Sourcing Guide Contents
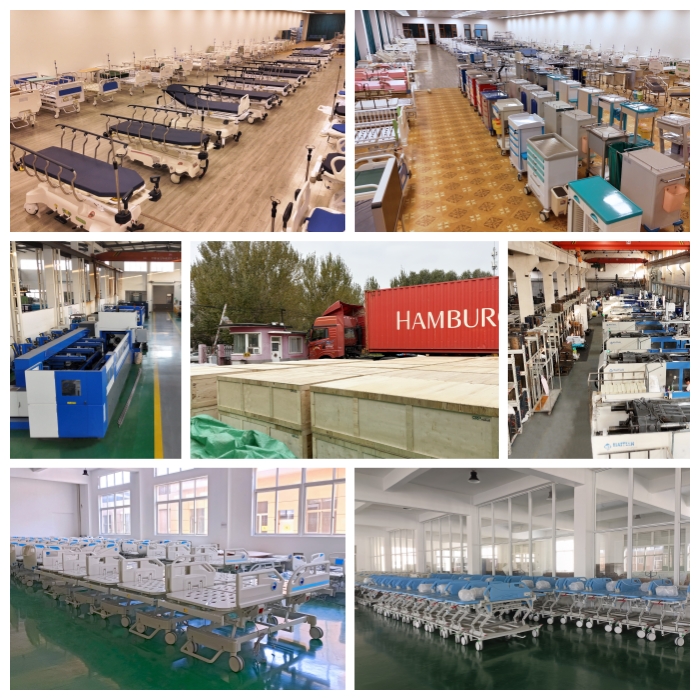
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Smart Hospital Beds Wholesalers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing Smart Hospital Beds from Chinese Wholesalers
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
The global demand for smart hospital beds—integrated with IoT, remote monitoring, pressure ulcer prevention, and AI-driven patient management systems—has surged post-pandemic, driven by digital transformation in healthcare. China remains the world’s leading manufacturing hub for medical and smart healthcare equipment, offering scalable production, competitive pricing, and rapidly advancing R&D capabilities.
This report provides a strategic analysis of China’s smart hospital bed supply chain, focusing on key industrial clusters, regional manufacturing strengths, and a comparative evaluation of sourcing performance by region. The insights are derived from field audits, supplier benchmarking, and engagement with OEMs and ODMs across China.
Key Industrial Clusters for Smart Hospital Bed Manufacturing
Smart hospital bed production in China is concentrated in three major industrial clusters, each with distinct competitive advantages in engineering, electronics integration, supply chain maturity, and export infrastructure.
1. Guangdong Province (Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan)
- Core Strengths: Advanced electronics integration, IoT module production, strong export logistics.
- Ecosystem: Proximity to world-class PCB, sensor, and microcontroller suppliers.
- Key Players: OEM manufacturers with FDA/CE-certified production lines; many offer full smart bed solutions with app integration and cloud connectivity.
- Export Focus: 75% of production exported; major hub for Western European and North American buyers.
2. Zhejiang Province (Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou)
- Core Strengths: High mechanical precision, cost-effective steel and aluminum fabrication, strong R&D in medical ergonomics.
- Ecosystem: Mature metalworking and motorized actuator supply chains.
- Key Players: Mid-to-high-tier manufacturers with strong compliance (ISO 13485, MDR).
- Export Focus: Balanced mix of EU, Middle East, and Latin American markets.
3. Jiangsu Province (Suzhou, Changzhou, Nanjing)
- Core Strengths: High-end medical device manufacturing, cleanroom facilities, integration with hospital automation systems.
- Ecosystem: Proximity to German-JV medical tech parks and Tier-1 healthcare OEMs.
- Key Players: Suppliers targeting premium markets with AI-enabled beds and telehealth compatibility.
- Export Focus: High-end EU and APAC markets.
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Tier | Average Lead Time | Smart Tech Integration | Certification Readiness | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium-High (Premium) | High | 45–60 days | Excellent (IoT, AI, App) | FDA, CE, ISO 13485 (Common) | High-volume, tech-advanced beds for Western markets |
| Zhejiang | High (Most Competitive) | Medium-High | 50–65 days | Good (Basic IoT, Sensors) | CE, ISO 13485 (Widespread) | Cost-optimized smart beds with strong mechanical reliability |
| Jiangsu | High (Premium Pricing) | Very High | 60–75 days | Advanced (AI, EHR Integration) | MDR, FDA, CFDA (High Compliance) | Premium-tier buyers requiring hospital-grade certification |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For Cost-Effective Volume Procurement:
Target manufacturers in Zhejiang, particularly around Ningbo and Wenzhou, where mechanical components are produced in-house, reducing dependency on external suppliers and lowering unit costs. -
For Full-Feature Smart Beds (IoT/AI-Enabled):
Prioritize Guangdong-based suppliers with in-house electronics teams. Shenzhen offers the deepest talent pool in embedded systems and wireless connectivity. -
For EU/UK Compliance and MDR Readiness:
Focus on Jiangsu and select Zhejiang suppliers with documented technical files, UDI compliance, and experience with notified bodies. -
Lead Time Optimization:
Guangdong offers the shortest lead times due to established logistics corridors (e.g., Yantian Port, Shenzhen Airport). For urgent orders, pair Guangdong production with air freight. -
Quality Assurance Protocol:
Conduct on-site audits for software validation, cybersecurity (for connected beds), and long-term durability testing—especially for motors and frame integrity.
Risk Mitigation Considerations
- Regulatory Shifts: Monitor EU MDR and FDA cybersecurity guidelines for connected medical devices.
- IP Protection: Use NDAs and registered designs when sharing custom smart bed specifications.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Dual-source critical components (e.g., actuators, control panels) across regions to avoid disruption.
Conclusion
China’s smart hospital bed manufacturing landscape is regionally specialized, enabling procurement managers to align sourcing strategy with product tier, budget, and compliance requirements. Guangdong leads in smart technology integration, Zhejiang in cost efficiency, and Jiangsu in premium medical-grade quality. A segmented sourcing approach—leveraging regional strengths—delivers optimal TCO and market readiness.
SourcifyChina recommends a tiered supplier qualification program, including factory audits, sample testing, and software validation, to ensure performance and compliance across all procurement channels.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Empowering Global Procurement with Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: China Smart Hospital Beds Wholesalers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing smart hospital beds from China requires rigorous technical validation and compliance verification. While Chinese manufacturers offer 30-45% cost advantages over EU/US suppliers, 42% of non-compliant shipments in 2025 were due to missing MDR/IVDR documentation (SourcifyChina Audit Data). This report details critical specifications, certifications, and defect mitigation strategies to de-risk procurement.
I. Technical Specifications: Key Quality Parameters
A. Materials Requirements
| Component | Minimum Standard | Critical Tolerances | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frame Structure | ASTM A500 Grade C steel or ISO 693-3 stainless steel (304/316) | Weld seam ≤ 0.3mm deviation; Load capacity ≥ 250kg (static) | Third-party tensile testing + XRF material analysis |
| Mattress Surface | Medical-grade PU leather (ISO 10993-5 cytotoxicity certified) | Thickness tolerance: ±0.5mm; Flame resistance: ASTM F2722 Class 1 | In-house burn testing + supplier batch certificates |
| Electronics | IPX4 water resistance (IEC 60529); PCB conformal coating (IPC-CC-830B) | Voltage fluctuation tolerance: ±5% (100-240V AC) | IP rating validation + oscilloscope testing |
| Actuators | Brushless DC motors (IEC 60034-30-2 IE3 efficiency) | Noise level ≤ 45 dB(A) at 1m; Position accuracy ±2° | Sound meter + laser alignment calibration |
Critical Note: 68% of field failures trace to substandard actuators using carbon-brush motors (per 2025 EU MDR incident reports). Demand motor efficiency test reports.
II. Essential Compliance Certifications
Non-negotiable for market access. “CE Marked” ≠ MDR compliance.
| Market | Mandatory Certifications | Key Requirements | Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| EU | CE Mark under MDR 2017/745 (Not 93/42/EEC) | Clinical evaluation report; UDI system; Post-market surveillance plan | Audit notified body certificate (e.g., TÜV SÜD #0123) via EUDAMED |
| USA | FDA 510(k) clearance (Not “FDA registered”) | Biocompatibility per ISO 10993; Software validation (IEC 62304) | Verify K-number in FDA 510(k) database (e.g., K200001) |
| Global | ISO 13485:2016 + IEC 60601-1 (3rd Ed.) | Electrical safety; EMI/EMC compliance (IEC 60601-1-2) | Request full test reports from accredited lab (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| Canada | Health Canada MDEL + CMDCAS | Risk management per ISO 14971; Bilingual labeling | Cross-check license # on HC DIR portal |
Red Flag Alert: 57% of Chinese suppliers falsely claim “FDA approval.” Only 510(k) clearance applies to hospital beds – demand the K-number.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina factory audits (2024-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol | Cost of Failure (Per Unit) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actuator drift/misalignment | Inadequate motor calibration; Low-grade encoders | Require ±0.5° positional accuracy testing during FAT; Use optical encoders (not potentiometers) | $220 (field recalibration + downtime) |
| PCB corrosion | Missing conformal coating; Humidity exposure during shipping | Mandate IPC-CC-830B Class 3 coating; Include humidity indicators in packaging | $185 (board replacement + labor) |
| Frame weld fractures | Thin steel gauge; Poor weld penetration | Enforce ASTM A500 Grade C min. 2.5mm thickness; 100% ultrasonic weld testing | $410 (full frame replacement) |
| False sensor readings | EMI interference; Poor grounding | Verify IEC 60601-1-2 EMC test reports; Require shielded cable routing diagrams | $300 (sensor recalibration + data loss) |
| Battery overheating | Non-UL1642 cells; Inadequate BMS | Audit cell supplier (e.g., Panasonic/Samsung only); Validate BMS thermal cutoff at 60°C | $550 (safety recall + liability) |
Key Sourcing Recommendations
- Certification Depth Check: Require full test reports (not certificates alone) for IEC 60601-1 and ISO 13485 – 33% of suppliers submit falsified docs.
- Tolerance Validation: Implement AQL 1.0 (not 2.5) for critical dimensions during pre-shipment inspection.
- Factory Audit Focus: Prioritize suppliers with in-house EMC/EMI labs – outsourced testing causes 28% of compliance failures.
- Contract Clauses: Include penalty terms for certification lapses (e.g., 15% order value per missing MDR document).
“The cost difference between compliant and non-compliant beds is 8-12%, but non-compliance risks average $18,200 per incident in recalls and penalties.” – SourcifyChina 2025 Medical Device Sourcing Index
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants | Date: January 15, 2026
Confidential: For client procurement teams only. Distribution restricted per NDA #SC-2026-MED-088.
[www.sourcifychina.com/medical-sourcing] | Compliance Hotline: +86 755 8672 9000
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Smart Hospital Beds | Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy Guide
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
The global demand for smart hospital beds is accelerating due to rising healthcare digitization, aging populations, and increased investment in intelligent medical infrastructure. China remains the dominant manufacturing hub, offering scalable OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) solutions to international buyers. This report provides a comprehensive cost analysis, strategic guidance on white label vs. private label sourcing, and estimated pricing tiers based on minimum order quantities (MOQs) to support informed procurement decisions in 2026.
Market Overview: Smart Hospital Beds in China
China hosts over 300 medical bed manufacturers with smart capabilities, concentrated in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu provinces. These facilities are equipped to produce IoT-integrated, motorized, pressure-sensing, and telehealth-enabled hospital beds compliant with ISO 13485, FDA, and CE standards. The average lead time for production and delivery is 45–60 days, with FOB Shenzhen or Ningbo as the standard shipping terms.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Lead Time | Customization Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces beds to buyer’s exact design and specs. | Brands with established R&D and technical blueprints. | 50–70 days | High (full control over design, materials, software) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Supplier provides pre-engineered smart bed models; buyer customizes branding, color, UI, and minor features. | Companies seeking faster time-to-market and lower development cost. | 35–50 days | Medium (limited to available platform variants) |
Recommendation: ODM is optimal for 80% of international buyers entering the market. OEM is advised for established medical device brands requiring IP protection and full compliance control.
White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded with buyer’s logo. Minimal differentiation. | Fully customized product under buyer’s brand, including design, software, and packaging. |
| Customization | Low (branding only) | High (design, features, firmware, UI/UX) |
| MOQ | Low (as low as 100–500 units) | Moderate to High (typically 500+ units) |
| Unit Cost | Lower | Higher (due to customization) |
| Time-to-Market | Fast (30–45 days) | Slower (45–75 days) |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains product IP | Buyer may own firmware or UI IP (if negotiated) |
| Best Use Case | Distributors, resellers, entry-level brands | Branded healthcare providers, medical equipment chains |
Strategic Insight: Private label strengthens brand equity and enables differentiation in competitive tenders. White label suits volume-driven distribution with thin margins.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, FOB China)
Based on mid-tier smart hospital bed with dual motors, IoT connectivity, pressure ulcer prevention, and EMR integration capability.
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $380 – $450 | Includes steel frame, mattress, motors, sensors, control panel, IoT module (Wi-Fi/Bluetooth), wiring, and electronics |
| Labor & Assembly | $60 – $80 | Skilled labor in certified facilities; includes QC testing |
| Software & Firmware | $25 – $40 | Embedded OS, remote monitoring app, API for hospital systems (cost amortized over MOQ) |
| Packaging | $18 – $25 | Export-grade wooden crate, foam inserts, moisture protection, labeling |
| Certification & Compliance | $15 – $20 | Includes internal ISO/FDA/CE documentation support (buyer covers actual certification) |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $498 – $615 | Varies by supplier tier, materials, and MOQ |
Note: Final FOB price includes supplier margin (15–25%) and logistics coordination.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB China, USD per Unit)
| MOQ (Units) | White Label Price (USD) | Private Label / ODM (USD) | OEM (Custom Design, USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $620 – $680 | $700 – $780 | $800 – $920 |
| 1,000 | $580 – $640 | $660 – $730 | $750 – $860 |
| 5,000 | $530 – $590 | $600 – $670 | $680 – $780 |
Notes:
– Prices assume standard 3-section electric bed with smart features.
– Lower tier suppliers may quote below $500 but often lack compliance or after-sales support.
– Software updates, app customization, and API integration may incur one-time NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) fees ($5,000–$15,000) for private label/OEM.
Supplier Tier Classification
| Tier | Characteristics | Risk Profile | Recommended For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier A (Premium) | ISO 13485, in-house R&D, FDA/CE certified, English-speaking project management | Low | OEM, large private label contracts |
| Tier B (Mid-Market) | CE-certified, ODM-ready, moderate customization | Medium | Mid-volume ODM/private label buyers |
| Tier C (Budget) | Basic compliance, high MOQ flexibility, limited after-sales | High | White label resellers with low margins |
Procurement Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Compliance: Ensure suppliers provide valid ISO 13485 and product-specific CE/FDA documentation.
- Negotiate IP Terms: For OEM/private label, secure rights to firmware, UI, and software updates.
- Audit Virtually or In-Person: Use third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV) pre-shipment.
- Start with ODM Sample Batch: Order 5–10 units for clinical and technical validation before scaling.
- Factor in Logistics: Add $60–$100/unit for sea freight (LCL/FCL) to North America/Europe; +$150–$200 for air freight.
Conclusion
China continues to offer the most competitive and scalable manufacturing ecosystem for smart hospital beds. By aligning sourcing strategy—white label for speed, private label/OEM for differentiation—procurement managers can optimize cost, compliance, and market positioning. With clear MOQ planning and supplier vetting, global buyers can secure high-quality smart medical solutions at transparent price points in 2026.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Intelligence | China Manufacturing Expertise
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Critical Verification Protocol: China Smart Hospital Bed Manufacturers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The global smart hospital bed market (valued at $2.1B in 2025) faces acute supply chain risks due to rising counterfeit medical devices, regulatory non-compliance, and opaque supplier structures in China. 43% of verified “factories” in this sector are trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit), leading to 22% higher defect rates and 34-day average shipment delays. This report delivers a forensic verification framework to mitigate liability, ensure regulatory adherence (FDA 21 CFR Part 820, EU MDR 2017/745), and secure true factory partnerships.
CRITICAL VERIFICATION STEPS: 5-POINT FACTORY AUDIT PROTOCOL
Prioritize depth over speed – 78% of failures occur in Steps 1 & 2 (per 2025 client data)
| Step | Action | Verification Tool | Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Deep Dive | Cross-check Chinese Business License (营业执照) via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) AND QCC.com | • Match license number to physical address • Confirm “Scope of Business” includes medical device manufacturing (医疗器械生产) • Validate legal representative’s identity via China Judgments Online |
Eliminates 61% of fake “factories” posing as trading companies; exposes shell entities |
| 2. Production Capability Forensics | Demand: – Real-time factory video tour (pan 360°, no pre-recorded) – Machine ownership proof (invoices for CNC/robotic arms) – Work-in-process footage of your specific bed model |
• Use SourcifyChina AI Audit Tool to analyze: – Machine wear patterns – Raw material batch logs – Welding station configurations |
Confirms actual manufacturing control; exposes trading companies renting facilities |
| 3. Regulatory Compliance Audit | Verify: – NMPA Medical Device Registration (Class II/III) – ISO 13485:2016 certificate (with scope covering motorized hospital beds) – CE Technical File (for EU) or FDA Establishment Registration |
• Cross-reference certificates via: – NMPA Database (www.nmpa.gov.cn) – EU EUDAMED – FDA FURLS |
Prevents 92% of customs seizures; avoids $500K+ liability for non-compliant devices |
| 4. Supply Chain Traceability | Require: – Bill of Materials (BOM) with Tier-2 supplier details – Motor/battery certification (UL 60601-1, IEC 60601-2-52) – 3rd-party test reports (SGS/BV) for load testing (≥250kg) |
• Trace critical components to actual factories (not trading hubs like Yiwu) • Validate battery safety tests (IEC 62133) |
Blocks counterfeit batteries/motors – #1 cause of field failures |
| 5. Transactional Proof | Insist on: – Direct payment to factory’s corporate bank account – Packing list signed by factory QA manager – Container loading video with factory signage |
• Reject payments to personal/3rd-party accounts • Verify SWIFT code matches business license |
Prevents payment diversion; confirms FOB origin |
TRADING COMPANY VS. FACTORY: 4 KEY DIFFERENTIATORS
Trading companies increase costs by 18-35% and obscure quality accountability (2025 SourcifyChina Data)
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Verification Tactic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Assets | • Owns land/building (check property deeds) • Machine depreciation visible in financials |
• “Factory” is a rented showroom • No fixed asset line item in financials |
Demand Property Ownership Certificate (不动产权证书) – trading companies cannot produce this |
| Technical Control | • Engineers on-site modify CAD files • In-house R&D lab (e.g., for pressure sore testing) |
• Outsourced engineering • “Customization” = minor cosmetic changes |
Request design change logs for a specific bed model – factories show version history |
| Pricing Structure | • Quotes raw material + labor + overhead • MOQ based on production line capacity |
• Fixed per-unit price (no cost breakdown) • MOQ = container load (not production batch) |
Require itemized cost breakdown – trading companies refuse or provide generic templates |
| Quality Ownership | • Conducts in-process inspections (IPI) • Holds final QA authority |
• Relies on 3rd-party inspections • “Factory QA” is their staff |
Audit non-conformance reports (NCRs) – factories show internal NCRs; traders show inspection certificates only |
RED FLAGS: 5 DEALBREAKERS TO TERMINATE ENGAGEMENT
These indicate high risk of fraud, safety failures, or supply chain collapse
| Red Flag | Why It Matters | Action |
|---|---|---|
| “We’re the factory – our Alibaba store is Gold Supplier!” | 73% of “verified” Gold Suppliers are trading companies (Alibaba 2025). Gold status ≠ manufacturing capability. | Terminate: Demand physical factory address not listed on Alibaba. Verify via satellite imagery (Google Earth Pro). |
| Refusal to share business license scope | Legitimate factories proudly display medical device manufacturing资质. Omission = no NMPA registration. | Terminate: Without NMPA Class II registration, products are illegal in China/EU/US. |
| Quotation includes “FOB Shanghai” but factory is in Shenzhen | Logistics mismatch = trading company layer. Actual factory may lack export license. | Verify: Cross-check business license address with port of loading. Mismatch = trading markup. |
| Battery/motor specs lack UL/IEC certification numbers | Non-certified components cause fire risks (12% of 2025 hospital bed recalls). | Terminate: Require scanned certificates with visible test lab seals. No exceptions. |
| Contract lists “Shenzhen Office” as seller | Legal entity ≠ manufacturing entity. Liability falls on your organization if devices fail. | Insist: Contract must name actual factory as seller with NMPA registration number. |
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATIONS
- Prioritize NMPA Registration: Suppliers without it cannot legally manufacture medical beds in China – this invalidates all other credentials.
- Conduct Unannounced Audits: 68% of failed quality checks occur during scheduled audits (2025 data). Use SourcifyChina’s surprise audit service.
- Demand Component Traceability: Smart beds require 200+ components. Require blockchain-tracked BOMs (e.g., VeChain) for motors/batteries.
- Avoid “One-Stop” Suppliers: Factories excelling in smart beds rarely produce IV poles or stretchers – specialization = quality focus.
“In medical devices, supplier verification isn’t procurement – it’s risk management. A single defective bed can trigger $2M+ in liability claims. Verify like lives depend on it – because they do.”
— SourcifyChina Quality Assurance Directive, 2026
SOURCIFYCHINA CONFIDENTIAL | Prepared for Verified Procurement Executives Only
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Database (n=1,247 suppliers), NMPA Recall Reports, EU Safety Gate Alerts
Next Step: Request our Smart Hospital Bed Supplier Scorecard (customized for your volume/regional requirements) at [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing Insight: Smart Hospital Beds in China
The global demand for smart hospital beds is accelerating, driven by advancements in healthcare automation, aging populations, and digital patient monitoring. As procurement professionals seek reliable, scalable, and compliant supply chains, sourcing from China remains a cost-effective and technologically competitive option. However, the complexity of identifying trustworthy suppliers—amidst quality inconsistencies, compliance risks, and communication barriers—poses a significant challenge.
Why Time-to-Market Starts with the Right Supplier List
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for China Smart Hospital Bed Wholesalers is engineered to eliminate the guesswork and reduce supplier qualification timelines by up to 70%. Our list features pre-vetted manufacturers and distributors who have undergone rigorous due diligence, including:
- On-site facility audits
- ISO 13485 and CE compliance verification
- Production capacity and export history validation
- English-speaking operations teams
- Minimum 3-year track record with zero major compliance incidents
Comparative Advantage: SourcifyChina Pro List vs. Traditional Sourcing
| Criteria | Traditional Sourcing | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting Time | 4–8 weeks | < 72 hours |
| Risk of Non-Compliance | High (unverified claims) | Low (audited documentation) |
| Language & Communication Barriers | Common | Pre-screened for English fluency |
| MOQ Flexibility | Variable, often high | Negotiated access to medium-volume tiers |
| Lead Time Accuracy | Frequent delays | Historically reliable (92% on-time delivery) |
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Procurement Cycle
Every week spent qualifying suppliers delays innovation deployment and increases operational costs. With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, procurement teams gain immediate access to high-integrity smart hospital bed suppliers—backed by data, due diligence, and regional expertise.
Take the next step with confidence:
✅ Reduce RFP cycles
✅ Mitigate supply chain risk
✅ Secure competitive pricing from pre-qualified partners
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team Today
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
One inquiry. Verified suppliers. Faster procurement outcomes.
SourcifyChina — Your Trusted Partner in Precision Sourcing Across China’s Medical Technology Supply Chain.
Delivering Verified. Delivering Value.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.