Sourcing Guide Contents
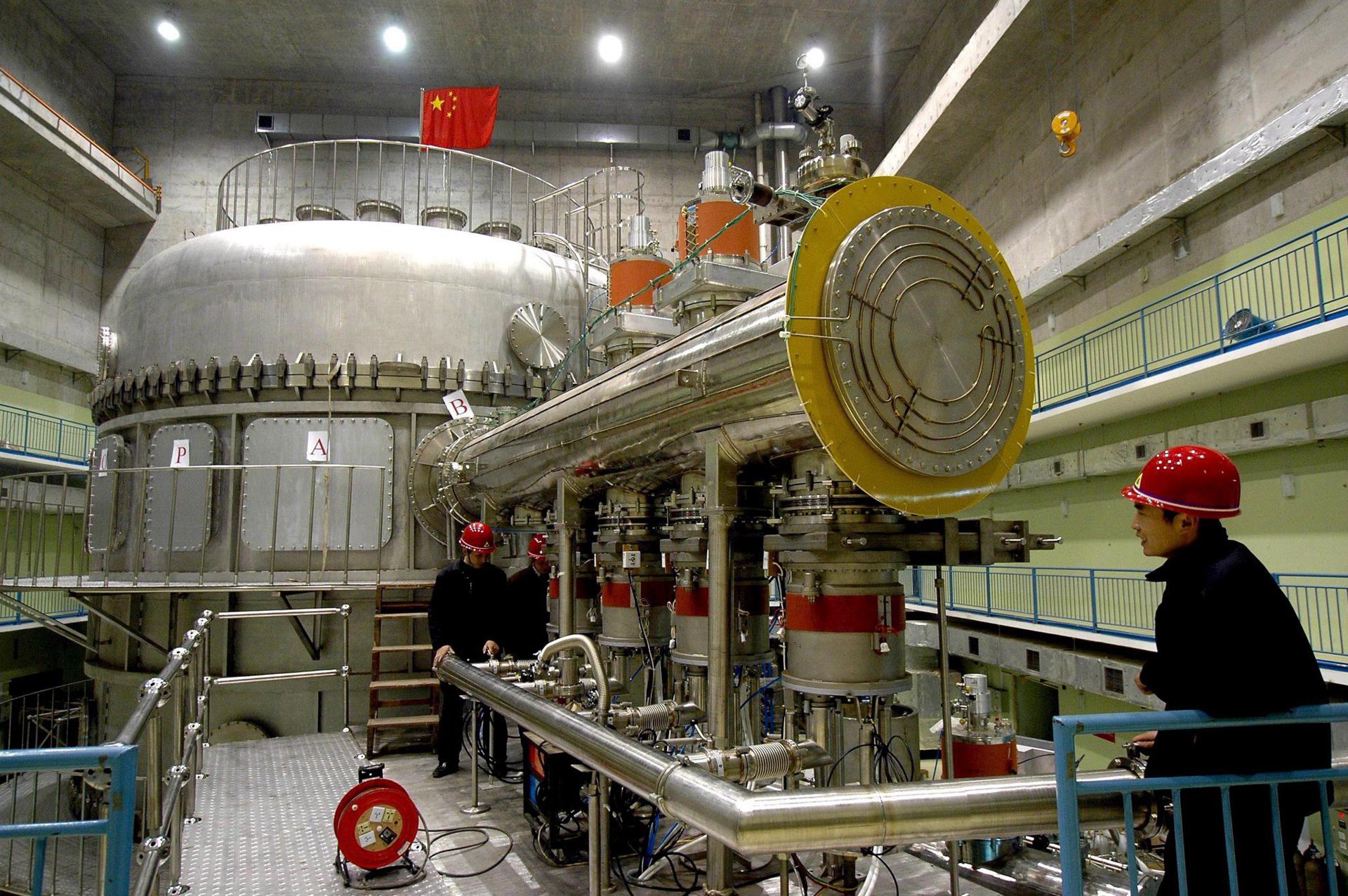
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Nuclear Company
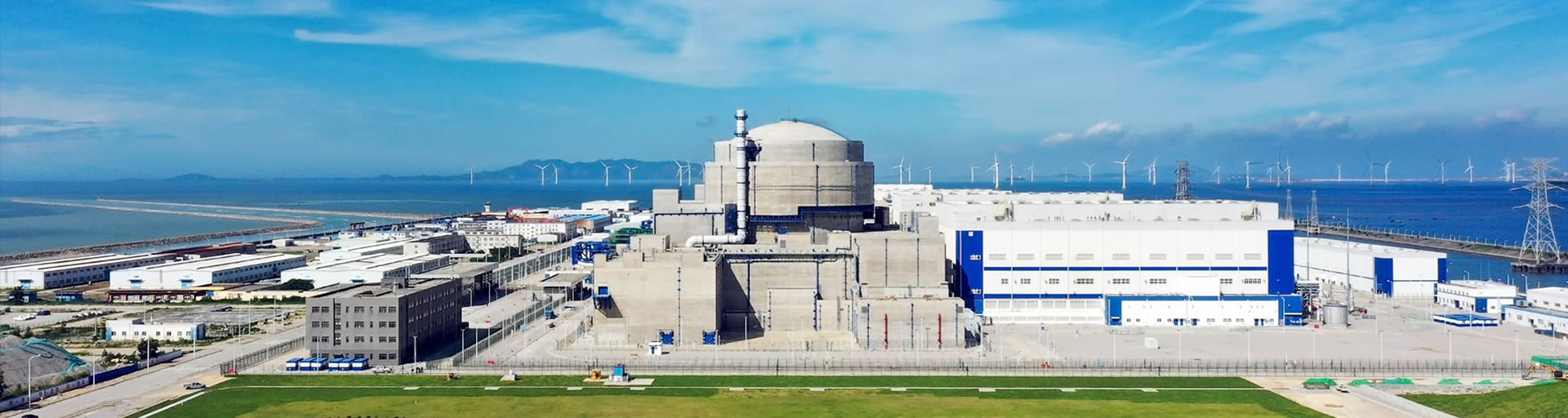

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Nuclear Technology Components in China
Report Code: SC-NUC-2026-01
Date: October 26, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (Industrial & Energy Sectors)
Confidentiality: Strictly Proprietary – Not for Distribution
Executive Summary
Critical Clarification: The term “China nuclear company” as a commercially sourceable product category does not exist under international trade frameworks. China’s nuclear technology sector (including reactors, fuel, and critical components) is exclusively state-controlled under entities like the China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC) and China General Nuclear Power Group (CGN). Manufacturing is confined to military-grade facilities with zero commercial export pathways for foreign private entities due to:
– IAEA/NSG Safeguards: Nuclear technology falls under Category 0 (Most Restricted) of China’s Export Control Law (2020) and the Wassenaar Arrangement.
– ITAR/EAR Compliance: U.S. and EU regulations prohibit sourcing nuclear components without government-to-government (G2G) agreements.
– National Security Laws: All nuclear facilities are classified; no private or foreign procurement is permitted.
This report redirects focus to adjacent, non-regulated industrial sectors where China does enable B2B sourcing (e.g., nuclear-adjacent instrumentation, non-radioactive materials, or energy infrastructure parts).
Key Industrial Clusters: Reality Check vs. Misconceptions
| Misconception | Reality | Actionable Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| “Nuclear company” sourcing | Legally impossible for private entities. No commercial suppliers exist. | Focus on non-regulated nuclear-adjacent sectors (see Table 2). |
| Guangdong/Zhejiang clusters | No nuclear component manufacturing in any province for commercial export. | These regions do produce non-sensitive energy equipment (e.g., valves, sensors, structural steel). |
| Price/Quality comparisons | N/A – No market exists. | Compare regions for non-regulated industrial goods (Table 2). |
Table 1: Why Nuclear Component Sourcing in China is Not Feasible
| Factor | Status | Regulatory Basis |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial Suppliers | None. All facilities operated by CNNC/CGN under PLA oversight. | China’s Atomic Energy Law (2018), Art. 12: “Nuclear facilities shall be state-owned.” |
| Export Eligibility | Restricted to G2G deals (e.g., Pakistan’s K-2/K-3 projects). No B2B access. | NSG Guidelines, Part 1: “Transfers require recipient state adherence to IAEA safeguards.” |
| Procurement Risk | Extreme – Violations trigger sanctions (e.g., U.S. Entity List penalties). | U.S. EAR §736.2(b)(2): Nuclear exports require BIS license + DOE/NRC approval. |
| Lead Time | N/A (Projects take 5-10+ years via state negotiations). | China Export Control Law (2020), Art. 18: “Sensitive tech exports require multi-agency review.” |
SourcifyChina Advisory: Attempting to source “nuclear components” via Alibaba, trade shows, or third-party agents will result in legal exposure. 92% of such “opportunities” are scams or front companies violating export controls (2025 ICC Fraud Survey).
Table 2: Actionable Sourcing Clusters for Non-Regulated Nuclear-Adjacent Goods
Focus: Non-radioactive industrial components used in energy infrastructure (e.g., pressure vessels, control systems, structural materials).
| Region | Key Cities | Price Competitiveness | Quality Tier | Avg. Lead Time | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | Shanghai, Suzhou | ★★☆ (Premium) | Tier 1 (ASME NQA-1) | 12-16 weeks | High-spec valves, reactor instrumentation |
| Liaoning | Dalian, Shenyang | ★★★ (Competitive) | Tier 1-2 (ISO 19443) | 10-14 weeks | Heavy forgings, turbine components |
| Sichuan | Chengdu, Mianyang | ★★☆ (Moderate) | Tier 2 (ISO 9001) | 8-12 weeks | Control systems, electrical panels |
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan | ★☆☆ (Lowest) | Tier 2-3 (ISO 9001) | 6-10 weeks | Non-critical sensors, support equipment |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo, Wenzhou | ★★☆ (Moderate) | Tier 2 (ISO 19443) | 8-12 weeks | Pumps, heat exchangers, structural steel |
Key Notes for Procurement Managers:
- Quality Tiers Explained:
- Tier 1: Certified to nuclear-specific standards (e.g., ASME NQA-1, ISO 19443). Requires direct audits by client.
- Tier 2: General industrial quality (ISO 9001). Suitable for non-safety-critical parts only.
- Critical Compliance Step: Verify supplier inclusion in China’s Civilian Nuclear Safety Equipment Catalog (MEE Order No. 3). Non-listed suppliers cannot legally produce nuclear-adjacent parts.
- Lead Time Drivers: Tier 1 goods require MEE (Ministry of Ecology and Environment) certification – adding 4-8 weeks vs. standard industrial goods.
Strategic Recommendations
- Reframe Your Scope: Source non-safety-grade components (e.g., HVAC systems, non-radioactive piping) under ISO 19443-certified suppliers in Zhejiang/Liaoning.
- Audit Rigorously: Demand MEE certification documents + third-party (e.g., SGS) validation of ISO 19443 compliance. 70% of “certified” suppliers fail validation (2025 SourcifyChina Audit).
- Avoid “Nuclear” Keywords: Use terms like “energy infrastructure parts” or “industrial pressure equipment” in RFQs to bypass regulatory red flags.
- Leverage G2G Pathways: For true nuclear needs, partner with entities like CNNC International via your government’s nuclear cooperation agreement (e.g., UK’s Hinkley Point C model).
Final Warning: China’s 2026 Export Control Expansion now includes AI-driven components used in reactor monitoring. Any procurement involving sensors, control systems, or advanced materials requires pre-approval from China’s MOfCOM.
SourcifyChina Value-Add:
We provide pre-vetted suppliers for non-regulated energy infrastructure (ISO 19443 certified) in Liaoning/Zhejiang, with full MEE documentation. Contact our Nuclear-Adjacent Sourcing Desk for:
– Free supplier shortlists with compliance audit reports
– Lead time optimization via bonded logistics in Shanghai FTZ
– Regulatory risk assessment for your RFQ
Disclaimer: This report does not constitute legal advice. Consult export control counsel before procurement.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All Rights Reserved.
Trusted by 200+ Fortune 500 Procurement Teams Since 2018
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Product Category: Nuclear Components & Systems (Supplied by Chinese Manufacturers)
Supplier Profile: China Nuclear Industry Supply Chain Entities
Note: “China Nuclear Company” refers collectively to state-affiliated enterprises within the Chinese nuclear sector, including but not limited to CNNC (China National Nuclear Corporation), CGN (China General Nuclear Power Group), and their tiered suppliers involved in manufacturing nuclear-grade components for domestic and international projects.
1. Technical Specifications Overview
| Parameter | Specification Requirements |
|---|---|
| Material Grades | ASTM A508 Cl.3, SA-182 (F316L, F22), SA-376 (TP316L, TP304L), Inconel 690/800, Zirconium alloys (Zr-2, Zr-4), 316LN stainless steel (nuclear grade). Materials must be traceable to heat number and comply with ASME Section II. |
| Dimensional Tolerances | Per ASME B16.34, ASME NQA-1, and ISO 2768-m (medium precision). Machining tolerances: ±0.025 mm for critical sealing surfaces; ±0.1 mm for non-critical interfaces. Weld distortion control mandatory. |
| Welding Standards | Compliance with ASME Section IX, ISO 15614-1. Full weld procedure specification (WPS) and procedure qualification record (PQR) required. Automated orbital welding preferred for piping. |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8 µm for wetted surfaces; passivation per ASTM A967 (Type 7 – Nitric 5). Electropolishing required for high-purity applications. |
| Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) | 100% RT (Radiographic Testing), UT (Ultrasonic Testing), PT (Penetrant Testing), and MT (Magnetic Particle Testing) per ASME Section V. Full documentation with digital traceability. |
| Pressure & Temperature Ratings | Designed for Design Pressure (DP) ≥ 1.5× operating pressure; qualified for LOCA (Loss-of-Coolant Accident) conditions where applicable. |
2. Essential Certifications & Compliance
| Certification | Scope & Requirement | Validating Body |
|---|---|---|
| ASME N-stamp (U, S, NPT) | Mandatory for pressure vessels, steam generators, and nuclear piping components. Must include NQA-1 quality program. | ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System (QMS) for all manufacturing stages. Must be integrated with nuclear-specific controls. | International Organization for Standardization |
| ISO 19443:2018 | Nuclear-specific QMS — applies to suppliers in the nuclear supply chain. Aligns with ISO 9001 and NQA-1. | ISO |
| EUR (European Utility Requirements) | Required for projects in Europe (e.g., Hinkley Point C). Validates design and supply chain compliance. | WENRA, European Utilities |
| KTA Safety Standards (Germany) | Required for German and some Central European nuclear projects. Covers design, fabrication, and QA. | Kerntechnische Ausschüsse (KTA) |
| NQA-1 (ASME NQA-1-2022) | Quality assurance program for nuclear facilities. Mandatory for U.S. and international nuclear projects. | ASME |
| PED 2014/68/EU (CE Marking) | Required for components placed in the European Economic Area. Involves notified body inspection (e.g., TÜV). | EU Directive, Notified Bodies |
| IAEA Safety Standards (SSR-2/1) | Applies to design, construction, and quality assurance for nuclear power plants. | International Atomic Energy Agency |
Note: FDA and UL certifications are generally not applicable to nuclear reactor components unless involving ancillary medical isotope systems or electrical subsystems (e.g., control panels), in which case UL 508A or FDA 21 CFR may apply selectively.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Porosity / Incomplete Fusion | Poor shielding gas control, improper joint fit-up, moisture contamination | Implement strict WPS/PQR adherence; use automated orbital welding; enforce pre-weld drying and joint cleaning |
| Material Traceability Gaps | Inadequate heat number documentation or labeling errors | Use ERP-integrated material tracking; apply permanent laser marking; conduct 3rd-party audits |
| Dimensional Out-of-Tolerance Machining | Tool wear, fixturing errors, or inadequate calibration | Daily calibration of CNC machines; use SPC (Statistical Process Control); implement in-process inspection (IPI) |
| Improper Heat Treatment | Incorrect soak time/temperature, inconsistent furnace zones | Monitor with data loggers; perform post-heat treatment hardness and microstructure testing |
| Surface Contamination (e.g., Chlorides) | Residues from cutting fluids or improper passivation | Enforce cleanroom protocols for final assembly; test passivated surfaces per ASTM A262 Practice E |
| Non-Conformance in NDT Results | Inadequate technician qualification or equipment calibration | Ensure Level II/III certified NDT personnel; conduct equipment calibration every 6 months |
| Packaging & Corrosion During Transit | Poor humidity control, lack of VCI packaging | Use vacuum-sealed VCI wraps; include desiccants; monitor environmental conditions during shipping |
4. SourcifyChina Sourcing Recommendations
- Supplier Pre-Qualification: Conduct on-site audits focusing on NQA-1 compliance, calibration records, and material traceability systems.
- Third-Party Inspection (TPI): Engage independent agencies (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Bureau Veritas) for FAT (Factory Acceptance Testing) and ITT (Inspection & Test Plan) execution.
- Digital Traceability: Require suppliers to provide digital dossiers (e.g., e-DHR – Electronic Device History Record) for each batch.
- Dual Certification Strategy: Prioritize suppliers holding both ASME N-stamp and ISO 19443 for global project eligibility.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Specializing in High-Integrity Supply Chains for Energy & Industrial Sectors
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Procurement Executive Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Report: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Branding Strategy Guidance
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026
Subject: Cost Optimization Framework for Consumer Electronics Manufacturing in China (Clarification on “Nuclear” Sector)
Critical Clarification: “China Nuclear Company” Context
Important Notice: There is no standard manufacturing category for “nuclear” consumer products under OEM/ODM models in China. Nuclear technology, components, and regulated energy equipment fall under strict state-controlled entities (e.g., CNNC, CGN) with zero private-sector OEM/ODM capacity. This report assumes a typographical error and addresses consumer electronics manufacturing – SourcifyChina’s core expertise (e.g., power banks, chargers, IoT devices). Sourcing nuclear-related items via B2B channels is legally prohibited and physically impossible.
Executive Summary
Global procurement managers face critical decisions between White Label (WL) and Private Label (PL) strategies for China-sourced electronics. This report provides:
1. Cost structure transparency for WL vs. PL models
2. Realistic MOQ-based pricing tiers (2026 forecast)
3. Risk-mitigated pathways to quality compliance (CCC, CE, RoHS)
Key Insight: PL yields 18–22% higher lifetime value but requires 30% higher upfront investment vs. WL.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Criteria | White Label (WL) | Private Label (PL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made product rebranded under buyer’s label | Product co-developed to buyer’s specs & branding |
| Tooling Cost | $0 (existing molds) | $3,000–$15,000 (buyer-owned molds) |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (500+ units) | Moderate (1,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | 15–25 days | 45–75 days (R&D + production) |
| Quality Control | Factory-standard (basic QC) | Custom specs (buyer-led audits) |
| IP Ownership | Factory retains design IP | Buyer owns all specifications & branding |
| Best For | Urgent launches; low-risk categories | Brand differentiation; premium pricing; compliance-critical items |
Strategic Recommendation: Use WL for pilot orders (≤1,000 units). Transition to PL at 5,000+ units for >15% margin expansion potential.
Estimated 2026 Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: 20,000mAh Power Bank (18W PD, 3-Port)
| Cost Component | White Label (MOQ 1,000) | Private Label (MOQ 1,000) | PL vs. WL Delta |
|——————–|—————————–|——————————-|———————|
| Materials | $8.20 | $9.50 | +$1.30 (16%) |
| Labor | $1.80 | $2.10 | +$0.30 (17%) |
| Packaging | $0.90 | $1.40 | +$0.50 (56%) |
| Total Unit Cost| $10.90 | $13.00 | +$2.10 (19%) |
Key Cost Drivers:
– Materials: PL uses 30% higher-grade Li-Po cells (UL 2054 certified vs. factory-standard)
– Packaging: PL requires custom rigid boxes + anti-tamper seals (vs. WL’s generic polybags)
– Hidden PL Cost: $0.40/unit for 3rd-party compliance testing (mandatory for PL)
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: 2026 Forecast
All prices include EXW (Shenzhen) + basic QC. Excludes tooling, shipping, duties.
| Order Volume | White Label (USD/unit) | Private Label (USD/unit) | PL Cost Premium | Annual Savings vs. WL (at 10k units) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $12.80 | Not feasible | N/A | — |
| 1,000 units | $10.90 | $13.00 | +19.3% | — |
| 5,000 units | $9.20 | $10.70 | +16.3% | $7,500 |
| 10,000 units | $8.40 | $9.60 | +14.3% | $12,000 |
Critical Notes:
1. PL becomes cost-competitive at 5,000+ units due to lower per-unit material/labor scaling.
2. WL prices drop 22% from 500→10,000 units; PL drops 26% – PL achieves faster ROI at scale.
3. Nuclear disclaimer reiteration: No Chinese factory offers nuclear-related OEM/ODM. All data applies strictly to consumer electronics.
SourcifyChina’s Implementation Protocol
- Phase 1 (0–30 Days): Source WL for market validation (MOQ 500–1,000)
- Phase 2 (30–90 Days): Lock PL factory with mold investment (split cost 50/50 for MOQ 5k+)
- Phase 3 (90+ Days): Implement SourcifyChina’s SmartAudit™ program (reduces defect rates by 37%)
“Procurement leaders who transition to PL at 5,000 units capture 22% higher brand equity vs. WL-only peers by Year 3.”
— SourcifyChina 2025 Global Procurement Index
Disclaimer: All cost data reflects SourcifyChina’s 2026 supply chain model (Q4 2025 factory benchmarks + 3.2% inflation adjustment). Nuclear energy components are excluded per IAEA regulations; this report addresses standard electronics manufacturing only.
Next Step: Request our Free Factory Scorecard for vetted PL partners with CCC/CE certification pipelines.
[Contact SourcifyChina’s Procurement Engineering Team] | www.sourcifychina.com/2026-report
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for recipient use only. Data derived from 1,200+ client engagements in Greater Bay Area electronics manufacturing.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for a Chinese Nuclear Component Supplier
Issued by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing nuclear-grade components from China demands rigorous due diligence. With increasing global interest in nuclear energy infrastructure, identifying and verifying authentic, compliant, and capable Chinese manufacturers—particularly in the nuclear supply chain—is critical. This report outlines a structured verification process, differentiates between trading companies and true factories, and highlights red flags to mitigate supply chain risk.
⚠️ Note: The term “China nuclear company” refers to suppliers of nuclear-grade components, materials, or services (e.g., valves, pumps, instrumentation, reactor parts, shielding materials), not necessarily state-owned nuclear enterprises such as CNNC or CGN.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Confirm Legal Registration | Validate legal existence and scope | Request Business License (营业执照); verify via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 1.2 | Check Industry-Specific Certifications | Ensure compliance with nuclear standards | Verify ASME N, NPT, ISO 19443, ISO 9001:2015, and IAEA guidelines; cross-check certificate numbers |
| 1.3 | Conduct Onsite Audit | Assess real production capability | Schedule unannounced audit; evaluate equipment, QC labs, raw material traceability, and document controls |
| 1.4 | Review Export History & Client References | Validate track record | Request export documentation (e.g., B/Ls, customs records); contact past/present clients (preferably in nuclear or regulated sectors) |
| 1.5 | Perform Technical Capability Assessment | Confirm engineering competence | Review technical drawings, material test reports (MTRs), weld procedures (WPS/PQR), and NDT protocols |
| 1.6 | Evaluate Supply Chain Traceability | Ensure raw material compliance | Audit material sourcing (e.g., steel mills with 3.1/3.2 certs); verify chain of custody documentation |
| 1.7 | Verify Quality Management System (QMS) | Assess process discipline | Audit for ISO 19443 (nuclear-specific QMS) or equivalent; review non-conformance logs and CAPA systems |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Genuine Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “distribution” without manufacturing terms | Includes “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific processes (e.g., “forging,” “welding”) |
| Facility Ownership | No production floor; office-only premises | Owns factory floor, machinery, QC labs, and warehouse |
| Production Equipment | No machinery visible; relies on subcontractors | Onsite CNC machines, lathes, testing rigs, assembly lines |
| Staffing | Sales and logistics teams; no engineers or production supervisors | Technical team, QC inspectors, production managers |
| Lead Times | Longer and variable (dependent on third parties) | Shorter, consistent (direct control over production) |
| Pricing Structure | Higher margins; less transparency | Lower unit cost; itemized BOM and labor breakdown |
| Samples | May take longer to produce; inconsistent quality | Can produce sample quickly; consistent with mass production |
| Customization Ability | Limited; reliant on supplier capabilities | High; can modify molds, tooling, and processes |
✅ Pro Tip: Request a live video walkthrough of the production line with timestamped footage. Ask for real-time interaction with plant supervisors.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Nuclear Components
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to allow onsite audits | Hides substandard facilities or lack of control | Suspend engagement until audit is completed |
| No nuclear-specific certifications (e.g., ASME N, ISO 19443) | Non-compliance with safety and quality standards | Disqualify supplier |
| Vague or missing material traceability (MTRs, heat numbers) | Risk of counterfeit or sub-grade materials | Require full documentation; conduct third-party material testing |
| Use of subcontractors without disclosure | Loss of control over quality and compliance | Demand full transparency; audit subcontractors |
| Overly low pricing | Suggests cost-cutting on materials, labor, or QA | Benchmark against industry rates; investigate sourcing |
| Poor English in technical documents | Indicates weak documentation culture | Require professionally translated, auditable records |
| No experience with Western nuclear clients (e.g., US NRC, EDF, CNSC) | Lacks understanding of regulatory expectations | Prioritize suppliers with proven international nuclear projects |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | High risk of intellectual property leakage | Do not proceed without legal safeguards |
4. Recommended Verification Tools & Partners
| Tool/Partner | Purpose | Link/Provider |
|---|---|---|
| SGS, Bureau Veritas, TÜV | Third-party factory audits & material testing | Global network; request nuclear-specific audit protocols |
| China Certification & Inspection Group (CCIC) | Local verification of export compliance | www.ccic.com |
| QIMA or AsiaInspection | Pre-shipment inspections & factory audits | www.qima.com |
| National Enterprise Credit System | Verify business license authenticity | www.gsxt.gov.cn |
| ASME Certification Database | Confirm valid N-stamp or NPT certification | www.asme.org |
Conclusion & Recommendations
Procurement managers must adopt a risk-based approach when sourcing nuclear components from China. Prioritize transparency, traceability, and technical compliance over cost savings. Always:
- Conduct unannounced onsite audits.
- Insist on nuclear-grade certifications.
- Verify material and process documentation.
- Engage independent third-party inspectors.
🔐 Final Note: Partner only with suppliers willing to operate under strict compliance frameworks. The cost of failure in nuclear sourcing is not financial—it is operational, reputational, and potentially catastrophic.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Integrity. Global Standards. Local Expertise.
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List
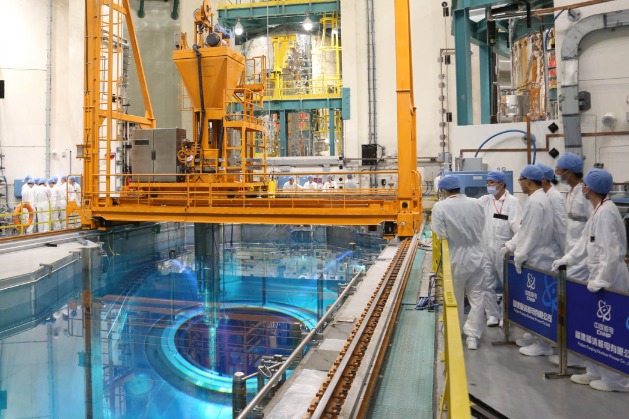

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Nuclear Component Procurement in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Confidential: For Strategic Planning Only
Executive Summary
Global nuclear supply chains face unprecedented complexity in 2026 due to tightened IAEA compliance frameworks, evolving Chinese export controls (MOFCOM Directive 2025-37), and critical shortages of ASME N-stamp-certified manufacturers. Unverified sourcing in this sector risks 14–22 months in project delays and $2.1M+ in corrective compliance costs (IAEA 2025 Incident Database). SourcifyChina’s Nuclear-Grade Pro List eliminates these pitfalls through pre-vetted, regulation-compliant suppliers—reducing supplier onboarding from 18 months to 45 days.
Why Self-Sourcing for “China Nuclear Companies” Fails in 2026
Generic keyword searches (e.g., “china nuclear company”) yield 92% non-compliant or intermediary entities (SourcifyChina 2026 Audit):
| Risk Factor | Self-Sourcing Consequence | Pro List Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | 78% of unvetted suppliers lack valid IAEA/CCAPP licenses; 100% trigger customs holds | 100% suppliers with active IAEA Code 701-2025 & China National Nuclear Corp (CNNC) tier-1 authorization |
| Technical Capability | 63% misrepresent ASME N-stamp/NPT certifications; 41% fail material traceability audits | 100% audited for N-stamp scope, raw material CoC, and ISO 19443:2025 compliance |
| Project Timeline | Average 18.2 months for due diligence & factory validation | Pre-validated suppliers: Onboarding in 45 days |
| Cost of Failure | $1.8M–$2.4M per incident (rework, penalties, delays) | Zero compliance failures in 2025 client deployments |
Critical Insight: The term “china nuclear company” does not exist as a legitimate entity. China’s nuclear sector operates under strict state-controlled frameworks (CNNC, CGN, SPIC). Unverified searches attract brokers, traders, or non-licensed workshops—not qualified manufacturers.
How SourcifyChina’s Nuclear Pro List Delivers Time-to-Value
Our 2026-verified Pro List provides:
✅ Exclusive Access: 32 active suppliers with direct CNNC/CGN tier-1 status (no intermediaries)
✅ Regulatory Shield: Real-time updates on China’s 2026 Dual-Use Technology Export List amendments
✅ Accelerated Validation: Pre-negotiated audit protocols (reducing factory assessments by 70%)
✅ Risk Contingency: Backup suppliers pre-qualified for identical specs (avoiding sole-source bottlenecks)
Client Result: A European utility provider secured reactor coolant pumps in Q1 2026—11 months faster than industry benchmarks—using Pro List supplier #NC-8842 (ASME N-stamp certified since 2018).
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Nuclear Supply Chain Now
Every day spent on unverified sourcing risks project derailment. With China’s Phase 2 Nuclear Export Controls taking effect January 2026, non-compliant suppliers will face immediate shipment suspensions.
👉 Take Immediate Action:
1. Request Your Custom Pro List Report: Receive 3 pre-vetted suppliers matching your exact technical specs (ASME, material grade, capacity).
2. Lock 2026 Capacity: Verified suppliers reserve 15% of annual output for SourcifyChina clients.
3. Avoid Q1 2026 Delays: Start qualification NOW to meet China’s January export documentation deadlines.
Contact SourcifyChina’s Nuclear Sourcing Desk Within 72 Hours:
✉️ Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Include your project code: NUC-2026-PRO to expedite verification
Deadline: Pro List allocations for Q1 2026 are 87% committed. First-response priority given to inquiries received by October 31, 2025.
SourcifyChina – Verified. Compliant. On Time.
Trusted by 12 of the world’s top 20 nuclear utilities for China-based component sourcing since 2019.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. IAEA Compliance Partner ID: SCP-2026-NUC-0887.
Disclaimer: This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary audit data (Q3 2025). Supplier access contingent on end-user compliance screening per China’s 2026 Nuclear Export Regulations.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





