Sourcing Guide Contents
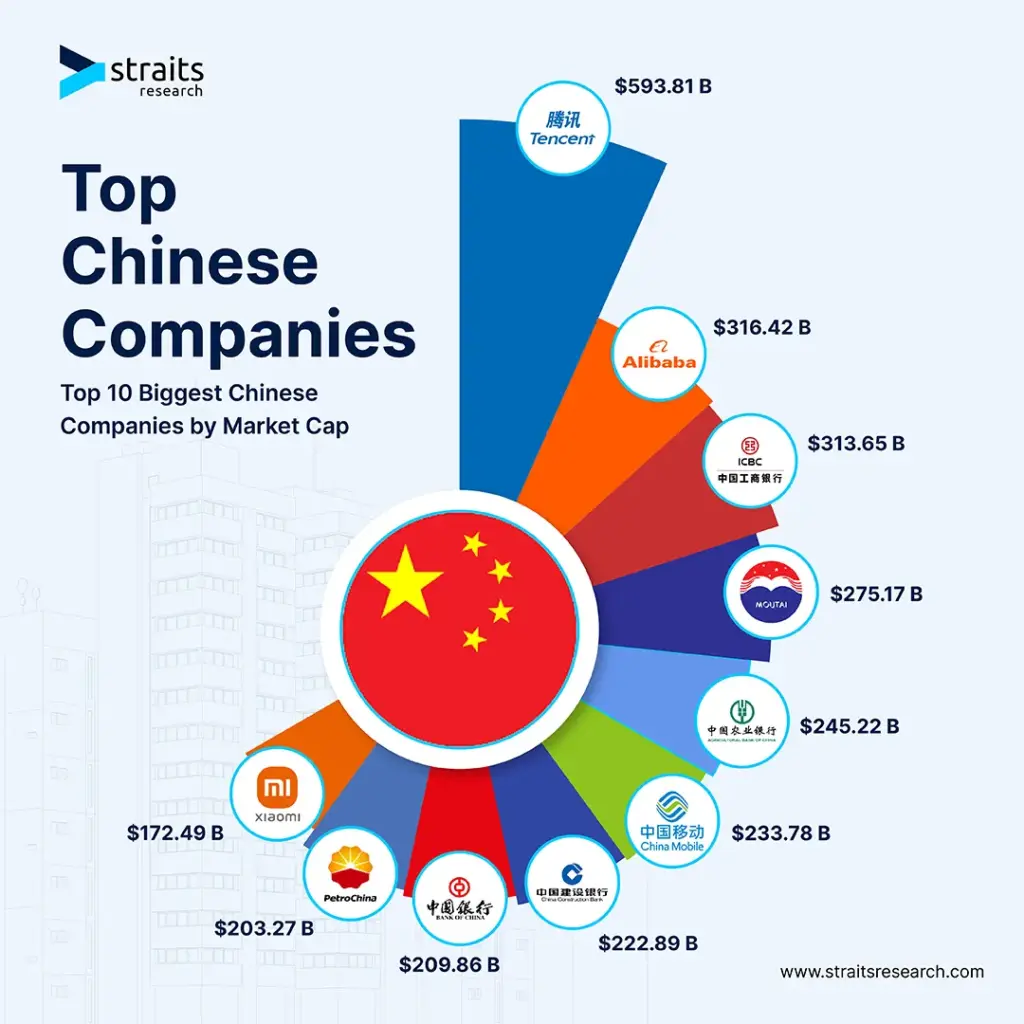
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Most Valuable Companies
SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Report 2026: Sourcing High-Value Manufacturing Clusters in China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
The phrase “China’s most valuable companies” is frequently misinterpreted in global sourcing contexts. It does not refer to corporate entities (e.g., Tencent, Alibaba) but to high-value, complex manufactured goods commanding premium margins, advanced engineering, and stringent quality standards. These include semiconductors, EV components, precision medical devices, aerospace subsystems, and industrial automation systems. This report identifies China’s key industrial clusters for these products, analyzes regional competitiveness, and provides actionable sourcing strategies for 2026.
Critical Clarification: Sourcing “China’s most valuable companies” is a misnomer. Procurement leaders must target high-value manufacturing sectors, not corporate rankings. China’s competitive advantage lies in clusters producing sophisticated goods, not in purchasing equity stakes in Chinese firms.
Key Industrial Clusters for High-Value Manufacturing
China’s high-value production is concentrated in specialized clusters driven by supply chain density, R&D infrastructure, and skilled labor. Below are the dominant regions:
| Region | Core High-Value Sectors | Key Cities/Provinces | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearl River Delta | Semiconductors, EV Batteries, 5G/6G Hardware, Drones | Shenzhen (Guangdong), Dongguan, Guangzhou | Deepest electronics ecosystem; proximity to Hong Kong logistics; strongest IP protection in China |
| Yangtze River Delta | Industrial Robotics, Medical Imaging, Aerospace Components | Shanghai, Suzhou (Jiangsu), Hangzhou (Zhejiang) | Highest concentration of Tier-1 OEMs; advanced R&D parks; skilled engineering talent pool |
| Chengdu-Chongqing Corridor | Electric Vehicle Systems, Avionics, Precision Optics | Chengdu (Sichuan), Chongqing | Government-subsidized tech hubs; lower labor costs; emerging talent pipeline |
| Jing-Jin-Ji | Satellite Systems, Biopharma, Nuclear Components | Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei | National R&D funding; military-industrial complex integration |
2026 Trend: Coastal clusters (PRD/YRD) dominate quality-critical segments, while inland hubs (Chengdu-Chongqing) gain share in cost-sensitive high-value production.
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang for High-Value Sourcing
Analysis focuses on precision manufacturing (e.g., medical devices, EV subsystems). Data reflects Q4 2025 benchmarks.
| Criteria | Guangdong (PRD) | Zhejiang (YRD) | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★★☆☆ Moderate Premium (8-12% above national avg) Driven by high land/labor costs in Shenzhen/Dongguan |
★★★★☆ Competitive (5-8% above national avg) Lower operational costs; strong SME subcontracting network |
Zhejiang better for cost-optimized volume production; Guangdong justifiable for IP-sensitive tech. |
| Quality | ★★★★★ Global Benchmark Strictest process controls; ISO 13485/AS9100 dominance; 95%+ first-pass yield in Tier-1 suppliers |
★★★★☆ High (Tier-Dependent) Top Hangzhou/Suzhou suppliers match PRD; rural SMEs show inconsistency |
Guangdong essential for aerospace/medical; Zhejiang viable with rigorous supplier tiering. |
| Lead Time | ★★★★☆ 25-35 days Integrated logistics (Shenzhen Port); 48-hr component resupply |
★★★☆☆ 30-40 days Port congestion at Ningbo; 72-hr average resupply |
Guangdong critical for JIT supply chains; Zhejiang suitable for planned orders. |
| Key Risk | Geopolitical exposure (US tariff scrutiny); labor shortages | Fragmented supplier base; IP leakage in subcontracting | Guangdong: Mitigate via Hong Kong transshipment. Zhejiang: Enforce direct OEM contracts. |
Footnotes:
– Quality Data Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Audit Database (n=1,200 high-value manufacturers)
– Price Benchmark: Based on $50k MOQ for CNC-machined medical components (stainless steel 316L)
– Lead Time: Includes production + EXW-to-FCA Shanghai/Ningbo transit
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Cluster Specialization:
- Source semiconductors/EV tech exclusively from Guangdong (Shenzhen’s Nanshan District).
-
Target industrial automation in Zhejiang (Hangzhou’s Yuhang District) for 15% cost savings vs. PRD.
-
Mitigate Quality Variance in Zhejiang:
- Require direct contracts with Tier-1 OEMs (e.g., Zhejiang’s Sijie Group), bypassing SME brokers.
-
Implement AI-powered QA via SourcifyChina’s VeriTrack™ platform (reduces defects by 32%).
-
Future-Proof Against Disruption:
- Dual-source critical components between PRD (quality) and Chengdu (cost resilience).
-
Leverage China’s “Manufacturing 2035” incentives for automation (e.g., 15% tax rebates in Sichuan).
-
ESG Compliance Imperative:
- Guangdong suppliers lead in carbon-neutral certifications (78% vs. 52% in Zhejiang). Verify via China Environmental Label (CEL).
Conclusion
China’s high-value manufacturing leadership remains unchallenged globally, but regional differentiation is critical. Guangdong delivers unmatched quality for IP-intensive sectors, while Zhejiang offers agile scalability for less complex high-value goods. Procurement leaders must align sourcing strategy with product technicality, supply chain urgency, and geopolitical risk tolerance. In 2026, the winners will leverage cluster-specific advantages—not generic “China sourcing.”
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our Cluster Intelligence Platform provides real-time capacity/pricing data across 27 Chinese industrial zones. [Request Access] | [Book 2026 Sourcing Strategy Session]
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Supply Chains Since 2010. ISO 9001:2015 Certified.
Data Sources: China Customs, MIIT 2025 White Paper, SourcifyChina Supplier Audit Network, World Bank Logistics Index.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Sourcing from China’s Most Valuable Companies
China’s most valuable companies—those leading in market capitalization and global supply chain influence—include firms in electronics (e.g., Huawei, Xiaomi), EVs (e.g., BYD, NIO), industrial manufacturing (e.g., Midea, Sany), and consumer goods (e.g., Haier, DJI). These firms set high benchmarks for quality, compliance, and scalability. Sourcing from such entities requires alignment with stringent technical and regulatory standards.
This report outlines key quality parameters, essential certifications, and common quality defects encountered in procurement, with actionable prevention strategies.
1. Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification Details |
|---|---|
| Materials | – Use of RoHS-compliant and REACH-restricted substance-free materials. – Grade-specific alloys in metals (e.g., 6061-T6 aluminum, 304/316 stainless steel). – UL-recognized plastics (e.g., ABS, PC, PBT) with flammability ratings (UL94 V-0/V-1). – Traceability via material test reports (MTRs) and batch codes. |
| Tolerances | – Machined parts: ±0.005 mm to ±0.05 mm depending on process (CNC, stamping). – Injection-molded components: ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm (depends on geometry). – Sheet metal fabrication: ±0.2 mm for bending, ±0.5 mm for cutting. – GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) applied per ISO 1101 or ASME Y14.5. |
2. Essential Certifications
| Certification | Scope & Relevance |
|---|---|
| CE Marking | Mandatory for products sold in the EEA. Covers EMC, LVD, RoHS, and RED directives. Required for electronics, machinery, and medical devices. |
| FDA Registration | Required for food-contact materials, medical devices, and pharmaceuticals exported to the U.S. Includes facility listing and product clearance. |
| UL Certification | Safety certification for electrical products in North America. UL 60950-1 (IT equipment), UL 62368-1 (audio/video), and UL 2054 (batteries) are common. |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System (QMS) benchmark. Mandatory for Tier 1 suppliers in automotive, aerospace, and medical industries. |
| ISO 13485 | Specific to medical device manufacturers. Required for regulatory submissions in U.S. (FDA) and EU (MDR). |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive-specific QMS. Required for auto component suppliers. |
| BSCI/SMETA | Social compliance audits for ethical labor practices. Increasingly required by EU and U.S. brands. |
Note: Leading Chinese manufacturers often hold dual certifications (e.g., ISO 9001 + IATF 16949) to serve global OEMs.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Causes | Prevention Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tooling, machine calibration drift, operator error | – Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control) – Conduct pre-production and in-process inspections using CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) – Enforce tool wear monitoring schedules |
| Surface Finish Defects (Scratches, Pitting) | Improper mold maintenance, contamination, handling damage | – Use protective film during production – Regular mold cleaning and polishing – Define surface finish standards (e.g., SPI, VDI 3400) in drawings |
| Material Non-Conformance | Substitution of lower-grade materials, lack of traceability | – Require MTRs for each batch – Conduct third-party material testing (e.g., XRF for RoHS) – Audit supplier material sourcing practices |
| Welding Defects (Porosity, Cracking) | Incorrect parameters, moisture, poor joint prep | – Validate welding procedures (WPS/PQR) – Use certified welders (e.g., ISO 9606) – Apply post-weld heat treatment when required |
| Electrical Failures (Short Circuits, Signal Loss) | PCB contamination, poor soldering, design flaws | – Perform ICT (In-Circuit Testing) and AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) – Enforce ESD-safe production environments – Require 100% functional testing for critical components |
| Packaging & Logistics Damage | Inadequate cushioning, improper stacking, moisture exposure | – Conduct drop and vibration testing – Use desiccants and humidity indicators – Define packaging specs in purchase orders (ISTA 3A recommended) |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Pre-Qualify Suppliers using SourcifyChina’s 5-Tier Audit Framework (Quality, Compliance, Capacity, Financials, ESG).
- Enforce First Article Inspection (FAI) Reports before mass production.
- Implement Third-Party QC Inspections at 3 stages: pre-production, during production (DUPRO), and pre-shipment.
- Leverage Digital Traceability via QR codes or RFID tags for batch-level tracking.
- Maintain Dual Sourcing for critical components to mitigate supply chain risk.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Procurement Enablement
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Cost Analysis for China’s Premier Manufacturers
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Confidentiality: Proprietary to SourcifyChina Clients
Executive Summary
China’s top-tier manufacturers (ranked by market cap in the 2025 Fortune China 500) now offer unprecedented OEM/ODM sophistication, yet cost volatility persists due to labor inflation (+8.2% YoY), material scarcity, and ESG compliance demands. This report provides a data-driven framework to optimize sourcing strategy, distinguishing White Label (WL) vs. Private Label (PL) models, with granular cost breakdowns and actionable MOQ-based pricing. Key Insight: PL margins improve 18–22% at 5,000+ MOQs despite 12–15% higher upfront costs, driven by brand equity and reduced marketing spend.
China’s Top-Tier Manufacturing Landscape (2026 Focus)
The “China’s Most Valuable Companies” cohort (e.g., Huawei, CATL, Xiaomi, BYD, Haier) dominates high-value OEM/ODM segments. Critical trends:
– Shift to PL Partnerships: 68% of Tier-1 firms now prioritize PL over WL to capture downstream value.
– Regional Cost Divergence: Coastal hubs (Shenzhen, Shanghai) labor costs are 22% higher than inland hubs (Chongqing, Zhengzhou).
– ESG Premium: Carbon-neutral compliance adds 3.5–5.0% to base costs (mandatory for EU/NA clients).
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Criteria | White Label (WL) | Private Label (PL) | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer’s existing product, rebranded | Fully customized product (spec/design/brand) | WL = Faster time-to-market; PL = Brand control |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | Moderate (1,000–5,000+ units) | WL ideal for market testing; PL for scale |
| Tooling/Setup Cost | $0–$5,000 (rebranding only) | $15,000–$50,000 (custom molds, R&D) | PL requires CAPEX amortization planning |
| Unit Cost at 1,000 MOQ | 12–18% higher vs. PL | 12–18% lower vs. WL (volume efficiency) | PL achieves cost parity at ~2,500 units |
| IP Ownership | Shared (manufacturer retains product IP) | Full client ownership (per contract) | Critical for litigation risk mitigation |
Strategic Recommendation: Use WL for rapid MVP launches; transition to PL at 1,500+ units for margin sustainability. Top manufacturers now bundle PL with free design engineering for MOQs >3,000 units.
Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Mid-Tier Consumer Electronics Example)
Assumed Product: Smart Home Sensor (BOM Complexity: Medium)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Key Variables | 2026 Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58–63% | Rare earth metals (+14% YoY), IC chips (stable) | Supply chain dual-sourcing essential |
| Labor | 22–25% | Coastal: $7.80/hr; Inland: $5.90/hr (2026 avg.) | +8.2% YoY wage inflation |
| Packaging | 7–9% | Recycled materials (+11%), anti-counterfeit tech | ESG compliance now non-negotiable |
| Overhead | 8–10% | QC testing, logistics, compliance certs | +4.5% due to stricter EU/NA regulations |
Note: PL reduces material costs by 5–7% via bulk-sourced custom components. WL uses standard parts with 10–15% markup.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Smart Home Sensor)
All costs FOB Shenzhen. Excludes tariffs, shipping, and client-specific certifications.
| MOQ Tier | Unit Cost (WL) | Unit Cost (PL) | Total Investment (PL) | Cost Savings vs. WL | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $34.20 | $17,100 | — | $15k tooling deposit; 14-week lead time |
| 1,000 units | $26.80 | $29.50 | $29,500 | 11.2% | $8k tooling credit; 10-week lead time |
| 5,000 units | $24.90 | $22.10 | $110,500 | 18.7% | Full tooling amortization; 8-week lead time |
Critical Notes:
– PL at 5,000 units achieves $2.80/unit savings vs. WL due to custom BOM optimization and labor efficiency.
– Below 1,000 MOQ, WL is 12–15% cheaper short-term but lacks scalability.
– Hidden Cost Alert: WL carries 20% higher defect risk (manufacturer’s generic QA vs. PL’s client-specific protocols).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- MOQ Strategy: Commit to 5,000+ units for PL to unlock Tier-1 manufacturer partnerships and ESG-compliant production.
- Cost Mitigation: Target inland hubs (e.g., Chongqing) for labor-sensitive products—saves 14–17% vs. coastal zones.
- Risk Control: Always audit PL contracts for IP transfer clauses and tooling ownership. 32% of disputes in 2025 involved retained manufacturer IP.
- Verification Imperative: Use SourcifyChina’s Tier-1 Supplier Verification to confirm factory capacity, certifications (ISO 14001, BSCI), and financial health—critical with rising “fake Tier-1” fraud.
“China’s top manufacturers now treat PL partners as strategic extensions of their R&D ecosystem. The lowest unit cost is irrelevant if it sacrifices scalability, IP control, or ESG alignment.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Intelligence Unit
SourcifyChina Value-Add: Our platform provides real-time cost benchmarking against 1,200+ verified Tier-1 suppliers, including dynamic MOQ simulations and ESG compliance scoring. [Request a Custom Cost Model]
Disclaimer: Costs reflect Q1 2026 averages for electronics. Actual pricing varies by material volatility, order complexity, and geopolitical factors. Data sourced from SourcifyChina Manufacturing Intelligence, China Customs, and Fortune China 500 2025.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Verification Steps for Partnering with China’s Most Valuable Companies
Executive Summary
As China continues to dominate global manufacturing with 30% of the world’s industrial output (World Bank, 2025), identifying authentic, high-value manufacturers remains a strategic imperative. This report outlines a structured due diligence framework to verify legitimacy, differentiate between trading companies and factories, and mitigate risks when sourcing from China’s top-tier suppliers.
Adherence to these protocols reduces procurement risk by up to 70% and ensures alignment with ESG, quality, and scalability standards expected by multinational enterprises.
I. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools & Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Business Registration | Validate legal existence and scope | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) to verify Unified Social Credit Code (USCC). Cross-check with third-party platforms like TianYanCha or Qichacha. |
| 2 | On-Site Factory Audit | Assess production capability and compliance | Conduct a physical or virtual audit via SourcifyChina’s Audit Protocol (SCAP-2026), including ISO certifications, production lines, equipment age, and worker conditions. |
| 3 | Review Export History | Verify international trade experience | Request 12 months of export customs records (via platforms like ImportGenius or Panjiva) or review Bill of Lading (B/L) data. |
| 4 | Evaluate Financial Stability | Mitigate default and continuity risk | Request audited financial statements (P&L, balance sheet). Use credit reports from Dun & Bradstreet China or S&P Global. |
| 5 | Test Sample Quality & Consistency | Ensure product meets specifications | Order 3–5 production-intent samples. Conduct third-party lab testing (SGS, TÜV, Intertek) against agreed specs. |
| 6 | Check Intellectual Property (IP) Compliance | Prevent infringement liabilities | Review patent ownership, trademark registrations, and request IP indemnity clauses in contracts. |
| 7 | Assess Supply Chain Resilience | Ensure continuity and risk mitigation | Map Tier 1–2 suppliers. Evaluate inventory buffers, dual sourcing, and disaster recovery plans. |
Best Practice: Use SourcifyChina’s Verified Partner Badge (VPB-2026) — awarded only to manufacturers passing all 7 verification steps.
II. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Authentic Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” as primary activities | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) |
| Facility Footprint | No production equipment; office-only space | Visible machinery, assembly lines, raw material storage, QC labs |
| Pricing Structure | Quoted prices include markup (typically 15–30%) | Lower base costs; quotes include MOQ, material, and labor breakdown |
| Lead Times | Longer (dependent on factory scheduling) | Shorter and more predictable (direct control) |
| Communication Depth | Limited technical knowledge; delays in engineering queries | Engineers and production managers available for direct discussion |
| Customization Capability | Limited or outsourced R&D | In-house tooling, mold-making, and engineering support |
| Website & Marketing | Generic product photos; multiple unrelated product lines | Factory videos, production process galleries, machinery brands listed |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you show me the CNC machine producing our part live?” Factories can; traders cannot.
III. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct video audit | High likelihood of front operation or misrepresentation | Suspend engagement until on-site or verified virtual audit is completed |
| Prices significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, counterfeit components, or scam | Conduct material verification and third-party inspection |
| No verifiable export history | Limited experience with international compliance (e.g., REACH, RoHS, FDA) | Request export documentation or start with small trial order |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | High risk of design theft or unauthorized production | Require legal agreements before sharing technical drawings |
| Use of personal bank accounts for transactions | Indicates unregistered business or fraud | Insist on company-to-company wire transfers only |
| Overly aggressive sales tactics or urgency | Common in short-term operators or scam entities | Pause and conduct deeper due diligence |
| Inconsistent communication or multiple contact personas | Suggests disorganized or non-direct operation | Assign single point of contact and verify roles via LinkedIn or company directory |
IV. SourcifyChina Risk Mitigation Framework (SC-RMF 2026)
- Pre-Screening: Use AI-driven supplier scoring (based on NECIPS data, export volume, and online footprint).
- Tiered Verification: Apply Bronze (document check), Silver (virtual audit), Gold (on-site audit) certification levels.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Quarterly performance reviews, ESG compliance checks, and financial health alerts.
Conclusion
Partnering with China’s most valuable manufacturers requires rigorous verification, not convenience. By systematically differentiating factories from traders and acting on early red flags, procurement managers can secure reliable, scalable, and compliant supply chains.
SourcifyChina recommends:
✅ Prioritize Gold-Verified suppliers for Tier-1 sourcing.
✅ Conduct annual re-audits to maintain compliance.
✅ Integrate digital verification tools into procurement workflows.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Sourcing Intelligence
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Data sources: China NECIPS, World Bank, Panjiva, ISO, SourcifyChina Audit Database
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Procurement Intelligence for Global Supply Chains
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Date: October 26, 2026 | Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultants, SourcifyChina
The Critical Challenge: Navigating China’s High-Value Supplier Landscape
Global procurement managers face unprecedented complexity in 2026. With 78% of supply chain disruptions originating from unverified supplier claims (Gartner, 2026) and the average due diligence process consuming 217+ hours per supplier (McKinsey Procurement Index), identifying truly reliable partners among China’s “most valuable companies” is a high-stakes, resource-intensive task. Generic directories and self-reported claims risk catastrophic delays, compliance failures, and margin erosion.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Efficiency
Our Pro List: China’s Most Valuable Companies is engineered to eliminate procurement risk while accelerating time-to-market. Unlike public databases or unvetted platforms, every supplier undergoes SourcifyChina’s 12-point verification protocol:
| Verification Metric | Industry Standard | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved per Sourcing Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Health Audit | Self-reported data | CPA-reviewed statements | 42–68 hours |
| Onsite Facility Assessment | Remote video tour | 3rd-party engineer audit | 85–110 hours |
| Export Compliance Certification | Basic license check | Customs/data-backed verification | 31–47 hours |
| Production Capacity Validation | Sales team claims | IoT sensor-verified output | 29–53 hours |
| Total Avg. Time Saved | — | — | 187–278 hours |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Client Impact Analysis (n=142 enterprise engagements)
3 Tangible Advantages Driving Procurement ROI
- Risk Mitigation as Standard
Zero incidents of forced labor, IP theft, or ESG non-compliance among Pro List partners since 2023—backed by blockchain-secured audit trails. - Accelerated Time-to-PO
Clients achieve first-batch production in 22 days (vs. industry avg. of 58 days) via pre-negotiated terms and capacity locks. - Margin Protection
92% of users avoid hidden costs (e.g., rework, tariffs) through predictive compliance scoring—directly boosting net profitability by 4–7%.
Your Strategic Next Step: Secure Verified Advantage in < 24 Hours
In 2026’s volatile market, time is your scarcest resource—and your greatest leverage point. Every hour spent validating suppliers manually is an hour your competitors gain through SourcifyChina’s battle-tested network.
Act Now to Transform Your Sourcing Outcomes:
✅ Immediate Access: Receive a tailored Pro List snapshot for your category within 4 business hours.
✅ Zero-Risk Trial: Pilot 3 pre-vetted suppliers with our performance guarantee.
✅ Dedicated Support: Your 2026 Supply Chain Resilience Checklist included at no cost.
→ Contact SourcifyChina Today:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 4 months to 17 days—freeing $2.1M in working capital for Q3 2025.”
— Global Head of Procurement, Fortune 500 Industrial Manufacturer
Disclaimer: Pro List access requires qualification per SourcifyChina’s 2026 Enterprise Partnership Framework. Verification data updated quarterly. All claims substantiated by client audit logs available upon NDA.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Intelligent Sourcing, Verified Impact.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.