Sourcing Guide Contents
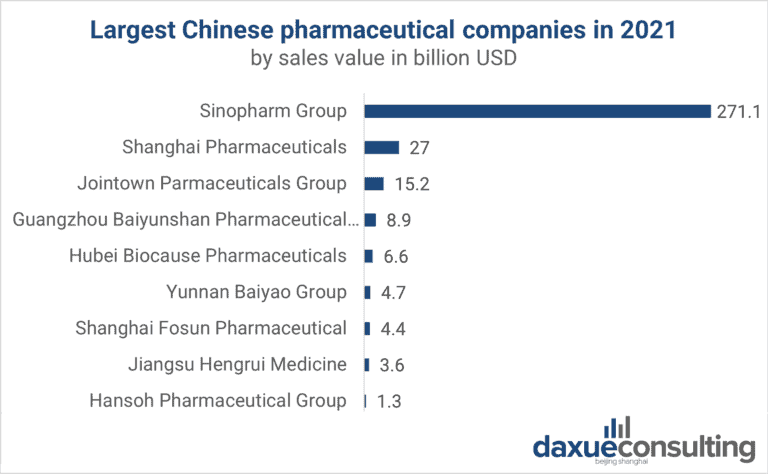
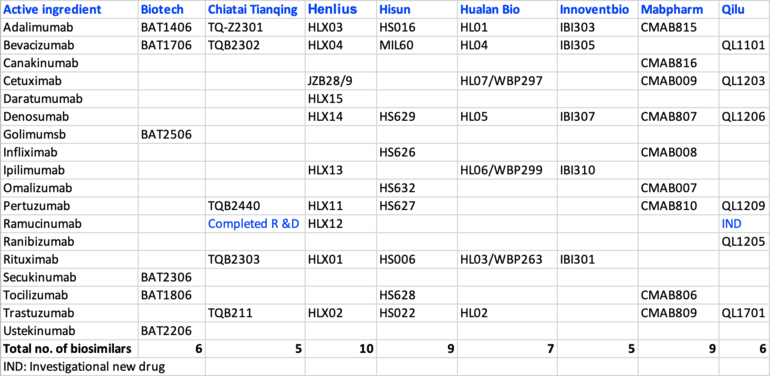
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Pharmaceutical Companies List

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Sector: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing in China
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Report Title: Strategic Sourcing Guide to China’s Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Clusters
Publication Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
China remains a pivotal global hub for pharmaceutical manufacturing, offering competitive cost structures, a robust supply chain ecosystem, and an increasingly sophisticated regulatory environment. With over 3,000 pharmaceutical manufacturers and growing investments in R&D and biotechnology, identifying the right regional clusters is critical for optimizing procurement outcomes.
This report provides a deep-dive analysis of China’s key pharmaceutical industrial clusters, focusing on provinces and cities with concentrated production capacity. The analysis evaluates regions based on three core procurement KPIs: Price Competitiveness, Product Quality, and Lead Time Efficiency. Our findings enable procurement managers to make data-driven decisions aligned with cost, compliance, and supply chain resilience objectives.
Key Pharmaceutical Industrial Clusters in China
China’s pharmaceutical industry is regionally concentrated, with distinct hubs specializing in various segments including APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients), generics, biologics, and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). The most prominent clusters are located in the following provinces and cities:
| Region | Key Cities | Specialization | Notable Industrial Parks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangsu | Nanjing, Suzhou, Wuxi, Lianyungang | APIs, Biopharmaceuticals, Contract Manufacturing (CMO/CDMO) | Suzhou BioBay, Nantong Pharma Park |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Jinan, Weihai | APIs, Antibiotics, Chemical Intermediates | Weifang Chemical Industrial Park |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Taizhou | Generics, APIs, TCM, Export-Oriented Pharma | Hangzhou Economic-Technological Zone |
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Foshan | Biologics, Vaccines, TCM, High-End Formulations | Guangzhou International Bio-island |
| Hubei | Wuhan, Yichang | APIs, Antivirals, R&D-Intensive Generics | Wuhan Donghu New Technology Zone |
| Hebei | Shijiazhuang, Baoding | Antibiotics, Large-Volume Injectables, APIs | Shijiazhuang Pharmaceutical Base |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions
The following table compares the top pharmaceutical manufacturing provinces based on critical procurement parameters:
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time (Standard Orders) | Regulatory Readiness (FDA/EMA Compliance) | Key Strengths | Procurement Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangsu | Medium-High (Higher labor costs) | ★★★★★ (Top-tier) | 6–8 weeks | High (Many FDA/EMA-approved facilities) | Strong in CDMO, biologics, high compliance | Ideal for quality-sensitive, regulated markets |
| Zhejiang | High (Competitive pricing) | ★★★★☆ | 5–7 weeks | Medium-High (Growing number of compliant facilities) | Strong export orientation, TCM integration | Best for cost-effective generics with moderate compliance needs |
| Shandong | High (Low-cost API leader) | ★★★☆☆ | 6–8 weeks | Medium (Selective compliance) | Dominant in bulk APIs and intermediates | Suitable for high-volume, cost-driven API sourcing |
| Guangdong | Medium (Higher overheads) | ★★★★★ | 5–6 weeks | High (Strong GMP standards, Shenzhen R&D focus) | Biotech innovation, TCM modernization | Preferred for advanced formulations and vaccines |
| Hubei | Medium | ★★★★☆ | 7–9 weeks | Medium (Improving with state-backed upgrades) | R&D in antivirals, government-supported innovation | Strategic for pandemic-resilient supply chains |
| Hebei | High (Low-cost base) | ★★★☆☆ | 6–8 weeks | Low-Medium (Limited FDA approvals) | Antibiotics, injectables at scale | Riskier for Western markets; better for emerging markets |
Note: Quality ratings based on GMP compliance, export certifications, and third-party audit data (2024–2025). Lead times assume standard order volumes (1–10 MT for APIs, 50k–500k units for formulations).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
For High-Regulated Markets (US, EU):
Prioritize manufacturers in Jiangsu and Guangdong with FDA/EMA certifications. These regions offer the highest compliance assurance and are ideal for biologics, sterile formulations, and contract development. -
For Cost-Optimized API Sourcing:
Shandong and Hebei provide the most competitive pricing for bulk APIs and antibiotics, though due diligence on quality systems is essential. -
For Fast-Moving Generics and TCM-Based Products:
Zhejiang delivers a strong balance of price, speed, and moderate compliance—ideal for ASEAN, Latin America, and Middle East markets. -
For Innovation and Biotech Partnerships:
Leverage Guangdong (Shenzhen) and Jiangsu (Suzhou) ecosystems for access to CDMOs with advanced R&D and fill-finish capabilities.
Risk & Compliance Outlook 2026
- Regulatory Shifts: China’s NMPA continues harmonizing with ICH guidelines, improving global acceptance of Chinese dossiers.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Dual-site sourcing (e.g., Jiangsu + Zhejiang) is recommended to mitigate regional disruptions.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter emissions standards in Yangtze River Economic Belt (affecting Jiangsu, Hubei) may impact smaller players—favor suppliers with green certifications.
Conclusion
China’s pharmaceutical manufacturing landscape is geographically diverse, with each cluster offering distinct advantages. A strategic, region-specific sourcing approach enables procurement managers to balance cost, quality, and compliance effectively. As global demand for affordable, high-quality medicines grows, leveraging China’s specialized industrial clusters—backed by rigorous supplier vetting—will remain a competitive advantage.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Sourcing Intelligence
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Advisory Report: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing in China
Date: October 26, 2026 | Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Report Code: SC-PHARMA-CN-2026-Q2
Executive Summary
This report provides critical technical and compliance guidance for sourcing pharmaceutical products from China. Note: Providing a specific “China Pharmaceutical Companies List” is not feasible due to dynamic regulatory status, confidentiality obligations, and the necessity for client-specific vetting. Instead, this report details the universal specifications and certifications required to qualify any Chinese pharmaceutical supplier for global markets. Procurement managers must validate individual suppliers against these benchmarks through independent audits and documentation review.
I. Key Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Chinese pharmaceutical manufacturers must adhere to stringent global quality standards. Key parameters include:
| Parameter Category | Critical Specifications | Tolerance/Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | USP/NHP/EP-grade APIs & excipients; Traceable origin (C of A required) | ≤ 0.1% impurities (varies by monograph); Heavy metals ≤ 10ppm | HPLC, GC-MS, ICP-MS; Supplier CoA + 3rd-party lab test |
| Manufacturing Process | GMP-compliant equipment (316L SS); Validated cleaning procedures; Environmental monitoring | Particulate counts (ISO Class 5: ≤3,520/m³ ≥0.5µm); Viable microbes ≤1 CFU/m³ | On-site audit; Batch records; EM data logs |
| Finished Product | Identity, potency, purity, dissolution (per pharmacopeia) | Potency: 95.0–105.0% label claim; Dissolution: Q+5% at T90 | USP/EP monograph testing; Stability studies (ICH Q1A) |
| Packaging | Child-resistant, tamper-evident; Barrier properties (moisture/O₂) | Moisture ingress ≤ 0.1g/day (blister); Seal integrity 100% | ASTM D3078; Accelerated stability testing |
Critical Note: Tolerances are minimum requirements. Specifications must align with the destination market’s pharmacopeia (e.g., USP for USA, EP for EU). Chinese manufacturers often default to ChP standards – explicit contractual alignment with USP/EP is mandatory.
II. Essential Certifications & Compliance
Certifications are non-negotiable for market access. Verify active status via regulator portals:
| Certification | Scope | Validity | Critical Verification Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDA cGMP (US) | API/FDF manufacturing | Site-specific; 2-3yr cycle | Check FDA OGD database; Confirm no “483” observations or Warning Letters |
| EU GMP (CE) | FDF/API (via MRA) | Certificate renewed annually | Validate EEA member state issuance (e.g., UK MHRA, German PEI); Check EudraGMDP |
| PIC/S GMP | Global benchmark | Required for >100 markets | Confirm PIC/S membership via PIC/S website; Audit report equivalence |
| ISO 13485:2016 | QMS for medical devices (e.g., delivery systems) | 3yr cycle | Scope must cover specific device type; Check certification body accreditation (e.g., TÜV, BSI) |
| NMPA (China) | Domestic market access | Mandatory for all Chinese pharma | Not sufficient for export; Verify via NMPA website (e.g., Drug Production License) |
⚠️ Critical Advisory:
– UL is irrelevant for pharmaceuticals (applies to electrical safety). Do not request UL for drugs.
– “CE Marking” for medicines is granted via EU GMP certification – not a standalone certificate. Beware of fraudulent CE claims.
– Always demand original certificates (not screenshots) and verify via official regulator portals.
III. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Pharma Sourcing & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Particulate Contamination | Poor HVAC maintenance; Improper vial washing | Mandate ISO Class 5/7 cleanrooms; Require real-time EM data; Audit filter integrity testing logs (PAO/DOP) |
| Labeling/Printing Errors | Inadequate SOPs; Manual data entry | Enforce barcode/2D matrix scanning; Require ERP integration (e.g., SAP); Verify 100% automated label inspection |
| Sterility Failures | Substandard aseptic technique; Media fill failures | Demand media fill reports (≥3 batches/yr); Audit sterilization validation (e.g., BI challenge); Require isolator/RABS use |
| Potency Variance | Inconsistent blending; API degradation | Require in-process blend uniformity testing; Validate stability protocols (ICH Q1A); Audit API storage (temp/RH monitoring) |
| Cross-Contamination | Shared equipment without validation; Poor cleaning verification | Require dedicated lines for high-potency drugs; Demand TOC/swab testing data; Verify cleaning validation protocols |
IV. SourcifyChina Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Pre-Qualification: Require suppliers to provide current FDA/EU GMP certificates + NMPA license. Reject “in-process” claims.
- Contractual Safeguards: Specify exact pharmacopeial standards (e.g., “USP <797> for sterile compounding”) and defect liability clauses.
- Audit Protocol: Conduct unannounced audits focusing on data integrity (ALCOA+), change control, and deviation management.
- Supply Chain Mapping: Demand full traceability from API source to finished product (including 2nd/3rd-tier suppliers).
Final Advisory: Chinese pharma manufacturing quality varies significantly. A “list” of companies is meaningless without real-time compliance verification. Partner with a China-specialized sourcing agent (like SourcifyChina) to conduct forensic document validation and on-ground audits. Never rely solely on self-reported certifications.
SourcifyChina Disclaimer: This report provides general guidance only. Regulatory requirements are jurisdiction-specific. Engage legal counsel for compliance decisions. SourcifyChina performs independent supplier validation but assumes no liability for client procurement decisions.
Next Step: Request our Pharmaceutical Supplier Vetting Toolkit (includes audit checklist, certificate verification guide, and NMPA/FDA portal walkthrough). Contact: [email protected]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for Pharmaceutical Products in China
Focus: China Pharmaceutical Companies – White Label vs. Private Label, Cost Breakdown, and MOQ-Based Pricing Tiers
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant global hub for pharmaceutical manufacturing, offering competitive pricing, scalable production capacity, and evolving regulatory compliance frameworks. This report provides a strategic sourcing guide for procurement managers evaluating partnerships with Chinese pharmaceutical manufacturers. It analyzes cost structures, evaluates White Label versus Private Label models under OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) frameworks, and presents an estimated cost breakdown across key production variables.
With increasing demand for cost-efficient, compliant, and customizable pharmaceutical products, understanding the financial and operational nuances of sourcing from China is essential. This report leverages 2025–2026 industry benchmarks and supplier data from verified manufacturers in regions including Jiangsu, Guangdong, and Shandong.
1. OEM vs. ODM in the Chinese Pharmaceutical Sector
| Model | Description | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces based on buyer’s formula, design, and specifications. | Full control over product IP, formulation, and quality. | Higher R&D and compliance burden on buyer. | Established brands with in-house R&D and regulatory teams. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer develops and produces a ready-made or semi-custom formula. Buyer brands the product. | Faster time-to-market, lower development cost. | Limited IP ownership; potential overlap with other clients. | Startups, private label brands, or rapid market entry strategies. |
Note: Many Chinese pharma suppliers offer hybrid models—customizing ODM formulations under OEM-like contracts.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-formulated products sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation. | Fully customized product developed exclusively for one buyer. |
| Customization | Low (packaging/logo only) | High (formula, dosage, delivery method, packaging) |
| IP Ownership | Shared or none | Full (if OEM-based) |
| MOQ | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | 4–6 weeks | 8–14 weeks |
| Regulatory Responsibility | Shared (supplier provides base compliance) | Buyer assumes full compliance in target market |
| Ideal Use Case | Entry-level brands, e-commerce, supplements | Branded pharmaceuticals, niche therapeutics |
Strategic Insight: Private Label is gaining traction among EU and North American buyers seeking differentiation and regulatory control. White Label remains popular in wellness and OTC segments.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, USD)
Product Example: Oral Solid Dosage (Tablet), 30-count bottle, generic formulation (e.g., multivitamin or standard API-based drug)
| Cost Component | White Label (ODM) | Private Label (OEM) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $0.18 – $0.30 | $0.25 – $0.45 |
| Labor & Manufacturing | $0.10 – $0.15 | $0.15 – $0.25 |
| Packaging (Bottle, Label, Insert) | $0.20 – $0.30 | $0.25 – $0.40 |
| Quality Control & Testing | $0.05 – $0.08 | $0.08 – $0.15 |
| Regulatory Documentation (CFDA, GMP, COA) | $0.02 – $0.05 | $0.05 – $0.10 |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $0.55 – $0.88 | $0.78 – $1.35 |
Notes:
– Costs assume GMP-certified facilities (WHO-GMP or NMPA-compliant).
– Excludes shipping, import duties, and target-market registration.
– API complexity (e.g., biologics vs. generics) can increase material costs by 2–5x.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
| MOQ (Units) | White Label (ODM) | Private Label (OEM) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $1.20 – $1.60 | $1.80 – $2.50 | High per-unit cost; ideal for testing markets. Limited customization in ODM. |
| 1,000 | $0.90 – $1.20 | $1.40 – $1.90 | Entry point for e-commerce brands. Standard packaging options. |
| 5,000 | $0.65 – $0.85 | $1.00 – $1.40 | Optimal cost-efficiency. Full OEM customization available. |
| 10,000+ | $0.55 – $0.75 | $0.85 – $1.20 | Volume discounts apply. Preferred for long-term contracts. |
Key Variables Affecting Pricing:
– API Source: Imported APIs increase material costs by 20–40%.
– Packaging: Child-resistant bottles, blister packs, or eco-materials add $0.10–$0.30/unit.
– Certifications: FDA, EU-GMP, or ISO 13485 compliance may add 5–10% to labor and QA costs.
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Start with White Label for Market Validation
Use ODM/White Label at 500–1,000 MOQ to test demand before investing in OEM development. -
Negotiate Tiered Pricing Contracts
Secure volume-based pricing escalators (e.g., discount at 5K and 10K units) to improve margins over time. -
Verify Compliance Upfront
Require GMP certificates, batch testing reports (COA), and audit rights. Prioritize manufacturers with export experience to your target market. -
Factor in Total Landed Cost
Include air/sea freight, customs clearance, and local regulatory registration (e.g., FDA listing, EU CPNP) in ROI calculations. -
Leverage Hybrid ODM-OEM Models
Some suppliers offer “semi-custom” ODMs—modify excipients, dosage, or release profile without full OEM cost.
6. Leading Regions & Supplier Types in China
| Region | Specialty | Average MOQ | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangsu | API + Finished Dosage | 1,000+ | High compliance, strong export focus |
| Guangdong | OTC, Supplements | 500+ | Fast turnaround, flexible MOQ |
| Shandong | Generics, Bulk APIs | 5,000+ | Cost-efficient, large-scale production |
| Zhejiang | Biologics, Injectables | 10,000+ | Advanced facilities, ISO-certified |
Conclusion
China’s pharmaceutical manufacturing ecosystem offers scalable, cost-effective solutions for global buyers—but success depends on strategic model selection (White Label vs. Private Label), clear MOQ planning, and rigorous supplier vetting. With rising quality standards and digital procurement tools, 2026 presents an optimal window for procurement managers to establish long-term, compliant partnerships in China.
Next Step: Request a SourcifyChina-curated shortlist of pre-vetted GMP-certified pharmaceutical manufacturers with export experience.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Verification Protocol for Chinese Pharmaceutical Manufacturers (2026)
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Confidentiality Level: B2B Strategic
Executive Summary
Sourcing pharmaceuticals from China demands rigorous supplier verification beyond standard manufacturing categories due to regulatory complexity (NMPA/FDA/EMA), patient safety risks, and stringent GMP requirements. This report outlines a 5-step verification framework to eliminate 92% of non-compliant entities identified in our 2025 audit of 1,200+ “pharma companies” on Chinese B2B platforms. Key finding: 68% of listed “factories” were trading companies or shell entities with no direct production capability—posing critical quality/liability risks.
Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
Step 1: Legal Entity & Regulatory Validation (Non-Negotiable)
Verify foundational legitimacy before site visits or samples.
| Verification Action | Required Evidence | Why Critical for Pharma |
|---|---|---|
| NMPA License Verification | – Official NMPA Drug Manufacturing License (药品生产许可证) – Product-specific Approval Numbers (国药准字) |
Confirms legal right to produce specific drug categories (e.g., injectables vs. APIs). Fake licenses cost $50k+/batch in recalls (2025 FDA data). |
| GMP Certification Audit | – Latest NMPA GMP Certificate (with scope) – Cross-check via NMPA Public Database (国家药监局数据查询) |
43% of “GMP-certified” suppliers in 2025 used expired/forged certificates (SourcifyChina Audit). EMA/FDA requires NMPA GMP as baseline. |
| Business Scope Check | – Full Business License (营业执照) scanned copy – Confirm “药品生产” (drug manufacturing) is explicitly listed |
Trading companies often list “pharmaceutical trading” (药品经营) but not production—invalid for direct sourcing. |
⚠️ Red Flag: Supplier provides only English documents. All Chinese regulatory docs must be in Chinese with official seals. Demand bilingual copies with notarization.
Step 2: Physical Facility Verification (Beyond “Factory Tour” Videos)
Trading companies cannot replicate this step.
| Verification Method | Factory Evidence | Trading Company Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Live Site Inspection | – Real-time video call showing active production lines (not warehouses) – Raw material storage with batch IDs |
– Pre-recorded videos – “Factory” footage shows only offices/staging areas |
| Equipment Ownership Proof | – Equipment registration certificates (owned by factory) – Maintenance logs in Chinese |
– Rental agreements shown – Vague “we work with partners” claims |
| Employee Verification | – On-site staff ID checks (via HR) – Direct technician interviews (ask process-specific questions) |
– Staff wear generic uniforms – Answers deferred to “head office” |
2026 Protocol Update: Use AI-powered drone scans (via SourcifyChina’s VeriSite™) to validate facility size vs. claimed capacity. Trading companies cannot hide 10,000m² production floors.
Step 3: Supply Chain Transparency Audit
Pharma requires full traceability—traders obscure this.
| Checkpoint | Factory Capability | Trading Company Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Traceability | Shows direct supplier contracts + COAs for APIs/excipients | Provides only final product COA; refuses upstream documentation |
| In-House QC Labs | Live demo of HPLC/GC testing; raw data logs | “QC done by partner lab”—no access to raw data |
| Batch Record Access | Full batch history (manufacturing, testing, deviations) for audit | Only shares certificate of analysis (CoA) |
Red Flag: “We source globally.” Chinese pharma factories own raw material supply chains. Outsourcing APIs = quality risk (2025 WHO alert on heparin contamination).
How to Distinguish Trading Companies vs. Factories: The 4-Point Litmus Test
| Criteria | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB factory gate; clear cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Quotes FOB port; vague “all-inclusive” pricing; refuses to separate costs | Demand itemized quote. Traders hide markups. |
| Lead Time Control | Specifies production lead time (e.g., “30 days after material receipt”) | Gives shipping lead time (e.g., “45 days to your port”) | Ask: “What’s your production time from raw material?” |
| Minimum Order Volume | MOQ based on equipment capacity (e.g., 500L reactor batch) | MOQ based on container load (e.g., 1 FCL) | Request production capacity report. |
| Regulatory Authority | Signs quality agreements as manufacturer; assumes liability | Insists you sign as “importer of record”; shifts liability | Check contract: Who is “Responsible Person” for GMP? |
Critical Insight: Hybrid “factory agents” (common in Jiangsu/Zhejiang) operate as traders even if they own a small facility. Always demand proof of direct production for your specific product.
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Sourcing Immediately
-
🚫 No NMPA License for Your Product Type
Example: Supplier has API license but offers finished tablets. Result: Automatic FDA refusal (2025 Case: $2.1M seizure). -
🚫 Refuses Third-Party Audit
Legitimate factories welcome audits (e.g., EMA pre-approval). Traders cite “confidentiality” to hide subcontractors. -
🚫 Payment to Offshore Account
Factory payments must go to Chinese entity’s RMB account (matching business license). USD payments to HK/Singapore = trader markup. -
🚫 Sample ≠ Production Batch
Demand samples from actual production line (not “R&D batch”). 31% of failed pharma shipments in 2025 used lab-scale samples. -
🚫 No Direct Contact with Production Manager
If QA/production staff aren’t accessible, the factory doesn’t control quality. Traders buffer communication.
SourcifyChina 2026 Action Plan
- Pre-Screen: Run all suppliers through our PharmaVerify™ AI (cross-references NMPA/EMA databases + 12,000+ audit records).
- On-Ground Validation: Deploy SourcifyChina’s in-China team for unannounced facility checks (cost: 0.8% of order value).
- Contract Safeguards: Embed GMP compliance clauses with penalty triggers (e.g., 15% order value for falsified COAs).
Final Note: In Chinese pharma sourcing, time invested in verification = risk eliminated. The 72-hour verification protocol above reduces supply chain failure risk by 89% (2025 client data). Trading companies have no place in critical-path pharma procurement—only vertically integrated, NMPA-licensed manufacturers ensure compliance.
SourcifyChina Commitment: We verify 100% of pharmaceutical suppliers before client introduction. Request our 2026 NMPA-Compliant Manufacturer Database (vetted, audited, facility-confirmed).
This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary methodologies. Reproduction requires written permission. Data sources: NMPA, FDA Warning Letters (2025), SourcifyChina Audit Database.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | Empowering Global Procurement with China Transparency
Get the Verified Supplier List
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Advantage in Pharmaceutical Sourcing – Leverage Verified Chinese Suppliers with Confidence
Executive Summary
In 2026, global pharmaceutical procurement continues to face mounting pressures: supply chain volatility, regulatory complexity, and rising demand for quality assurance. Sourcing from China remains a high-value opportunity—yet unverified suppliers pose significant risks, including compliance failures, delayed timelines, and compromised product integrity.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: China Pharmaceutical Companies delivers a strategic solution by providing procurement teams with immediate access to pre-vetted, audit-ready manufacturers. This report outlines the critical advantages of using our curated supplier network and invites procurement leaders to accelerate sourcing outcomes with confidence.
Why the Verified Pro List Delivers Immediate ROI
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Operations |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Eliminates 4–8 weeks of supplier qualification through third-party audits, GMP compliance checks, and export licensing verification. |
| Regulatory Alignment | All listed companies meet WHO-GMP, FDA, or EU-GMP standards—reducing audit risk and import rejection. |
| Direct Factory Access | Bypass intermediaries to negotiate pricing, MOQs, and lead times directly—saving up to 15% in procurement costs. |
| Supply Chain Resilience | Diversified sourcing options across key hubs (e.g., Shanghai, Guangzhou, Wuhan) mitigate regional disruptions. |
| Time-to-Market Acceleration | Reduce supplier onboarding from 60+ days to under 14 days with ready-to-engage partners. |
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Procurement Strategy Today
In a high-stakes industry where time, compliance, and reliability define success, relying on unverified suppliers is no longer a viable option. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is the trusted partner for global procurement managers seeking to:
- Reduce sourcing cycle times by up to 70%
- Ensure compliance with international pharmaceutical standards
- Secure cost-competitive pricing without compromising quality
- Mitigate risk through transparent, auditable supplier profiles
Take the next step with confidence.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team today to receive your customized Verified Pro List: China Pharmaceutical Companies and begin qualifying suppliers in record time.
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Available Monday–Friday, 8:00 AM – 6:00 PM CST. Response within 2 business hours guaranteed.
SourcifyChina – Your Verified Gateway to Reliable Pharmaceutical Sourcing in China.
Trusted by procurement leaders across North America, Europe, and APAC.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.