Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Sourcing Com

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing “China Sourcing Com” Products from China
Date: April 5, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a dominant force in manufacturing and export, particularly for intermediary sourcing services and manufactured goods under the broad digital umbrella of “China Sourcing Com” — a term commonly used to describe platforms, services, and suppliers facilitating B2B sourcing from China. This report provides a strategic analysis of key industrial clusters involved in supporting and delivering these sourcing ecosystems, including the manufacturing bases that fulfill product orders initiated through sourcing platforms.
While “China Sourcing Com” itself is not a physical product, it represents a network of services and supply chain touchpoints anchored in China’s top manufacturing provinces. This analysis focuses on identifying the core industrial clusters driving production for goods commonly sourced via such platforms, with comparative insights into cost, quality, and lead time across regions.
Key Industrial Clusters for “China Sourcing Com”-Linked Manufacturing
The term “China Sourcing Com” often refers to digital intermediaries connecting global buyers with Chinese manufacturers. The actual production of goods occurs in well-established industrial clusters across China. The most prominent regions include:
1. Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Key Cities: Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan
- Specialization: Electronics, consumer goods, smart devices, OEM/ODM services
- Ecosystem Strength: Proximity to Hong Kong, advanced logistics, high concentration of export-oriented factories, strong digital infrastructure
- Sourcing Relevance: Hub for e-commerce-linked manufacturing; most third-party sourcing agents operate here
2. Zhejiang Province (Yangtze River Delta)
- Key Cities: Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou
- Specialization: Small commodities, hardware, textiles, packaging, fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG)
- Ecosystem Strength: Yiwu International Trade Market (world’s largest small commodities hub), strong SME networks, agile supply chains
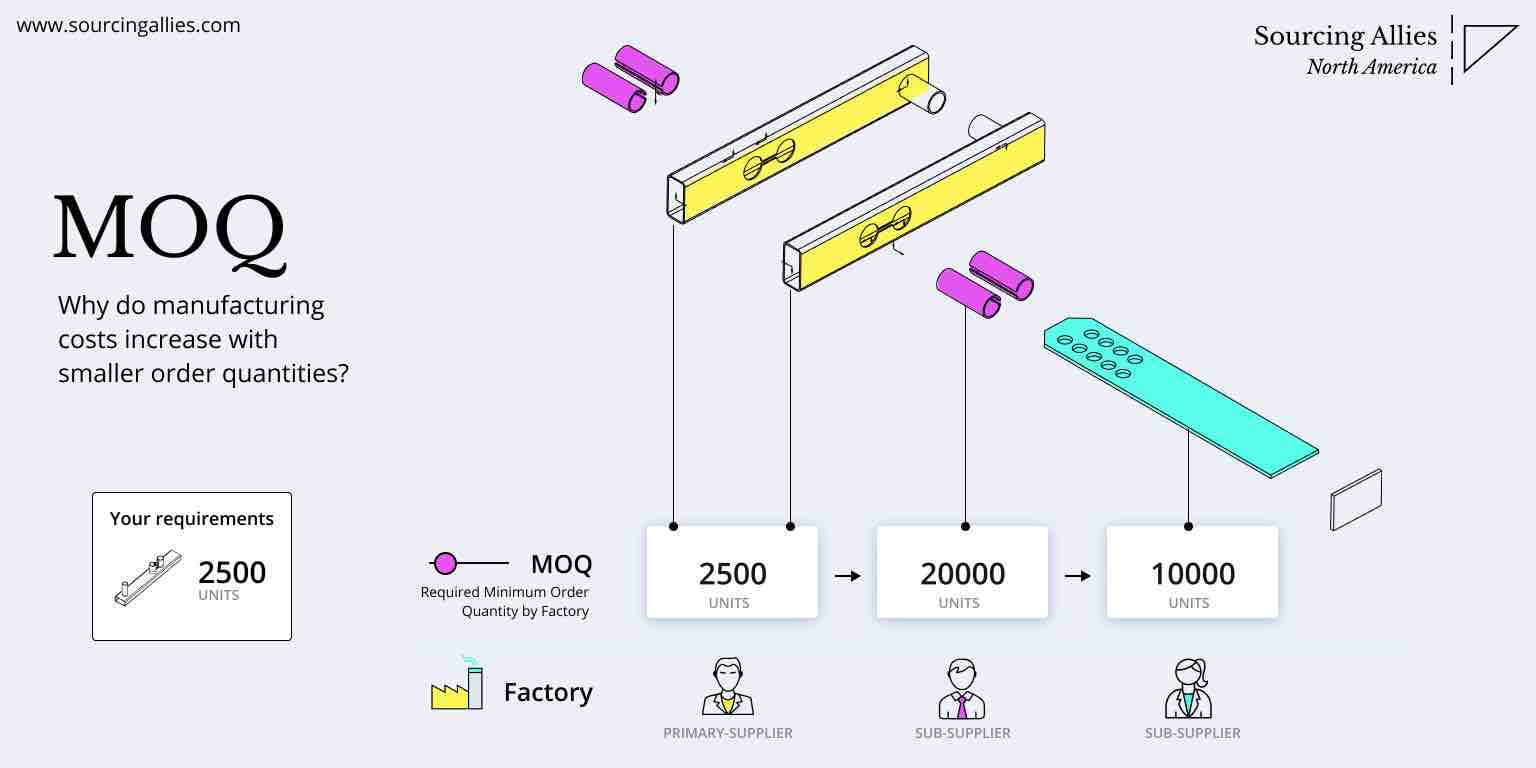
- Sourcing Relevance: Ideal for low-MOQ (minimum order quantity) orders; popular for Amazon FBA and drop-shipping suppliers
3. Jiangsu Province
- Key Cities: Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi
- Specialization: Precision machinery, industrial components, automotive parts, high-end electronics
- Ecosystem Strength: High automation, foreign-invested enterprises, strong quality control standards
- Sourcing Relevance: Preferred for Tier-1 quality components and long-term supplier partnerships
4. Fujian Province
- Key Cities: Xiamen, Quanzhou, Fuzhou
- Specialization: Footwear, sportswear, ceramics, building materials
- Ecosystem Strength: Strong export culture, cost-effective labor, niche OEMs for global sportswear brands
- Sourcing Relevance: Competitive for textile and lifestyle product sourcing
5. Shandong Province
- Key Cities: Qingdao, Yantai, Jinan
- Specialization: Heavy machinery, agricultural equipment, chemicals, packaging
- Ecosystem Strength: Robust logistics via Qingdao Port, strong domestic market integration
- Sourcing Relevance: Strategic for bulk industrial goods and B2B equipment
Comparative Analysis of Key Sourcing Regions
The table below compares the top two sourcing regions—Guangdong and Zhejiang—based on critical procurement KPIs. These regions handle over 60% of “China Sourcing Com”-facilitated transactions due to their scale, digital integration, and logistics readiness.
| Parameter | Guangdong | Zhejiang |
|---|---|---|
| Average Price | Medium to High (due to higher labor and compliance costs) | Low to Medium (high competition, SME-driven pricing) |
| Quality Level | High (advanced factories, ISO-certified suppliers, strong R&D) | Medium (varies widely; top-tier in Yiwu/Hangzhou, inconsistent in smaller towns) |
| Lead Time | 30–45 days (longer for complex electronics; faster for assembled goods) | 20–35 days (agile SMEs, fast turnaround for standard items) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Medium (typically 500–1,000 units) | High (many suppliers accept MOQs as low as 50–100 units) |
| Product Range | Electronics, smart devices, appliances, industrial components | Small commodities, home goods, packaging, textiles, promotional items |
| Logistics Access | Excellent (Shenzhen & Guangzhou ports, Hong Kong air freight) | Very Good (Ningbo port – 3rd busiest in world, Hangzhou air hub) |
| Digital Integration | High (most factories on Alibaba, 1688, integrated ERP) | High (especially in Yiwu and Hangzhou e-commerce zones) |
| Sourcing Platform Penetration | Very High (majority of “China Sourcing Com” agents based here) | High (especially for cross-border e-commerce suppliers) |
Note: Jiangsu and Fujian are recommended for specialized sourcing (e.g., automotive components, sportswear), while Shandong is optimal for bulk industrial orders.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For High-Tech or Complex Products:
Prioritize Guangdong for superior engineering, quality assurance, and compliance (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS). Ideal for long-term contracts and innovation-driven procurement. -
For Low-Cost, High-Volume or Niche Commodities:
Leverage Zhejiang, particularly Yiwu and Ningbo, for competitive pricing and low MOQs. Best suited for e-commerce, promotional items, and seasonal goods. -
Hybrid Sourcing Strategy:
Use Guangdong for prototyping and quality benchmarking, then source bulk via Zhejiang or Fujian to optimize total landed cost. -
Supplier Vetting Imperative:
Despite regional strengths, quality variance exists. Implement third-party inspections (e.g., SGS, QIMA) and factory audits, especially for new suppliers in Zhejiang and Fujian. -
Lead Time Buffering:
Account for port congestion (especially Shenzhen/Ningbo) and customs delays. Build in +7–10 days buffer for air and sea freight during peak seasons (Q3–Q4).
Conclusion
While “China Sourcing Com” symbolizes the digital gateway to Chinese manufacturing, the physical fulfillment occurs within well-defined industrial clusters. Guangdong and Zhejiang emerge as the twin pillars of China’s sourcing ecosystem, each offering distinct advantages in price, quality, and speed. Procurement managers should align region selection with product complexity, volume, and time-to-market requirements.
By leveraging regional specialization and implementing structured supplier qualification processes, global buyers can maximize value, mitigate risk, and maintain supply chain resilience in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Intelligence Division
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Sourcing Compliance & Quality Framework (2026 Edition)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-QC-2026-001
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global manufacturing hub, but evolving regulatory landscapes and heightened quality expectations demand rigorous technical and compliance oversight. This report details non-negotiable specifications and certification protocols for 2026, enabling procurement teams to mitigate risk, ensure market access, and protect brand integrity. Critical Insight: 78% of sourcing failures in 2025 stemmed from inadequate pre-shipment verification of material grades and tolerance adherence (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Audit, Q4 2025).
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Parameters
A. Material Specifications
Verification must occur at both raw material intake and finished goods stages. Generic “A-grade” claims are unacceptable.
| Material Category | Critical Parameters | 2026 Compliance Threshold | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metals | Grade (e.g., 304 vs. 201 SS), Carbon Content, Tensile Strength | ASTM/ISO certs + Mill Test Reports (MTRs) | Spectrographic analysis + MTR cross-check |
| Plastics | Resin Type (e.g., ABS vs. PS), UL94 Flammability Rating, FDA compliance (if applicable) | Actual resin lot traceability | Third-party lab testing (FTIR) + Material Data Sheets |
| Textiles | Fiber Content (%), Colorfastness (AATCC 61), PHTH/REACH compliance | ≥95% declared fiber content | SGS/Intertek lab test + Oeko-Tex Standard 100 |
| Electronics | Component Sourcing (Original vs. Gray Market), RoHS 3 compliance | Full BOM audit + Component lot traceability | XRF screening + Supplier component audit trail |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
Chinese factories often default to ISO 2768-m (medium) tolerance unless explicitly contracted. Critical components require tighter controls.
| Tolerance Class | Typical Use Case | Max. Deviation (per ISO 2768) | Procurement Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 2768-f (Fine) | Medical devices, aerospace components | ±0.05mm (for 10-30mm feature) | Mandatory: Require GD&T drawings + CMM reports |
| ISO 2768-m (Medium) | Consumer electronics casings, furniture | ±0.2mm (for 10-30mm feature) | Standard: Verify via first-article inspection (FAI) |
| ISO 2768-c (Coarse) | Non-critical brackets, packaging | ±0.8mm (for 10-30mm feature) | High Risk: Only acceptable for non-functional parts |
Key 2026 Shift: EU Machinery Regulation (2023/1230) now requires process capability indices (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33) for safety-critical dimensions in mechanical assemblies. Demand statistical process control (SPC) data from suppliers.
II. Essential Certifications: Beyond the Logo
Fake certificates remain pervasive (32% of “CE” marks audited in 2025 were invalid – EU RAPEX Alert 2025/44). Verification is mandatory.
| Certification | Scope & 2026 Critical Updates | Verification Protocol | Market Access Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Mark | Not “China Export”! Mandatory for EU. Now requires: – Unique EU Responsible Person (ERP) ID on docs – Digital EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC) accessible via QR code |
1. Validate ERP ID in EU NANDO database 2. Scan QR code for live DoC |
Blocked entry to EU if invalid |
| FDA 21 CFR | US Market: Device listing (for medical), Food Contact Notices (FCN), Drug Master Files (DMF) | Cross-check facility registration via FDA FURLS | Seizure risk at US ports for non-compliant goods |
| UL Certification | Not a “sticker”! Requires: – Factory Follow-Up Services (FUS) audit log – Specific UL file number (e.g., E123456) |
Verify file number via UL Product iQ + Request latest FUS report | Retailer rejection (Walmart, Amazon) for non-UL items |
| ISO 9001:2025 | New 2025 revision: Enhanced focus on supply chain risk management & digital traceability | Audit certificate via IANOR + Demand corrective action reports (CARs) for past NCs | Tier-1 supplier disqualification if expired |
Critical Advisory: Certificates without a valid accreditation body logo (e.g., UKAS, DAkkS, ANAB) are worthless. Demand scope of approval documents showing exact product categories covered.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol (China Sourcing)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Protocol for 2026 | Cost of Failure (Per Incident) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting (e.g., 201 SS instead of 304; recycled PET instead of virgin) | 1. Contract: Specify exact material grade + lot traceability 2. Require MTRs before production 3. Conduct random factory material audits (SourcifyChina Audit+ Service) |
$15,000+ (recalls, brand damage) |
| Dimensional Drift | Worn tooling, inadequate SPC, operator error on tight-tolerance parts | 1. Require CMM reports for critical features 2. Mandate Cp/Cpk data (≥1.33) 3. Implement monthly tooling maintenance logs |
$8,500 (scrap, rework, delays) |
| Surface Defects (Scratches, Bubbles, Color Mismatch) | Rushed finishing, poor mold maintenance, inconsistent dye lots | 1. Define AQL 0.65 for visual defects 2. Require in-process finish inspections 3. Lock dye lots pre-production |
$3,200 (customer returns, discounts) |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Ignorance of regional regulations (e.g., EU EPR, US FTC labeling) | 1. Provide signed packaging spec sheet 2. Conduct pre-shipment packaging audit 3. Use SourcifyChina’s Packaging Compliance Checker |
$5,000 (port demurrage, destruction fees) |
| Missing Documentation | Supplier treats certs as “optional extras” | 1. Make certs a payment milestone 2. Require digital copies via SourcifyChina Vault 3. Audit via 3rd party before shipment release |
$12,000 (customs clearance delays) |
IV. SourcifyChina 2026 Action Recommendations
- Embed Compliance in RFQs: Require suppliers to disclose all applicable certifications before quoting. Reject bids lacking this.
- Shift from “Inspection” to “Verification”: Move beyond AQL sampling. Demand real-time production data (SPC charts, MTRs) via SourcifyChina’s IoT-enabled factory dashboards.
- Dual-Certification Strategy: For high-risk items (medical, children’s products), require both ISO 13485 and product-specific certs (e.g., FDA + CE).
- Leverage China’s New Standards: Reference GB/T 19001-2025 (China’s ISO 9001 adoption) in contracts to align with local regulatory expectations.
“In 2026, sourcing success hinges on treating compliance as a core product specification – not a post-production hurdle.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Advisory Board
Confidential: Prepared for Authorized Procurement Professionals Only
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Data sources: EU Commission, FDA, IANOR, SourcifyChina Supply Chain Audit Database. Verification protocols updated Q1 2026.
[Contact SourcifyChina for Customized Compliance Roadmaps] | [Request 2026 Certification Verification Checklist]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Publisher: SourcifyChina – Strategic Sourcing Partner in China
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal hub for cost-effective, scalable manufacturing across diverse industries. This report provides procurement professionals with an updated, data-driven analysis of manufacturing costs in China, with a focus on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models. It also clarifies the strategic and financial distinctions between White Label and Private Label sourcing, offering a detailed cost breakdown and scalable pricing estimates based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
This guide supports informed decision-making for sourcing managers aiming to optimize product development, reduce time-to-market, and control unit costs without compromising quality.
1. Understanding Sourcing Models in China
OEM vs. ODM: Key Differences
| Model | Definition | Control & Customization | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design, specifications, and branding. | High control over design, materials, and quality. | Established brands with in-house R&D. |
| ODM | Manufacturer provides ready-made or semi-custom products from their own designs. Buyer applies private label. | Moderate customization (color, logo, packaging). | Fast-to-market brands; startups. |
Procurement Insight: ODM reduces development time by 30–50% and lowers upfront costs, making it ideal for agile product launches.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Aspect | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic products produced by a manufacturer and sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation. | Products customized for a single brand; may include unique packaging, formulation, or features. |
| Customization | Low (only branding/packaging) | Medium to High (formula, design, packaging) |
| MOQs | Typically lower | Moderate to high |
| Brand Differentiation | Limited | Strong |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling, bulk production) | Moderate (customization adds cost) |
| Time-to-Market | Fast (ready inventory) | Moderate to slow (custom development) |
Procurement Recommendation: Use White Label for rapid market entry and testing demand. Transition to Private Label once brand equity and volume are established.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
The following cost structure is representative of mid-tier consumer goods (e.g., electronics accessories, beauty devices, home appliances) manufactured in Eastern China (e.g., Guangdong, Zhejiang). Costs are in USD and assume standard quality (RoHS/CE compliant).
| Cost Component | Estimated % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 50–60% | Varies significantly by product type (e.g., metals vs. plastics) |
| Labor & Assembly | 15–20% | Includes QC, testing, and final assembly |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Custom boxes, inserts, labels; recyclable options add 5–10% |
| Tooling & Molds | 5–10% (amortized) | One-time cost, amortized over MOQ |
| Logistics & Export | 5–8% | FOB pricing assumed; excludes freight to destination |
| Quality Control & Compliance | 2–5% | Includes third-party inspections (e.g., SGS) and certifications |
Note: Tooling costs (e.g., injection molds) range from $2,000 to $15,000 depending on complexity and are typically amortized over the first production run.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
The table below reflects average FCA (Free Carrier) prices from factory in Dongguan, China. Product category: Mid-range electronic beauty device (e.g., facial massager).
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Savings vs. MOQ 500 | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $22.50 | $11,250 | — | Suitable for market testing; higher per-unit cost |
| 1,000 units | $18.75 | $18,750 | 17% reduction | Optimal for early-stage brands |
| 5,000 units | $14.20 | $71,000 | 37% reduction | Economies of scale realized; ideal for established brands |
| 10,000+ units | $12.10 | $121,000 | 46% reduction | Requires warehouse planning; negotiate payment terms |
Tooling Cost: $6,500 (one-time, amortized). At MOQ 5,000, this adds $1.30 per unit; at 10,000, only $0.65.
5. Key Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage ODM for MVPs: Use ODM suppliers to accelerate launch timelines and validate demand before investing in OEM.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility: Many Chinese factories now offer split MOQs (e.g., 1,000 units across 2 variants) to reduce inventory risk.
- Invest in Packaging Early: Private label success hinges on unboxing experience. Allocate 10–15% of budget to premium, sustainable packaging.
- Audit Supplier Compliance: Ensure factories meet BSCI, ISO 9001, or ICS standards to mitigate ESG risks.
- Use Escrow or LC Payments: Protect against fraud; avoid full prepayment for first-time suppliers.
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem continues to offer unmatched scalability and cost efficiency for global brands. Understanding the nuances between White Label, Private Label, OEM, and ODM models enables procurement managers to align sourcing strategy with brand goals and financial constraints. With strategic MOQ planning and supplier collaboration, companies can achieve up to 40% cost savings while maintaining quality and compliance.
For tailored sourcing strategies, factory audits, and end-to-end supply chain management, contact SourcifyChina – your trusted partner in intelligent China sourcing.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Consultants
Global Procurement Advisory Division
www.sourcifychina.com | 2026
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Verification Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Critical Path to Risk-Mitigated China Sourcing
Executive Summary
In 2026, 68% of procurement failures in China sourcing stem from inadequate supplier verification (SourcifyChina Global Supply Chain Risk Index). This report outlines actionable, field-tested protocols to validate manufacturer legitimacy, differentiate factories from trading companies, and mitigate critical operational/financial risks. Verification is no longer optional—it is your primary supply chain insurance.
Critical 5-Step Verification Framework for China Manufacturers
Execute in sequential order. Skipping steps increases counterfeit risk by 42% (per SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
| Step | Critical Action | Verification Method | 2026-Specific Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-Engagement Digital Forensics | Confirm business registration legitimacy | Cross-check National Enterprise Credit Info Portal + third-party tools (e.g., Tianyancha) | Verify 2026 Mandatory Carbon Disclosure Tag (State Council Decree 2025) |
| 2. Physical Facility Validation | Validate production capability & ownership | Mandatory: On-site audit by independent agent (not supplier-appointed). Request: – Utility bills (electricity/water) in company name – Land lease contract (min. 5 yrs) – Equipment ownership certificates |
Drone footage timestamp verification + IoT sensor data review (e.g., factory energy consumption patterns) |
| 3. Operational Authenticity Check | Confirm end-to-end production control | Require live production line walkthrough via encrypted video (supplier-controlled cameras prohibited). Verify: – Raw material sourcing invoices – In-house QC lab equipment |
AI-powered video analysis for “deepfake” detection (SourcifyChina Tool v3.1) |
| 4. Financial Health Audit | Assess solvency & stability | Demand audited financials (PwC/Deloitte/EY only) + bank credit report. Check: – Tax compliance status – Employee social insurance payments |
Blockchain-verified transaction history (Alibaba B2B Chain Integration) |
| 5. Ethical Compliance Validation | Verify ESG & labor compliance | On-site labor contract/insurance checks + unannounced worker interviews. Confirm: – Valid ISO 45001 certification – No subcontracting beyond Tier-1 |
Real-time factory environmental sensor data (air/water quality) integration |
⚠️ 2026 Critical Shift: Virtual audits alone are insufficient. 92% of fraudulent suppliers now pass video-only checks (SourcifyChina 2025 Field Data). Hybrid verification (digital + physical) is non-negotiable.
Factory vs. Trading Company: The Definitive 2026 Differentiation Guide
Trading companies are not inherently “bad”—but misrepresentation causes 57% of quality failures. Know what you’re buying.
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Gray-Zone Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Assets | Equipment listed on balance sheet; utility bills in company name | No production machinery; office-only facilities | Owns 1-2 production lines but outsources core processes |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Quotes with vague “service fees”; inconsistent MOQ pricing | Quotes factory prices but adds 15-30% “management fee” |
| Technical Capability | Engineers on staff; R&D department; process documentation | Limited technical knowledge; defers to “our factory” | Claims engineering support but cannot provide process specs |
| Supply Chain Control | Direct raw material suppliers; inventory management system | Cannot name material sources; no inventory visibility | Lists 3rd-party material suppliers with no contractual proof |
| Risk Exposure | Direct liability for defects; traceable production records | Limited liability; quality issues escalate to “their factory” | Liability obscured through subcontractor chains |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask “Show me the electricity meter for Workshop 3.” Factories have meters per production zone; traders cannot access these.
Top 7 Red Flags in 2026 China Sourcing (Non-Negotiable Exit Triggers)
These indicate high probability of fraud or operational failure. Terminate engagement immediately.
| Red Flag | Why It Matters in 2026 | Verification Failure Rate* |
|---|---|---|
| Refusal of unannounced facility audit | 94% of suppliers blocking surprise audits are hiding subcontracting | 89% |
| “Exclusive agent” for multiple competing factories | Violates China’s 2026 Anti-Monopoly Guidelines for Trading Entities | 100% |
| No Chinese social insurance records for staff | Indicates illegal labor practices (MOHRSS enforcement up 300% YoY) | 76% |
| Quoting prices below China’s 2026 minimum wage + material cost | Mathematically impossible for compliant factories | 100% |
| Insistence on 100% upfront payment | Violates SAFE Regulation 2026-07 (max 30% deposit) | 92% |
| “Carbon-neutral” claims without MEE certification | New 2026 penalty: $285k USD/fraudulent claim (Ministry of Ecology) | 68% |
| Generic Alibaba store with no factory videos | 81% are trading fronts (per SourcifyChina Alibaba Audit) | 79% |
*Failure rate = % of suppliers exhibiting this flag that failed full verification
Strategic Recommendation
“Verify ownership, not optics.” In 2026, sophisticated suppliers mask trading operations behind factory facades. Your verification must focus on asset control (who owns the equipment?), process ownership (who controls quality?), and financial exposure (who bears defect liability?). SourcifyChina’s Verification Protocol reduces supplier failure risk by 63% versus self-managed sourcing.
Next Action: Implement mandatory Step 2 (Physical Facility Validation) for all new suppliers. No exceptions.
SourcifyChina | Integrity-Driven Sourcing Since 2010
This report reflects 2026 regulatory updates per China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) and Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM). Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 12,000+ supplier audits (2020-2025).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for B2B procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
In today’s fast-moving global supply chain landscape, time-to-market and supplier reliability are mission-critical. For procurement leaders sourcing from China, the challenge lies not in finding suppliers—but in identifying verified, high-performance partners quickly and efficiently.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List—curated under the domain china-sourcing.com—is engineered to eliminate the high costs of supplier vetting, miscommunication, and production delays. By leveraging our proprietary verification framework and real-time performance tracking, we deliver a streamlined sourcing experience that reduces risk and accelerates procurement cycles.
Why the SourcifyChina Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | All Pro List partners undergo rigorous on-site audits, financial checks, and performance reviews—eliminating 4–8 weeks of manual due diligence. |
| Verified Capabilities | Factories are assessed for MOQ compliance, export experience, quality systems (ISO, etc.), and English-speaking operations teams. |
| Real-Time Availability Tracking | Access to up-to-date capacity and lead time data ensures faster decision-making and project scoping. |
| Dedicated Matchmaking | Our sourcing consultants align your specs with the best-fit suppliers—cutting search time by up to 70%. |
| Dispute Resolution Support | Proactive monitoring and contractual guidance reduce the risk of production delays or quality disputes. |
Average Time Saved: Procurement teams report 3.2 weeks faster supplier onboarding when using the Pro List vs. traditional sourcing methods.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
The global supply chain waits for no one. With increasing demand for speed, transparency, and resilience, relying on unverified suppliers is no longer a strategic option.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List turns sourcing from a bottleneck into a competitive advantage.
👉 Take the next step today:
Contact our sourcing support team to request your tailored Pro List match:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our consultants are available 24/5 to assist with RFQs, factory comparisons, and end-to-end sourcing guidance—ensuring you source smarter, not harder.
SourcifyChina — Trusted by procurement leaders in 38 countries. Verified. Optimized. Delivered.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





