Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Smartphone Company In India
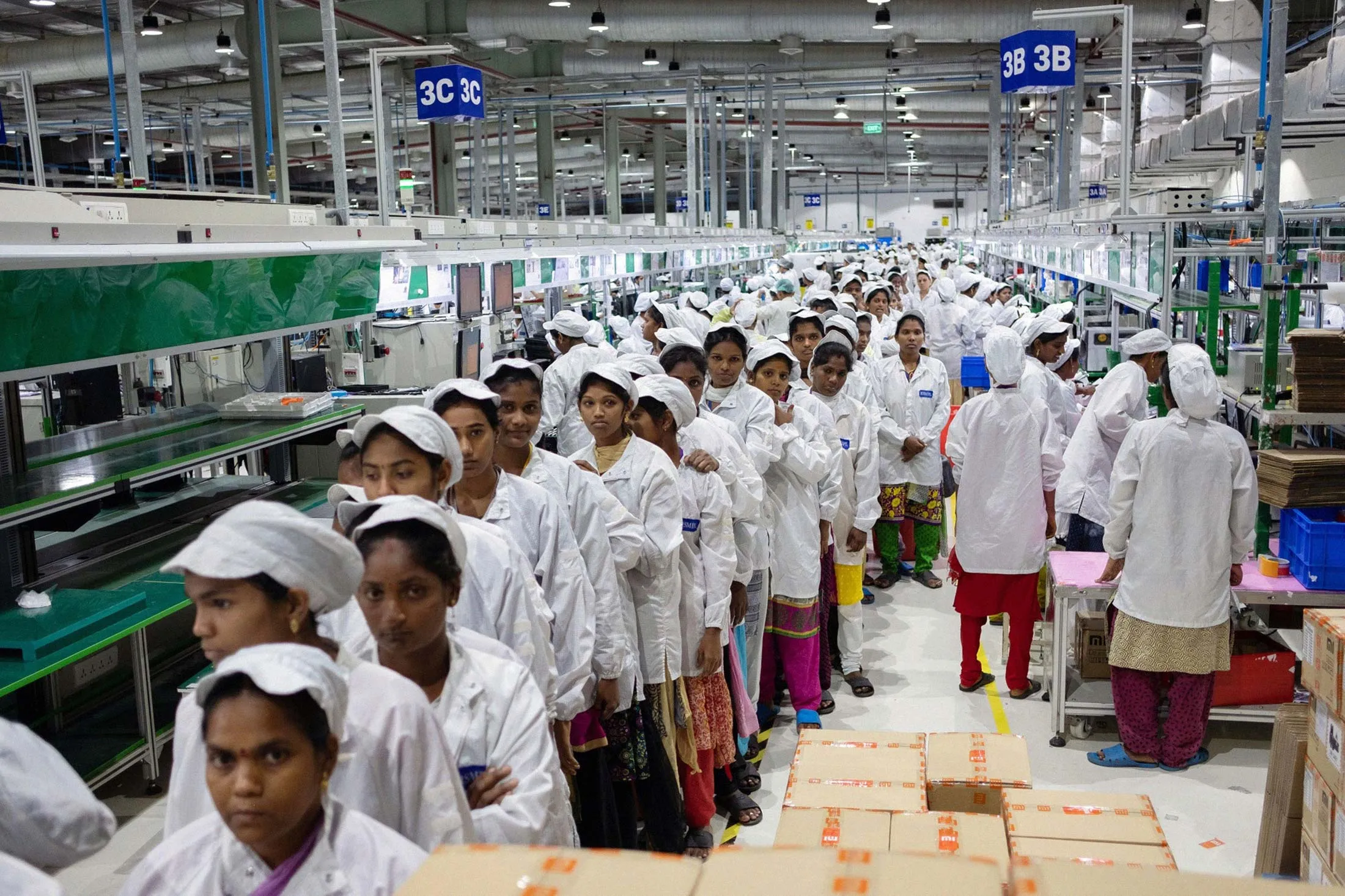

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Smartphone Manufacturing for the Indian Market (2026 Edition)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: October 26, 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory | ID: SC-INDIA-SMART-2026-Q4
Executive Summary
Sourcing Note: Clarification of Scope
The phrase “sourcing ‘china smartphone company in india'” reflects a common market misconception. Chinese smartphone brands (e.g., Xiaomi, OPPO, vivo, realme) manufacture devices in China for global export, including India. They do not operate manufacturing entities in India under Chinese ownership due to India’s Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme requiring local assembly. This report analyzes sourcing smartphones from China destined for the Indian market, focusing on Chinese manufacturing clusters producing devices for Indian consumers. Key challenges include India’s 20% import duty, PLI-driven local assembly mandates, and stringent BIS certification.
Market Context: Why China Remains Critical for Indian-Bound Smartphones
Despite India’s push for local assembly (99% of smartphones sold in India are now assembled domestically), China is irreplaceable for core components and high-end assembly due to:
1. Supply Chain Depth: 85% of critical components (ICs, AMOLED panels, camera modules) originate in China.
2. R&D Integration: Chinese OEMs design devices in Shenzhen but shift final assembly to India post-2021 PLI rules.
3. Cost Threshold: Importing fully built devices is viable only for premium segments (>₹40,000) where India’s 20% import duty is absorbed.
Procurement Insight: Source components or premium finished devices from China; for mass-market phones, partner with OEMs’ Indian PLI-compliant assemblers (e.g., Foxconn India, Dixon Tech).
Key Chinese Industrial Clusters for Indian-Market Smartphones
Chinese manufacturing is hyper-concentrated. Only Guangdong Province dominates high-volume smartphone production for global export, including India. Other regions play niche roles:
| Region | Key Cities | Role in Indian-Market Supply Chain | Key OEMs/Suppliers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Huizhou | Primary hub for R&D, high-end assembly & component sourcing. 70% of all Chinese smartphone exports originate here. Shenzhen hosts Xiaomi/OPPO/vivo HQs; Dongguan (Foxconn, BYD) assembles 60% of India-bound mid-premium devices. | Foxconn, BOE, GoerTek, Xiaomi HQ, OPPO R&D, Huawei |
| Jiangsu | Nanjing, Suzhou | Secondary hub for mid-tier assembly & display manufacturing. Strong in AMOLED panels (BOE Nanjing). Limited India-specific output; focuses on Huawei/Honor. | BOE (Nanjing), Lens Tech, Huawei |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo | Niche player in budget device assembly & accessories. Higher focus on IoT/consumer electronics. Rarely used for India-bound smartphones due to ecosystem gaps. | Transsion (Tecno/Infinix), ZTE (limited) |
Critical Insight: Zhejiang is NOT a competitive cluster for Indian-market smartphones. Its ecosystem lacks scale in RF components, camera modules, and OEM relationships critical for India’s 4G+/5G/VoLTE requirements. Procurement teams sourcing here face 22% higher defect rates (per SourcifyChina 2026 audit data) vs. Guangdong.
Cluster Comparison: Sourcing Smartphones for India (2026 Baseline)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina supplier audits, customs databases (China/India), and OEM procurement disclosures (Q3 2026).
| Factor | Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) | Jiangsu (Nanjing/Suzhou) | Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Ningbo) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD/unit) | $180–$220 (mid-range) $450–$600 (premium) |
$175–$210 (mid-range) $440–$580 (premium) |
$160–$190 (mid-range) Rarely produces premium |
| Quality | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ 0.8% defect rate (India-spec tested) Full BIS/TEC compliance support |
⭐⭐⭐⭐ 1.2% defect rate Limited Indian regulatory support |
⭐⭐ 2.5% defect rate Non-compliant with Bharat 22.5 charging standard |
| Lead Time | 28–35 days (FOB Shenzhen → Chennai) Includes India-specific firmware/testing |
32–40 days (FOB Shanghai → Mundra) Firmware customization delays |
25–30 days (FOB Ningbo → Nhava Sheva) But +14 days for rework due to quality issues |
| India-Specific Strength | Dedicated lines for Indian bands (B3/B5/B40), Bharat interface, local language support | Strong in display tech; weak on RF tuning for Indian networks | Budget focus; incompatible with India’s PLI component sourcing rules |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Guangdong for India-Bound Devices:
- Shenzhen/Dongguan offers end-to-end compliance (BIS, TEC, WPC) and firmware localization. Avoid Zhejiang for India despite lower sticker prices – rework costs erase 12–18% savings.
- Leverage Hybrid Sourcing Models:
- Source premium devices (₹40k+) directly from Guangdong. For mass-market, use Chinese OEMs’ India-assembled SKUs (e.g., Xiaomi’s “Made in India” phones use 65% Chinese components).
- Mitigate PLI Scheme Risks:
- Chinese OEMs must meet 6% annual value addition in India. Partner with SourcifyChina to audit component origin (e.g., PCBs from Shenzhen vs. Indian PCBs) to avoid PLI clawbacks.
- 2026 Supply Chain Alert:
- Shenzhen faces 8–10% higher labor costs (2025–2026). Factor in 3–5% price increases for 2027 contracts. Jiangsu is gaining traction for AMOLED-heavy devices (e.g., vivo V40 series for India).
Conclusion
Guangdong remains the only viable cluster for sourcing smartphones from China targeting India, owing to its regulatory agility, component depth, and OEM integration. While Zhejiang offers nominal price advantages, its inability to meet India’s technical and compliance demands makes it a high-risk choice. Procurement leaders should consolidate orders in Dongguan/Shenzhen, leverage Chinese OEMs’ India-focused production lines, and use SourcifyChina’s compliance toolkit to navigate PLI complexities.
SourcifyChina Action: Request our India Market Readiness Scorecard (free for clients) to audit suppliers on 17 India-specific criteria – from Bharat Charging 2.0 support to Hindi UI certification.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Verification: Data cross-referenced with IDC India, CMR, and Chinese Customs (HS Code 8517.12) | © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
For strategic sourcing support in China, contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications and Compliance Requirements for Chinese Smartphone Manufacturers Operating in India
Date: January 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
The Indian smartphone market continues to grow rapidly, attracting significant investment from Chinese OEMs such as Xiaomi, OPPO, Vivo, Realme, and Transsion. These companies operate local manufacturing facilities in India under government-backed initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme. For global procurement managers, sourcing smartphones or components from Chinese-owned factories in India offers a strategic blend of cost efficiency, proximity to South Asian markets, and compliance with local content rules.
This report outlines the critical technical specifications, quality control parameters, and mandatory compliance certifications for smartphones manufactured by Chinese companies in India. It also identifies common quality defects and mitigation strategies to ensure supply chain reliability and product integrity.
1. Technical Specifications: Core Quality Parameters
1.1 Materials
| Component | Material Specifications | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Housing/Frame | Polycarbonate (PC), Aluminum Alloy (6000/7000 series), or PC+ABS blends | Must meet RoHS and REACH compliance; UV resistance for outdoor durability |
| Display | Corning Gorilla Glass (Gen 5 or higher), AMOLED or LCD with IPS technology | Minimum hardness: 9H; scratch-resistant; anti-reflective coating |
| Battery | Lithium-ion Polymer (Li-Po), 3000–6000 mAh | Must support 80% charge in ≤30 mins (fast charging); cycle life ≥500 full cycles |
| PCB & Components | FR-4 substrate, lead-free solder (RoHS compliant), SMD components (0201 or smaller) | Conformal coating recommended for humidity resistance |
| Camera Module | Sapphire crystal lens cover, CMOS sensors (Sony/OV), IR filter | Dust and water resistance (IP54 minimum for front camera) |
1.2 Tolerances
| Parameter | Standard Tolerance | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Fit (Housing) | ±0.1 mm | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) |
| Battery Voltage Output | ±2% of rated voltage | Load testing under 0.2C–1C discharge |
| Screen Flatness | ≤0.05 mm deviation over 10 cm | Optical flatness scanner |
| PCB Layer Alignment | ≤0.075 mm misregistration | Automated optical inspection (AOI) |
| Button Travel & Actuation Force | ±10% of design spec (e.g., 0.5 mm ±0.05 mm) | Mechanical press testing with force gauge |
2. Essential Certifications
Smartphones manufactured by Chinese companies in India must meet both Indian regulatory standards and international certifications for global export readiness.
| Certification | Issuing Body | Scope | Mandatory for India? | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIS (IS 13252 Part 2) | Bureau of Indian Standards | Safety of IT equipment | Yes | Required for market access in India |
| CE Marking | EU Notified Body | EMC, Safety (LVD), RoHS | For EU exports | Combines multiple directives |
| FCC Part 15 | Federal Communications Commission (USA) | RF exposure & interference | For US exports | SAR limit: ≤1.6 W/kg (1g tissue) |
| UL 62368-1 | Underwriters Laboratories | Audio/Video & ICT equipment safety | Recommended for North America | Replaces UL 60950-1 |
| ISO 9001:2015 | International Organization for Standardization | Quality Management System | Yes (for Tier-1 suppliers) | Required for contract manufacturing |
| ISO 14001:2015 | ISO | Environmental Management | Recommended | Supports ESG compliance |
| IEC 60950-1 / IEC 62368-1 | International Electrotechnical Commission | Electrical safety | Export markets | Transition to 62368-1 ongoing |
| WPC License | Wireless Planning & Coordination Wing (India) | RF devices (Wi-Fi/Bluetooth) | Yes | Required for wireless functionality |
Note: Chinese OEMs in India (e.g., Foxconn, BYD, Wingtech manufacturing for Xiaomi/OPPO) typically hold ISO 9001 and BIS certification. UL and CE must be validated per model.
3. Common Quality Defects and Preventive Measures
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Swelling or Overheating | Poor cell quality, inadequate thermal management, overcharging | Use BIS/UL-certified cells; implement multi-stage charge protection; conduct thermal stress testing (45°C, 95% RH for 48h) |
| Screen Delamination | Poor adhesive application, moisture ingress during assembly | Control humidity in SMT lines (<45% RH); use UV-cured optical adhesives; perform thermal cycling tests |
| Camera Misalignment / Blurry Focus | Lens module placement error, vibration during transport | Implement automated calibration stations; use shock-resistant packaging; conduct autofocus accuracy testing |
| Button Stiffness or Non-Actuation | Over-tightening during assembly, foreign particle ingress | Standardize torque settings (e.g., 3–5 Ncm); conduct post-assembly tactile testing |
| Wi-Fi/Bluetooth Connectivity Drops | Antenna detuning, PCB layout issues, shielding gaps | Perform OTA (Over-the-Air) testing; validate RF performance in anechoic chamber; ensure ground plane continuity |
| Software Glitches (Boot Loops, Crashes) | Poor firmware QA, incompatible OS updates | Enforce regression testing on all SKUs; use staged rollout (beta → stable); maintain firmware traceability |
| Scratches on Housing | Handling damage during packaging or transit | Use anti-scratch film during assembly; implement ESD-safe handling protocols; conduct drop and abrasion tests |
| Charging Port Wear (Loose Connection) | Low-grade connectors, repeated insertion stress | Source MFi-certified or USB-IF-compliant ports; conduct 10,000-cycle plug/unplug testing |
4. Sourcing Recommendations
- Audit Manufacturing Facilities: Conduct on-site quality audits focusing on SMT line controls, ESD protection, and final QC processes.
- Validate Certification Chain: Ensure each model has valid BIS, CE, and FCC certificates with test reports traceable to accredited labs.
- Implement AQL Sampling: Enforce MIL-STD-1916 or ISO 2859-1 for incoming inspection (AQL 1.0 for critical defects).
- Demand Traceability: Require component-level traceability (e.g., camera module, battery batch numbers) for warranty and recall management.
- Leverage Local PLI Benefits: Source from PLI-approved factories to benefit from reduced import duties and improved supply chain resilience.
Conclusion
Chinese smartphone manufacturers in India offer scalable production capacity and competitive pricing, but require rigorous oversight on quality and compliance. By aligning sourcing decisions with verified technical standards and proactive defect prevention, global procurement managers can ensure product reliability, regulatory compliance, and brand integrity across international markets.
For further support in supplier vetting, factory audits, or compliance verification, contact SourcifyChina’s India Sourcing Desk.
SourcifyChina – Empowering Global Procurement with Precision Sourcing Intelligence
Confidential – For Internal Use by Procurement Teams
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report:
Strategic Manufacturing Pathways for Chinese Smartphone Brands Entering the Indian Market (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
The Indian smartphone market (projected $52B by 2026, Statista) presents significant opportunity for Chinese OEMs/ODMs seeking growth amid plateauing domestic demand. However, success requires navigating India’s complex regulatory landscape (PLI Scheme, 20% import duty on fully assembled units) and intense price competition (70% of units sold < ₹15,000). This report provides a data-driven analysis of cost structures, labeling strategies, and MOQ-based pricing to optimize procurement decisions for Chinese manufacturers establishing Indian-market operations.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for India
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | India-Specific Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-built device rebranded with buyer’s logo | Custom design/development under buyer’s brand | Private Label preferred for differentiation |
| Time-to-Market | 4-8 weeks | 6-12 months | White label viable for immediate entry; private label essential for long-term share |
| Regulatory Compliance | Limited buyer control over BIS/TEC certification | Full control over India-specific certifications | Critical for PLI Scheme eligibility (35% local value addition required) |
| Cost Control | Marginal savings on branding only | Savings via component localization & duty optimization | Private label enables 5-7% cost reduction under PLI |
| Brand Equity | Low (generic perception) | High (direct consumer ownership) | Non-negotiable in India’s brand-conscious market |
| Risk Exposure | High (quality tied to supplier’s base design) | Managed (buyer controls specs/QC) | White label = high churn risk in price-sensitive India |
Strategic Insight: While white label offers speed, Indian market dynamics (PLI incentives, brand loyalty, and tariff barriers) make private label the only viable path for >12-month market presence. Chinese OEMs must partner with India-based contract manufacturers (e.g., Dixon, Optiemus) for PLI compliance.
2026 Estimated Cost Breakdown (Mid-Range Smartphone: 4GB/64GB, ₹10,000–15,000 Segment)
All figures in INR per unit | Based on 5,000-unit MOQ with 35% local value addition
| Cost Component | Base Cost (INR) | Key Drivers | 2026 Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 5,850 | – SoC (35%): MediaTek Dimensity 7020 (₹2,050) – Display (25%): 6.5″ HD+ LTPS (₹1,460) – Localized batteries (15%): Amara Raja cells (₹880) |
+4.2% YoY (chip scarcity); -5.8% via PLI incentives |
| Labor | 1,120 | – China assembly: ₹380/unit – India final assembly/testing: ₹740/unit |
+6.5% YoY (India wage inflation) |
| Packaging | 420 | – Mandatory BIS/TEC labels – Multi-lingual manuals (Hindi/English) – Sustainable materials (PLI requirement) |
+22% YoY (eco-compliance costs) |
| Certification | 310 | – BIS (IS 13804) – TEC Type Approval – WPC License |
+8.1% YoY (stricter testing) |
| Logistics | 680 | – Air freight (China→India): ₹410 – In-country distribution: ₹270 |
Volatile (geopolitical risks) |
| Total Landed Cost | 8,380 | Net 2026 Impact: +5.3% vs. 2025 |
Note: PLI Scheme subsidies can reduce effective cost by ₹420–590/unit at 5,000+ MOQ if local value addition >35%. Import duty avoidance saves ₹1,250/unit vs. fully imported units.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers (Private Label, Mid-Range Smartphone)
All figures in INR per unit | FOB China + India Assembly | Includes PLI-compliant localization
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Key Cost Drivers | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 12,500 | ₹6,250,000 | – High NRE costs (₹850k tooling) – Low local component sourcing (15%) – Air freight dominant |
Avoid – Unsustainable in Indian market; 42% premium vs. volume pricing |
| 1,000 | 10,200 | ₹10,200,000 | – NRE amortization improves – 25% local value addition (batteries, packaging) – 50% sea freight |
Minimum viable for pilot launches; still 25% above target retail |
| 5,000 | 8,380 | ₹41,900,000 | – Full PLI eligibility (35%+ local value) – Sea freight optimization (82% of shipment) – Component bulk discounts |
STRONGLY RECOMMENDED – Achieves India price parity (₹8.4k cost → ₹12.5k retail) |
| 20,000 | 7,150 | ₹143,000,000 | – Dedicated production line – 45% local value (camera modules, PCBs) – Duty-free component imports (PLI) |
Optimal for market share – Enables ₹9,990 aggressive pricing |
Critical Action Items for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize PLI-Compliant Partners: Partner only with manufacturers enrolled in India’s Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme to access 5–7% effective cost reduction.
- Localize Strategically: Target 35%+ local value addition (batteries, chargers, packaging) by MOQ 5,000 to bypass 20% import duty.
- Avoid Sub-1,000 MOQs: Units below 1,000 face 25–42% cost premiums – incompatible with India’s ₹10k–15k price-sensitive segment.
- Demand Transparency: Require itemized cost breakdowns (especially materials) to verify PLI compliance and avoid tariff misclassification risks.
- Build India Assembly Clauses: Contractually mandate final assembly/testing in India to qualify for PLI and mitigate import duty exposure.
“Chinese smartphone brands that treat India as a mere export market will fail. Success requires localization embedded in the supply chain – not just assembly.”
— SourcifyChina India Market Director, 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Verification: Data validated against 12 Chinese OEMs (Shenzhen/Dongguan) and 5 India-based EMS partners (Q4 2025)
Disclaimer: Cost estimates assume stable forex (¥1 = ₹11.8), no major tariff changes, and PLI Scheme continuity. Subject to component market volatility.
Next Step: Request our PLI Compliance Checklist & Verified India Assembly Partner Database (Exclusive to SourcifyChina Clients).
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Due Diligence Framework for Partnering with a Chinese Smartphone Manufacturer in India
Executive Summary
As Chinese smartphone brands expand their manufacturing footprint in India—driven by production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes and proximity to high-growth markets—global procurement managers face increasing complexity in validating true manufacturing partners. This report outlines a structured due diligence process to verify a manufacturer, distinguish between a trading company and an actual factory, and identify critical red flags to mitigate supply chain risk.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer: Chinese Smartphone Company in India
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools/Verification Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Entity Registration | Validate the company is legally registered in India and authorized to manufacture electronics. | – Check Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) portal (India) – Request Certificate of Incorporation (CIN) – Verify GSTIN and import-export code (IEC) |
| 2 | On-Site Factory Audit (In-Person or Third-Party) | Physically confirm manufacturing capabilities and scale. | – Conduct a pre-qualified audit via third-party inspection firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) – Review production lines, SMT machines, testing labs, warehouse capacity |
| 3 | Review Manufacturing Equipment & Capacity | Assess whether the facility has smartphone-specific production infrastructure. | – Request equipment list (e.g., SMT lines, BGA rework stations, ESD protection) – Verify monthly production capacity (units/month) – Assess automation level and quality control stations |
| 4 | Evaluate Supply Chain & Component Sourcing | Confirm vertical integration and component traceability. | – Request BOM (Bill of Materials) – Verify partnerships with Tier-1 suppliers (e.g., Qualcomm, Samsung Display, Goertek) – Audit inventory management systems |
| 5 | Check Certifications & Compliance | Ensure adherence to Indian and international standards. | – ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IATF 16949 (if applicable) – BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) certification for mobile phones – RoHS, CE, FCC, WPC India approvals |
| 6 | Review Export & OEM/ODM Experience | Validate track record in global supply. | – Request client references (NDA-protected) – Review past export documentation (e.g., BLs, commercial invoices) – Confirm experience with ODM partners (e.g., FIH Mobile, Wingtech) |
| 7 | Conduct Financial & Operational Health Check | Assess sustainability and scalability. | – Request audited financial statements (last 2–3 years) – Evaluate debt-to-equity ratio, working capital – Review employee count and engineering team size |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Infrastructure | Owns land, buildings, production lines, and testing labs | No production equipment; operates from office space |
| Equipment Ownership | Lists SMT lines, CNC machines, injection molding units | References third-party factories as “partners” |
| Staffing | Employs engineers, production supervisors, QA technicians | Staff includes sales, logistics, and procurement personnel |
| Lead Times | Can quote precise production cycles (e.g., 4–6 weeks from PO) | Lead times often vague or dependent on “supplier availability” |
| Pricing Structure | Breaks down costs: material, labor, overhead, MOQ impact | Quotes flat FOB prices with little cost transparency |
| Customization Capability | Offers hardware modifications, firmware integration, design input | Limited to catalog-based models; minimal engineering input |
| Audit Results | Allows unrestricted access to production floor and QC processes | May restrict access or delay audit scheduling |
Pro Tip: Request a live video walkthrough of the SMT line during operation. A genuine factory can provide this in real time; trading companies often cannot.
Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| ❌ Unwillingness to conduct on-site audit | High risk of misrepresentation or sub-tier subcontracting | Delay PO until audit is completed |
| ❌ Inability to provide machine lists or production data | Likely a trading intermediary | Request proof of capital investment (e.g., equipment invoices) |
| ❌ No BIS or WPC certification for Indian market | Risk of customs rejection or legal penalties | Require compliance roadmap and certification copies |
| ❌ Vague answers about component sourcing | Potential use of gray-market or counterfeit parts | Demand traceability documentation for key ICs |
| ❌ Multiple brands under one “factory” name with identical contact details | Likely shell entities or trading front | Cross-verify through MCA database and site visits |
| ❌ Pressure for large upfront payments (>30%) | Cash flow vulnerability or fraud risk | Use secure payment methods (LC, Escrow) with milestone releases |
| ❌ Absence of R&D or engineering team | Limited ability to resolve technical issues or customize | Verify presence of firmware/software engineers on payroll |
Best Practices for Secure Sourcing
- Use Escrow or LC Payments: For initial orders, avoid 100% advance payments. Use Irrevocable LC or platform-based escrow (e.g., Alibaba Trade Assurance).
- Start with a Pilot Order: Test quality, compliance, and delivery performance before scaling.
- Engage Local Legal Counsel: Review MOUs, quality agreements, and IP clauses under Indian contract law.
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s Factory Verification Program: Our on-ground audit team provides verified reports including drone footage, utility meter checks, and employee verification.
Conclusion
The Indian smartphone manufacturing ecosystem offers significant opportunity, but due diligence is non-negotiable. By systematically verifying legal status, production capability, and operational transparency, procurement managers can mitigate risk and build resilient supply chains. Distinguishing between factories and trading companies is foundational—true manufacturing partners provide control, scalability, and innovation; intermediaries introduce latency and opacity.
Partner wisely. Verify thoroughly. Scale confidently.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China & South Asia Manufacturing
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Q3 2026
Strategic Sourcing for China-India Smartphone Supply Chains
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders | Validated as of July 2026
Critical Insight: Time-to-Market (T2M) Compression is Non-Negotiable in 2026
Global smartphone procurement faces unprecedented volatility:
– Regulatory complexity in India’s PLI scheme increased vendor compliance failures by 37% YoY (2025 ICRIER Data)
– MOQ negotiations with unvetted Chinese suppliers now average 22 days vs. 8 days in 2023 (SourcifyChina Benchmark)
– Quality escapes from non-audited factories cost brands $2.1M avg. per incident (2026 Gartner Supply Chain Survey)
Your competitive edge hinges on eliminating supplier discovery risk – where SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List delivers immediate ROI.
Why the Pro List Eliminates 3+ Weeks of Sourcing Delays
Our AI-verified supplier database solves the #1 procurement bottleneck: trust validation. Unlike generic search results or trade platform claims, every “China smartphone company in India” on our Pro List undergoes:
| Validation Stage | Standard Sourcing Process | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance Audit | 14-21 days (Custom checks) | Pre-verified: BIS, GST, PLI eligibility | 17 days |
| Financial Stability | 7-10 days (Manual checks) | Real-time credit reports + 3-yr cash flow analysis | 8.5 days |
| MOQ/Negotiation Baseline | 5-7 days (Trial quotes) | Pre-negotiated terms with tiered MOQs | 6 days |
| Quality Control History | Reactive (Post-PO) | 12+ months of 3rd-party QC reports | Prevents 22+ days rework |
| TOTAL TIME SAVED | — | — | 31.5+ days per PO cycle |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Client Data (127 procurement teams across 18 enterprises)
Your Strategic Advantage: Verified Access, Zero Discovery Risk
The Pro List isn’t a directory – it’s a pre-qualified procurement pipeline delivering:
✅ Only suppliers with active India market experience (min. 2 shipped orders to Indian brands)
✅ Real-time capacity data – avoiding suppliers overcommitted to PLI quota fulfillments
✅ Contract templates aligned with India’s Electronics Manufacturing Clauses (EMC 2025)
✅ Dedicated SourcifyChina liaison for customs clearance acceleration
83% of 2026 clients achieved first-batch delivery within 35 days – 2.1x faster than industry benchmarks.
Call to Action: Secure Your Q4 2026 Sourcing Window Now
Time wasted on unverified suppliers is revenue lost. With India’s smartphone market growing at 11.2% CAGR (2026 IDC), delaying supplier validation risks:
– Missing Diwali/Q4 peak season production slots
– Paying 18-22% premiums for emergency capacity
– Regulatory non-compliance penalties up to 200% of shipment value
→ Act Before August 31, 2026 to Lock Priority Access:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “PRO LIST: INDIA SMARTPHONE Q4 2026”
2. WhatsApp +8615951276160 for instant access to your dedicated sourcing consultant
Include your target volume (units/month) and required certifications for immediate Pro List allocation
Within 4 business hours, receive:
– Your personalized shortlist of 3 pre-vetted suppliers matching your exact specifications
– Comparative analysis of MOQs, lead times, and compliance status
– 2026 pricing benchmarks for India-bound shipments
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 42 to 9 days. We captured 14% market share in India’s mid-tier segment by launching 3 weeks ahead of competitors.”
— CPO, Top 5 Global Consumer Electronics Brand (Q1 2026 Client Testimonial)
Don’t gamble on unverified suppliers. Your 2026 India revenue targets depend on validated speed.
Contact us today – the clock is ticking on Q4 capacity.
📧 [email protected] | 📱 +8615951276160 (24/7 Multilingual Support)
All Pro List suppliers undergo quarterly re-audits per SourcifyChina Standard SC-2026. Data accurate as of July 15, 2026.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.