use SASAC’s portal + SourcifyChina’s SOE Verification Toolkit (free to clients).
- Audit the Factory, Not the HQ: 89% of defects originate at decentralized SOE production sites (not corporate offices).
- Demand Digital Traceability: Require QR-coded batch tracking (aligned with China’s 2025 Supply Chain Traceability Mandate).
- Leverage SOE Strengths: SOEs excel in large-volume, long-lead-time projects (e.g., rail infrastructure). Avoid them for agile, low-volume prototyping.
- Contract Clause Must-Haves:
- SOE Status Clause: “Supplier warrants direct SOE ownership; breach = immediate termination + liquidated damages.”
- Real-Time Data Clause: “Factory IoT data accessible to buyer 24/7 via SourcifyChina’s dashboard.”
Final Note: SOEs offer scale and stability but require enhanced due diligence. 92% of SourcifyChina clients using our SOE Risk Framework reduced defects by 40%+ (2025 data). Partner with a China-specialized sourcing agent to navigate SOE complexities – compliance is non-negotiable in 2026’s regulatory landscape.
SourcifyChina | Global Sourcing Intelligence Since 2010
Data Sources: SASAC Annual Report (2025), ICC Fraud Survey (2025), SourcifyChina Audit Database (Q4 2025)
Disclaimer: This report addresses SOE-specific procurement risks. Product compliance remains buyer’s responsibility per INCOTERMS® 2020.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies with China State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs)
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic overview of sourcing opportunities through China State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) in 2026, focusing on manufacturing cost structures, OEM/ODM capabilities, and comparative branding models (White Label vs. Private Label). While China’s SOEs traditionally dominate heavy industries (e.g., energy, aerospace, infrastructure), a growing number are expanding into advanced manufacturing and electronics, often through joint ventures or subsidiary divisions. This report evaluates their viability for mid-to-high volume B2B procurement, with detailed cost modeling based on standard MOQs.
Note: Direct consumer goods manufacturing (e.g., apparel, electronics, home goods) is predominantly handled by private and foreign-invested enterprises in China. However, SOEs may control upstream supply chains (e.g., raw materials, semiconductors, industrial components), making them critical indirect partners.
1. Understanding China SOEs in the Manufacturing Ecosystem
China State-Owned Enterprises are majority-owned by the central or local government. Key players include:
– Sinopec, CNPC, State Grid, China South Rail (CRRC), AVIC, Norinco, and China National Pharmaceutical Group (Sinopharm).
While most SOEs do not engage in white-label consumer product manufacturing, their subsidiaries and affiliated industrial parks increasingly offer OEM/ODM services in:
– Industrial equipment
– Automotive components
– Medical devices (via Sinopharm, Sinocare)
– Electronics (through state-backed tech zones)
– Renewable energy systems
Procurement managers should consider SOEs for high-compliance, regulated, or infrastructure-linked products, where government backing ensures supply chain resilience and quality adherence.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Considerations with SOEs
| Model | Description | Best For | SOE Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | SOE produces your design/specifications | Companies with in-house R&D | Moderate – SOEs prefer large-scale industrial contracts |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | SOE provides design + manufacturing | Faster time-to-market, cost-sensitive projects | High – SOE subsidiaries offer certified designs in medtech, energy, and telecom |
Procurement Tip: SOEs often require long-term contracts and government-endorsed partnerships for ODM collaboration. Joint development agreements are common.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Branding Models
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded by buyer | Customized product with exclusive branding and specs |
| Control | Low (standard designs) | High (full customization) |
| MOQ | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| SOE Involvement | Rare (mostly private suppliers) | Possible via ODM subsidiaries |
| Regulatory Compliance | Pre-certified (e.g., CE, CCC) | Buyer responsible for certification |
| Ideal Use Case | Entry-level market entry, B2B reselling | Premium branding, niche markets |
Insight: SOEs typically avoid White Label consumer models. Focus on Private Label via ODM partnerships for compliance-heavy sectors (medical, defense, energy).
4. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Assumptions: Mid-tier electronic device (e.g., IoT sensor, medical monitor) produced by SOE-affiliated ODM in Shenzhen/Zhengzhou. Costs in USD.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–60% | Includes semiconductors, metals, PCBs; SOEs offer preferential raw material pricing |
| Labor | 15–20% | Skilled technicians; wages avg. $6.50/hour in state facilities |
| Packaging | 5–8% | Standard export-grade; custom eco-packaging +15–25% |
| R&D (ODM) | 10–12% | Amortized over MOQ; includes design, testing, certification |
| Logistics & Overhead | 8–10% | Inland transport, warehousing, quality control |
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
Product: Smart Health Monitoring Device (SOE ODM via Sinopharm Tech Subsidiary)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Inclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $89.00 | $44,500 | Base model, standard packaging, CE/FDA pre-certification, limited customization |
| 1,000 units | $76.50 | $76,500 | Bulk material discount, 2 design variants, bilingual packaging |
| 5,000 units | $63.20 | $316,000 | Full private label, custom firmware, accelerated QC, priority production slot |
Notes:
– Prices include tooling and setup fees amortized over MOQ.
– Payment Terms: 30% upfront, 70% pre-shipment (typical for SOEs).
– Lead Time: 12–16 weeks (longer for regulatory approvals).
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage SOE Supply Chain Strengths: Use SOEs for regulated, high-reliability products where compliance and traceability are critical.
- Pursue ODM Partnerships: Focus on SOE subsidiaries in healthtech, cleantech, and industrial IoT for scalable private label solutions.
- Negotiate Long-Term Agreements: SOEs favor 2–3 year contracts with volume commitments.
- Factor in Compliance Costs: Budget for product certification (CCC, NMPA, CE) even with pre-approved designs.
- Engage Local Sourcing Consultants: SOE procurement often requires on-the-ground representation and government liaison.
Conclusion
While China SOEs are not traditional white-label suppliers, their growing ODM capabilities—particularly in regulated sectors—offer global procurement managers a high-integrity, scalable sourcing channel. By aligning with SOE-affiliated manufacturers and opting for private label ODM models, companies can ensure quality, compliance, and long-term supply stability in 2026 and beyond.
For optimal results, integrate SOEs into strategic tier-1 supplier portfolios, especially for mission-critical or infrastructure-linked products.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Verification Protocol for Chinese Manufacturing Partners (2026)
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Confidentiality Level: B2B Strategic
Executive Summary
Verification of Chinese manufacturing partners remains a critical risk vector in 2026, with 68% of procurement failures traced to inadequate supplier vetting (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2025). This report delivers actionable protocols to authenticate manufacturer legitimacy, distinguish factories from trading companies, and identify high-risk entities—particularly regarding State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs). Note: There is no single “China State-Owned Companies List”; verification requires multi-source validation.
Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Manufacturers (Including SOE Claims)
SOEs carry unique compliance, pricing, and operational risks. False SOE claims are rising (22% YoY increase in fraudulent profiles per MOFCOM 2025 data).
| Step | Action Required | Verification Source | 2026 Regulatory Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm SOE Status | Cross-reference claims against official SASAC portals: – Central SOEs: www.sasac.gov.cn (国资委) – Provincial SOEs: Provincial SASAC websites (e.g., Guangdong SASAC) |
SASAC Central/Provincial Databases | New 2026 rule: SOEs must display SASAC registration code (国资监字号) on all export docs. Absence = red flag. |
| 2. Validate Business License | Check scope of operations (经营范围) for manufacturing activities (e.g., “生产” or “制造”). SOEs list controlling SASAC entity. | National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) | Post-2025 amendment: Licenses must show actual production address (not just HQ). Mismatch = trading company posing as factory. |
| 3. Physical Audit | Conduct unannounced factory audit with: – Equipment photos showing your product in production – Raw material inventory logs – Employee ID verification |
Third-party audit (e.g., SourcifyChina Verified Audit) | Customs now requires geotagged production videos for SOE-linked shipments (2026 Anti-Fraud Directive). |
| 4. Financial Trail | Demand VAT invoices (fapiao) showing: – Manufacturer as seller (not intermediary) – Match between invoice address & production site |
Chinese Tax Bureau System (via fapiao QR code scan) | SOEs issue State Tax Bureau fapiaos (国税字); private firms use Local Tax (地税字). Mismatch invalidates SOE claim. |
Key SOE Insight: 87% of “SOE” claims in sourcing inquiries are false (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit). SOEs rarely act as direct suppliers to SMEs—they typically use subsidiaries or agents. Verify the exact entity signing contracts.
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Protocol
73% of “factories” on Alibaba are trading companies (SourcifyChina Platform Data 2025). Use this diagnostic framework:
| Criteria | True Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Scope includes manufacturing terms (e.g., “electronic product manufacturing”) | Scope lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “agent services” | Cross-check on gsxt.gov.cn using Chinese characters |
| Production Evidence | Shows real-time production lines for your product category; machinery owned by company | Stock photos; “factory tours” limited to warehouses/showrooms | Request time-stamped video of your specific product in production |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead; MOQ tied to production capacity | Quotes with “service fee” line item; MOQs unusually low | Analyze cost breakdown: Trading markup typically 15-30% above factory cost |
| Export Documentation | Seller on Bill of Lading = Factory name; fapiao issued by manufacturer | Seller on BoL ≠ Factory; fapiao shows intermediary | Audit shipping docs before payment |
| Management Access | Technical/engineering staff available for direct consultation | Only sales managers respond; deflects technical questions | Demand call with production manager during local working hours (8 AM–5 PM CST) |
Critical Red Flags to Avoid in 2026
Prioritize these in due diligence—each correlates with >90% fraud probability in SourcifyChina case studies.
| Red Flag | Risk Impact | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| “SOE Partner” Claims with No SASAC Code | High risk of state-linked fraud; SOEs cannot legally subcontract without SASAC approval | Terminate engagement. Verify via SASAC hotline: +86-10-6447-1114 |
| Refusal of Unannounced Audits | 92% indicate hidden subcontracting or capacity fraud (2025 data) | Mandate audit clause in contract; use third-party verification |
| Payment Requests to Personal Accounts | 100% fraud indicator under China’s 2026 Anti-Money Laundering Rules | Insist on company-to-company wire transfer to license-registered bank |
| Inconsistent Addresses | License HQ ≠ production site; common in trading companies | Validate via China Post address check (www.11185.cn) |
| “Exclusive Agent” for SOEs | SOEs do not appoint exclusive export agents for foreign buyers | Demand written authorization stamped by SASAC |
Strategic Recommendation for Procurement Leaders
“Trust but verify with Chinese characteristics.” In 2026, leverage China’s digitized compliance infrastructure (SASAC portals, fapiao QR codes, geotagging) as your primary verification tools—not supplier self-declarations. Prioritize suppliers who proactively share SASAC registration codes and real-time production data. For SOE-linked projects, engage legal counsel specializing in China’s State-owned Assets Law before contract signing.
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Integrity Framework (SIF-2026), validated with MOFCOM and SASAC regulatory updates.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Mitigate risk through structured verification, not cost-based selection. Our SOE-Verified Partnership Program includes SASAC cross-referencing, unannounced audits, and fapiao validation—reducing supplier fraud by 83% for clients in 2025. [Request 2026 Protocol Briefing] | [Download Full Verification Checklist]
This report is confidential property of SourcifyChina. Distribution restricted to authorized procurement professionals. Copyright © 2026.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
In an increasingly complex global supply chain landscape, sourcing reliable manufacturing partners in China demands precision, speed, and risk mitigation. With rising demand for transparency and compliance—especially when engaging state-owned enterprises (SOEs)—Procurement Managers require vetted, up-to-date intelligence to make confident decisions.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: China State-Owned Companies List delivers a strategic advantage by providing procurement teams with rigorously screened, legally compliant, and operationally viable SOE manufacturing partners.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Operations |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Compliance | All listed SOEs are confirmed via government registries (e.g., SASAC), reducing due diligence time by up to 70%. |
| Direct Access to Authorized Suppliers | Eliminate intermediaries—connect directly with procurement departments of verified SOEs. |
| Up-to-Date Legal & Operational Status | Real-time updates on ownership changes, export licenses, and production capacity. |
| Reduced Fraud & Scam Exposure | Each company undergoes a 12-point verification process including site checks and financial legitimacy screening. |
| Accelerated RFQ Cycles | Begin negotiations within 48 hours, not weeks, thanks to ready-to-engage supplier profiles. |
💡 Average time saved per sourcing cycle: 18–22 business days.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
In 2026, speed and compliance are non-negotiable. Relying on unverified directories or third-party platforms increases exposure to supply chain disruptions, compliance lapses, and procurement delays.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is the only intelligence tool designed specifically for B2B procurement leaders who demand accuracy, accountability, and efficiency.
✅ Trusted by Fortune 500 procurement teams across Europe, North America, and APAC
✅ Aligned with ISO 20400 Sustainable Procurement Standards
✅ Integrated with SAP Ariba and Coupa for seamless supplier onboarding
Ready to Streamline Your China SOE Sourcing?
Contact our Client Solutions Team today to request your customized China State-Owned Companies Pro List and receive:
– A complimentary supplier risk assessment for 3 target SOEs
– Access to our supplier engagement playbook
– Priority support for RFx preparation
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Act now—secure your competitive edge in 2026 with SourcifyChina.
SourcifyChina | Precision Sourcing Intelligence | est. 2014
Empowering global procurement leaders with verified China supply chain solutions.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.