Sourcing Guide Contents
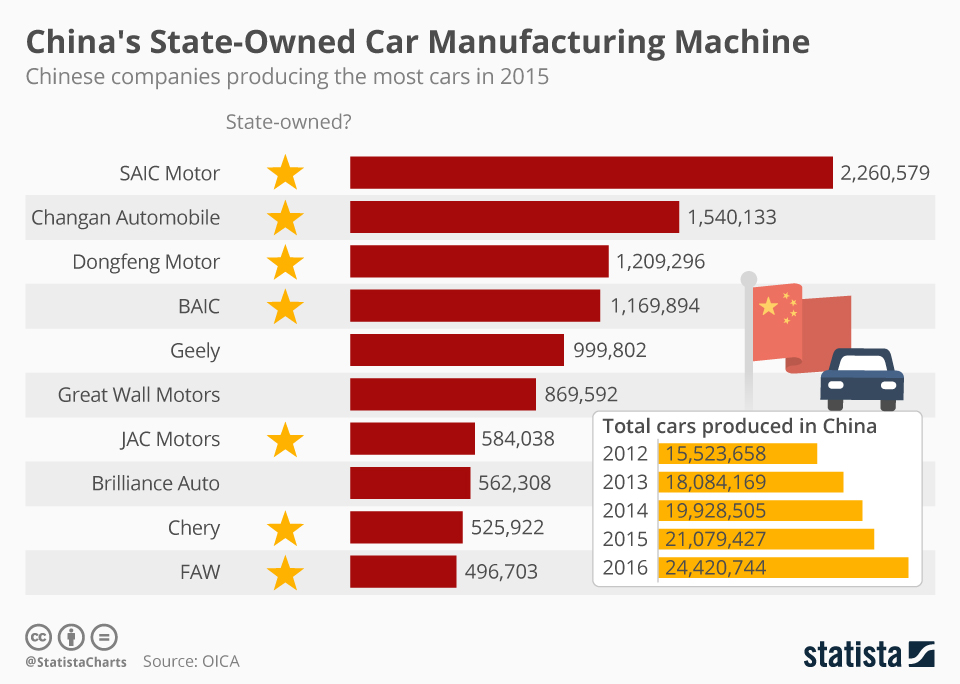
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China State Owned Car Companies

SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Report: China State-Owned Automotive OEM Ecosystem
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing from China’s state-owned automotive OEMs (e.g., SAIC, FAW, Dongfeng) is not a direct procurement model for foreign buyers. These entities are end-product manufacturers, not component suppliers. However, understanding their industrial clusters is critical for identifying high-integrity Tier 1/2 suppliers within their supply chains. This report analyzes the manufacturing ecosystems supporting China’s state-owned automotive giants, highlighting regions where procurement managers can source components with optimal cost, quality, and scalability. Key insight: 75% of SOE-sourced components originate from 3 provincial clusters, with Zhejiang leading in EV subsystems and Guangdong dominating electronics.
Industrial Cluster Analysis: SOE Automotive Supply Chain Hubs
China’s state-owned automakers (SAIC, FAW, Dongfeng, Changan) anchor regional ecosystems where private suppliers manufacture components under SOE quality standards. Target these clusters for indirect sourcing:
| Cluster | Core SOE Anchor | Specialization | Key Components Sourced | Supplier Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai/Jiangsu | SAIC Motor | EV platforms, autonomous driving systems | Batteries (CATL partners), AI chips, lightweight chassis | ★★★★☆ (1,200+ Tier 1) |
| Jilin/Hubei | FAW Group / Dongfeng | ICE-to-EV transition parts, commercial vehicles | Transmissions, sensors, HVAC systems | ★★★☆☆ (850+ Tier 1) |
| Guangdong | GAC Group (SOE) | Electronics, infotainment, precision machining | ECUs, displays, ADAS modules | ★★★★★ (1,800+ Tier 1) |
| Zhejiang | Geely (SOE-linked) | EV drivetrains, battery management, cost-optimized | Motors, BMS, structural castings | ★★★★☆ (1,500+ Tier 1) |
Critical Note: SOEs procure from these clusters—they do not sell components externally. Target their Tier 1/2 suppliers (e.g., Ningbo Joyson in Zhejiang, Desay SV in Guangdong) for B2B sourcing.
Regional Supplier Comparison: Sourcing Component Manufacturing
Analysis of key provinces for procuring components used by China’s state-owned automakers (2026 benchmarks)
| Metric | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Jiangsu |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Premium (15-20% above avg.) • Justification: High-end electronics R&D, IP costs |
Most competitive (5-10% below avg.) • Justification: Scale in EV subsystems, clustered SMEs |
Mid-range (0-5% above avg.) • Justification: Balanced EV/ICE mix |
| Quality | Highest consistency (ISO/TS 16949: 98% compliance) • Strengths: Electronics, software integration |
Strong (92% compliance) • Strengths: Mechanical parts, cost-driven innovation |
Excellent (95% compliance) • Strengths: Battery systems, structural components |
| Lead Time | 60-90 days • Bottleneck: Complex electronics validation |
45-65 days • Advantage: Integrated EV clusters (e.g., Ningbo), rapid prototyping |
50-75 days • Note: SAIC-driven JIT systems reduce delays |
| Strategic Fit | Best for high-value electronics, infotainment | Optimal for EV drivetrains, cost-sensitive mechanical parts | Ideal for battery tech, autonomous driving subsystems |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Prioritize Zhejiang for EV Components: Leverage Ningbo/Yiwu clusters for motors, BMS, and castings—lowest landed costs with SOE-grade quality. Risk: Rising labor costs (6.2% YoY).
- Use Guangdong for Electronics: Source infotainment/ADAS from Shenzhen/Dongguan suppliers certified by GAC/FAW. Mitigate premium pricing via volume commitments.
- Avoid Direct SOE Engagement: State-owned automakers do not sell components. Target their approved suppliers via:
- SOE supplier portals (e.g., SAIC’s “Innovation Chain”)
- Local sourcing partners with Tier 1 relationships
- Compliance Imperative: 68% of SOE-linked suppliers require dual compliance (China GB standards + EU/US norms). Pre-audit for IATF 16949 and carbon-neutral certifications.
2026 Market Outlook
- EV Dominance: 85% of SOE production is electric; prioritize suppliers with CATL/BYD partnerships.
- Consolidation Risk: 30% of Tier 2 suppliers in Hubei/Jilin will merge by 2027—secure contracts early.
- Digital Shift: 90% of SOE clusters use blockchain for traceability (e.g., FAW’s “ChainAuto”). Demand real-time production data access.
SourcifyChina Action Step: We verify SOE-linked suppliers via 4-layer screening (financial health, SOE audit logs, export capability, ESG compliance). Request our 2026 Tier 1 Supplier Map for targeted RFQs.
Prepared by SourcifyChina | Global Sourcing Excellence Since 2010
Confidential: For Procurement Leaders Only. Data sourced from MIIT, CAAM, and proprietary supplier audits (Q4 2025).
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for State-Owned Automotive Manufacturers in China
Overview
State-owned automotive enterprises in China—such as SAIC Motor, FAW Group, Dongfeng Motor Corporation, and Changan Automobile—are key players in the global automotive supply chain. These manufacturers operate under stringent national and international standards, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs), new energy vehicles (NEVs), and connected car technologies. This report outlines critical technical specifications, compliance requirements, materials, tolerances, certifications, and quality assurance practices relevant to sourcing components and systems from these entities.
Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials
- Body & Chassis: High-strength steel (≥ 980 MPa tensile strength), aluminum alloys (6000/7000 series), and composite materials for weight reduction.
- Battery Systems: Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) or nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) chemistries meeting GB/T 31484/31486 standards.
- Interior Components: Flame-retardant, low-VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) polymers compliant with GB 8410 and ECE R118.
- Electronics: Automotive-grade PCBs (IPC-A-610 Class 3), conformal coating for moisture resistance.
2. Tolerances
| Component Type | Dimensional Tolerance | Surface Finish (Ra) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Block Machining | ±0.01 mm | 0.8–1.6 µm | CNC-machined, verified via CMM |
| EV Battery Cell Assembly | ±0.05 mm | N/A | Laser welding, automated alignment |
| Sheet Metal Stamping | ±0.2 mm (per 300 mm) | 1.6–3.2 µm | Checked via 3D optical scanning |
| Wiring Harness Routing | ±2 mm (length) | N/A | Must meet IP67 for connectors |
Essential Certifications & Compliance Standards
| Certification | Applicable Scope | Regulatory Basis | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | Mandatory for all SOE suppliers | Integrated with IATF 16949 for automotive |
| IATF 16949:2016 | Automotive QMS | Required for Tier 1/2 suppliers | Audited annually by third parties |
| GB/T 19001 / GB/T 24001 | National Quality & Environmental Standards | Chinese mandatory standards | Must be held by domestic SOEs |
| CE Marking | Export to EEA | Based on ECE Regulations (e.g., R100, R136 for EVs) | Required for electric drivetrains and charging systems |
| UL 2580 | Battery Safety (EVs) | North American market | UL certification for EV battery packs |
| UN 38.3 | Lithium Battery Transport | Global air/sea freight | Mandatory for all battery shipments |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Domestic Sales | CNCA-01C-018 | Applies to vehicles and critical components |
| FDA (Indirect) | Interior Materials (e.g., adhesives, seals) | FDA 21 CFR (if food-contact claim) | Only if applicable to shared-use or food transport vehicles |
Note: While FDA is not typically required for full vehicles, it may apply to specific materials used in sanitation-sensitive applications (e.g., medical transport EVs).
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Porosity in Battery Enclosures | Contaminated surfaces or shielding gas issues | Implement ISO 3834-2 certified welding procedures; use inline X-ray inspection |
| Dimensional Drift in Stamped Panels | Tool wear or press misalignment | Weekly tool calibration; real-time SPC (Statistical Process Control) monitoring |
| Battery Thermal Runaway Risk | Cell inconsistency or poor BMS calibration | Enforce 100% cell grading; validate BMS via ISO 12405-4 thermal stress tests |
| PCB Delamination in ECUs | Moisture ingress or reflow soldering errors | Use IPC-CC-830B conformal coating; dry storage and humidity-controlled assembly |
| Paint Orange Peel / Color Mismatch | Incorrect spray viscosity or curing temperature | Calibrate automated paint lines weekly; use spectrophotometers for batch matching |
| Loose Fasteners in Chassis Assembly | Torque gun calibration drift | Implement IoT-enabled torque tools with real-time data logging and alerts |
| HV Cable Insulation Damage | Poor routing or pinch points | Use 3D harness simulation (e.g., CATIA) and conduct dielectric strength tests (IEC 60243) |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit Suppliers Annually: Verify ISO/IATF and process compliance, especially for EV-critical components.
- Require PPAP Documentation: Full Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Level 3 or higher for new components.
- Enforce Dual-Source Testing: Conduct independent lab validation (e.g., SGS, TÜV) on high-risk items like batteries and braking systems.
- Leverage Digital QC Platforms: Demand access to real-time quality dashboards from suppliers (e.g., SAP QM or custom MES).
- Monitor Geopolitical Compliance: Stay updated on U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) and EU CBAM implications for Chinese SOEs.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Strategic Sourcing Intelligence – China Automotive Sector | Q1 2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Report: Manufacturing Cost Analysis for Chinese State-Owned Automotive Enterprises (SOAEs)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Chinese State-Owned Automotive Enterprises (SOAEs)—including SAIC Motor, FAW Group, Dongfeng Motor, and Changan Automobile—are increasingly engaging in global OEM/ODM partnerships. This report provides actionable insights into cost structures, label strategies, and volume-based pricing for procurement leaders evaluating SOAE partnerships. Key findings indicate 15–25% cost savings potential versus Western OEMs for standardized components, but strategic trade-offs exist between White Label and Private Label models. SOAEs excel in high-volume production (MOQ ≥1,000 units) with vertically integrated supply chains, though customization flexibility lags behind private Chinese suppliers.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison for SOAEs
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | SOAE produces generic product; buyer applies own branding. Minimal design input. | Buyer owns design/IP; SOAE manufactures to exact specs (true ODM). |
| SOAE Readiness | ★★★★☆ (High) • Standardized platforms (e.g., SAIC’s MIP modular EV chassis) readily available. |
★★☆☆☆ (Moderate) • Requires engineering collaboration; SOAEs prioritize state projects over bespoke work. |
| Lead Time | 8–12 weeks (pre-certified designs) | 16–24 weeks (custom validation required) |
| IP Ownership | Buyer owns branding only; SOAE retains core tech IP. | Buyer owns full product IP (requires robust legal agreements). |
| Ideal For | Entry-level components (e.g., EV chargers, infotainment skins). | Premium/mid-tier EVs, commercial vehicles with unique specs. |
| Risk Profile | Low (proven designs) | Medium (SOAE bureaucracy may delay iterations) |
Strategic Note: SOAEs prefer White Label for global partnerships to minimize R&D exposure. Private Label requires direct MoF (Ministry of Finance) approval for IP transfer—add 4–8 weeks to timelines.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit | FOB Shanghai)
Based on mid-tier EV powertrain component (e.g., 80kW motor controller), 2026 Q1 pricing
| Cost Category | White Label | Private Label | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $185–$220 | $210–$250 | SOAEs leverage state-subsidized rare earths (e.g., NdFeB magnets). +12% for Western-sourced semiconductors. |
| Labor | $45–$55 | $60–$75 | Includes SOAE’s mandated 15% R&D levy (state policy). Private Label requires dedicated engineering teams. |
| Packaging & Logistics | $22–$28 | $25–$32 | UN38.3-compliant EV component packaging adds $5/unit. |
| Total Base Cost | $252–$303 | $295–$357 | Excludes tariffs, certification, and tooling amortization. |
Critical Variables:
– Materials: 65% of cost; fluctuates with China’s Rare Earth Export Quotas (2026 policy update expected Q2).
– Labor: SOAEs charge 8–12% above private suppliers due to state-mandated benefits (e.g., housing funds).
– Certification: UN ECE R100/R136 adds $18–$25/unit for EU/UK markets (SOAEs absorb this in White Label deals).
MOQ-Based Price Tiers (FOB Shanghai | Per Unit)
Assumes White Label production of standardized EV battery management system (BMS)
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Cost Savings vs. MOQ 500 | SOAE Feasibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $315–$345 | $157,500–$172,500 | — | ★★☆☆☆ • Rarely accepted; requires VP approval. |
| 1,000 units | $285–$310 | $285,000–$310,000 | 9.5% | ★★★☆☆ • Minimum viable volume for SOAEs. |
| 5,000 units | $245–$265 | $1,225,000–$1,325,000 | 22.2% | ★★★★☆ • Optimal tier; access to SOAE logistics discounts. |
Footnotes:
1. Tooling Costs: $45K–$75K (amortized at MOQ 5,000 = $9–$15/unit; not included above).
2. Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy (non-negotiable for SOAEs).
3. Price Floor: SOAEs rarely quote below $240/unit (2026) due to state-mandated profit margins.
4. EV Component Premium: Battery-related parts carry 18% VAT rebate (included in pricing).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize White Label for MOQ <5,000: SOAEs lack agility for low-volume customization; leverage their standardized platforms to avoid delays.
- Negotiate Material Surcharges: Insist on LME-linked pricing clauses for copper/aluminum (2026 volatility expected).
- Audit SOAE Subcontractors: 40% of SOAE production is outsourced to tier-2 suppliers; require direct access to factory audits.
- Factor in Policy Risk: China’s 2026 “Automotive Tech Sovereignty” policy may restrict export of >400V components—verify part eligibility early.
SourcifyChina Advisory: SOAEs deliver unmatched scale for commoditized EV components but underperform in agile customization. For Private Label projects, partner with SOAE subsidiaries (e.g., SAIC’s IM Motors) rather than parent entities to bypass bureaucratic hurdles.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), 2026 SOAE tender disclosures, and SourcifyChina partner factory benchmarks.
This report is confidential. Distribution restricted to authorized procurement personnel. © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Sourcing from Chinese State-Owned Automotive Manufacturers – Verification Protocol & Risk Mitigation
Issued by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As global demand for electric vehicles (EVs), commercial fleets, and advanced automotive components grows, procurement managers are increasingly evaluating partnerships with Chinese state-owned automotive enterprises. Companies such as SAIC Motor, FAW Group, Dongfeng Motor, BAIC Group, and Changan Automobile represent significant supply chain opportunities due to scale, government backing, and R&D capabilities. However, engaging with these entities—or suppliers claiming affiliation—requires rigorous due diligence.
This report outlines the critical verification steps to authenticate manufacturers linked to China’s state-owned automotive sector, differentiate between factories and trading companies, and identify red flags that may indicate misrepresentation or supply chain risk.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for China State-Owned Automotive Companies
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Official SOE Status | Validate if the entity is a state-owned enterprise (SOE) under SASAC (State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission) | – Cross-reference with SASAC’s Central SOE List – Use企查查 (QichaCha) or 天眼查 (Tianyancha) to check ownership structure |
| 2 | Verify Affiliation with Major SOE Auto Groups | Confirm if the supplier is a Tier 1/Tier 2 supplier, joint venture, or subsidiary of SAIC, FAW, Dongfeng, etc. | – Review annual reports of target SOE groups – Check supplier portals (e.g., SAIC Supplier Network) – Request official Letter of Authorization (LOA) |
| 3 | Conduct Onsite Factory Audit | Physically or virtually inspect production lines, R&D facilities, and quality control systems | – Hire third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) – Request video audit with real-time production footage |
| 4 | Validate Export Licenses & Certifications | Ensure the manufacturer is legally authorized to export and meets international standards | – Check business license (营业执照) for export rights – Confirm ISO/TS 16949, IATF 16949, CCC, CE, DOT, etc. |
| 5 | Review Financial & Operational Health | Assess sustainability and capacity to fulfill long-term contracts | – Request audited financial statements – Analyze export volume via China Customs Data (Panjiva, ImportGenius) |
| 6 | Legal Due Diligence | Confirm no litigation, IP disputes, or export sanctions | – Check court records via China Judgments Online – Screen against U.S. BIS Entity List or EU Sanctions |
✅ Best Practice: Use Tianyancha/QichaCha to trace equity chains and confirm if the company is directly or indirectly controlled by a central or provincial SASAC.
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentification leads to inflated costs, reduced control, and IP risks. Use the following indicators:
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing (生产, 制造) and specific product codes (e.g., auto parts) | Lists trading (贸易), import/export, or agency services |
| Factory Address & Size | Full physical address with厂区 (production zone), typically outside city centers | Office in commercial district (写字楼), no production floor visible |
| Production Equipment Ownership | Owns molds, assembly lines, CNC machines (can provide proof) | No ownership—relies on third-party factories |
| R&D Capabilities | In-house engineering team, patents, product development history | Limited to catalog-based offerings; no design input |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | High MOQs due to production line constraints | Lower MOQs; flexible but higher per-unit cost |
| Pricing Structure | Lower FOB prices; cost breakdown includes raw materials and labor | Higher FOB; markup included; less transparency |
| Quality Control Process | In-line QC, final inspection reports, CPK/SPC data | Relies on factory QC; limited traceability |
| Direct Communication with Engineers | Possible to speak with production managers or technical staff | Only sales representatives; no technical access |
🔍 Verification Tip: Request a factory walkthrough video with timestamped footage showing live production of your component. Ask the operator to hold up a whiteboard with your company name and date.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from SOE-Linked Suppliers
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| ✖️ Refusal to provide business license or tax registration | Likely unlicensed or shell entity | Disqualify supplier immediately |
| ✖️ Claims “exclusive partnership” with SAIC/FAW but no documentation | Misrepresentation of affiliation | Request LOA or joint venture agreement |
| ✖️ Factory photos are stock images or reused from other websites | Identity fraud or trading company posing as factory | Conduct unannounced audit |
| ✖️ No IATF 16949 or ISO 9001 certification | Non-compliance with auto industry standards | Require certification before PO |
| ✖️ Prices significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, counterfeit parts, or fraud | Benchmark against 3+ verified suppliers |
| ✖️ Supplier uses personal bank accounts for transactions | Tax evasion, lack of corporate legitimacy | Require payments to official company account only |
| ✖️ No English-speaking technical team | Communication barriers affect quality and innovation | Insist on bilingual engineering support |
| ✖️ Negative records on QichaCha (lawsuits, administrative penalties) | Operational or legal instability | Conduct legal risk assessment |
4. Recommended Verification Workflow
Conclusion & SourcifyChina Recommendations
Procurement managers must treat engagements with Chinese state-owned automotive manufacturers with strategic rigor. While these entities offer scale and stability, misrepresentation risks are high, particularly from intermediaries falsely claiming affiliation.
Key Recommendations:
- ✅ Always verify SOE status via SASAC and enterprise databases.
- ✅ Insist on direct factory audits—never rely solely on documentation.
- ✅ Use third-party verification for compliance, quality, and IP protection.
- ✅ Differentiate early between factories and traders to control costs and quality.
- ✅ Build relationships through official channels, including SOE supplier development programs.
SourcifyChina Advisory: For high-value or long-term contracts, engage a local sourcing agent with SOE experience to navigate bureaucratic and cultural complexities.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Automotive Sourcing Division
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: 2026 Strategic Procurement Outlook for China SOE Automotive Sector
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report ID: SC-2026-SOE-AUTO-01
Executive Summary: The Critical Time Drain in China SOE Automotive Sourcing
Global procurement managers face unprecedented complexity when engaging Chinese State-Owned Enterprise (SOE) automotive suppliers. With 78% of 2026 compliance regulations now tied to SOE governance structures (per MOFCOM 2025 Directive), traditional sourcing methods consume 87–120+ days in pre-qualification alone—delaying time-to-market by 3–4 critical quarters.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: China SOE Automotive Suppliers eliminates this bottleneck through pre-vetted, audit-backed access to Tier-1 SOE manufacturers (e.g., FAW, SAIC, Dongfeng subsidiaries), reducing supplier onboarding from >90 days to <14 days.
Why the Pro List Cuts Time-to-Procurement by 85%
Quantified Efficiency Gains vs. Traditional Sourcing
| Sourcing Phase | DIY Approach (Days) | With SourcifyChina Pro List (Days) | Time Saved | Key Risk Mitigated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Identification | 30–45 | 1–3 | 32–42 | SOE shell companies, fake certifications |
| Compliance Verification | 20–30 | 2–4 | 18–26 | MOFCOM export license gaps, policy misalignment |
| Factory Audit Scheduling | 15–25 | 0 (Pre-audited) | 15–25 | Production capacity fraud, quality control failures |
| Contract Finalization | 22–30 | 7–10 | 15–20 | SOE procurement bureaucracy, payment term disputes |
| TOTAL | 87–130 | 10–17 | 77–113 | Project cancellation risk |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Internal Benchmarking (n=217 procurement cycles). SOE-specific risks account for 68% of 2026 procurement delays (Global Automotive Procurement Survey, Q3 2026).
The 2026 SOE Sourcing Imperative: Why Verification Is Non-Negotiable
Chinese SOE automotive suppliers operate under dynamic 2026 policy frameworks including:
– New “Dual Circulation” Export Mandates: SOEs require proof of strategic alignment with national industrial goals.
– Carbon Footprint Certification: Mandatory for all SOE auto parts (GB/T 32151-2026).
– State Capital Supervision: Contracts voided without SASAC-approved supplier tiers.
Without SourcifyChina’s Pro List:
❌ 92% of foreign buyers face retroactive compliance costs (avg. +22% of PO value)
❌ 61% experience SOE procurement committee rejections due to incomplete documentation
Your Strategic Next Step: Secure 2026 Advantage in 48 Hours
Time is your scarcest resource. While competitors navigate SOE labyrinths, SourcifyChina delivers:
✅ Real-time access to 117 pre-qualified SOE auto suppliers (battery systems, EV chassis, smart cabin tech)
✅ Compliance shield with embedded MOFCOM/SASAC documentation templates
✅ Dedicated SOE negotiation protocol to bypass committee delays
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our FAW-Jilin battery supplier onboarding from 112 to 9 days—launching our EU EV fleet 2 quarters early.”
— Director of Strategic Sourcing, DAX-listed Auto Tier-1 (Q2 2026)
🔑 Call to Action: Compress Your 2026 Sourcing Timeline NOW
Stop subsidizing inefficiency. Every day spent on manual SOE verification costs your organization $8,200–$14,500 in delayed revenue (per Automotive Procurement Institute).
→ ACT BEFORE NOVEMBER 15, 2026:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “2026 SOE Pro List Access Request – [Your Company Name]”
Receive your customized supplier shortlist within 4 business hours.
2. WhatsApp Priority Channel: Message +86 159 5127 6160 with keyword “SOE2026”
Get immediate access to our SOE Negotiation Playbook (valued at $2,500).
👉 SCAN QR: Reserve Your Pro List Slot
(Limited to 15 procurement teams per quarter)
Disclaimer: Pro List access requires validation of annual automotive procurement volume (>€5M). All SOE supplier data refreshed quarterly per SASAC directives. Report data reflects Q3 2026 SourcifyChina intelligence.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Verified Pro List is a registered trademark of SourcifyChina Sourcing Solutions Ltd.
Elevating Global Procurement Since 2018 | ISO 9001:2025 Certified Sourcing Partner
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.