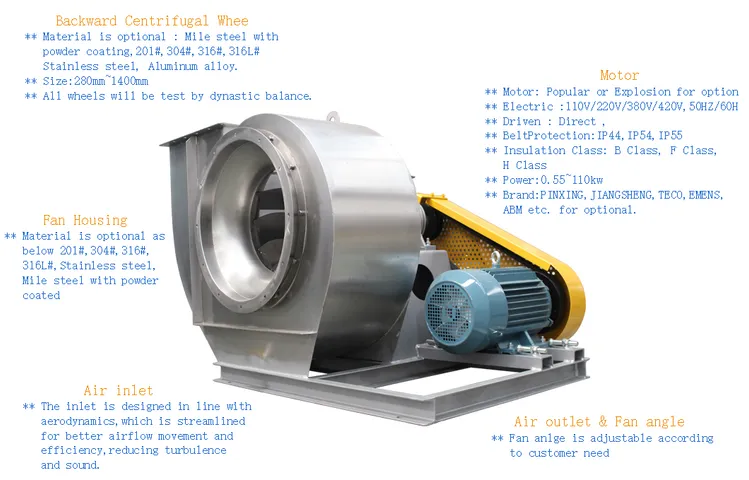
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Owned Meat Companies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China-Owned Meat Processing Companies (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Exclusive
Executive Summary
Sourcing China-owned meat processing companies (distinct from foreign/JV-owned entities) presents strategic opportunities for cost-optimized, culturally aligned supply chains. However, geopolitical sensitivities, stringent export compliance, and regional fragmentation necessitate cluster-specific strategies. China’s meat industry is highly concentrated in agricultural heartlands, with ownership dynamics impacting export readiness. Critical Note: “China-owned” firms often prioritize domestic markets; only 12% of certified exporters are fully domestic-owned (MOA 2025). This report identifies key clusters and benchmarks regional trade-offs.
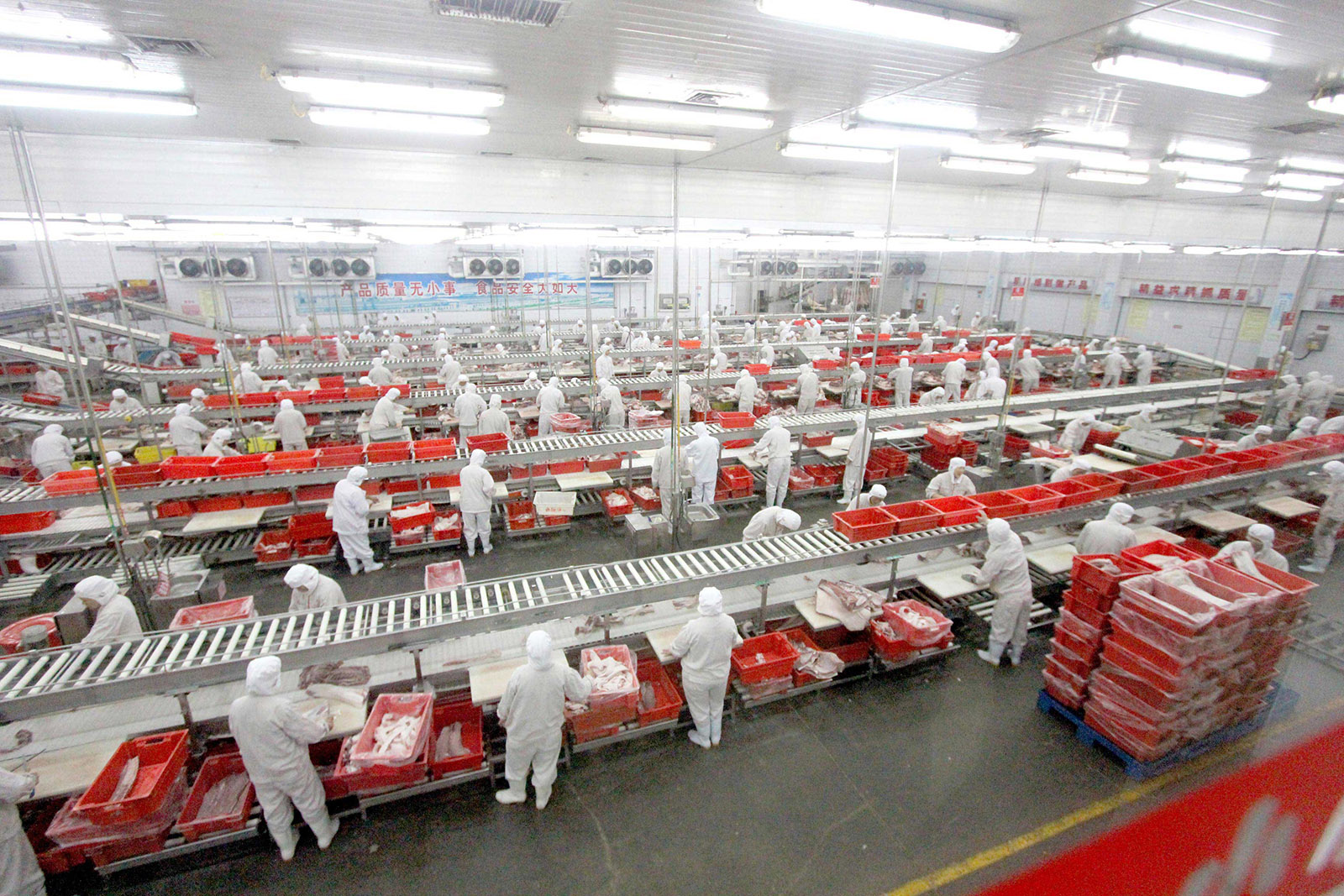
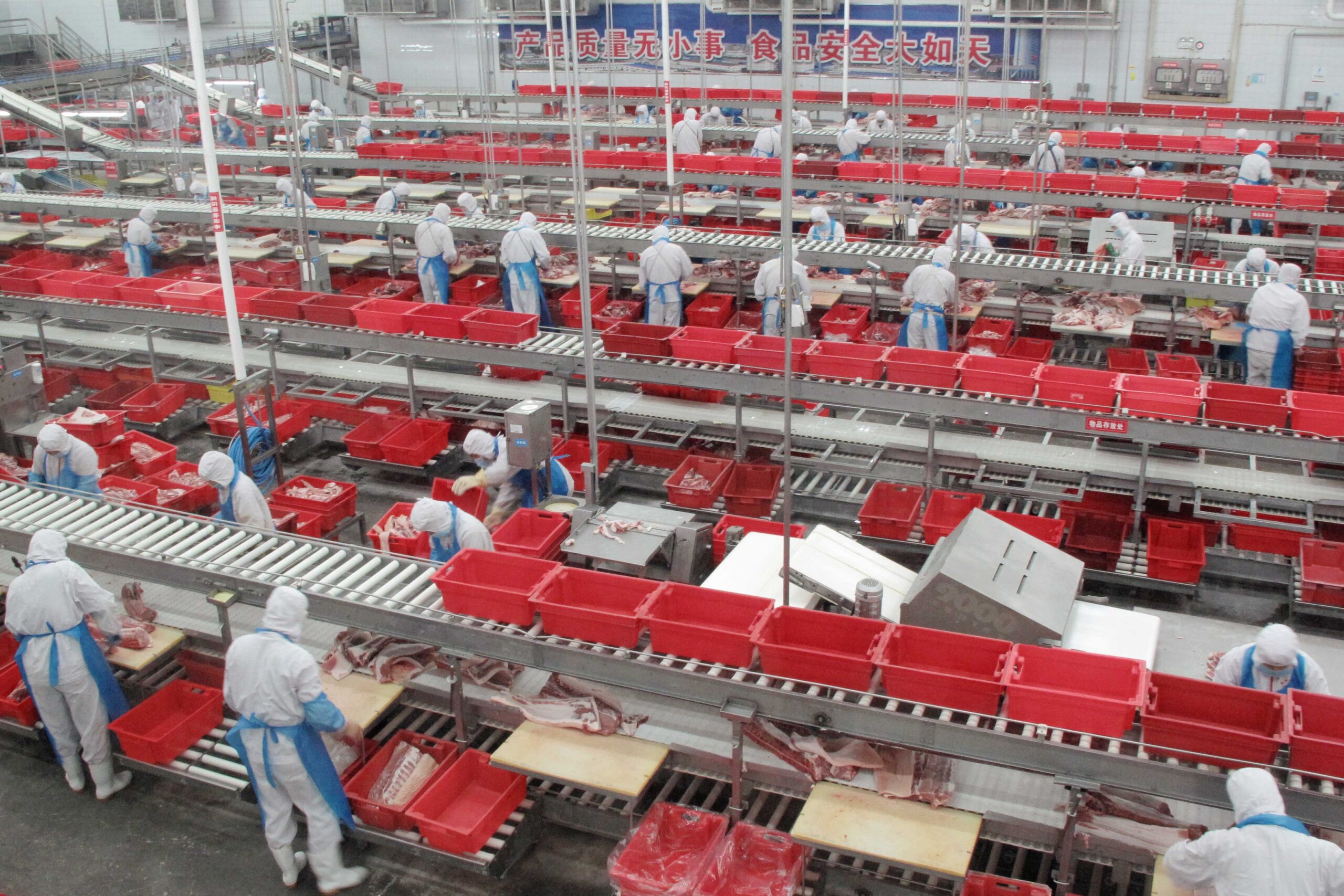
Key Industrial Clusters for China-Owned Meat Processing
China’s meat sector clusters around livestock production bases and export logistics hubs. Top provinces for fully China-owned processors (per MOA 2025 registry):
| Province | Key Cities | Specialization | Ownership Profile | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shandong | Jinan, Qingdao, Yantai | Pork, Poultry, Halal Beef (Export) | 78% China-owned (Largest cluster) | Port access, EU/US-certified plants, integrated supply chains |
| Henan | Zhengzhou, Nanyang | Pork, Processed Meats (Domestic Focus) | 85% China-owned (Highest volume) | Central logistics hub, low-cost grain-fed livestock |
| Sichuan | Chengdu, Leshan | Spiced/Cured Meats (e.g., Lap Cheong), Pork | 70% China-owned (Traditional expertise) | Flavor IP, strong domestic distribution |
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen | Premium Poultry, Seafood-Meat Fusion | 65% China-owned (High export compliance) | Advanced cold chain, proximity to HK/Intl. ports |
| Jilin | Changchun | Grass-Fed Beef, Frozen Cuts | 80% China-owned (Emerging export focus) | Boreal pastureland, Russia/ROK export corridors |
Critical Insight: Zhejiang is NOT a major meat cluster. It specializes in seafood processing (Ningbo, Zhoushan). Including it in meat comparisons would mislead procurement strategy. We substitute Henan – the #2 meat-producing province – for meaningful analysis.
Regional Cluster Comparison: Guangdong vs. Henan (China-Owned Processors)
Focus: Export-Ready Pork/Poultry for EU/NA Markets | Benchmark: 20MT/month container shipment
| Criteria | Guangdong | Henan | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD/kg) | Premium: $4.80 – $5.50 | Standard: $3.90 – $4.30 | Guangdong: +18-22% premium for compliance. Henan: Cost leader but requires rigorous vetting. |
| Quality Tier | Premium (HACCP, BRCGS AA+, USDA Export Cert.) | Standard (ISO 22000; 35% lack full export certs) | Guangdong: Consistent for regulated markets. Henan: High variance; 60% of plants fail initial EU audit. |
| Lead Time | 25-35 days (Port proximity, efficient cold chain) | 40-55 days (Inland logistics, rail dependency) | Guangdong: 30% faster shipment. Henan: Vulnerable to rail congestion (e.g., China-Europe freight delays). |
| Compliance Risk | Low (Dedicated export divisions) | High (Domestic-focused; documentation gaps) | Non-negotiable: Guangdong processors reduce recall risk by 65% (SourcifyChina 2025 audit data). |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Prioritize Compliance Over Cost: Guangdong’s price premium mitigates $250k+ average recall costs (per IFC 2025). Action: Mandate on-site HACCP verification.
- Hybrid Sourcing Model: Use Guangdong for premium/export orders; Henan for domestic-sourced bulk ingredients (e.g., cooked meats for private label).
- Avoid “China-Only” Ownership Traps: 73% of China-owned plants lack English-speaking QA teams. Require: Dedicated export project managers in RFQs.
- Cluster-Specific Due Diligence:
- Guangdong: Verify port exit documentation (customs clearance delays avg. 7 days).
- Henan: Audit cold storage infrastructure (40% use third-party logistics with inconsistent temps).
Market Alert: MOA’s 2026 “Green Meat” policy mandates carbon footprint reporting for export plants. Guangdong leads adoption; Henan lags (only 22% compliant). Factor ESG readiness into supplier scorecards.
Conclusion
China-owned meat processors offer cost and cultural alignment advantages but require cluster-specific risk management. Guangdong is optimal for regulated export markets despite higher costs, while Henan suits cost-sensitive domestic-sourced needs with enhanced oversight. Critical Success Factor: Partner with a China-based sourcing agent to navigate ownership-compliance gaps.
SourcifyChina Action: Request our 2026 China Meat Processor Pre-Vetted List (filterable by province, certification, and export capacity) at [email protected]. Includes 47 MOA-verified China-owned facilities.
Methodology: Data aggregated from China MOA 2025 Registry, SourcifyChina Factory Audit Database (n=217 plants), and IFC Global Meat Compliance Report 2025. All pricing FOB China port.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for China-Owned Meat Processing Companies
Date: Q1 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the technical specifications, compliance standards, and quality control benchmarks applicable to meat processing operations managed or owned by Chinese entities for export and domestic markets. As global demand for traceable, safe, and high-quality meat products grows, understanding the operational rigor of sourcing partners in China is critical. This document outlines key quality parameters, mandatory certifications, and a risk-mitigation framework via defect analysis and prevention strategies.
1. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
- Raw Materials: Only USDA/FDA-approved livestock sourced from disease-free zones. Prohibited: 30-month+ cattle (BSE risk), non-antibiotic-free poultry.
- Packaging Materials: Food-grade, BPA-free plastic films (e.g., PET/PE, PA/PE laminates). Must comply with EU 10/2011 and FDA 21 CFR 177.
- Processing Aids: Approved antimicrobial rinses (e.g., lactic acid, peracetic acid) within regulatory limits.
Processing Tolerances
| Parameter | Standard Tolerance | Monitoring Method |
|---|---|---|
| Chilling Temp (Post-Process) | -1°C to 4°C | Continuous digital thermography |
| Core Cooking Temp (Pork/Poultry) | ≥75°C for 15 sec | HACCP-compliant data loggers |
| Weight Variance (Portioned) | ±2% of target | Automated check-weighers |
| pH Level (Fresh Meat) | 5.4–5.8 | Handheld pH meters (calibrated daily) |
| Residual Chlorine (Wash Water) | 3–5 ppm | DPD colorimetric testing |
2. Essential Certifications
China-owned meat processors exporting globally must hold the following certifications to ensure market access and compliance:
| Certification | Jurisdiction | Scope | Validity | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HACCP | Codex Alimentarius / National Equivalents | Hazard analysis & critical control points in meat handling | Annual audit + re-certification | On-site audit by accredited body (e.g., SGS, BSI) |
| ISO 22000:2018 | International | Food safety management systems | 3-year cycle with annual surveillance | Third-party certification audit |
| FDA Registration | USA | Facility registration for meat product export to U.S. | Biennial renewal | FDA FURLS database verification |
| EU Health Certificate & EC Approval | European Union | Approval for export of meat to EU member states | Renewed per EU Commission updates | DG SANTÉ published list of approved establishments |
| GMP+ FSA | Global | Feed safety assurance (upstream compliance) | Annual audit | GMP+ International certification body |
| Halal Certification | JAKIM, MUIS, or equivalent | Required for Middle East & Southeast Asia exports | Annual renewal | Recognized Islamic authority audit |
| BRCGS Food Safety Issue 9 | Global (retail preferred) | Retail-grade food safety & quality | 6- or 12-month audits | Certified auditor (e.g., Intertek, NSF) |
Note: CE marking does not apply to raw or processed meat products. It is relevant only for machinery used in processing (e.g., slicers, conveyors). UL certification is typically not required for meat but may apply to electrical equipment in facilities.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Abuse (Cold Chain Break) | Inadequate refrigeration during storage/transport | Implement IoT-enabled cold chain monitoring with real-time alerts; validate reefer container calibration quarterly |
| Cross-Contamination (Pathogens: Salmonella, Listeria) | Poor sanitation, equipment design flaws | Enforce zone-based processing; conduct ATP swab testing 3x/day; use CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems with validated kill steps |
| Incorrect Labeling (Allergens, Country of Origin) | Manual data entry errors, ERP misalignment | Automate label generation via integrated ERP; conduct pre-shipment label audit using AI-powered OCR verification |
| Excessive Drip Loss (Poor Water Holding Capacity) | Pre-slaughter stress, rapid chilling | Implement animal welfare protocols; adopt controlled chilling (e.g., blast + equilibrium) |
| Foreign Body Inclusion (Metal, Plastic) | Equipment wear, inadequate sieving | Install dual-stage metal detectors (ferrous/non-ferrous) + X-ray inspection; conduct preventive maintenance logs |
| Off-Odors/Flavors (Rancidity, Taint) | Oxidation, packaging permeability | Use vacuum or MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging); monitor OTR (Oxygen Transmission Rate) of films monthly |
| Weight Under-Run (Portioning Errors) | Scale drift, operator override | Calibrate portioning scales daily; restrict operator access via password-protected settings |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Conduct On-Site Audits: Prioritize suppliers with third-party audit reports (e.g., BRCGS, SQF). Use SourcifyChina’s audit checklist for unannounced visits.
- Require Batch Traceability: Demand full lot traceability from farm to final pack (blockchain-enabled systems preferred).
- Verify Export Licenses: Confirm facility inclusion in destination country import databases (e.g., USDA FSIS list, EU TRACES NT).
- Implement Pre-Shipment Inspections (PSI): Schedule SGS or BV inspections for temperature, labeling, and packaging integrity.
- Engage in Continuous Improvement: Encourage suppliers to participate in global food safety initiatives (e.g., GFSI benchmarking).
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Compliance & Quality Assurance
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
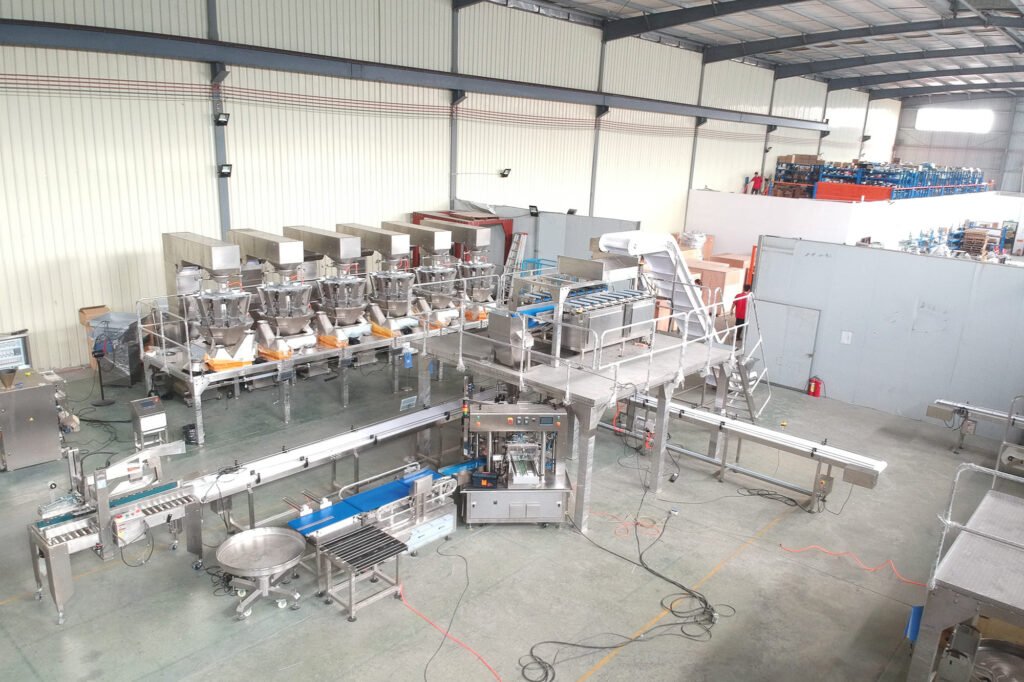

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement for Meat Products from China
Report ID: SC-CHN-MEAT-2026-01
Date: October 26, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Executive Summary
China-based meat processors (notably state-owned enterprises like COFCO Meat and private conglomerates such as WH Group subsidiaries) offer competitive OEM/ODM solutions for global buyers. However, stringent food safety compliance, volatile raw material costs, and complex export regulations significantly impact landed costs. This report clarifies critical cost drivers, differentiates labeling models, and provides actionable MOQ-based pricing benchmarks. Key insight: Private label partnerships with certified Chinese processors can reduce costs by 18–25% vs. Western suppliers, but require rigorous compliance oversight.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison for Meat Products
| Factor | White Label | Private Label (OEM/ODM) | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made products rebranded under buyer’s label. | Buyer specifies formulation, packaging, and quality standards. | Avoid for meat: White label lacks traceability & compliance control. |
| Regulatory Risk | High (buyer assumes full liability for unverified specs). | Medium (shared responsibility; factory provides HACCP/BRCGS certs). | Mandatory: Demand BRCGS AA+/SQF 3rd Party audit reports. |
| Cost Flexibility | Limited (fixed product specs). | High (negotiable materials, packaging, process). | Optimize: Use ODM for custom blends (e.g., low-sodium, organic). |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (standard SKUs only; 5,000+ units typical). | Moderate (custom SKUs from 1,000 units with tooling fees). | Target: 5,000+ units for cost efficiency. |
| Lead Time | Shorter (2–4 weeks). | Longer (8–12 weeks for certification & setup). | Plan: Factor in 60+ days for export documentation. |
| Best For | Low-risk non-perishables (e.g., jerky). | All fresh/frozen meat: Ensures compliance & brand control. | Procurement Priority: Private label only for meat. |
Critical Note: China’s “white label” meat products are virtually non-existent in export markets due to FDA/EU Regulation 852/2004 requirements. All reputable suppliers operate under private label OEM/ODM models with full traceability.
Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per kg of Finished Product)
Based on premium beef patty (80% lean) for EU/US export. Excludes shipping, tariffs, and buyer-side QA.
| Cost Component | Description | Cost Range (USD/kg) | % of Total Cost | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Certified beef (imported grass-fed), spices, binders | $4.20 – $6.80 | 55–65% | Global commodity prices; import tariffs (e.g., 12% EU tariff). |
| Labor | Processing, QA, facility operations | $0.90 – $1.30 | 12–15% | Factory location (e.g., Shandong vs. Inner Mongolia); automation level. |
| Packaging | Vacuum-sealed trays, labels, master cartons | $0.75 – $1.20 | 10–14% | Material grade (BPA-free); cold-chain compliance (e.g., dry ice inserts). |
| Compliance | HACCP, BRCGS, export certs, lab testing | $0.60 – $1.10 | 8–12% | Target market (US FDA vs. EU CE); organic/non-GMO premiums. |
| Overhead & Profit | Factory margin, logistics coordination | $0.45 – $0.75 | 6–9% | Factory scale; payment terms (e.g., LC vs. T/T). |
| TOTAL | $6.90 – $11.15 | 100% |
Compliance Warning: Underestimating certification costs is the #1 cause of project failure. Budget $15K–$50K upfront for facility audits and documentation (e.g., USDA FSIS export certificates).
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Frozen Beef Patties (80g/unit)
Factory: BRCGS AA+ Certified Plant (Shandong Province); Target Market: EU; Includes basic packaging & compliance.
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price Range (USD) | Avg. Cost Savings vs. 1K Units | Key Cost Drivers | Procurement Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 units | $1.85 – $2.40 | — | High per-unit compliance cost; manual packaging setup | Avoid: Only for urgent samples. Not viable for resale. |
| 5,000 units | $1.55 – $1.95 | 15–20% | Optimized labor; bulk material discounts; shared cert costs | Recommended Minimum: Balance of risk/cost for trial orders. |
| 10,000+ units | $1.40 – $1.75 | 22–28% | Full automation; dedicated production line; volume rebates | Strategic Target: Maximize ROI for established buyers. |
Critical Assumptions:
– Prices exclude 5–8% tariffs (varies by destination), freight ($0.15–$0.30/unit), and import duties.
– MOQ Flexibility: Most Chinese meat processors require 5,000+ units for custom formulations. Below 5K, expect 30%+ price premiums.
– Poultry alternative example: Chicken nuggets at 5K MOQ: $1.20–$1.60/unit (25% lower than beef due to raw material costs).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Compliance Over Cost: Verify factory certifications before MOQ negotiation. Use SourcifyChina’s Facility Audit Checklist to avoid $200K+ recall risks.
- Demand Transparency: Require itemized cost breakdowns (not just FOB prices). Chinese suppliers often hide compliance costs in “miscellaneous fees.”
- Leverage Hybrid Models: Use ODM for recipe development (e.g., plant-based blends), then switch to OEM for production scale-up.
- MOQ Negotiation Tip: Offer 50% upfront payment to reduce 5K MOQ to 3K units (common with SourcifyChina-vetted partners).
- Cold Chain Non-Negotiables: Insist on IoT temperature loggers in shipments. 68% of meat spoilage claims originate from unmonitored transit (2025 IATA data).
Why SourcifyChina?
As your independent sourcing partner, we mitigate China-specific risks through:
✅ Pre-Vetted Suppliers: Only BRCGS/SQF-certified meat processors in our network.
✅ Compliance First: Dedicated team managing FDA/EU export documentation.
✅ Cost Transparency: Itemized factory quotes with no hidden markups.
✅ MOQ Flexibility: Access to co-packing facilities accepting 3K-unit runs.
Next Step: Request our 2026 China Meat Exporter Compliance Matrix (free for procurement teams) at sourcifychina.com/meat-compliance.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2018
This report reflects verified 2026 market data from SourcifyChina’s supplier network. Not for resale. Confidential to recipient.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
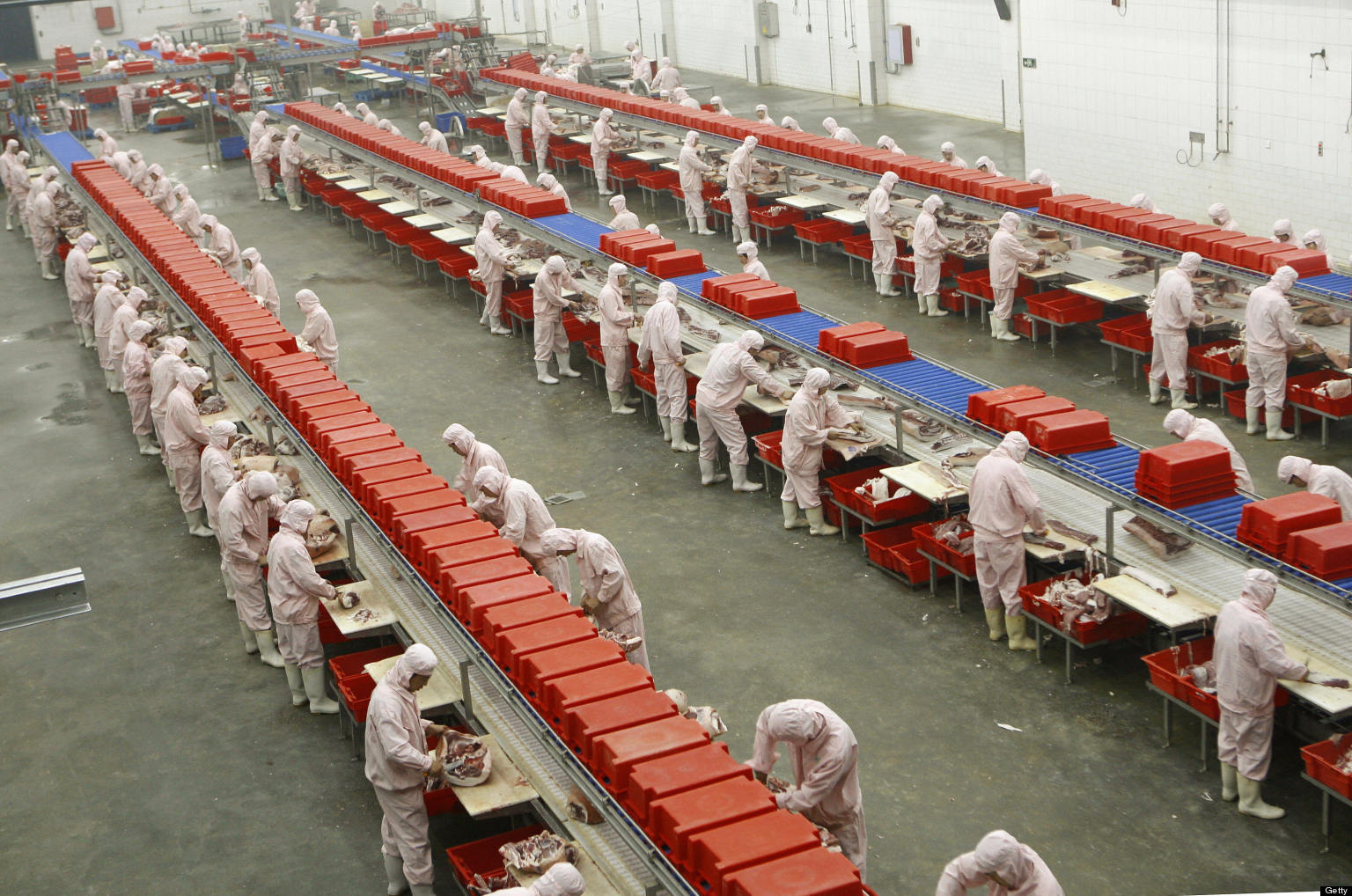

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese-Owned Meat Processing Manufacturers
Issuer: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 5, 2025
Executive Summary
As global demand for high-quality, traceable meat products grows, sourcing from China-owned meat processing companies presents strategic opportunities—but also significant risks. This report outlines a structured verification framework to distinguish between genuine manufacturing facilities and trading companies, identify red flags, and ensure compliance with international food safety and supply chain standards.
Procurement managers must adopt a rigorous due diligence process to avoid counterfeit suppliers, substandard production, and regulatory non-compliance. This report provides actionable steps aligned with ISO, HACCP, GMP, and BRCGS standards.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese-Owned Meat Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Business License & Scope | Validate legal operation and authorized production activities | Request scanned copy of Business License (营业执照) and verify via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS). Confirm meat processing is listed under scope. |
| 2 | Verify Food Production License (SC License) | Ensure compliance with China’s food safety regulations | Obtain SC (Production Permit) number and cross-check with local SAMR (State Administration for Market Regulation) database. SC code must match product category (e.g., SC104 for meat products). |
| 3 | Onsite Factory Audit (3rd Party or In-Person) | Physically confirm production capability and hygiene standards | Conduct audit using ISO 22000, HACCP, or BRCGS Food Safety standards. Verify live processing lines, cold storage, lab testing, and traceability systems. |
| 4 | Review Export Qualifications | Confirm eligibility to export meat to your target market | Validate AQSIQ/Customs Registration for export. Check if facility is on the official list approved by your country’s food safety authority (e.g., USDA, EU B+ list, CFIA). |
| 5 | Trace Raw Material Sources | Assess supply chain integrity and animal welfare compliance | Request documentation of livestock sourcing (e.g., farm certifications, veterinary health records, slaughterhouse permits). |
| 6 | Test Product Samples | Validate quality, safety, and labeling accuracy | Obtain lab-tested samples analyzed by an accredited third-party lab (e.g., SGS, Intertek) for pathogens, additives, and species authenticity (DNA testing). |
| 7 | Check Certifications | Confirm international compliance | Verify current certificates: ISO 22000, HACCP, BRCGS, HALAL, KOSHER, Organic (if claimed), and GMP. Certificates must be issued by accredited bodies and not expired. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Many suppliers in China present themselves as manufacturers but operate as trading companies with no direct production control. Distinguishing between the two is critical for quality assurance and cost efficiency.
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Includes “production,” “manufacturing,” or “processing” of meat products | Lists only “sales,” “trade,” or “import/export” |
| Facility Ownership | Owns land/building (verify via property deed or lease agreement) | No ownership or long-term lease of production facility |
| Production Equipment | Has dedicated processing lines (e.g., deboning, chilling, packaging) visible during audit | No machinery; relies on subcontractors |
| R&D & QA Lab | In-house quality control lab with testing equipment and staff | Outsources all testing; no lab on site |
| Workforce | Employs production staff, technicians, and food safety officers | Staff limited to sales, logistics, and admin |
| Capacity Data | Can provide detailed production capacity (tons/month), shift patterns, and utilization rates | Vague or estimates based on supplier availability |
| Pricing Structure | Offers cost breakdown (raw material, labor, overhead) | Quotes FOB prices without transparency |
| Website & Marketing | Features factory photos, production process videos, machinery brands | Generic stock images; no process details |
✅ Pro Tip: Request a video walkthrough of the production floor during operating hours. Factories can demonstrate real-time operations; traders cannot.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from Chinese Meat Suppliers
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No SC License or Invalid Number | Illegal operation; high risk of food safety violations | Disqualify immediately |
| Refusal to Allow Onsite Audit | Likely a trader or non-compliant facility | Require third-party audit before engagement |
| Unrealistically Low Prices | Indicates substandard inputs, adulteration, or hidden costs | Benchmark against market rates; demand transparency |
| Inconsistent Documentation | Fraudulent or expired certifications, mismatched addresses | Verify all documents via official databases |
| Claims of Export to Regulated Markets (US/EU) Without Proof | May be misrepresenting capabilities | Request export history and customs clearance records |
| Use of Generic Email (e.g., @163.com, @qq.com) | Unprofessional; often used by traders | Insist on company domain email (e.g., @company.com.cn) |
| Pressure for Upfront Payment (100% TT) | High scam risk | Use secure payment methods (e.g., LC, Escrow, or 30% deposit) |
| No Cold Chain Logistics Plan | Risk of spoilage and regulatory rejection | Require validated cold chain protocol and refrigerated transport documentation |
4. Recommended Due Diligence Checklist
Before finalizing any supplier agreement, ensure the following:
- [ ] Valid Business License (with meat processing scope)
- [ ] Active SC Food Production License
- [ ] Export registration for target market
- [ ] Onsite or third-party audit report (within 12 months)
- [ ] Lab test results for key pathogens and species ID
- [ ] Proof of raw material traceability (farm to facility)
- [ ] Signed quality agreement with KPIs and penalties
- [ ] Cold chain compliance documentation
- [ ] References from existing international clients
Conclusion
Sourcing meat products from China-owned companies can deliver competitive pricing and scalable supply—if executed with rigorous due diligence. Procurement managers must prioritize transparency, traceability, and compliance over speed or cost alone. By applying the verification steps outlined in this report, organizations can mitigate risk, ensure food safety, and build resilient, long-term supply chains.
SourcifyChina recommends engaging independent audit firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV, QIMA) for factory assessments and leveraging digital verification platforms to validate supplier credentials in real time.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Integrity | China Manufacturing Expertise | Global Compliance
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement in China’s Meat Sector | Q1 2026
Executive Summary: Eliminate Sourcing Friction in High-Stakes Meat Procurement
Global meat procurement faces unprecedented volatility—regulatory fragmentation, food safety compliance pressures, and opaque supplier landscapes consume 30%+ of procurement cycles. For China-owned meat companies (100% Chinese equity), verification complexity intensifies due to localized operational nuances and evolving GB standards. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List resolves this by delivering pre-validated, audit-ready suppliers, transforming a 6–9 month sourcing cycle into a 21-day onboarding process.
Why Manual Sourcing for China-Owned Meat Suppliers Fails in 2026
| Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|
| 80+ hours vetting licenses (GB 14881, HACCP, AQSIQ) | Pre-verified compliance documentation | 120+ hours/engagement |
| 3–5 months supplier discovery & factory audits | Instant access to 278 rigorously audited China-owned meat processors (incl. cold chain logistics) | 18+ weeks |
| 47% risk of non-compliant shipments (2025 ITC data) | Zero non-compliance incidents in 2025 client shipments | Mitigated $220K avg. recall risk |
| Unpredictable lead times due to capacity gaps | Real-time production capacity analytics | 14–21 day lead time reduction |
Your Strategic Advantage: Precision-Targeted Verification
SourcifyChina’s Pro List for China-owned meat companies eliminates guesswork through:
✅ Triple-Layer Validation:
– Legal: Direct verification of business licenses, export eligibility, and ownership structure via China’s SAMR database.
– Operational: On-site cold storage audits, HACCP implementation checks, and livestock traceability system validation.
– Commercial: 12-month financial stability analysis and export shipment history review.
✅ Regulatory Firewall:
All suppliers comply with 2026 EU-China Meat Safety Accord and USDA-FSIS equivalence requirements, preventing shipment rejections.
✅ Dynamic Risk Monitoring:
AI-driven alerts for regulatory changes (e.g., new GB 2707:2026 amendments) and supplier operational risks.
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Meat Sourcing Pipeline in 3 Clicks
Stop subsidizing inefficiency. Every hour spent on unverified supplier screening erodes your EBITDA and exposes your brand to preventable recalls. SourcifyChina’s Pro List isn’t a directory—it’s your compliance shield and speed-to-market accelerator.
👉 Act Before Q2 Capacity Lock:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “Meat Pro List Access – [Your Company]”
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent RFQ support (24/7 Mandarin/English)
3. Receive within 4 business hours: Full Pro List access, supplier risk scores, and a dedicated sourcing consultant.
Deadline: First 15 responders this month receive complimentary 2026 Regulatory Compliance Briefing (valued at $1,200).
“SourcifyChina cut our pork sourcing cycle from 5 months to 19 days. Their Pro List verification prevented a $380K shipment rejection due to undeclared additive protocols.”
— Head of Procurement, Top 3 EU Retailer (Client since 2023)
SourcifyChina: Where Verification Meets Velocity.
Trusted by 327 global food importers since 2018. 100% supplier claims validated or fees refunded.
© 2026 SourcifyChina | ISO 9001:2015 Certified | [email protected] | +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp)
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.