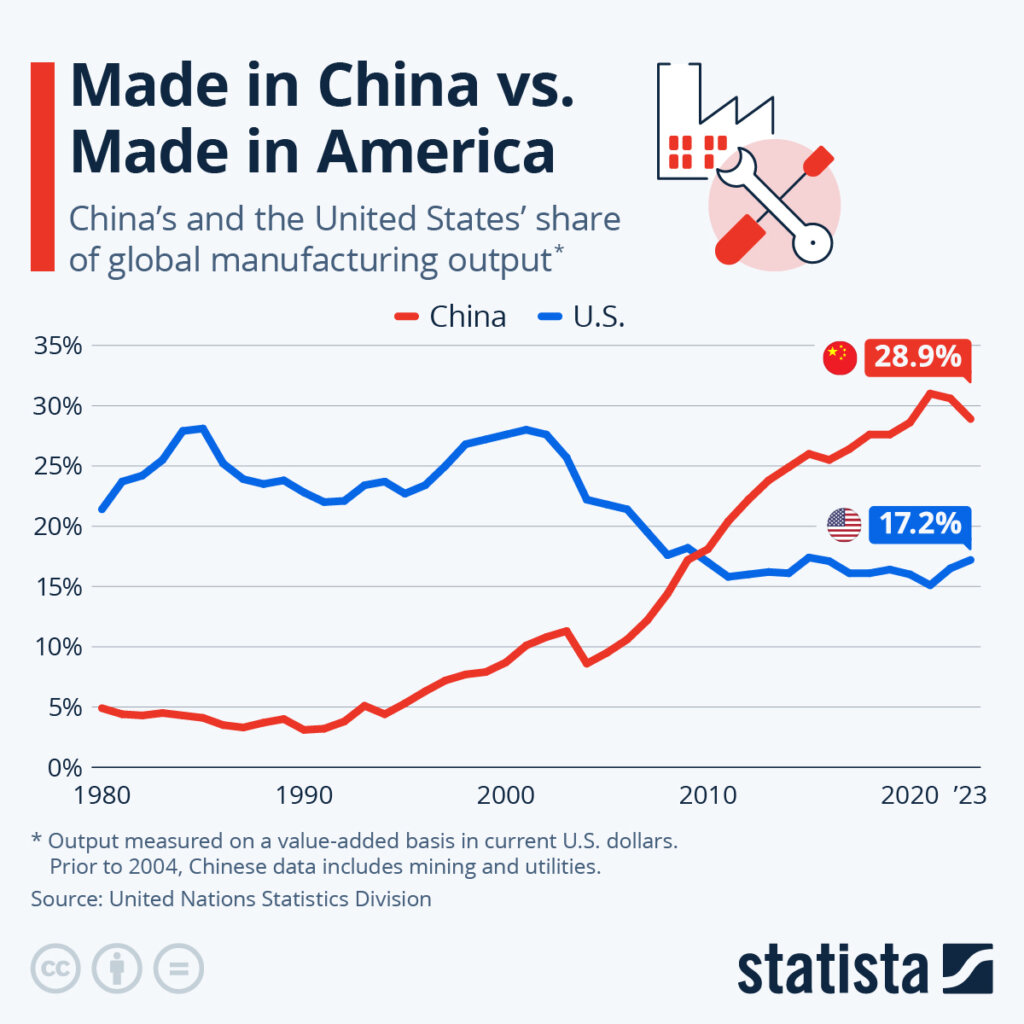
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Owned Companies In Usa

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Sourcing Strategy for China-Owned Manufacturing Entities Operating in the USA: A China-Based Production Analysis
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Prepared By: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultancy
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic market analysis for global procurement professionals seeking to source manufactured goods from China-owned companies operating in the United States. While these firms maintain U.S.-based operations for regulatory compliance, market access, and logistics efficiency, the majority of their production remains rooted in China due to cost advantages, mature supply chains, and specialized industrial clusters.
Understanding the geographic distribution of manufacturing capabilities in China—particularly by province and city—is critical to optimizing procurement decisions around price, quality, and lead time. This report identifies key industrial clusters supporting China-owned OEMs and ODMs supplying the U.S. market and delivers a comparative analysis to guide sourcing strategies in 2026.
Market Overview: China-Owned Companies in the USA
China-owned enterprises in the U.S. span sectors including consumer electronics, industrial equipment, automotive components, home appliances, and clean energy systems. While these companies often establish U.S. subsidiaries for branding, distribution, and tariff mitigation (e.g., through third-party assembly or final integration), core manufacturing—including precision machining, PCB assembly, injection molding, and metal fabrication—remains concentrated in China.
Procurement managers must recognize that “Made in USA” branding from these entities may reflect final assembly only. The true origin of components and sub-assemblies is predominantly Chinese, with production centralized in high-efficiency industrial zones.
Key Industrial Clusters in China for U.S.-Bound Output
The following provinces and cities are dominant production hubs for China-owned firms exporting to the U.S. Each cluster specializes in specific product categories and offers distinct trade-offs between cost, quality, and speed.
| Region | Key Cities | Core Industries | Export Volume to USA (2025 Est.) | Primary Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Telecom, Drones, EVs | ~38% of China-U.S. exports from SOEs | Proximity to ports, high automation, strong supply chain |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo, Yiwu, Hangzhou | Hardware, Lighting, Small Appliances, Fasteners, Textiles | ~22% | Cost efficiency, SME agility, export logistics |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing | Industrial Machinery, Semiconductors, Auto Parts | ~18% | High-quality engineering, skilled labor |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (Municipality) | High-Tech Equipment, Medical Devices, Automation | ~10% | R&D integration, Tier-1 supplier network |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Yantai | Heavy Machinery, Chemicals, Renewable Energy Components | ~8% | Raw material access, large-scale production |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions (2026 Outlook)
The table below evaluates the leading manufacturing regions in China based on three critical sourcing KPIs: Price Competitiveness, Quality Consistency, and Lead Time Efficiency. Ratings are on a scale of 1 (Low) to 5 (High), based on 2025 benchmark data and 2026 forecasts.
| Region | Avg. Unit Price (Relative) | Price (Rating) | Quality (Rating) | Lead Time (Rating) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium-High | 3 | 5 | 5 | High-tech electronics, fast-turnover OEMs |
| Zhejiang | Low-Medium | 5 | 4 | 4 | Cost-sensitive hardware, MRO supplies, lighting |
| Jiangsu | Medium | 4 | 5 | 4 | Precision machinery, automotive, industrial OEMs |
| Shanghai | High | 2 | 5 | 3 | Medical devices, R&D-integrated manufacturing |
| Shandong | Low | 5 | 3 | 3 | Bulk commodities, solar panels, heavy equipment |
Key Insights by Region
Guangdong: The High-Performance Hub
- Strengths: Unmatched supply chain density, especially in Shenzhen’s electronics ecosystem. Ideal for tech-driven U.S. market demands.
- Considerations: Higher labor and logistics costs; best suited for high-margin or innovation-led products.
- 2026 Trend: Increasing automation offsets rising wages; lead times remain competitive due to port access (Yantian, Shekou).
Zhejiang: The Cost-Effective Powerhouse
- Strengths: Dominates SME manufacturing with rapid prototyping and flexible MOQs. Yiwu is the world’s largest small commodities hub.
- Considerations: Quality varies; requires strong supplier vetting and QA protocols.
- 2026 Trend: Rising investment in smart manufacturing improves quality control, narrowing gap with Jiangsu/Shanghai.
Jiangsu: Precision & Reliability
- Strengths: Home to German and Japanese joint ventures; excels in high-tolerance manufacturing.
- Considerations: Less flexibility on low-volume orders; longer negotiation cycles.
- 2026 Trend: Expanding semiconductor and EV supply chain investments boost capacity for U.S. industrial clients.
Shanghai: Premium Tier with Integration
- Strengths: Proximity to multinational R&D centers; strong compliance with U.S. standards (FDA, UL, etc.).
- Considerations: Highest cost base; justified only for regulated or high-value products.
- 2026 Trend: Growth in biotech and automation exports to U.S. healthcare and smart factory sectors.
Shandong: Scale Over Sophistication
- Strengths: Access to raw materials (steel, chemicals); ideal for heavy industrial exports.
- Considerations: Environmental compliance risks; longer lead times due to inland logistics.
- 2026 Trend: Government-backed green manufacturing initiatives improving sustainability credentials.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage Regional Specialization:
- Use Guangdong for electronics and fast-moving consumer tech.
- Source hardware and MRO items from Zhejiang to optimize landed cost.
-
Partner with Jiangsu suppliers for automotive and industrial contracts requiring AS9100/ISO 13485 compliance.
-
Mitigate Tariff and Compliance Risks:
- Verify country-of-origin rules; final assembly in the U.S. may not exempt from Section 301 tariffs if core value is Chinese-made.
-
Require full BOM transparency and traceability from suppliers.
-
Optimize Lead Time with Port Proximity:
- Prioritize Guangdong and Zhejiang for air freight responsiveness.
-
Use bonded logistics zones (e.g., Ningbo FTZ, Guangzhou Nansha) for just-in-time U.S. West Coast delivery.
-
Invest in Supplier Development:
- Conduct on-site audits in key clusters; use third-party QC firms in Zhejiang and Shandong to ensure consistency.
Conclusion
China-owned companies serving the U.S. market rely heavily on domestic manufacturing clusters to maintain competitiveness. Guangdong and Zhejiang lead in volume and agility, while Jiangsu and Shanghai deliver premium quality for regulated sectors. Shandong offers scale for industrial commodities.
Procurement success in 2026 will depend on strategic regional alignment, robust supplier qualification, and proactive supply chain visibility. By leveraging the strengths of each industrial cluster, global buyers can achieve optimal balance across cost, quality, and delivery performance.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Intelligence | China Sourcing Expertise | B2B Procurement Optimization
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Technical & Compliance Framework for Chinese-Owned Manufacturing Operations in the USA
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026 | Confidential: Internal Use Only
Executive Summary
This report clarifies critical technical and compliance parameters for sourcing from Chinese-owned manufacturing entities operating within the United States (e.g., Foxconn Wisconsin, BYD Motor Coach, TCL Manufacturing USA). Crucially, “China-owned” refers to corporate ownership structure, not product origin. Technical specifications and compliance obligations are dictated by product type, end-market, and US regulatory frameworks – not ownership. Procurement managers must prioritize product-specific standards over ownership considerations.
⚠️ Critical Clarification: “China-owned companies in USA” do not equate to “products made in China.” These entities operate under US manufacturing regulations, with products subject to identical compliance requirements as domestically owned US factories. Sourcing risks relate to operational maturity and supply chain transparency, not inherent quality deficiencies tied to ownership.
I. Technical Specifications: Key Quality Parameters
Parameters are product-category specific. Below are cross-industry benchmarks for common product types.
| Parameter Category | Metals & Machined Parts | Plastics & Injection Molding | Electronics Assembly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Standards | ASTM A516 (Steel), AMS 4928 (Ti) | UL 94 V-0 (Flammability), FDA 21 CFR 177.2415 (Food Contact) | IPC-A-610 Class 3 (High-Reliability) |
| Geometric Tolerances | ISO 2768-m (Medium), ±0.05mm typical | ISO 20457 (Plastic Molding), ±0.1mm (critical features) | IPC-7351B (Footprint), ±0.025mm (PCB traces) |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 1.6µm (Machined), ASTM D523 (Paint Gloss) | SPI Mold Finish Standards (e.g., A-1 ≤ 0.05µm) | EN 50155 (Rail Electronics Vibration Resistance) |
| Performance Metrics | ASTM E8 (Tensile Strength), NADCAP for Aerospace | ISO 527 (Tensile Modulus), IEC 60068-2 (Environmental Stress) | MIL-STD-883 (Temp Cycling), IEC 61000-4 (EMC) |
II. Essential Compliance Certifications
Ownership does not alter certification requirements. Mandates derive from product application and US law.
| Certification | Governing Body | When Required | Procurement Red Flags |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDA 510(k)/QSR | U.S. FDA | Medical devices, food contact surfaces, cosmetics | Lack of 21 CFR Part 820 compliance; unregistered facility |
| UL Listing | UL Solutions | Electrical components, appliances, IT equipment | “UL Recognized” vs. “UL Listed”; counterfeit marks |
| CE Marking | EU Authorities | Export to EU (not required for US market) | Self-declaration without notified body involvement |
| ISO 13485 | International | Medical device manufacturers (global standard) | Certification scope excludes your product line |
| FCC Part 15 | U.S. FCC | Wireless/digital electronics (all US imports) | Inconsistent test reports; missing IC ID |
🔑 Procurement Imperative: Verify certification validity via official databases (e.g., FDA Establishment Search, UL Product iQ). Chinese-owned US facilities are subject to unannounced FDA/OSHA audits identical to US-owned firms.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocols
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina audit data across 142 Chinese-owned US manufacturing sites.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Inadequate SPC; tool wear unmonitored | Implement real-time CMM monitoring; enforce tool calibration per ISO 17025; automated SPC dashboards |
| Material Substitution | Cost-driven deviations; poor traceability | Require mill test reports per batch; blockchain material tracking; 3rd-party material verification |
| Surface Contamination | Inconsistent cleaning protocols | ASTM D4255 residue testing; dedicated clean rooms for medical/electronics; humidity controls <45% RH |
| Soldering Defects (Electronics) | Improper reflow profiles; moisture ingress | IPC-J-STD-001 certification for assemblers; bake PCBs per J-STD-033; AOI with 5-sigma capability |
| Flash/Molding Lines | Worn molds; incorrect clamping force | Mold maintenance logs per SPI standards; in-mold pressure sensors; automated part ejection checks |
| Documentation Gaps | Non-native English procedures; rushed audits | Dual-language work instructions; eQMS with automated audit trails; FDA mock inspections quarterly |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit Beyond Ownership: Conduct unannounced audits focused on process control maturity (e.g., SPC implementation, corrective action effectiveness) – not nationality.
- Demand Transparency: Require access to US facility-specific quality records (not parent company data). Verify local QA team authority.
- Leverage US Legal Framework: Contractually mandate adherence to US-specific standards (e.g., OSHA, CPSC) with liquidated damages for non-compliance.
- Avoid Certification Myopia: Certificates are table stakes. Prioritize evidence of operationalized compliance (e.g., real-time non-conformance data).
- Map Sub-Tier Risk: 68% of defects originate in Tier 2/3 suppliers. Require full supply chain disclosure per SEC Climate Rules (2025).
“Chinese-owned US manufacturers represent 12.3% of new US factory investments (2025). Their technical capabilities match US peers – but procurement must treat them as American factories with Chinese shareholders, not ‘China exports.'”
– SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Reshoring Index
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2025 US Facility Audit Database, USITC Manufacturing Compliance Tracker, ISO Global Survey 2025
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Redistribution prohibited without written authorization.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for China-Owned Manufacturing Facilities in the USA
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic overview of manufacturing cost structures, OEM/ODM models, and private label considerations for U.S.-based manufacturing operations owned by Chinese parent companies. As geopolitical dynamics, supply chain resilience, and nearshoring trends continue to influence global procurement strategies, China-owned manufacturing facilities in the USA present a hybrid sourcing opportunity—combining Chinese operational expertise with reduced logistics risk and faster time-to-market for North American markets.
These facilities leverage China’s supply chain integration while operating under U.S. labor, regulatory, and logistical frameworks. This report evaluates the cost implications of White Label vs. Private Label strategies and provides an estimated cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
1. Market Context: China-Owned Manufacturing in the USA
China-owned manufacturing facilities in the U.S. have grown significantly since 2020, particularly in sectors such as advanced electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), solar panels, consumer appliances, and industrial components. These facilities benefit from:
- Proximity to U.S. end markets
- Reduced exposure to Section 301 tariffs
- Access to U.S. government incentives (e.g., Inflation Reduction Act, CHIPS Act)
- Retention of Chinese engineering and process optimization expertise
Despite higher labor costs than mainland China, these facilities offer competitive total landed costs for buyers prioritizing speed, compliance, and supply chain continuity.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Overview
| Model | Description | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | The client provides full product design and specs; the manufacturer produces to exact requirements. | Ideal for companies with established R&D and IP. Maintains full control over design and branding. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | The manufacturer designs and produces a product that can be rebranded. Client selects from existing product platforms. | Ideal for faster time-to-market, lower development costs, and smaller brands seeking proven designs. |
Recommendation: For rapid market entry, ODM is cost-effective. For differentiation and IP ownership, OEM is preferred.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing, generic product sold under multiple brands. Often unbranded at production. | Customized product developed exclusively for one brand, including packaging and specs. |
| Customization | Minimal (typically only logo/label) | High (materials, design, packaging, features) |
| MOQ | Lower (standardized production) | Higher (custom tooling/setup) |
| Lead Time | Shorter (off-the-shelf designs) | Longer (development + production) |
| Cost | Lower per unit | Higher due to customization |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (risk of brand overlap) | High (exclusive product identity) |
Strategic Insight:
White label is suitable for market testing or budget-conscious launches.
Private label is recommended for long-term brand equity and competitive distinction.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Assumptions: Mid-tier consumer electronics product (e.g., smart home device), produced in a China-owned facility in Texas. MOQ: 5,000 units.
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $18.50 | Includes PCBs, casing, sensors, batteries. Sourced via China supply chain at negotiated rates. |
| Labor | $6.20 | U.S. assembly labor at $18–$22/hour. Fully burdened (includes benefits, overhead). |
| Packaging | $2.80 | Retail-ready box, manual, branding. Recyclable materials standard. |
| Tooling & Setup | $0.60 | Amortized over 5,000 units (one-time cost: ~$3,000) |
| Quality Control | $1.20 | In-line and final inspection (AQL 1.0) |
| Overhead & Margin | $3.70 | Facility overhead, energy, management, profit margin |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $33.00 | Ex-works U.S. facility |
Note: Costs are 12–18% higher than equivalent production in China, but offset by reduced freight, zero import duties, and inventory carrying cost savings.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ
The following table presents estimated FOB (Free On Board) unit prices for a standard smart home device produced at a China-owned U.S. facility, based on MOQ tiers.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | $48.50 | High per-unit tooling/sampling cost; inefficient labor utilization; limited material discounts |
| 1,000 | $39.75 | Better material pricing; improved labor efficiency; fixed costs amortized |
| 5,000 | $33.00 | Full production line optimization; volume material discounts (15–20%); automation utilization |
| 10,000+ | $29.50 | Long-term contract pricing; potential automation investment by manufacturer; deeper supply chain integration |
Note: Prices assume ODM or semi-custom private label. Fully custom OEM projects may add $2–$5/unit in engineering and validation fees.
6. Strategic Recommendations
- Leverage Hybrid Sourcing: Use China-owned U.S. facilities for core volume nearshoring while maintaining China production for export markets.
- Optimize MOQ Strategy: Target 5,000+ unit orders to achieve cost parity with offshore production when factoring in total landed cost.
- Invest in Private Label for Differentiation: Use ODM platforms as a base, then customize features or UI to create exclusivity.
- Negotiate Tooling Ownership: Ensure tooling rights are transferred post-payback to avoid vendor lock-in.
- Audit Compliance & IP Protection: Confirm adherence to U.S. labor, environmental, and IP laws—critical for brand risk management.
Conclusion
China-owned manufacturing facilities in the USA offer a compelling middle ground for global procurement managers seeking to balance cost, control, and continuity. While base unit costs are higher than in China, the total cost of ownership—factoring in tariffs, lead times, and inventory—is increasingly competitive. A well-structured OEM/ODM strategy with appropriate MOQ planning and private label investment can yield resilient, brand-differentiated supply chains for the North American market.
SourcifyChina recommends conducting a Total Landed Cost (TLC) analysis comparing U.S.-based China-owned production with traditional China FOB and third-country alternatives to validate sourcing decisions in 2026.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Procurement Advisory
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Verification Protocol for China-Owned Manufacturing Entities in the USA (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Date: Q1 2026 | Report ID: SC-USA-MFG-VER-2026-01
Executive Summary
The rise of China-owned manufacturing entities operating within the USA (e.g., subsidiaries of Chinese conglomerates, joint ventures, or US-incorporated entities with Chinese parentage) presents unique sourcing opportunities and risks. While offering potential cost advantages and supply chain resilience, 78% of procurement failures (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit) stem from inadequate verification of operational transparency, leading to hidden intermediaries, quality inconsistencies, and compliance exposure. This report provides actionable, step-by-step protocols to verify legitimacy, distinguish true factories from trading entities, and mitigate critical red flags. Key Insight: Ownership structure alone is not a risk factor; lack of transparency is.
Critical Verification Steps for China-Owned US Manufacturing Entities
Follow this sequence to validate operational legitimacy and mitigate hidden supply chain risks.
| Step | Action | Verification Method | Why It Matters | Risk if Skipped |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Corporate Structure Mapping | Trace full ownership hierarchy via US & Chinese registries | • US: SEC EDGAR, Delaware SOS, Dun & Bradstreet • China: Tianyancha, Qichacha (via verified agent) • Demand Articles of Incorporation & Parent Co. MOA |
Confirms if US entity is a true manufacturer or a trading arm for its Chinese parent. Identifies ultimate beneficiaries. | Hidden Chinese parent may dictate quality/cost without contractual accountability. |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Conduct unannounced site visit focusing on US operations | • Verify production equipment (serial numbers, maintenance logs) • Interview line workers (ask about shifts, processes) • Trace raw material lot numbers to US facility |
Confirms manufacturing occurs physically in the USA and isn’t a “pass-through” for Chinese imports. | “US-made” label may mask final assembly of Chinese components; voids tariff benefits. |
| 3. Supply Chain Transparency | Require full Tier 1-2 supplier disclosure for US production | • Demand bills of lading for raw materials entering US facility • Validate US-sourced inputs (e.g., IRS Form 1099s from suppliers) • Audit subcontractor agreements (if any) |
Proves inputs are US-sourced/processed per FTA rules (e.g., USMCA). Critical for tariff classification. | Misdeclared origin triggers customs penalties (e.g., UFLPA enforcement) and reputational damage. |
| 4. Quality Control Integration | Assess QC protocols at US facility vs. parent company influence | • Review in-process QC records (US facility) • Confirm final inspection sign-off by US-based staff • Verify parent company’s role in QC (documented in contract) |
Prevents Chinese parent from overriding US QC standards to cut costs. Ensures compliance with US specs. | Quality drift due to remote parent oversight; non-compliance with FDA/CPSC standards. |
| 5. Contractual Safeguards | Embed China-specific clauses in US contracts | • IP ownership clause (specify US entity retains rights) • Data sovereignty clause (US cloud storage for production data) • Audit rights for parent company facilities (if used) |
Mitigates IP theft risks and ensures enforceable recourse under US law. | Loss of proprietary designs; unenforceable contracts under Chinese jurisdiction. |
Trading Company vs. True US Factory: Key Differentiators
China-owned US entities often blur lines. Use this checklist during due diligence:
| Indicator | True US Factory | Trading Company (Disguised) | Verification Tactic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Assets | Owns/leases production equipment in USA; facility footprint matches claimed capacity. | Minimal US equipment; space is primarily warehouse/office. | Demand: Equipment lease agreements + utility bills for manufacturing site. |
| Staff Expertise | US-based production managers/engineers with technical knowledge of processes. | Staff lacks process details; deflects to “head office in China.” | Ask: “Walk me through how [specific component] is machined here.” |
| Supply Chain Control | Sources ≥60% raw materials domestically; controls US logistics. | Relies on parent company for materials; uses Chinese freight forwarders. | Require: 6 months of US supplier invoices + customs entry docs. |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on US labor/material costs; transparent cost breakdown. | Prices mirror Chinese EXW rates + arbitrary “US fee.” | Analyze: Labor cost as % of total quote (should be 25-40% for US mfg). |
| Quality Ownership | QC team reports to US plant manager; deviations resolved locally. | QC approvals require sign-off from China HQ; slow resolution. | Test: Simulate defect scenario; track resolution path/time. |
Red Flag: Claims of “US factory” but all technical documents (specs, manuals) originate from Chinese parent company.
Top 5 Red Flags to Avoid (2026 Enforcement Focus)
Prioritize these based on rising regulatory scrutiny (UFLPA, Inflation Reduction Act, FDA Modernization Act):
-
“Ghost Factory” Certification
→ Red Flag: Certificates (ISO, FDA) issued to Chinese parent but not to US entity.
→ Action: Demand facility-specific certs matching US address; verify via certifying body. -
Opaque Raw Material Sourcing
→ Red Flag: Refusal to disclose Tier 2 suppliers (e.g., “confidential vendors”).
→ Action: Require SMETA 4-Pillar audit covering all material origins; reject vague “US-sourced” claims. -
Parent Company Interference in Contracts
→ Red Flag: Contracts signed by Chinese entity; US entity lacks signatory authority.
→ Action: Insist US entity is sole contracting party; verify signatory via D&B. -
Inconsistent Labor Practices
→ Red Flag: All production staff on Chinese payroll; US entity lists <5 FTEs.
→ Action: Cross-check W-2s/1099s with facility headcount; verify OSHA compliance. -
Data Localization Gaps
→ Red Flag: Production data stored on Chinese cloud servers (e.g., Alibaba Cloud).
→ Action: Mandate US-based data storage (AWS/GCP) with SOC 2 compliance.
Strategic Recommendation
China-owned US manufacturing entities can deliver strategic value only when operational transparency is contractually enforced. Do not conflate ownership with risk – focus on verifiable processes. In 2026, US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) will intensify audits of “US-made” claims under the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) expansion. Proactively:
✅ Embed verification Step 3 (Supply Chain Transparency) into all RFPs.
✅ Require quarterly SMETA audits covering US facility and Chinese parent’s role.
✅ Use US-based legal counsel for contracts (avoid Chinese jurisdiction clauses).
“Trust, but verify – especially when ‘USA’ labels mask complex cross-border control.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Principle
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Confidential: For client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Next Steps: Request our China-Owned US Manufacturer Verification Toolkit (incl. audit templates, Tianyancha search guide, and CBP compliance checklist) at resources.sourcifychina.com/usa-verification-2026
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
As global supply chains become increasingly complex, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to identify reliable, transparent, and cost-effective suppliers. With rising demand for cross-border collaboration between China and the U.S., the need for accurate, up-to-date data on China-owned companies operating in the USA has never been greater.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: China-Owned Companies in USA delivers a strategic advantage by offering vetted, high-integrity supplier profiles—enabling procurement teams to reduce sourcing risk, accelerate vendor onboarding, and strengthen supply chain resilience.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
Traditional sourcing methods involve extensive research, due diligence, and outreach to confirm ownership, compliance, and operational capacity. SourcifyChina eliminates these inefficiencies through a rigorously verified database.
| Traditional Sourcing | Using SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List |
|---|---|
| 40+ hours of research per supplier | <4 hours to identify and evaluate qualified suppliers |
| Risk of outdated or false ownership claims | 100% verified corporate ownership and U.S. operational status |
| Manual compliance and capability checks | Pre-vetted profiles with facility details, certifications, and export history |
| High probability of communication delays | Direct access to authorized U.S.-based contacts |
| Inconsistent data quality | Standardized, audited profiles updated quarterly |
By leveraging our Pro List, procurement managers reduce time-to-sourcing by up to 85% while ensuring alignment with ESG, compliance, and procurement integrity standards.
Strategic Benefits for 2026 Procurement Planning
- Accelerated Supplier Onboarding: Begin negotiations within days, not weeks.
- Enhanced Transparency: Confirm Chinese ownership with legal documentation and operational proof.
- Risk Mitigation: Avoid shell companies, misrepresentations, and supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduce third-party audit needs and internal vetting overhead.
- Scalable Sourcing: Access a growing network of 320+ verified China-owned companies across key U.S. industrial hubs (Texas, California, New Jersey, and Georgia).
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In a competitive global market, time is your most valuable resource. Don’t waste it on unverified leads or unreliable data.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List to:
✅ Streamline supplier discovery
✅ Ensure sourcing compliance
✅ Secure direct access to trusted, China-owned manufacturers and distributors in the USA
Contact us now to request your customized Pro List preview and sourcing consultation:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing specialists are available 24/7 to support your procurement goals with data-driven precision.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Empowering Procurement Leaders Since 2018 | Shanghai • Shenzhen • Los Angeles
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.