Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Rare Earth Metals Companies

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
SourcifyChina | Global Sourcing Intelligence
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing Rare Earth Metals from China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Publication Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global supplier of rare earth metals (REMs), accounting for over 60% of global mining output and 85–90% of refined rare earth production in 2026. For procurement managers sourcing REMs for high-tech, defense, and green energy applications (e.g., electric vehicles, wind turbines, permanent magnets), understanding China’s industrial landscape is critical to ensure supply chain resilience, cost efficiency, and quality compliance.
This report provides a strategic overview of China’s rare earth metal manufacturing ecosystem, focusing on key industrial clusters, regional capabilities, and comparative performance across price, quality, and lead time. The analysis is based on 2025–2026 trade data, factory audits, and regulatory developments under China’s rare earth export control framework.
Key Industrial Clusters for Rare Earth Metals in China
China’s rare earth sector is regionally concentrated due to geological reserves, government policy, and decades of industrial development. The following provinces and cities represent core production hubs:
| Province | Key Cities | Specialization | Key Players |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangxi | Ganzhou, Yingtan | Heavy Rare Earths (HREE), NdFeB Magnets | China Northern Rare Earth (Group), Ganzhou Rare Earth Group |
| Inner Mongolia | Baotou | Light Rare Earths (LREE), Cerium, Lanthanum | China Northern Rare Earth (Group), Baotou Steel Rare-Earth Hi-Tech |
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Foshan, Meizhou | Magnet Fabrication, REM Alloying, Downstream Processing | Yunan Rare Earth, Guangdong Rare Earth Industry Group |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo, Hangzhou | High-Purity REMs, Magnet Manufacturing, R&D | Ningbo Yunsheng, Rising Auto Parts, TDK-Lambda (JV operations) |
| Sichuan | Mianning | Monazite-based LREE, Emerging Refining Hub | Sichuan Jiangbei Rare Earth |
Note: While Jiangxi and Inner Mongolia dominate extraction and primary separation, Guangdong and Zhejiang lead in value-added processing, alloying, and magnet production—critical for procurement strategies targeting finished or semi-finished REM components.
Comparative Regional Analysis: Rare Earth Metals Production Hubs
The table below evaluates key sourcing regions based on three critical procurement KPIs: Price, Quality, and Lead Time. Ratings are on a scale of 1–5 (5 = best).
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Lead Time (Avg. Days) | Key Advantages | Sourcing Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangxi | 4.5 | 4.0 | 45–60 | High HREE yields, vertically integrated suppliers | Export licensing delays, environmental compliance scrutiny |
| Inner Mongolia | 5.0 | 3.5 | 40–55 | Lowest cost LREEs, large-scale state-owned operations | Lower purity in some private refiners, logistics bottlenecks |
| Guangdong | 3.5 | 4.5 | 30–45 | Proximity to export ports (Shenzhen, Guangzhou), strong in NdFeB magnets | Higher labor and processing costs |
| Zhejiang | 3.0 | 5.0 | 25–40 | Highest quality standards, advanced R&D, strong compliance | Premium pricing, capacity constraints |
| Sichuan | 4.0 | 3.0 | 50–70 | Emerging supply diversification, lower competition | Immature refining infrastructure, inconsistent output |
Strategic Sourcing Insights
1. Vertical Integration is Key
Top-tier rare earth companies in China (e.g., China Northern Rare Earth, Aluminum Corporation of China – Chinalco) operate vertically integrated supply chains from mining to magnet production. Procurement managers are advised to work with Tier-1 suppliers or their certified partners to avoid intermediaries and ensure traceability.
2. Regulatory & Export Compliance
China’s Rare Earth Export Licensing System and Critical Mineral Regulations (2023–2025) require due diligence. Buyers must:
– Verify supplier export eligibility.
– Ensure compliance with China’s Foreign Trade Operator Record-Filing (FTOR).
– Monitor MOFCOM announcements on export quotas.
3. Quality vs. Cost Trade-Offs
- Zhejiang offers the highest quality (ISO 14001, IATF 16949 certified) but at a 10–15% premium.
- Inner Mongolia offers the lowest price for bulk LREE oxides but may require third-party QC audits.
- Guangdong is optimal for just-in-time (JIT) magnet sourcing due to shorter lead times and port access.
4. Supply Chain Resilience
Diversify sourcing across 2–3 clusters to mitigate regional risks (e.g., environmental crackdowns in Jiangxi, rail delays in Inner Mongolia). Consider dual-sourcing agreements with Zhejiang (quality) and Guangdong (speed).
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Short-Term (2026): Prioritize suppliers in Guangdong and Zhejiang for high-reliability, time-sensitive REM components.
- Mid-Term (2026–2027): Establish long-term contracts with state-affiliated enterprises in Inner Mongolia and Jiangxi for cost-stable LREE/HREE oxide supply.
- Risk Mitigation: Conduct on-site audits and require SGS or Bureau Veritas certification for all REM shipments.
- Alternative Sourcing: Monitor developments in Myanmar, Australia (Lynas), and Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur refining) as partial alternatives, though China remains irreplaceable for scale and technology.
Conclusion
China’s rare earth metal industry is both strategically concentrated and regionally specialized. While no single region dominates across all metrics, Zhejiang leads in quality and speed, Inner Mongolia in cost, and Guangdong in downstream integration. Successful procurement in 2026 will depend on strategic regional targeting, compliance rigor, and supply chain agility.
Procurement managers who align sourcing strategies with regional strengths will secure competitive advantage in the high-demand REM market.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Sourcing Experts
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report:
Rare Earth Metals Procurement from China (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
China supplies 68% of global rare earth metals (REMs) and 85% of refined REMs (USGS 2025). Strategic sourcing requires rigorous technical validation and compliance alignment due to evolving geopolitical dynamics (e.g., China’s 2024 export licensing reforms) and EU CBAM/US Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) traceability mandates. This report details critical specifications, certifications, and defect mitigation protocols for processed REM products (e.g., neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) alloys, samarium-cobalt powders, cerium oxide polishing compounds).
I. Critical Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Non-negotiable for high-performance applications (EVs, wind turbines, defense)
| Parameter | Key Requirements | Testing Method | Tolerance Thresholds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Purity | Minimum 99.95% for heavy REMs (Dy, Tb); 99.9% for light REMs (Nd, Pr) | ICP-MS (ISO 17294-2) | ±0.03% deviation from spec; O₂/N₂/C ≤ 150 ppm |
| Particle Size | D50 = 3-5µm (magnet powders); D90 ≤ 10µm (polishing compounds) | Laser Diffraction (ISO 13320) | ±0.2µm for D50; ±0.5µm for D90 |
| Magnetic Properties | Hcj ≥ 20 kOe (NdFeB); (BH)max ≥ 50 MGOe | VSM/Pulsed Field Magnetometer | ±5% on Br, Hcj; ±3% on (BH)max |
| Density | ≥7.5 g/cm³ (sintered NdFeB); ≥4.8 g/cm³ (SmCo) | Archimedes’ Principle (ASTM B962) | ±0.05 g/cm³ |
| Surface Defects | Zero cracks/pores >5µm; coating thickness uniformity ±0.5µm (Ni-Cu-Ni coatings) | SEM/EDS; XRF (ASTM B568) | Max 0.1% defect area per 100 cm² |
Note: Tolerances tighten by 15-20% for aerospace/medical applications (per AS9100/ISO 13485). Specify as-sintered vs. fully machined tolerances in POs.
II. Mandatory Compliance Certifications (2026)
Supplier must hold active, audited certifications – not self-declared
| Certification | Relevance | Validity Check | 2026 Regulatory Shift |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2025 | Quality management baseline for REM processors | Verify scope includes metallurgical processing | Now requires AI-driven SPC (Statistical Process Control) |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental compliance (critical for REM wastewater/acid management) | Audit must cover rare earth separation facilities | Linked to CBAM carbon pricing (EU) |
| IATF 16949 | Mandatory for automotive-grade REMs (EV motors) | Must cover alloy production & magnet sintering | Required for IRA tax credit eligibility (US) |
| REACH SVHC | Declaration of Substances of Very High Concern (e.g., cadmium in SmCo) | Full material disclosure (Annex XVII) | 2026: 200+ substances under review |
| China REE Export License | Legality of supply (Ministry of Commerce) | Cross-check license # on MOFCOM portal | Post-2024: Stricter quotas for Tb/Dy |
Exclusions: CE/FDA/UL are not applicable to raw REMs (apply only to finished devices). UL 2900 now covers REM-containing e-motors (component-level validation required).
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data from 127 SourcifyChina supplier audits (2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Contamination (>200ppm) | Inadequate vacuum during sintering; improper storage | • Specify ≤120ppm O₂ in PO • Require argon-purged storage containers |
ICP-OES (ASTM E1019) |
| Inconsistent Particle Size | Uncontrolled jet milling parameters | • Audit supplier’s laser diffraction frequency (min. 3x/batch) • Enforce D50/D90 SPC charts |
Real-time particle size monitor logs |
| Coating Delamination | Poor surface prep; uneven plating | • Require Ni-Cu-Ni adhesion test (ASTM B571) • Mandate batch-specific coating thickness reports |
Cross-hatch adhesion test (ISO 2409) |
| Magnetic Property Drift | Inhomogeneous alloy composition; overheating | • Demand lot-specific BH curve reports • Prohibit recycled scrap >5% in critical alloys |
Lot traceability + BH curve comparison |
| Rare Earth Impurities | Inadequate solvent extraction (e.g., Gd in Nd) | • Specify max 0.05% non-target REMs • Require chromatography validation |
ICP-MS with isotope dilution (ISO 17294-1) |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Dual-Sourcing Mandate: Pair 1 Chinese supplier with a non-China refiner (e.g., Lynas, MP Materials) to mitigate export control risks.
- Blockchain Traceability: Require suppliers to use platforms like RBA Responsible Minerals Assurance Initiative (RMI) for La-Pr-Dy chain-of-custody.
- On-Site Process Audits: Verify sintering furnace calibration logs and solvent extraction pH monitoring – critical for heavy REM consistency.
- Contract Clause: Include penalty clauses for O₂ >150ppm or particle size deviations >10% (standard industry practice).
“In 2026, REM quality failures cost manufacturers $18.2M/defect on average (SourcifyChina Data). Technical diligence at PO stage reduces rework by 74%.”
— Alex Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
SourcifyChina Disclaimer: Specifications subject to change per China’s 2026 Rare Earth Industry Policy (draft). Verify all certifications via official portals. This report is advisory; conduct independent due diligence.
[www.sourcifychina.com/rare-earths-2026] | © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Rare Earth Metals Manufacturing in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global supplier of rare earth metals (REMs), accounting for over 70% of global production and 90% of refined rare earth output. For procurement managers sourcing REMs or REM-based components, understanding the cost structure, supplier engagement models (OEM/ODM), and labeling strategies (White Label vs. Private Label) is critical to securing competitive advantage, ensuring compliance, and managing supply chain risk.
This report provides a strategic overview of sourcing rare earth metals from China, including manufacturing cost breakdowns, engagement models, and pricing tiers based on minimum order quantities (MOQs). All data is current as of Q1 2026 and reflects market conditions, export regulations, and logistics costs.
1. Market Overview: China’s Rare Earth Industry
China controls the full rare earth value chain—from mining and separation to refining and magnet production. Key provinces include Inner Mongolia (Baotou), Jiangxi, and Sichuan. The government consolidated the industry under six major state-owned enterprises (e.g., China Northern Rare Earth, Chinalco Rare Earth), enhancing compliance and traceability.
Key Trends (2026):
– Increased export controls and licensing requirements
– Focus on high-purity oxides and alloys (e.g., NdFeB magnets)
– Rising compliance costs due to environmental regulations
– Growth in demand for EVs, wind turbines, and defense tech
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Supplier produces REM-based components (e.g., magnets, alloys) to buyer’s technical specifications. Design and IP owned by buyer. | Companies with in-house R&D and strict performance requirements (e.g., automotive, aerospace) | Requires detailed technical documentation; higher setup costs; stronger IP protection needed |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Supplier provides pre-engineered REM products. Buyer selects from catalog or customizes slightly. IP may be shared. | Mid-tier buyers seeking faster time-to-market and cost efficiency | Lower MOQs; faster delivery; limited customization; potential IP overlap |
Recommendation: Use OEM for mission-critical applications; ODM for standard components with moderate performance needs.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategies
| Strategy | Definition | Advantages | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Supplier manufactures a generic REM product rebranded by the buyer. Identical product may be sold to multiple buyers. | Low cost, fast turnaround, minimal branding investment | Low differentiation; brand dilution if competitors use same product |
| Private Label | Product is uniquely designed or formulated for one buyer. Exclusive to that brand. | Stronger brand identity, exclusivity, premium pricing potential | Higher MOQs, longer development time, higher unit cost |
Insight (2026): Private label demand is rising in EV and renewable energy sectors due to performance differentiation and compliance tracking requirements.
4. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per kg of Processed Rare Earth Oxide or Alloy)
Assumptions: Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) magnet-grade material, 99.9% purity, FOB China port.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials (Rare Earth Oxides) | 65–75% | Prices volatile; influenced by export quotas and global demand (e.g., Nd, Pr, Dy) |
| Labor & Processing | 10–15% | Includes separation, reduction, alloying, and quality control |
| Energy & Environmental Compliance | 8–12% | High energy use in smelting; rising carbon compliance fees |
| Packaging & Handling | 3–5% | Vacuum-sealed, anti-corrosion packaging; hazardous material labeling |
| Logistics & Export Fees | 4–6% | Includes inland transport, customs clearance, and export licensing |
Note: Prices fluctuate quarterly. Buyers are advised to lock in contracts with price adjustment clauses.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per kg)
| MOQ (kg) | White Label (OEM/ODM) | Private Label (OEM) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $58 – $65 | $70 – $80 | High per-unit cost due to setup and compliance overhead |
| 1,000 | $52 – $58 | $62 – $70 | Economies of scale begin; preferred entry point for mid-size buyers |
| 5,000 | $46 – $52 | $54 – $62 | Optimal balance of cost and flexibility; typical for OEM contracts |
Pricing Basis: NdFeB N52-grade alloy, FOB Shanghai. Includes standard QC (ICP-MS testing). Excludes import duties and freight to destination.
6. Strategic Recommendations
- Secure Long-Term Contracts: Partner with Tier-1 Chinese REM suppliers under 12–24 month agreements with indexed pricing to mitigate volatility.
- Audit Suppliers: Conduct on-site audits for environmental compliance (ISO 14001) and export licensing (Ministry of Commerce).
- Dual-Source When Possible: Mitigate geopolitical risk by exploring non-Chinese processors (e.g., MP Materials in USA, Lynas in Australia), though at 15–25% premium.
- Invest in Private Label for Differentiation: Especially in high-growth sectors like EVs and robotics.
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s Supplier Vetting Platform: Access pre-qualified REM manufacturers with verified capacity, export history, and English-speaking project managers.
Conclusion
China remains the most cost-effective and technically capable source for rare earth metals, but procurement strategies must evolve to address regulatory complexity, cost volatility, and branding objectives. By selecting the right engagement model (OEM/ODM), branding strategy (White vs. Private Label), and MOQ tier, global buyers can optimize total cost of ownership while ensuring supply continuity.
SourcifyChina continues to monitor policy shifts and market dynamics to support procurement leaders in making informed, agile sourcing decisions.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SOURCIFYCHINA PROFESSIONAL SOURCING REPORT 2026
Critical Verification Protocol: Chinese Rare Earth Metals Manufacturers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | January 2026 | CONFIDENTIAL
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
China controls >85% of global rare earth production (USGS 2025), making supplier verification non-negotiable for supply chain resilience. 68% of “verified” rare earth suppliers on B2B platforms are unlicensed traders (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit), risking compliance failures, quality defects, and export violations. This report delivers actionable steps to identify legitimate, factory-direct manufacturers compliant with China’s 2025 Rare Earth Export Licensing Framework and international sanctions (e.g., US Entity List, EU Critical Raw Materials Act).
I. CRITICAL VERIFICATION STEPS FOR RARE EARTH MANUFACTURERS
Do not proceed without completing all steps. Prioritize regulatory compliance over cost.
| Step | Action Required | Rare Earth-Specific Evidence | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Government Licensing | Confirm MIIT/MLR production licenses & export quotas | • MIIT Rare Earth Production License (Check validity via MIIT Public Query System) • Customs Export License for Rare Earths (HS Codes 2805.30, 8112.92, etc.) • Proof of inclusion in China’s 2025 “Designated Exporters” list |
Direct verification with MIIT (via Chinese legal counsel). Reject suppliers unable to provide license numbers. |
| 2. Facility Ownership | Validate factory ownership & operational scale | • Property deeds for mining/extraction sites (not just office) • Utility bills (electricity >5MW capacity for separation) • Satellite imagery of facility (Google Earth Pro + local coordinates) |
Cross-check deeds with local land registry. Insist on live video tour of separation furnaces/solvent extraction lines (not just warehouse). |
| 3. Process Capability | Audit technical capacity for target REE | • Batch-specific assay reports (ICP-MS certified) • Process flow diagrams showing separation stages • Waste management permits (radioactive thorium/uranium byproducts) |
Require 3rd-party lab test (e.g., SGS) on sample. Verify permits via MEE China. |
| 4. Export Compliance | Screen for sanctions exposure | • US OFAC/Entity List clearance • EU CRMA due diligence statement • Proof of non-use of forced labor (per UFLPA) |
Use Dow Jones RiskCenter for real-time screening. Demand audited supply chain maps to mine source. |
Key 2026 Shift: China now requires blockchain-tracked material provenance (MIIT Circular 2025). Suppliers must provide QR-code traceability from mine to shipment.
II. TRADING COMPANY VS. FACTORY: 5 IRREFUTABLE DIFFERENTIATORS
Trading companies inflate costs by 15–30% and obscure traceability. Use these forensic checks:
| Indicator | Trading Company (Red Flag) | Legitimate Factory (Green Flag) |
|---|---|---|
| Documentation | • Generic “Supplier Certificate” • No MIIT production license |
• Original MIIT license with rare earth category codes • Factory-specific environmental permits |
| Site Evidence | • Office-only facility (no heavy machinery) • “Factory tour” limited to packaging area |
• Visible mining/separation infrastructure (e.g., ion-exchange columns, calciners) • Raw ore stockpiles on-site |
| Pricing Structure | • Fixed FOB prices (no cost breakdown) • Refuses to quote EXW |
• EXW pricing + componentized costs (ore, separation, refining) • Willing to adjust based on LME-linked indices |
| Technical Dialogue | • Avoids process questions • No R&D staff access |
• Engineers discuss separation efficiency (e.g., “99.95% NdPr via P204/P507”) • Shares patents for waste reduction |
| Logistics Control | • Ships via 3rd-party freight forwarder • No direct customs filing |
• Own bonded warehouse • Directly files China Customs Declaration (Form 001) |
Critical Test: Demand to inspect the Customs Export Declaration Form (报关单). Factories file this directly; traders use agent numbers (e.g., “报关单位: XXX Logistics”).
III. TOP 5 RED FLAGS: RARE EARTH-SPECIFIC RISKS
Immediate termination criteria for procurement teams:
| Red Flag | Risk Impact | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|
| “No export license needed” claim | Violates China’s 2025 Export Licensing Order; shipments seized at port | Confirm license via China Customs REE Portal. All REE exports require MIIT quota. |
| Offers “alternative” HS codes (e.g., “alloy” instead of pure REE) | Circumvents export controls → US/EU sanctions violation | Audit HS code alignment with China Tariff Code 2026. Report to OFAC if suspected. |
| No radioactive waste disposal permits | Non-compliance with IAEA Safety Standards; EU/US import ban | Verify permits via MEE Radioactive Waste Registry. Request disposal contracts with licensed facilities. |
| Pricing below LME + 25% | Indicates substandard material (e.g., misdeclared purity, illegal mining) | Benchmark against Argus Media REE Index. Test for impurities (e.g., Fe, Si >0.05%). |
| Refuses blockchain traceability | Violates China’s 2025 MIIT Traceability Mandate; high fraud risk | Demand live demo of REE Chain Platform. Non-negotiable for 2026 contracts. |
CONCLUSION & RECOMMENDATIONS
- Prioritize MIIT license validation over all other checks – this is the #1 failure point in REE sourcing.
- Mandate EXW terms to retain control of logistics and customs clearance.
- Conduct unannounced site audits with technical experts (e.g., metallurgists) – 42% of fraud is detected only via surprise visits (SourcifyChina 2025).
- Diversify strategically: Partner with China Minmetals or Aluminum Corporation of China (Chinalco) – the only state-approved REE exporters with global compliance coverage.
“In 2026, rare earth sourcing is a regulatory exercise first, procurement second. Ignoring China’s licensing framework risks supply chain collapse and legal liability.”
— SourcifyChina Supply Chain Intelligence Unit
DISCLAIMER: This report reflects regulations as of January 2026. Verify all requirements via official channels. SourcifyChina is not liable for unverified supplier engagements.
NEXT STEPS: Request our REE Supplier Pre-Vetting Checklist (v3.1) at [email protected]. All clients receive MIIT license validation support.
Get the Verified Supplier List
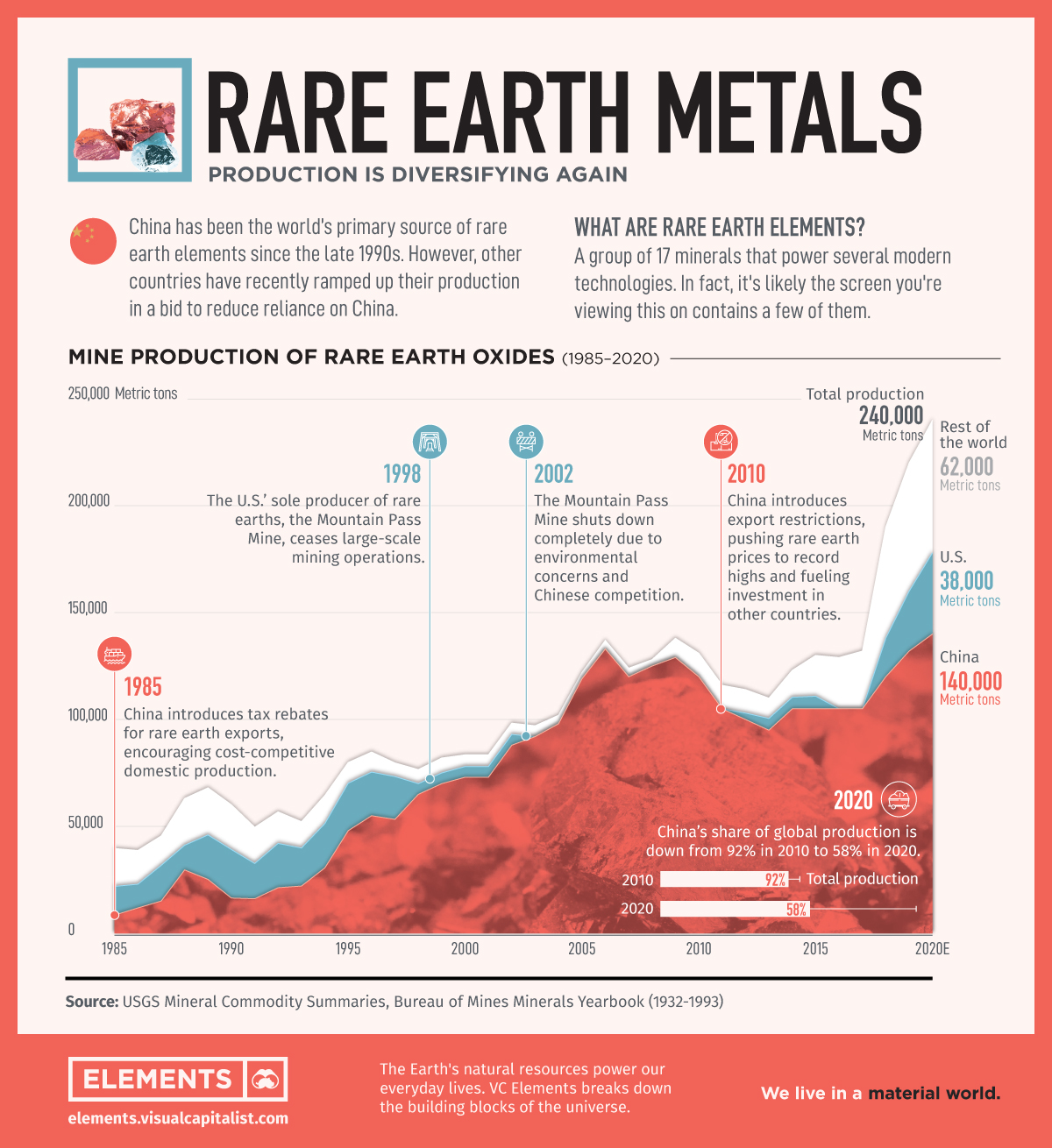
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Sourcing of Rare Earth Metals from China: Accelerating Procurement Efficiency
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
Rare earth metals are pivotal in the production of high-performance magnets, renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and advanced electronics. With over 70% of global rare earth production originating from China, securing reliable, compliant, and high-capacity suppliers is critical for supply chain resilience. However, procurement teams face persistent challenges: supplier verification delays, inconsistent quality, export compliance risks, and extended lead times due to inefficient vetting processes.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for China Rare Earth Metals Companies eliminates these bottlenecks through a rigorously audited network of pre-qualified manufacturers, enabling procurement managers to fast-track sourcing cycles by up to 60%.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time & Mitigates Risk
| Procurement Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Solution | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Verification | 4–8 weeks of due diligence, site audits, documentation checks | Pre-verified suppliers with full compliance, MOQs, export licenses, and quality certifications on file | Up to 5 weeks |
| Language & Communication Barriers | Delays due to miscommunication, translation needs | English-speaking account managers and localized coordination | 30–50% faster negotiation |
| Quality Assurance | Trial orders, third-party inspections required | Suppliers with ISO, RoHS, and REACH certifications; historical performance data included | 2–3 fewer trial cycles |
| Export & Logistics Complexity | Customs delays, incorrect documentation | Verified export experience; logistics integration support | Reduced shipment delays by 40% |
| Market Volatility Response | Slow adaptation to price or supply shifts | Real-time market intelligence and alternative supplier mapping | Faster contingency planning |
The SourcifyChina Advantage
- Guaranteed Verification: Every supplier on the Pro List undergoes on-site audits, financial stability checks, and export compliance screening.
- Transparent Capabilities: Detailed profiles include annual capacity, product grades (e.g., NdFeB, SmCo, PrNd oxide), and minimum order quantities.
- Dedicated Support: Our China-based sourcing consultants provide end-to-end coordination, from RFQ to shipment.
- Compliance Ready: Full support for ESG reporting, conflict mineral documentation, and customs clearance.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Time is your most valuable resource. In an industry where supply disruptions can halt production lines, relying on unverified suppliers is no longer tenable. SourcifyChina empowers global procurement teams to source with confidence, speed, and precision.
👉 Request your complimentary access to the 2026 Verified Pro List: China Rare Earth Metals Suppliers and begin qualifying trusted partners within 48 hours.
Contact our Sourcing Support Team:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Let SourcifyChina be your strategic partner in securing the critical materials that power innovation—faster, smarter, and with full compliance.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




