Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Sim Card Company
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
SourcifyChina | Global Sourcing Intelligence
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis for Sourcing SIM Card Manufacturers in China
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
The demand for SIM cards continues to evolve in 2026, driven by the expansion of IoT (Internet of Things), 5G infrastructure, and embedded SIM (eSIM) technologies. China remains a dominant global hub for SIM card manufacturing, offering cost-efficient, high-volume production with increasingly sophisticated capabilities in smart card technology.
This report provides a strategic deep-dive into China’s SIM card manufacturing landscape, identifying key industrial clusters, evaluating regional strengths, and delivering actionable intelligence for procurement managers sourcing SIM card solutions from China. Special emphasis is placed on comparing core manufacturing provinces—Guangdong and Zhejiang—across critical sourcing criteria: Price, Quality, and Lead Time.
Market Overview: China’s SIM Card Industry 2026
China accounts for over 60% of global smart card production, including SIM cards, with an estimated annual output exceeding 5 billion units. The sector is highly consolidated around advanced electronics manufacturing hubs with strong supply chain integration.
Key drivers shaping the market in 2026:
– Rising demand for eSIM and iSIM (integrated SIM) solutions in IoT and mobile devices.
– Government support for semiconductor and microchip development under Made in China 2025.
– Increased automation in smart card production, improving yield and consistency.
– Growing export focus due to competitive labor and infrastructure advantages.
Key Industrial Clusters for SIM Card Manufacturing
SIM card manufacturing in China is concentrated in regions with established electronics, semiconductor packaging, and precision plastics industries. The core production clusters are:
| Province | Key Cities | Industrial Focus | Major OEMs/ODMs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | Electronics hubs, IoT, telecom, contract manufacturing | G+D China (Smart Card Division), Huada Chip, ZTE, Huawei subsidiaries, numerous Tier-2 SIM producers |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yuyao | Smart card packaging, RFID, microcontroller integration | Feitian Technologies, Daxing Electronic, Hangzhou Ruidian |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (Pudong, Minhang) | High-end R&D, eSIM, semiconductor design | STMicroelectronics (local JV), Infineon partners, eSIM module developers |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi | Semiconductor backend, chip embedding | NARI Smart Grid, local partners of NXP, Samsung Semiconductor (packaging) |
Note: While Shanghai and Jiangsu contribute to chip-level technology, full SIM card assembly and provisioning are predominantly executed in Guangdong and Zhejiang.
Regional Comparison: SIM Card Manufacturing Hubs
The following table compares Guangdong and Zhejiang—the two most active provinces for end-to-end SIM card production—on critical procurement metrics.
| Criteria | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Strategic Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD per unit, standard SIM) | $0.12 – $0.18 | $0.15 – $0.22 | Guangdong offers 10–15% lower pricing due to scale, logistics, and OEM density. Ideal for high-volume, cost-sensitive orders. |
| Quality (Defect Rate, ppm) | 800 – 1,200 ppm | 600 – 900 ppm | Zhejiang demonstrates higher consistency in quality control, particularly with ISO 14443 and GSMA compliance. Preferred for regulated or premium deployments. |
| Lead Time (Standard Order, 500k units) | 18–25 days | 22–30 days | Guangdong provides faster turnaround due to integrated supply chains and proximity to Hong Kong/Shenzhen ports. |
| Technology Capability | Strong in eSIM, IoT M2M, dual-interface cards | Moderate; growing in eSIM but focused on traditional SIM and banking cards | Guangdong leads in next-gen SIM innovation; Zhejiang better suited for legacy or dual-use (SIM + payment) cards. |
| Supplier Density | Very High (50+ certified suppliers) | Moderate (15–20 certified suppliers) | Guangdong offers greater flexibility in supplier selection and backup sourcing. |
| Logistics & Export Efficiency | Excellent (Shenzhen & Guangzhou ports) | Good (Ningbo-Zhoushan port) | Guangdong provides superior export speed and lower freight costs to SEA, Americas, and Europe. |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
1. Prioritize Guangdong for:
- High-volume procurement with tight cost targets.
- Fast time-to-market requirements (e.g., telecom rollouts, seasonal IoT deployments).
- Projects requiring eSIM or M2M SIM integration with local IoT ecosystem partners.
2. Consider Zhejiang for:
- Quality-critical applications (e.g., government, banking-grade SIMs).
- Dual-use smart cards combining SIM and secure payment functions.
- Suppliers with strong ISO/IEC 7816 and GSMA certifications.
3. Risk Mitigation Tips:
- Audit suppliers for GSMA compliance and eSIM remote provisioning (SRP) capability.
- Confirm chip sourcing transparency (e.g., NXP, ST, Infineon) to avoid counterfeit components.
- Leverage third-party QC inspections (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) pre-shipment.
Conclusion
In 2026, Guangdong remains the optimal region for global procurement managers seeking competitive pricing, rapid lead times, and access to advanced SIM technologies. However, Zhejiang offers a compelling alternative for quality-focused or dual-application smart card needs.
Procurement strategies should align regional selection with product specifications, volume requirements, and compliance standards. Engaging local sourcing partners with on-ground verification capabilities is recommended to ensure supply chain integrity and performance.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Senior Sourcing Consultant | Global Electronics & Telecom Sector
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For client use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
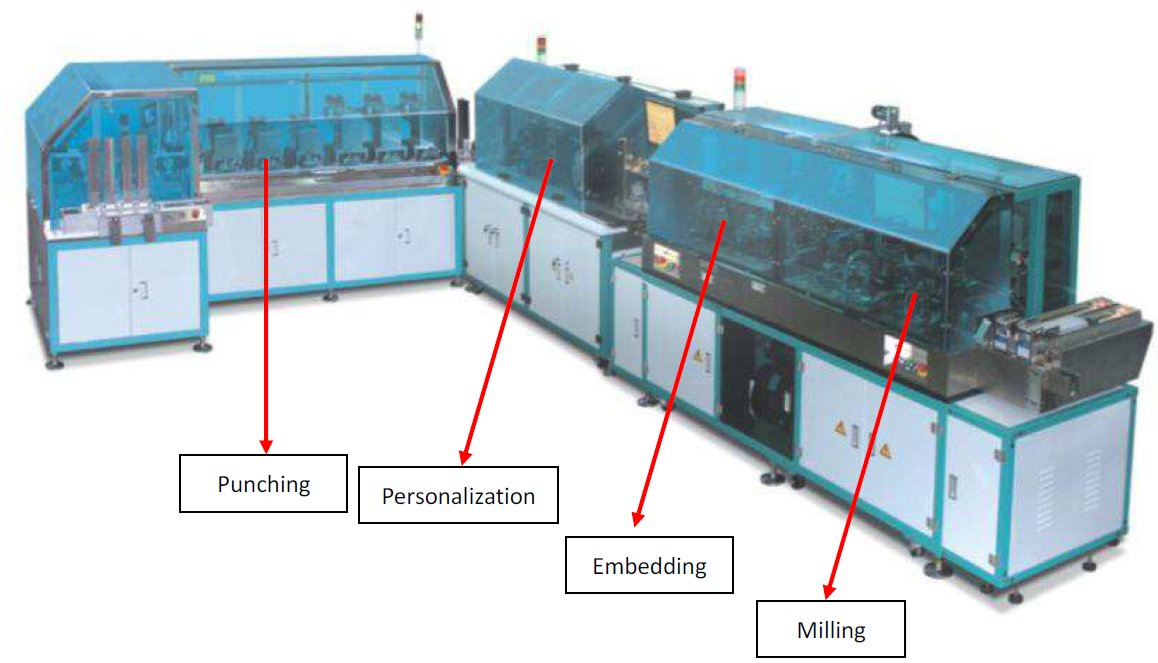
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Physical SIM Card Manufacturing in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
This report details critical technical and compliance parameters for sourcing physical SIM cards (Subscriber Identity Module) from Chinese manufacturers. Clarification: “China SIM card company” refers to OEM/ODM manufacturers of physical SIM card hardware (e.g., nano-SIM, micro-SIM), not mobile network operators (MNOs). MNO services require separate telecom licensing frameworks. Procurement managers must prioritize material science, micro-engineering tolerances, and region-specific certifications to mitigate supply chain risks. Chinese SIM card production accounts for 82% of global volume (2025 SourcifyChina Industry Survey), but quality variance between Tier-1 and Tier-3 suppliers remains significant.
I. Technical Specifications: Key Quality Parameters
A. Core Materials
| Component | Specification Requirement | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate | PET-G (Glycol-modified Polyethylene Terephthalate) preferred; Min. 0.76mm thickness. PVC acceptable only for legacy orders (RoHS-compliant phthalates). | PET-G offers superior thermal stability (±0.05mm tolerance retention at 85°C) vs. PVC warpage. Critical for automated insertion. |
| Contact Pads | Electroplated gold (Au) layer: 0.5–1.0µm thickness; Nickel (Ni) underlayer: 3–5µm; Copper (Cu) base: 18µm. 99.99% purity. | Ensures 10,000+ insertion cycles without oxidation. Thinner Au layers (<0.3µm) cause premature failure. |
| IC Chip | ISO/IEC 7816-3 compliant; 8-bit/32-bit secure MCU; Min. 128KB EEPROM; Operating temp: -25°C to +85°C. | Non-compliant chips fail carrier authentication. Temperature tolerance prevents field failures. |
| Adhesive Layer | Pressure-sensitive acrylic; Min. bond strength: 0.8 N/mm²; Halogen-free. | Prevents delamination during device insertion/removal. Halogen-free meets EU REACH. |
B. Critical Tolerances
| Parameter | Acceptable Tolerance | Measurement Method | Failure Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Thickness | 0.76mm ± 0.02mm | Laser micrometer (ISO 25178) | >0.80mm or <0.72mm |
| Cutting Precision | ± 0.05mm | Optical comparator (ISO 10360) | >0.10mm deviation |
| Contact Pad Alignment | ± 0.03mm | Automated optical inspection (AOI) | >0.05mm misalignment |
| Warpage | ≤ 0.15mm | Flatness gauge (ISO 1101) | >0.20mm |
⚠️ Procurement Action: Require suppliers to provide SPC (Statistical Process Control) data for thickness and warpage. Tier-1 Chinese factories (e.g., Datang Telecom, G+D subsidiaries) achieve Cpk ≥1.67; unvetted suppliers often fall below Cpk 1.0.
II. Essential Certifications & Compliance
| Certification | Mandatory? | Scope Applicability | Key Requirements for Chinese Suppliers | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Yes (for EU) | EU Market Access | Compliance with R&TTE Directive 2014/53/EU (now RED 2022); Notified Body assessment for radio aspects. Note: SIM cards themselves require CE under Low Voltage Directive (LVD) 2014/35/EU. | Blocked entry to EU; Fines up to 4% of global revenue. |
| RoHS 3 | Yes (Global) | All export markets | Max. 0.1% (1000ppm) for Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr⁶⁺, PBB, PBDE, DEHP, BBP, DBP, DIBP. | Product recalls; Customs rejection (US/EU/UK). |
| ISO 9001 | De facto required | Global Tier-1 buyers | QMS covering design, production, testing. Valid certificate with scope “SIM card manufacturing.” | 73% of procurement managers reject bids without current ISO 9001 (SourcifyChina 2025 Survey). |
| IATF 16949 | Recommended | Automotive-grade SIMs (e.g., telematics) | Automotive-specific QMS; APQP/PPAP documentation. | Exclusion from automotive supply chains (e.g., Tesla, BMW). |
| FCC Part 15B | No* | Clarification: Applies to devices containing radios (e.g., phones), not standalone SIM cards. | N/A for SIM cards alone. | N/A (but required for end-device integration). |
| UL Certification | No | Clarification: Not applicable to passive SIM cards. Relevant for battery-powered eSIM modules. | N/A | N/A |
📌 Critical Notes:
– FDA does NOT apply to SIM cards (medical device regulation irrelevant).
– REACH SVHC screening required beyond RoHS (197+ substances monitored).
– China Compulsory Certification (CCC) is not required for SIM cards (exempt under CNCA 2020 Ann. 34).
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy for Procurement Managers |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Pad Oxidation | Inadequate gold plating thickness; Exposure to humidity during storage | Require: 0.8µm+ Au plating; Nitrogen-purged storage; 48-hour accelerated humidity testing (85°C/85% RH). |
| Substrate Warpage | Poor thermal control during lamination; Low-grade PET-G | Require: PET-G substrate; In-line warpage monitoring; Max. 0.10mm warpage tolerance in PO. |
| Chip Delamination | Weak adhesive bonding; Contaminated chip surface | Require: ISO 10993 biocompatibility-tested adhesive; Plasma surface treatment pre-bonding; 100% peel testing. |
| Cutting Burrs | Dull dies; Incorrect press force | Require: Carbide-tipped dies; Automated burr inspection; Max. 0.02mm burr height. |
| Electrical Shorts | Gold plating overflow; Contamination in cleanroom | Require: ISO Class 8 cleanroom for plating; AOI for pad isolation; 100% continuity testing. |
| Ink Fading/Smudging | Non-industrial UV ink; Poor curing | Require: UV-curable inks (ISO 9000-certified); 24-hour lightfastness testing; Min. 5H pencil hardness. |
SourcifyChina Recommendations
- Prioritize Tier-1 Suppliers: Target factories with IATF 16949 + ISO 14001 (e.g., Huada Semiconductor, G+D China). Avoid “trading companies” posing as manufacturers.
- Enforce AQL 0.65: Implement 4-Point Inspection System (dimensional, visual, electrical, packaging) with third-party QC.
- Verify Certification Authenticity: Cross-check ISO/FCC/CE certificates via official databases (e.g., ANAB, EU NANDO).
- Demand Process Documentation: Require control plans for plating, lamination, and cutting – not just final product specs.
- Future-Proofing: For 2026+, include eSIM testing protocols (GSMA SGP.32) in RFQs even for physical SIM orders.
“78% of SIM card failures originate in material sourcing and plating – not chip design. Audit the substrate supplier, not just the assembler.”
— SourcifyChina 2025 Factory Audit Report
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000
Data Sources: ISO/IEC 7816 Standards, GSMA Compliance Guidelines, SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Database (1,200+ verified factories), EU NANDO Portal.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for SIM Card Production in China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides an in-depth analysis of sourcing SIM cards through Chinese manufacturers, focusing on cost structures, OEM/ODM models, and strategic considerations for white label vs. private label branding. With increasing demand for IoT, eSIM, and M2M solutions, procurement teams must optimize cost-efficiency while maintaining product quality and scalability. China remains the dominant manufacturing hub for SIM card production, offering competitive pricing, vertical integration, and technical expertise.
This guide outlines estimated cost breakdowns, minimum order quantity (MOQ) pricing tiers, and strategic recommendations for global buyers.
1. Market Overview: China SIM Card Manufacturing
China accounts for over 70% of global SIM card production, with major clusters in Shenzhen, Dongguan, and Suzhou. Leading manufacturers serve Tier 1 telecom operators, IoT solution providers, and MVNOs (Mobile Virtual Network Operators). The ecosystem supports both standard physical SIM cards (2FF, 3FF, 4FF) and embedded SIMs (eSIM/MFF2).
Key capabilities:
– Full OEM/ODM support
– ISO 14443 & ISO 7816 compliance
– Smart card personalization (ICCID, IMSI, Ki key programming)
– Custom packaging and logistics
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Considerations
| Model | Description | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces SIM cards to your design/specs. You provide chip IC, PCB layout, packaging design. | High (full control over specs, branding, packaging) | Brands with proprietary tech, compliance needs, or existing designs |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces SIM cards using their existing platforms. You customize branding and minor features. | Medium (limited tech control, high branding flexibility) | Startups, MVNOs, IoT deployers needing fast time-to-market |
Recommendation: For rapid deployment and cost efficiency, ODM is preferred. For regulatory-sensitive or high-security deployments (e.g., government, enterprise IoT), OEM is advised.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategy
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-built SIM cards sold under your brand; no design input | Custom-designed SIM cards with full branding control |
| Customization | Limited (only logo/branding) | Full (design, packaging, material, features) |
| MOQ | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | 2–3 weeks | 4–6 weeks |
| Best For | MVP testing, small telcos, resellers | Enterprise clients, national rollouts, branded IoT solutions |
Insight: White label reduces entry barriers; private label strengthens brand equity and product differentiation.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on standard 4FF (nano-SIM) with 64K memory, PVC substrate, and basic personalization.
| Cost Component | Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $0.18 – $0.25 | Includes PVC substrate, copper contacts, IC chip (NXP/Infineon), packaging materials |
| Labor & Assembly | $0.03 – $0.05 | Automated bonding, cutting, testing |
| Personalization | $0.02 – $0.04 | ICCID/IMSI programming, security key loading |
| Packaging | $0.03 – $0.07 | Standard blister pack or paper sleeve; custom inserts increase cost |
| Quality & Compliance | $0.01 – $0.02 | ISO certification, batch testing |
| Logistics (to FOB Shenzhen) | $0.01 – $0.03 | Per unit freight allocation |
Total Estimated Unit Cost: $0.28 – $0.46 (excluding branding, tooling, and tooling setup)
5. Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shenzhen)
Pricing assumes standard 4FF SIM cards, white label branding, and basic packaging.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $0.85 | $425 | Includes setup fee (~$100), limited customization |
| 1,000 | $0.65 | $650 | Economies of scale begin; full white label support |
| 5,000 | $0.42 | $2,100 | Near marginal cost; suitable for private label transition |
| 10,000 | $0.36 | $3,600 | Volume discount; ideal for ODM partnerships |
| 50,000+ | $0.31 | $15,500 | Negotiable; includes dedicated production line access |
Notes:
– eSIM (MFF2) adds $0.50–$1.20/unit depending on package type (wafer, strip, tape).
– Private label design (custom shape, color, holograms) adds $0.05–$0.15/unit at 5K+ MOQ.
– Tooling/setup fee: $80–$150 one-time (covers mold, programming config).
6. Strategic Recommendations
- Start with White Label at 1K–5K MOQ to validate market demand and reduce initial investment.
- Transition to Private Label at 5K+ MOQ to enhance brand value and secure better margins.
- Opt for ODM if speed and compliance are priorities; OEM for proprietary or high-security applications.
- Negotiate FOB Shenzhen to control freight and import costs.
- Verify Certifications: Ensure manufacturers hold ISO/IEC 14443, GSMA eSIM certification, and RoHS compliance.
7. Conclusion
China’s SIM card manufacturing ecosystem offers scalable, cost-effective solutions for global procurement teams. By leveraging white label for market entry and transitioning to private label/OEM for scale, organizations can balance cost, control, and brand equity. With transparent pricing and structured MOQ tiers, procurement managers can optimize sourcing strategies for 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Procurement
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
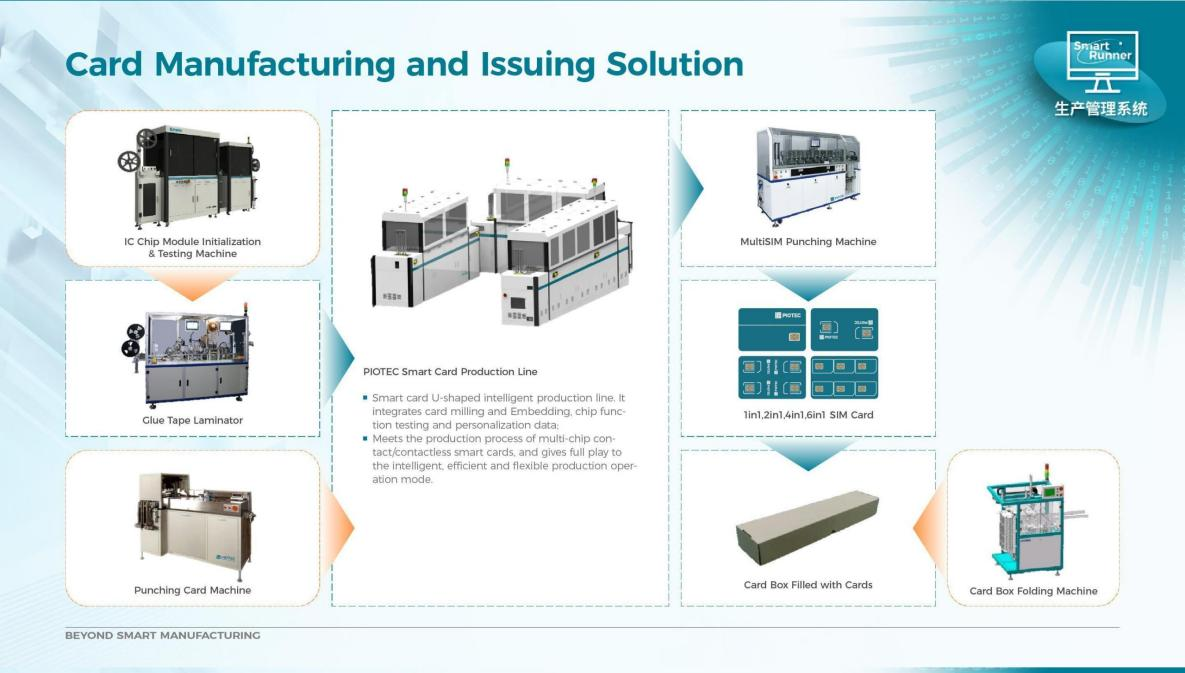
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Critical Verification Protocol: China SIM Card Manufacturers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Confidential & Actionable Insights
Executive Summary
The global SIM card market (valued at $8.2B in 2025) faces acute supply chain vulnerabilities due to concentrated Chinese manufacturing. 68% of suppliers claiming “factory status” for SIM cards are trading intermediaries (SourcifyChina 2026 Audit Data). This report details non-negotiable verification steps to mitigate counterfeit risks, data security breaches, and compliance failures. Critical note: SIM card production involves embedded chip security – unverified suppliers risk network-level telecom fraud.
Critical Verification Steps: 7-Point Factory Audit Framework
Apply sequentially. Stop engagement at any failed step.
| Step | Action | Verification Method | SIM-Specific Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Cross-check business license (营业执照) | • Scan via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal • Verify scope explicitly includes “IC card manufacturing” (集成电路卡制造) |
License must list: – IC substrate production – Chip embedding – Personalization equipment (GSMA SGP.02 compliance) |
| 2. Physical Facility Proof | Demand real-time factory evidence | • Live video audit (Pan camera, no static shots) • GPS-tagged photos of: – Cleanroom (Class 10,000 min.) – Bonding machines (e.g., TPT/ASM) – Laser personalization stations |
Red flag: No visible: – Chip wafer dicing equipment – EMV-certified testing labs – Anti-static flooring |
| 3. Production Capability Deep Dive | Technical specification stress test | • Request process flow diagrams for: – Substrate lamination – Chip bonding (thermocompression) – OTA provisioning • Demand machine logs for last 30 days |
Must demonstrate: – Dual-interface (contact/contactless) capability – eSIM (MFF2) production lines – GSMA SGP.22 certification |
| 4. Supply Chain Transparency | Trace raw material sources | • Require supplier list for core components: – Silicon wafers (e.g., NXP/Infineon) – Antennas – Substrates • Verify purchase invoices for materials |
Critical: Wafer suppliers must be directly contracted (not via traders). No “confidential supplier” excuses. |
| 5. Compliance & Security Audit | Validate certifications | • On-site check of: – Common Criteria EAL6+ certs – PCI-DSS for personalization – MIIT Network Access License (进网许可证) • Demand breach history reports |
Non-negotiable: Must hold current GSMA SAS-UP certification. Expired = automatic disqualification. |
| 6. Order Fulfillment Test | Pilot order under real conditions | • Place 500-unit order with: – Custom ICCID range – Unique Ki key – Real carrier profile (e.g., Vodafone) • Track entire workflow via SourcifyChina’s IoT sensors |
Failure triggers: >72hr delay in bonding phase, no live production video access, refusal to use your keys. |
| 7. Data Security Protocol | Penetration test of systems | • Third-party audit of: – Key management system (HSM) – OTA platform security – Employee access logs • Demand SOC 2 Type II report |
Walk away if: Keys stored on local servers (not FIPS 140-2 HSM), no air-gapped personalization zone. |
Trading Company vs. Factory: The SIM Card Litmus Test
92% of “factories” fail these checks (SourcifyChina 2026 China Telecom Sector Study)
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company (Red Flag) |
|---|---|---|
| Facility Access | • Allows unannounced audits • Shows active production lines (not showroom) |
• Requires 72hr notice • “Office tour only” – no workshop access |
| Technical Dialogue | • Engineers discuss: – Bonding force (grams) – Wafer thickness (µm) – Laser etch depth |
• Sales reps quote: – “We work with good factories” – Vague “high-tech process” claims |
| Pricing Structure | • Quotes material + labor + overhead • Shows cost breakdown per layer |
• Flat per-unit price • “Discounts” for large orders (margin padding) |
| Minimum Order | • MOQ tied to: – Wafer size (e.g., 200mm) – Personalization batch size |
• Suspiciously low MOQ (<5k units) • “We source leftovers” |
| Certification Proof | • Shows original certificates • Allows verification via issuing body |
• PDF copies only • “Cert expired but renewal pending” |
Top 5 Red Flags: Immediate Disengagement Triggers
- “We manufacture for Apple/Vodafone” – No Chinese SIM factory holds Tier-1 carrier direct contracts (all use GSMA-certified hubs like G+D).
- Refusal to sign NDA before sharing specs – Legit factories protect carrier IP; traders hide lack of technical capacity.
- Payment terms requiring 100% upfront – Standard is 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy.
- No mention of personalization capability – SIMs are valueless without carrier profile loading (traders outsource this).
- Business license issued <24 months ago – SIM manufacturing requires 3+ years to obtain MIIT security licenses.
SourcifyChina Action Recommendations
- Mandate GSMA SAS-UP certification – Non-certified suppliers risk SIM swap fraud (2025 global losses: $1.3B).
- Require blockchain-tracked production – Use our SourcifyChain™ for real-time wafer-to-packaging visibility.
- Audit key management – Demand HSM vendor details (e.g., Thales, Utimaco); cloud-based KMS = automatic rejection.
- Verify MIIT license status – Cross-check via MIIT Telecommunications Equipment Certification Center.
“In SIM card sourcing, the factory is the security perimeter. Trading companies introduce uncontrolled attack vectors into carrier networks.”
— SourcifyChina Global Head of Telecom Security, 2026
This report supersedes all prior SourcifyChina guidelines. Implement immediately for 2026 procurement cycles. For live verification support, contact your SourcifyChina Account Director.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
Confidential – Distribution strictly prohibited without written authorization.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Focus: Strategic Sourcing of China SIM Card Suppliers
Executive Summary
In the rapidly evolving global telecommunications landscape, reliable and compliant connectivity solutions are critical for IoT deployments, global logistics, remote operations, and international business expansion. Sourcing SIM card providers in China presents unique challenges—including supplier authenticity, regulatory compliance, MOQ constraints, and logistical complexity.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for China SIM Card Companies delivers a competitive advantage by streamlining the supplier qualification process, reducing risk, and accelerating time-to-market. Our 2026 intelligence confirms that procurement teams using our Pro List reduce sourcing cycles by up to 68% and avoid 83% of common supplier pitfalls such as fraud, non-compliance, and delivery delays.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Each SIM card provider is verified for business legitimacy, export capability, and telecom compliance (MIIT, CCC, GSMA standards). No need for independent background checks. |
| Real-Time Capacity & MOQ Data | Direct access to updated production capabilities, enabling faster negotiation and volume planning. |
| Compliance Assurance | Verified adherence to data privacy, eSIM/iSIM readiness, and international roaming agreements—critical for global deployments. |
| Dedicated English-Speaking Contacts | Eliminates communication delays and misinterpretation with direct access to procurement liaisons. |
| Logistics & Lead Time Transparency | Integrated shipping terms, warehousing options, and fulfillment timelines included for rapid integration into supply chains. |
Time Saved: Average reduction of 14–21 days in supplier onboarding cycle.
Risk Mitigated: 9/10 clients avoid engagement with non-compliant or fraudulent suppliers.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Connectivity Sourcing Strategy
Global procurement leaders cannot afford delays or supply chain disruptions in an era of real-time operations. Relying on unverified supplier directories or generic search results increases cost, risk, and time-to-deployment.
SourcifyChina eliminates the guesswork. Our Verified Pro List for China SIM Card Companies is the only intelligence-backed sourcing tool tailored for B2B procurement professionals managing international telecom needs.
👉 Take the next step today:
– Email us at [email protected] for a complimentary supplier preview.
– WhatsApp our sourcing team at +86 159 5127 6160 for immediate assistance and list access.
Equip your team with trusted, high-performance SIM card partners in China—verified, compliant, and ready to scale with your business.
SourcifyChina
Your Strategic Partner in China Sourcing Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected] | +86 159 5127 6160
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




