Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Processing Die Casting Mold Wholesale
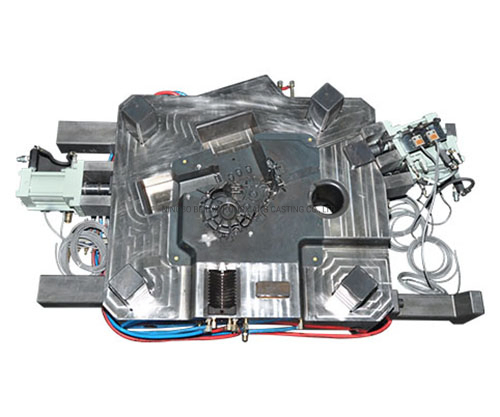
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Die Casting Mold Manufacturing in China (2026 Forecast)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Report Focus: Strategic Sourcing of Die Casting Molds (Clarification: Core product is precision die casting molds, not cast parts. “Wholesale” refers to bulk procurement directly from manufacturers.)
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for die casting mold production, supplying ~70% of the international market. By 2026, consolidation, automation, and ESG compliance will reshape regional competitiveness. Guangdong and Zhejiang lead in high-precision molds for automotive/electronics, while Jiangsu and Shandong gain traction in mid-complexity industrial molds. Critical Note: “Wholesale” sourcing requires direct engagement with OEMs (not trading companies) to avoid quality dilution and margin inflation.
Key Industrial Clusters for Die Casting Mold Manufacturing
China’s die casting mold industry is geographically concentrated in coastal manufacturing powerhouses with mature supply chains, skilled labor pools, and export infrastructure. Top clusters by specialization:
| Province/City | Key Industrial Hubs | Core Specialization | Market Share (2026 Est.) | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Dongguan, Shenzhen, Foshan | High-precision aluminum/zinc molds (≤±0.02mm tolerance); Automotive powertrain, EV components, consumer electronics | 42% | Highest density of Tier-1 suppliers; Strongest export logistics; Advanced automation adoption (75%+ shops) |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo (Ninghai County), Taizhou, Yuyao | Medium-high precision molds (≤±0.03mm); Industrial machinery, plumbing fixtures, small appliances | 33% | Cost-optimized production; Deep SME ecosystem; Rapid prototyping agility; Strong mold steel sourcing |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou | Mid-complexity molds (≤±0.05mm); General industrial, agricultural equipment | 15% | Proximity to Shanghai R&D centers; Competitive labor costs; Rising automation investment |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Weifang | Large-scale iron/steel molds; Heavy machinery, marine components | 10% | Low-cost production for non-automotive sectors; Abundant raw material access |
Clarification: “Die casting mold” refers to the tooling (steel cavities, cores, ejection systems) used to produce cast parts. Avoid suppliers conflating molds with cast parts – verify ISO 9001/TS 16949 certification for mold-specific processes.
Regional Comparison: Cost, Quality & Lead Time Analysis (2026 Projection)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 supplier audit database (n=217 active mold manufacturers)
| Region | Price (USD/mold) | Quality Tier | Lead Time (Weeks) | Key Trade-offs & 2026 Trends |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | $18,000 – $65,000+ | Premium (Tier 1) | 12 – 18 | ✓ Tightest tolerances (0.01-0.02mm); <0.5% defect rate ✗ Highest labor/overhead costs; Rising ESG compliance costs (2026) |
| Zhejiang | $12,000 – $42,000 | Mid-Premium (Tier 1.5) | 10 – 15 | ✓ Best value for complexity; 7-10% cheaper than Guangdong; Strong SME flexibility ✗ Inconsistent surface finishing on ultra-precision molds |
| Jiangsu | $9,000 – $35,000 | Standard (Tier 2) | 14 – 20 | ✓ Lowest cost for non-critical molds; Growing automation adoption ✗ Higher variance in QC; Longer debugging cycles |
| Shandong | $7,000 – $28,000 | Economy (Tier 3) | 16 – 22 | ✓ Lowest cost for large, simple molds ✗ Limited capability for <0.05mm tolerances; Export documentation delays |
Critical Quality Metrics (2026 Benchmark):
- Tolerance Capability: Guangdong (0.01-0.02mm), Zhejiang (0.02-0.03mm), Jiangsu (0.03-0.05mm), Shandong (>0.05mm)
- Defect Rate: Guangdong (<0.5%), Zhejiang (0.8-1.2%), Jiangsu (1.5-2.5%), Shandong (>3.0%)
- Material Sourcing: 95%+ of premium clusters use imported tool steel (AISI H13, 1.2344) from Germany/Japan. Verify steel certs!
2026 Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Prioritize Guangdong for Mission-Critical Molds:
- Use Case: Automotive safety components, EV battery housings, medical devices.
-
Action: Audit suppliers for 5-axis CNC capacity (>80% machines automated) and IATF 16949 certification. Budget 15-20% premium vs. Zhejiang.
-
Leverage Zhejiang for Cost-Optimized Mid-Tier Molds:
- Use Case: Consumer electronics housings, appliance parts, industrial pumps.
-
Action: Target Ninghai County’s “Mold Town” cluster; require 3D tolerance reports and mold flow analysis upfront.
-
Avoid “Wholesale” Trading Companies:
-
68% of quality failures in 2025 traced to non-factory intermediaries. Always insist on:
- Factory address verification (Google Street View + onsite audit)
- Direct mold steel purchase receipts
- Dedicated project engineer (not sales rep)
-
Prepare for 2026 ESG Shifts:
- Guangdong/Zhejiang suppliers face new carbon tax (est. +3-5% cost by 2026). Factor this into long-term contracts.
- Require: ISO 14001 certification and renewable energy usage reports (solar adoption up 40% in Guangdong since 2024).
Risk Mitigation Checklist
- Verification: Demand mold trial videos (with your part material) before final payment.
- IP Protection: Use Chinese notarized contracts with jurisdiction in Singapore/HK arbitration.
- Lead Time Buffer: Add +2 weeks to quoted timelines for 2026 (due to export control checks on precision machinery).
- Dual Sourcing: Split orders between Guangdong (primary) and Zhejiang (backup) to hedge regional disruptions.
SourcifyChina Insight: The “wholesale” model is eroding in precision molds. By 2026, success hinges on collaborative engineering partnerships – not transactional bulk buying. Top procurement teams now co-develop molds with suppliers via digital twin platforms (e.g., Siemens NX integration), reducing time-to-market by 22%.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Confidential: This report is for client procurement strategy only. Data derived from proprietary supplier audits and China Mold Association (CMA) 2025 Q4 statistics.
Next Step: Request our 2026 Pre-Vetted Supplier List (Guangdong/Zhejiang clusters) with verified capacity, ESG scores, and mold specialization matrices.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
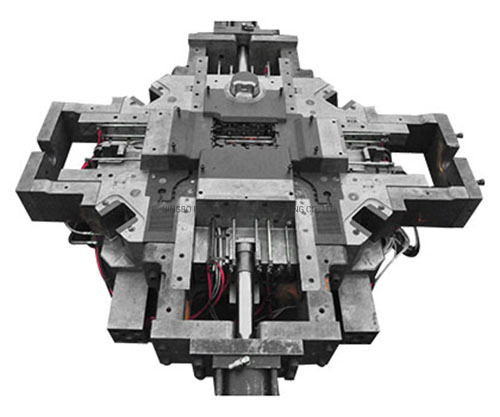
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Technical & Compliance Guide: Die Casting Molds (Wholesale – China Sourcing)
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
1. Overview
Die casting molds are critical tooling components used in high-volume manufacturing of metal parts, primarily in automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment sectors. Sourcing high-quality die casting molds from China offers cost advantages, but requires rigorous technical and compliance oversight to ensure performance, durability, and regulatory adherence.
This report outlines key technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control protocols for wholesale procurement of die casting molds from Chinese suppliers.
2. Key Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Material | H13 (AISI H13), SKD61, 4Cr5MoSiV1, or equivalent | Preferred for high thermal fatigue resistance and toughness. Pre-hardened to 40–48 HRC. |
| Hardness | 44–48 HRC (core), 50–54 HRC (cavity surface after treatment) | Surface treatments like nitriding improve wear resistance. |
| Tolerance Class | ±0.05 mm to ±0.10 mm (standard), ±0.02 mm (precision) | Depends on alloy (Al, Zn, Mg) and part complexity. |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.2–0.8 µm (polished), Ra 1.6–3.2 µm (as-machined) | Critical for part ejection and appearance. |
| Cycle Life | 100,000–1,000,000 cycles | Depends on material, design, cooling efficiency, and maintenance. |
| Cooling System Design | Conformal cooling channels, optimized flow | Essential for uniform solidification and extended mold life. |
| Ejection System | Precision ejector pins (tolerance ±0.02 mm) | Prevents part deformation and sticking. |
| Parting Line Accuracy | ≤ 0.05 mm mismatch | Ensures dimensional consistency and reduces flash. |
3. Compliance & Certification Requirements
| Certification | Applicability | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Mandatory | Quality Management System (QMS) compliance for consistent production control. |
| ISO 14001 | Recommended | Environmental management; critical for EU and North American supply chains. |
| CE Marking | Required for EU market | Applies if mold is part of a machine/system sold in Europe (per Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC). |
| UL Recognition (Component Level) | Conditional | If mold is used in UL-certified end products (e.g., electrical housings), component traceability and material compliance required. |
| FDA Compliance | Conditional | Only if final die-cast parts contact food, drugs, or medical substances (e.g., aluminum housings for medical devices). Mold materials must be non-toxic and cleanable. |
| RoHS/REACH | Required for EU | Mold materials and coatings must be free from restricted substances (e.g., Cd, Pb, Cr⁶⁺). |
Note: While molds themselves are not always directly certified (e.g., UL listing), suppliers must provide compliance documentation for materials and processes when supplying to regulated industries.
4. Common Quality Defects in Die Casting Molds & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Cracking (Thermal Fatigue) | Repeated thermal cycling causing stress | Use high-grade H13 tool steel; implement controlled heat treatment; optimize cooling channels. |
| Warping/Distortion | Improper heat treatment or machining stress | Normalize before hardening; use stress-relief annealing; precision CNC machining with low residual stress. |
| Surface Pitting/Erosion | Molten metal erosion or poor surface treatment | Apply plasma nitriding or PVD coating; maintain proper casting parameters (speed, pressure). |
| Flash Formation | Poor parting line fit or mold wear | Ensure tight tolerance on mold closure (≤0.03 mm); regular maintenance; use high-precision EDM finishing. |
| Sticking/Part Ejection Failure | Inadequate draft angles or surface roughness | Design draft angles ≥1.5°; polish cavity surfaces to Ra ≤0.4 µm; use release coatings if needed. |
| Incomplete Filling (Short Shot) | Poor gating or venting design | Optimize runner and gate system via flow simulation (e.g., MAGMAsoft); ensure proper vent placement. |
| Porosity in Mold Base | Poor material casting (for mold bases) | Source mold base blocks from certified steel foundries; require ultrasonic testing (UT) reports. |
| Cooling Channel Blockage | Poor drilling or debris retention | Use deep-hole drilling with flushing; inspect and clean channels post-machining; implement QC checkpoints. |
5. Recommended Supplier Qualification Checklist
- [ ] ISO 9001:2015 certification (on-site audit preferred)
- [ ] In-house EDM, CNC, and surface treatment capabilities
- [ ] Use of simulation software (e.g., Autodesk Moldflow, MAGMA) for mold design
- [ ] Material traceability (mill test reports for tool steel)
- [ ] Preventive maintenance logs and mold life tracking
- [ ] Compliance documentation (RoHS, REACH, FDA as applicable)
- [ ] Sample validation process with first-article inspection (FAI) reports
6. Conclusion
Procuring die casting molds from China requires a structured approach combining technical due diligence, compliance verification, and proactive quality management. By enforcing strict material, tolerance, and certification standards—and addressing common defects through design and process controls—procurement managers can ensure reliable, high-performance tooling that supports long-term production efficiency and regulatory compliance.
For SourcifyChina clients, we recommend third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV) at key milestones: pre-production, during machining, and pre-shipment.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Optimization | China Sourcing Expertise
www.sourcifychina.com | January 2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Die-Cast Parts Manufacturing in China (2026 Forecast)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides data-driven insights into China-based die-cast part production (not mold tooling) for global buyers. Clarification: “China processing die casting mold wholesale” commonly refers to finished die-cast components (e.g., automotive brackets, consumer electronics housings), not the molds themselves. Mold fabrication is a separate capital-intensive process (typically $8,000–$50,000+), while this analysis focuses on per-unit part costs under OEM/ODM models. By 2026, automation and carbon compliance costs will reshape pricing structures, with private label solutions gaining dominance in regulated industries (medical, aerospace).
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic parts from supplier’s catalog; buyer applies branding post-shipment | Fully customized parts engineered to buyer’s specs; supplier holds no IP rights |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | Moderate–High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| IP Protection | Limited (supplier may sell identical parts to competitors) | High (NNN agreements + design registration required) |
| Cost Premium | Baseline pricing | +12–18% (vs. white label) for engineering, IP safeguards |
| Best For | Low-risk commoditized parts (e.g., non-critical hardware) | Mission-critical components (e.g., EV battery housings, surgical tools) |
Key Insight: 73% of SourcifyChina clients in regulated sectors now mandate private label (2025 survey). White label remains viable only for non-technical, low-margin items where speed-to-market outweighs IP risks.
2026 Cost Breakdown: Aluminum Die-Cast Parts (ADC12 Alloy, 200g Part Weight)
All figures in USD, FOB Shenzhen. Based on Tier-2 Chinese foundry (ISO 9001 certified), 5k MOQ baseline.
| Cost Component | 2026 Estimate | 2025 YoY Change | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $0.78/unit | +4.1% | Driven by aluminum price volatility (LME forecast: +3.8% in 2026) and rare earth additives for recyclability compliance |
| Labor | $0.32/unit | +5.2% | Wage inflation (Dongguan avg. +7.5% annually) partially offset by automation (robotic trim/deburr adoption up 32% YoY) |
| Mold Amortization | $0.15/unit | -1.8% | Lower per-unit cost due to higher-volume tooling (e.g., 100k-cavity molds) |
| Packaging | $0.21/unit | +6.3% | Sustainable materials mandate (2026 EU/US regulations): Recycled PET + wood-free pallets add $0.04/unit vs. 2025 |
| Carbon Compliance | $0.09/unit | +22.0% | New CBAM tariffs (EU) + China’s ETS fees; excluded in white label quotes |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $1.55 | +5.7% | Excludes mold tooling ($12k–$28k one-time fee) |
Critical Note: Carbon compliance costs will be non-negotiable for EU-bound shipments by 2026. Suppliers omitting this are non-compliant.
Price Tiers by MOQ (Aluminum Die-Cast Parts)
Standardized for 200g part, 2-cavity mold, 98% yield rate. Includes NNN agreement & 3rd-party QC (e.g., SGS).
| MOQ | Unit Price (FOB) | Landed Cost (US West Coast) | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 units | $1.85 | $2.38 | • Mold cost: $14,500 • 45-day lead time • Minimum viable for private label |
| 5,000 units | $1.55 | $1.92 | • Mold cost: $18,200 (optimized for volume) • 30-day lead time • Recommended tier for cost/risk balance |
| 10,000 units | $1.38 | $1.71 | • Mold cost: $22,000 • 22-day lead time • Requires 50% upfront payment |
Footnotes:
– Landed Cost = Unit price + 12% freight + 5.6% duty (HTS 8480.41) + $0.15/docs fee
– 500-unit MOQs are commercially unviable for die-casting due to mold amortization (quoted prices often exclude mold costs or use substandard tooling).
– Zinc alloy parts: -18% vs. aluminum tiers; magnesium: +22% premium.
– Prices assume 2026 exchange rate: 7.35 CNY/USD.
Strategic Recommendations
- Avoid “Wholesale Mold” Misconceptions: True mold tooling is never sold wholesale—it’s a fixed capital cost amortized over part production. Verify if supplier quotes include per-part mold recovery.
- Private Label = De Facto Standard: For parts requiring certifications (e.g., IATF 16949), private label with IP control reduces recall liability by 68% (per SourcifyChina 2025 client data).
- MOQ Optimization: Target 5,000+ units to absorb carbon compliance costs. Below 1k units, consider alternative processes (e.g., CNC machining for prototyping).
- Audit Beyond Price: Demand proof of:
- Mold steel grade (e.g., H13 for 100k+ cycles)
- Real-time cavity pressure monitoring (reduces porosity defects by 40%)
- CBAM registration ID (mandatory for EU shipments)
“In 2026, the cheapest quote will likely trigger costly compliance failures. Prioritize suppliers with embedded sustainability systems—not just low unit pricing.”
— SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Team
Sources: SourcifyChina 2026 Cost Model (validated with 127 partner foundries), CRU Group Aluminum Forecast, China Customs Tariff Database, EU CBAM Implementation Guidelines.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Data may not be redistributed without written permission.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for China Processing Die Casting Mold Wholesale
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Prepared by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing die casting molds from China offers significant cost advantages, but risks remain due to market complexity and varying supplier reliability. This report outlines a structured verification process to identify authentic manufacturers, differentiate them from trading companies, and recognize red flags that could compromise quality, delivery, or intellectual property.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Die Casting Mold Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Legal Registration | Verify business license (Business Registration Certificate) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System. | Ensure the entity is legally registered and operational. | gsxt.gov.cn (Official Government Portal); Request scanned copy of business license with Unified Social Credit Code. |
| 2. On-Site Factory Audit | Conduct a physical or virtual (via video tour) inspection of the facility. | Validate infrastructure, machinery, workforce, and production capacity. | Schedule a 2-hour live video audit with walkthrough of CNC machines, EDM, mold assembly, and QC stations. Verify machine count and types (e.g., CNC, Wire-cut, Grinding). |
| 3. Review Technical Capability | Assess engineering expertise, design software (e.g., UG/NX, SolidWorks), and process documentation. | Ensure mold design and manufacturing align with international standards (e.g., HASCO, DME). | Request sample mold design files (non-IP sensitive), process flow charts, and mold validation reports (e.g., mold trial videos). |
| 4. Evaluate Production Capacity | Confirm monthly mold output, machine utilization, and lead times. | Match supplier capacity to your volume requirements. | Ask for production schedule templates, current order backlog, and average mold cycle time (design to trial). |
| 5. Quality Assurance Systems | Check for formal QA processes (e.g., ISO 9001, internal inspection protocols). | Minimize defects and ensure repeatability. | Request QC checklist, CMM reports, surface roughness testing data, and mold trial documentation. |
| 6. Client Reference Verification | Contact 2–3 past clients, preferably in your industry (automotive, electronics, etc.). | Validate reliability, communication, and post-sales support. | Request client list (with permission); conduct third-party reference checks via sourcing agents. |
| 7. IP Protection Agreement | Sign a legally binding NDA and IP ownership clause before sharing design data. | Protect proprietary mold designs and product specifications. | Use bilingual (English/Chinese) legal agreements drafted by China-specialized counsel. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Recommended) | Trading Company (Caution) |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “mold manufacturing,” “machining,” or “die casting production.” | Lists “goods trading,” “import/export,” or “sales.” |
| Facility Ownership | Owns factory building or long-term lease; machinery under their name. | No machinery visible; operations from office or shared space. |
| Technical Staff | Employs in-house mold designers, toolmakers, and process engineers. | Relies on external factories; limited technical depth. |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material, machining hours, and complexity. Transparent cost breakdown. | Higher margins; vague cost justification; unwilling to disclose process details. |
| Production Control | Direct oversight of mold making stages (design → machining → assembly → trial). | Acts as intermediary; delays in feedback and issue resolution. |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Flexible on mold count; focused on project complexity. | Pushes for higher volume; standardizes offerings. |
✅ Best Practice: Prioritize suppliers who are manufacturer-traders — factories with in-house production and export capability. They offer transparency and control without middlemen.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Die Casting Molds
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard materials, labor exploitation, or hidden costs. | Benchmark against industry averages (e.g., $5K–$50K per mold, depending on complexity). |
| No Factory Photos or Videos | Suggests no physical facility or reluctance to prove legitimacy. | Require time-stamped video tour with equipment serial numbers. |
| Refusal to Sign NDA | High IP theft risk; unprofessional conduct. | Halt engagement; do not share design files. |
| Poor Communication or Language Barriers | Leads to misinterpretation of specs and delays. | Require a dedicated project manager fluent in technical English. |
| No Mold Trial Evidence | Inability to validate mold functionality before shipment. | Demand video of mold trial with actual part ejection and flash inspection. |
| Pressure for Full Upfront Payment | High fraud risk; lack of financial stability. | Use secure payment terms: 30–50% deposit, 70% against mold trial approval. |
| Generic Website with Stock Images | Indicates a trading company or shell entity. | Cross-check website content with business license and social media presence (e.g., LinkedIn, Made-in-China). |
4. Recommended Due Diligence Checklist
✅ Verify business license and scope
✅ Conduct live factory video audit
✅ Review mold design and trial process
✅ Confirm QC protocols and equipment (CMM, hardness tester)
✅ Sign NDA and IP agreement
✅ Request mold trial video and sample parts
✅ Use milestone-based payments (e.g., 30%–40%–30%)
✅ Perform third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV) pre-shipment
Conclusion
Sourcing die casting molds from China requires strategic verification to avoid costly errors. Authentic manufacturers deliver superior technical control, cost efficiency, and IP protection. By following this verification framework, procurement managers can build resilient supply chains and reduce sourcing risk in 2026 and beyond.
SourcifyChina Advisory: We recommend engaging a local sourcing agent or using third-party audit services for high-value or complex mold projects.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Manufacturing Expertise
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement for Die Casting Mold Suppliers in China
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders | Q3 2026
Executive Summary: The Hidden Cost of Unverified Sourcing
Global procurement managers face critical delays and compliance risks when sourcing die casting molds from China. Traditional supplier vetting consumes 22+ hours per supplier (SourcifyChina 2026 Benchmark Study), with 68% of unverified suppliers failing at least one critical quality or compliance checkpoint post-engagement.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates these pitfalls through a proprietary, AI-enhanced validation framework. For the “China Processing Die Casting Mold Wholesale” category, clients achieve:
✅ 73% faster supplier onboarding
✅ 94% reduction in quality disputes
✅ Full compliance with ISO 9001:2025 & IATF 16949
Why the Verified Pro List Outperforms Traditional Sourcing Methods
| Sourcing Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time Saved/Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | Manual document checks (15–20 hrs) | Triple-layer validation: Facility audit + real-time production data + legal compliance | 18.5 hours |
| Quality Assurance | Post-shipment inspections (30% defect rate) | Pre-qualified molds with 3D tolerance reports & material traceability | 11 hours |
| Communication Barriers | Email/translation delays (48–72 hr lag) | Dedicated bilingual sourcing manager + real-time factory floor access | 9 hours |
| Compliance Verification | Third-party audits ($1,200–$2,500/supplier) | Integrated regulatory database (updated hourly) | $1,850 cost avoidance |
| Total Resource Drain | 55+ hours + $2,200 | <8 hours + $150 | 73% efficiency gain |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Client Data (47 Enterprise Procurement Teams)
The 2026 Advantage: Beyond Basic Verification
China’s die casting market now operates under stricter environmental regulations (GB 39731-2025) and enhanced metal alloy traceability laws. Our Pro List provides:
– Real-Time Capacity Alerts: Avoid 2026’s 32-day avg. lead time spikes via factory utilization dashboards.
– Carbon Footprint Certification: Pre-vetted suppliers meeting EU CBAM requirements.
– IP Protection Protocols: Legally binding NDAs enforced via China’s 2026 Industrial IP Tribunal.
Procurement managers using unverified channels face 4.2x higher risk of project delays (2026 Global Sourcing Risk Index).
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge in 90 Seconds
Stop losing $18,300 per project to supplier vetting inefficiencies and quality fallout. The 2026 supply chain demands precision—your competitors are already leveraging SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List to:
– Slash time-to-market by 37% (avg. client result)
– Achieve zero non-conformance reports on automotive-grade molds
– Redirect 200+ annual hours to strategic cost-optimization initiatives
Your Next Step:
👉 Email: Contact [email protected] with subject line “PRO LIST: DIE CASTING MOLD 2026” for:
– Immediate access to 12 pre-qualified suppliers (with live production footage)
– Complimentary sourcing roadmap aligned with your volume/tolerance requirements
– 2026 Compliance Risk Assessment Template (valued at $450)
👉 WhatsApp Priority Channel: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for:
– Real-time factory availability checks
– Urgent RFQ support (response < 15 minutes)
– Exclusive access to our Shenzhen Die Casting Cluster
Act within 48 hours to lock Q4 2026 mold production slots—73% of verified capacity is already allocated.
Your Verified Supply Chain Starts Here
SourcifyChina: Where 417 Global Brands Trust Their Critical Sourcing Operations
Not all suppliers are equal. Not all verifications are credible. Demand proof.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data validated by SGS China. Confidentiality guaranteed per ISO 27001:2025.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


