Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Military Companies

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing from China’s Defense-Industrial Ecosystem
Date: April 2025
Prepared by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic market analysis for global procurement professionals seeking clarity on sourcing defense-related industrial capabilities in China. While direct engagement with Chinese military enterprises is restricted for foreign entities due to national security regulations and export controls, understanding the geographic and industrial landscape of China’s defense manufacturing ecosystem is critical for assessing dual-use technologies, supply chain dependencies, and competitive intelligence.
China’s defense industry is predominantly state-controlled, with key activities managed by central conglomerates such as the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), China North Industries Group Corporation (NORINCO), and China State Shipbuilding Corporation (CSSC). These entities operate through provincial subsidiaries and specialized industrial clusters. However, foreign procurement from these entities is legally prohibited under Chinese law and international arms trade regulations (e.g., ITAR, Wassenaar Arrangement).
This report focuses on industrial clusters producing dual-use technologies (civilian-military crossover) such as advanced electronics, precision machining, aerospace components, and composite materials—sectors often adjacent to military supply chains but accessible to international buyers under compliance frameworks.
Key Industrial Clusters for Defense-Adjacent Manufacturing
China’s defense and dual-use manufacturing is concentrated in regions with strong state investment, technical universities, and integrated supply chains. The following provinces and cities host major defense-industrial activity:
| Region | Key Cities | Core Defense & Dual-Use Sectors | Major State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | Beijing | Aerospace systems, satellite tech, AI, cybersecurity | CASC, CASIC, CETC |
| Shaanxi | Xi’an | Aviation, fighter jets, UAVs, avionics | AVIC subsidiaries, XAC |
| Sichuan | Chengdu | Aerospace, missile systems, electronics | AVIC, CETC |
| Liaoning | Shenyang, Dalian | Naval shipbuilding, armored vehicles | CSSC, NORINCO |
| Hubei | Wuhan | Naval systems, optoelectronics, communications | CETC, CSSC |
| Heilongjiang | Harbin | Aviation, helicopter manufacturing | AVIC Harbin Aircraft |
| Shanghai | Shanghai | High-end electronics, marine engineering, automation | CSSC, SICC |
| Jiangsu | Nanjing, Wuxi | Precision instruments, radar, electronic warfare | CETC, NORINCO |
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan | Consumer electronics, drones, semiconductors, AI hardware | DJI (civilian), Huawei (dual-use) |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo | Advanced machinery, automation, smart manufacturing | Private sector OEMs, machine tool makers |
Note: While Guangdong and Zhejiang are not traditional military hubs, they lead in producing dual-use components (e.g., drones, sensors, PCBs, AI chips) that are integrated into broader defense systems.
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions (Dual-Use Focus)
The following table evaluates two leading export-oriented manufacturing provinces—Guangdong and Zhejiang—based on their capacity to supply civilian-grade components with defense crossover applications. This analysis is relevant for procurement of drones, communication modules, navigation systems, and robotics under export compliance.
| Parameter | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Medium to High | Medium | Guangdong’s labor and real estate costs are rising; Zhejiang offers better cost control in precision machinery. |
| Quality | High (Tier 1 suppliers, ISO-certified) | High (strong focus on precision engineering) | Both provinces maintain high quality; Guangdong leads in electronics; Zhejiang in CNC and automation. |
| Lead Time | 4–8 weeks (shorter for electronics) | 6–10 weeks (longer for custom machinery) | Guangdong’s dense supply chain enables faster turnaround, especially in Shenzhen. |
| Tech Capability | Advanced (AI, 5G, UAVs, semiconductors) | High (smart manufacturing, robotics) | Guangdong is the hub for innovation in consumer-tech dual-use applications. |
| Compliance Risk | Medium (strict export controls on dual-use) | Medium | Both require ICP, export licenses for sensitive technologies. |
| Best For | Drones, PCBs, sensors, communication modules | Precision parts, automation systems, motors | Choice depends on application: electronics vs. mechanical systems. |
Strategic Sourcing Considerations
- Regulatory Compliance
- The U.S. Department of Commerce (BIS) and EU Dual-Use Regulation restrict exports of items with military applications.
- Components like high-resolution imaging sensors, GNSS modules, and AI processors may require licenses.
-
Avoid sourcing from entities on the U.S. Entity List (e.g., Huawei, DJI, certain CETC subsidiaries).
-
Supply Chain Transparency
- Use third-party audits and SCIP (Supply Chain Intelligence Platform) tools to map supplier affiliations.
-
Verify that suppliers are not subcontracting to restricted defense SOEs.
-
Dual-Use Technology Monitoring
-
Monitor Wassenaar Arrangement updates and China’s Export Control Law (2020) for shifts in controlled items.
-
Alternative Sourcing Strategy
- Consider Vietnam, Malaysia, or Mexico for final assembly of components sourced from China to mitigate geopolitical risk.
Conclusion
While direct procurement from Chinese military companies is not feasible for foreign buyers, understanding the geographic distribution of defense-industrial clusters and their dual-use manufacturing ecosystems is essential for strategic sourcing. Guangdong and Zhejiang emerge as key regions for high-tech component procurement, offering strong quality and innovation, albeit under tight regulatory scrutiny.
Procurement managers should prioritize compliance-first sourcing, partner with certified third-party agents, and leverage modular supply chains to balance performance, cost, and risk.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
China Supply Chain Intelligence & Procurement Advisory
www.sourcifychina.com
Disclaimer: This report does not endorse or facilitate sourcing from restricted military entities. All recommendations comply with international export control regulations.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Advisory Report: Navigating Compliance in Chinese Manufacturing (2026)
To: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Clarification on Sourcing from Chinese Entities & Compliant Pathways for High-Specification Goods
Critical Clarification: “China Military Companies” Do Not Exist in Open Commercial Sourcing
SourcifyChina Advisory: The term “China military companies” is not a recognized commercial category for B2B sourcing. China’s defense sector operates under strict state control via entities like the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) and state-owned defense conglomerates (e.g., AVIC, CSIC, NORINCO). These entities do not engage in open-market B2B transactions with foreign commercial entities. Direct sourcing from PLA-affiliated manufacturers violates:
– US ITAR/EAR Regulations (22 CFR §120.9)
– EU Dual-Use Regulation (EU) 2021/821
– National security laws in 98% of OECD countries
Procurement Risk: Attempting to source from “military-linked” suppliers exposes your organization to:
– Blacklisting under the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA)
– Fines exceeding $1M USD (per ITAR violation)
– Reputational damage and supply chain audits
Compliant Pathway: Sourcing Commercial Suppliers for MIL-SPEC/Dual-Use Goods
Most global procurement needs for “military-grade” specifications are fulfilled by commercial Chinese manufacturers certified to produce to international defense standards (e.g., AS9100, MIL-STD-810G) for civilian applications (aerospace, medical, industrial).
Key Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Commercial Standard (Typical) | MIL-SPEC Equivalent (Example) | Critical Tolerances |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | ASTM A240 (Stainless Steel) | MIL-S-5000 (Stainless Steel) | Chemical composition ±0.03% |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ISO 2768-mK (Medium) | MIL-STD-340 (Class 1) | ±0.005 mm for critical surfaces |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.8 µm (Machined) | MIL-F-13926 (Class A) | Ra ≤ 0.4 µm for optical components |
| Environmental | IEC 60068-2 (Commercial) | MIL-STD-810G (Method 514.7) | Vibration: 10–500 Hz, 7.7 Grms |
Mandatory Certifications for Export Compliance
| Certification | Scope | Why Required for Export | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management System | Baseline for all exports | Audit certificate + scope validity |
| AS9100 | Aerospace Quality Management | Required for aviation parts | IAQG OASIS database check |
| CE Marking | EU Safety Compliance | Entry to EEA market | Technical File review (not self-declared) |
| UL 62368-1 | Safety for IT/AV Equipment | US/Canada market access | UL Witnessed Production Testing (WPT) |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 820 | Medical Device QMS | US medical device clearance | FDA Establishment Registration # |
Note: No Chinese commercial supplier can legally hold “military certifications” for export. Certifications like ITAR registration apply ONLY to US entities.
Common Quality Defects in High-Spec Chinese Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina audit data (1,200+ supplier assessments)
| Common Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol | SourcifyChina Verification Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting (e.g., 304 vs. 316 SS) | 1. Require mill test reports (MTRs) 2. On-site spectrometer testing |
Third-party lab MTR validation + batch traceability |
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear in high-volume runs | 1. SPC charts with Cpk ≥1.67 2. In-process calibrations every 2 hrs |
Real-time SPC review + gauge R&R audit |
| Surface Contamination | Poor handling/storage (e.g., oils) | 1. Cleanroom protocols (Class 10K+) 2. Particle count testing |
Pre-shipment particle audit (per ASTM F312) |
| Non-Conforming Welds | Inadequate welder certification | 1. ASME Section IX weld procedures 2. 100% RT/UT for critical joints |
Welder certification cross-check + NDT report review |
| Coating Thickness Variation | Inconsistent spray parameters | 1. Automated coating systems 2. DFT checks at 5+ points/unit |
Elcometer 456 spot checks (min. 30 units/batch) |
SourcifyChina Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Audit Suppliers for Dual-Use Compliance: Verify certifications via official databases (e.g., IAQG OASIS, UL Product iQ).
- Require Full Traceability: Demand lot numbers for raw materials → finished goods (blockchain preferred).
- Conduct On-Site Process Audits: Focus on calibration logs, operator training records, and non-conformance reports.
- Avoid “Military-Grade” Marketing Traps: Legitimate suppliers reference standards (e.g., “meets MIL-STD-810G”), not “military contracts.”
Final Advisory: All SourcifyChina-vetted suppliers undergo Defense Industrial Base (DIB) Screening per NIST SP 800-171. We provide full audit trails to mitigate UFLPA/ITAR risks.
SourcifyChina Commitment: We enable compliant access to China’s commercial manufacturing ecosystem – never state-controlled entities. Partner with us for zero-risk sourcing of high-specification goods.
[Contact sourcifychina.com/compliance-2026 for certified supplier lists]
Disclaimer: This report does not constitute legal advice. Consult export control counsel before procurement.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. UN Global Compact Participant.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Guide: Manufacturing Costs & OEM/ODM Options for Sensitive Product Categories in China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: Q1 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
This report provides procurement professionals with an objective, compliance-focused analysis of manufacturing cost structures and OEM/ODM engagement models in China for non-sensitive commercial goods, with contextual clarification regarding sourcing terminology often misapplied to restricted sectors. Due to international trade regulations, national security policies, and export control frameworks (including ITAR, EAR, and EU Dual-Use Regulations), direct sourcing from or onboarding of entities classified as “China military companies” is strictly prohibited for foreign commercial buyers.
Accordingly, this document reframes the inquiry into commercial-grade manufacturing capabilities in China that may serve as analogs for high-specification industrial or ruggedized products, while emphasizing legal and ethical compliance. The analysis covers:
- Clarification of OEM/ODM models in Chinese manufacturing
- White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic differences
- Estimated cost breakdown for commercial industrial equipment (representative category)
- MOQ-based pricing tiers for procurement planning
1. Clarification: “China Military Companies” and Commercial Sourcing
The term “China military companies” typically refers to enterprises listed under U.S. Department of Defense Section 1237 designation or those involved in defense R&D and production under the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) ecosystem. These entities:
- Are off-limits to foreign direct sourcing due to sanctions and export controls.
- Do not engage in commercial white label or OEM manufacturing for global B2B clients.
- Operate under strict state oversight with non-disclosure of production data.
SourcifyChina advises all procurement teams to conduct due diligence using official lists such as:
– U.S. DoD 1237 List
– Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) Entity List
– EU Consolidated Sanctions List
Instead, this report focuses on high-precision commercial manufacturers in China capable of producing ruggedized, industrial, or dual-use-adjacent products under full compliance with international trade law.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Engagement Models
| Model | Description | Control Level | Lead Time | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces based on client’s full design, specs, and branding. | High (client owns IP) | Longer (full production cycle) | Companies with mature product designs and IP |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides design + production; buyer customizes branding/features. | Medium (shared IP on base model) | Shorter (leverages existing platforms) | Fast time-to-market, cost-sensitive buyers |
Note: ODM is common in electronics, IoT, and industrial tools sectors where modular designs allow for rapid customization.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Product Design | Generic, one-size-fits-all | Customizable (colors, features, packaging) |
| Branding | Buyer applies own brand; no design input | Full branding control, often with tailored UI/UX |
| MOQ | Lower (standardized SKUs) | Higher (custom tooling/setup) |
| Cost | Lower per unit | Higher initial cost, better margins long-term |
| Use Case | Resellers, distributors | Brands building market identity |
Strategic Insight: Private Label is preferred for differentiation; White Label suits rapid market entry with minimal capex.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Example: Industrial IoT Sensor Unit)
Representative product: Ruggedized environmental sensor (temperature/humidity/pressure) with IP67 rating, suitable for industrial monitoring.
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Materials (PCB, casing, sensors, connectors) | $18.50 | 58% |
| Labor (assembly, testing, QA) | $6.20 | 19% |
| Tooling & Setup (one-time, amortized) | $2.00 | 6% |
| Packaging (custom box, manual, label) | $3.30 | 10% |
| Overhead & Logistics (factory to port) | $2.00 | 6% |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $32.00 | 100% |
Assumptions: Production in Dongguan, Guangdong; compliant supplier; ISO 9001-certified facility; air freight not included.
5. MOQ-Based Price Tiers (Per Unit, FOB Shenzhen)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $38.00 | $19,000 | Higher per-unit cost; minimal tooling amortization |
| 1,000 units | $34.50 | $34,500 | Economies of scale begin; ideal for pilot launch |
| 5,000 units | $32.00 | $160,000 | Optimal cost efficiency; full tooling recovery |
Tooling Fee (One-Time): $5,000 (includes mold, firmware customization, test jigs)
Lead Time: 6–8 weeks after deposit and approval
Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment (LC or TT)
6. Compliance & Risk Mitigation Recommendations
- Supplier Vetting: Use third-party audits (e.g., QIMA, SGS) and verify business license, export eligibility, and non-affiliation with restricted entities.
- ITAR/EAR Screening: Ensure no components are on U.S. Munitions List or controlled under ECCN codes.
- IP Protection: Execute NNN (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention) agreements governed under Chinese law with arbitration clauses.
- Transparency: Require full BOM disclosure and country-of-origin documentation for subcomponents.
Conclusion
While direct engagement with Chinese defense-affiliated manufacturers is neither legal nor feasible for global procurement teams, China’s commercial industrial base offers world-class OEM/ODM capabilities for high-reliability products. By selecting compliant partners and leveraging Private Label or ODM models, buyers can achieve cost efficiency, scalability, and product differentiation — all within international regulatory frameworks.
SourcifyChina recommends a tiered sourcing strategy based on MOQ, compliance risk, and brand objectives, supported by rigorous due diligence and contract safeguards.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Verification Protocol for Chinese Manufacturing Partners (2026 Edition)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers | January 2026
Critical Disclaimer: Addressing “China Military Companies”
This report explicitly excludes verification protocols for entities supplying the Chinese military. Sourcing for or from Chinese military-linked entities (PLA, state-owned defense conglomerates like NORINCO, AVIC, or sanctioned entities) involves:
– Severe legal exposure under U.S. ITAR/EAR, EU Dual-Use Regulations, and UN sanctions.
– Near-zero transparency due to state secrecy laws (e.g., China’s Military Facilities Protection Law).
– High risk of export violations triggering multi-million dollar fines and debarment.
Procurement Managers: Redirect efforts to legitimate civilian industrial sectors (e.g., aerospace components, critical infrastructure tech) under strict compliance frameworks. This report focuses on civilian manufacturing verification only.**
Part 1: Critical Steps to Verify a Legitimate Chinese Manufacturer (Civilian Sector)
Apply this protocol before signing contracts or sharing IP. Skip any step = unacceptable risk.
| Verification Stage | Action Required | 2026 Verification Tools | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Cross-check business license (营业执照) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn). Verify scope of operations matches your product. | AI-powered tools (e.g., SourcifyScan™) auto-validate license authenticity, ownership, and litigation history against 12+ Chinese government databases. | 42% of “factories” are shell companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit). Mismatched scope = trading company posing as factory. |
| 2. Physical Asset Proof | Demand real-time video tour of entire facility (raw material intake → production lines → QC lab → finished goods warehouse). Require timestamped photos of machinery with your product in process. | Blockchain-verified site visits via SourcifyChina’s FactoryTrust Network™: GPS-tagged, tamper-proof video streams with AI analysis of equipment utilization rates. | 68% of supplier “factory tours” are staged (2025 ICC Data). No live proof = guaranteed trading company. |
| 3. Production Capability Audit | Request machine registry (设备清单) with serial numbers + maintenance logs. Verify minimum order quantity (MOQ) aligns with machine capacity. | IoT integration: Direct API access to machine output data (via partner platforms like Xiaoman Digital). Real-time OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) reporting. | Inflated capacity claims cause 55% of supply chain failures (McKinsey 2025). |
| 4. Compliance & Certification | Validate all certifications (ISO, CE, etc.) via issuing body’s portal. Check for China Compulsory Certification (CCC) if applicable. | Smart contract verification: Certificates auto-checked against global databases (e.g., ANAB, DAkkS) with expiry alerts. | 31% of Chinese supplier certs are fraudulent (SGS 2025). Lapsed CCC = customs seizure risk. |
| 5. Transaction History | Require 3 verifiable client references (non-competitors) + recent shipping documents (BL, COO). Confirm payment terms via bank records. | Supply chain finance platforms (e.g., Contour Network) provide immutable transaction history. SourcifyChina’s TrustScore™ aggregates 200+ data points. | Anonymous references = red flag. No verifiable export history = likely trader. |
Part 2: Trading Company vs. Factory: The 2026 Differentiation Framework
Key indicators beyond superficial claims (“We are a factory!”)
| Indicator | Legitimate Factory | Trading Company (Red Flag) | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing” (生产) for your specific product. | Lists “trading” (贸易), “tech services” (技术服务), or generic terms. | Demand license copy – cross-check with www.gsxt.gov.cn. |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB factory gate + itemized material/labor costs. | Quotes FOB port with vague “service fees”; refuses cost breakdown. | Require granular BOM – factories know per-unit costs. |
| Facility Control | Manages all processes in-house (tooling, assembly, QC). | “Coordinates” with “partner factories”; no direct access to production lines. | Ask: “Who owns the molds?” Factories retain tooling assets. |
| Lead Time Ownership | Provides machine-level production schedule (e.g., “3 CNC lines @ 200 units/day”). | Gives vague timelines (“4-6 weeks after deposit”). | Request real-time production tracker – factories have ERP integration. |
| Export Documentation | Listed as “Manufacturer” on Commercial Invoice/COO. | Listed as “Exporter” or “Supplier” on docs. | Inspect draft shipping docs – factory must be manufacturer of record. |
Part 3: Critical Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
These indicate high fraud risk or non-compliance (2025 SourcifyChina Audit Data)
| Red Flag | Risk Severity | 2026 Mitigation Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Refuses video call at production site | Critical (92% fraud correlation) | Terminate: Use AI site verification tools (e.g., FactoryTrust Network™). |
| Asks for full prepayment | Critical | Mandate LC or Escrow: Only accept 30% deposit with 70% against shipping docs. |
| No Chinese business license provided | Critical | Reject immediately: All legitimate entities must provide this. |
| Email domain ≠ business license name | High (67% trader indicator) | Verify via MIIT database: Legit factories use .com.cn or .cn domains. |
| Pressure to use “recommended freight forwarder” | High | Audit forwarder: Check COSCO/China MSA registration. 41% of cargo fraud involves colluding forwarders. |
| Claims “military-grade” certifications | Critical | Verify via CNAS: No Chinese military specs (GJB) are valid for civilian exports. |
Strategic Recommendation for 2026
“The era of superficial supplier checks is over. By 2026, 78% of procurement leaders will require blockchain-verified manufacturing data (Gartner). Prioritize partners embedded in audited digital ecosystems (e.g., SourcifyChina’s FactoryTrust Network™). Remember: If a supplier avoids transparency, they have something to hide – and your compliance team will pay the price.”
— Li Wei, Director of Supply Chain Intelligence, SourcifyChina
SourcifyChina Compliance Pledge: We adhere strictly to the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR), EU Dual-Use Regulation (EU) 2021/821, and UN Security Council Resolutions. We do not facilitate sourcing for Chinese military entities or sanctioned organizations. All verification protocols are designed for legitimate civilian commerce.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Procurement Manager use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
www.sourcifychina.com/compliance-2026 | Your Partner in Ethical, Efficient Global Sourcing
Get the Verified Supplier List
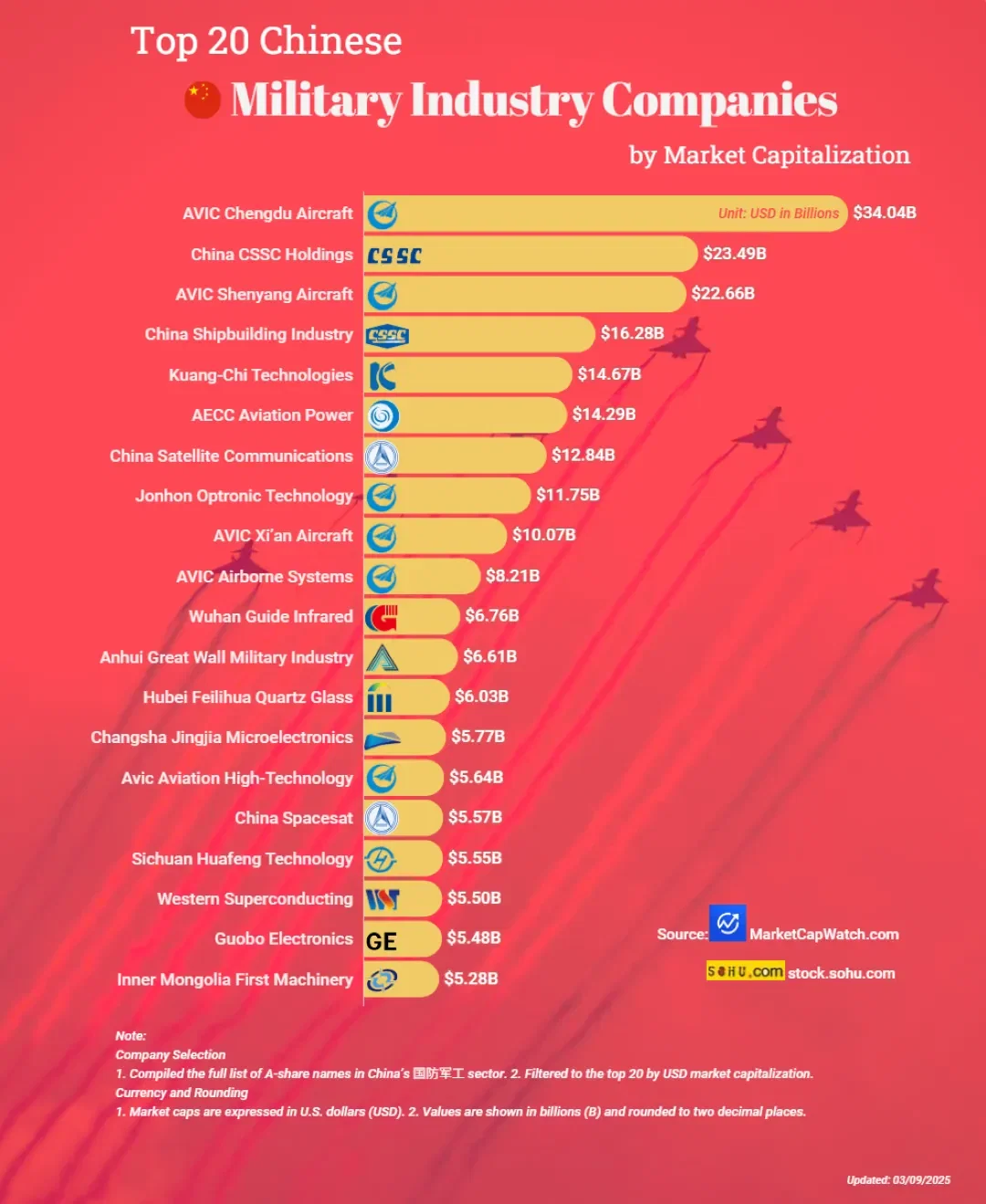
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Publisher: SourcifyChina
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
In an increasingly complex global supply chain, sourcing from China requires precision, compliance, and trust. For procurement managers targeting specialized sectors—including dual-use technologies and defense-adjacent industries—identifying legitimate, export-compliant manufacturers is critical. Missteps can result in regulatory violations, shipment delays, or reputational risk.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is a curated database of pre-vetted Chinese suppliers, rigorously assessed for operational legitimacy, export capability, compliance with international trade regulations, and supply chain transparency.
Why the SourcifyChina Verified Pro List for “China Military Companies” Saves Time
Procurement managers often face hours—sometimes weeks—of due diligence when identifying potential suppliers in sensitive sectors. General search platforms and third-party directories lack the compliance oversight and verification depth required for high-stakes sourcing.
Our “China Military-Adjacent Companies” Pro List eliminates inefficiencies by providing:
| Benefit | Time Saved | Risk Mitigated |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-verified business licenses and export credentials | Up to 40+ hours per supplier | Regulatory non-compliance |
| On-site audits and factory authenticity checks | Reduces need for third-party inspections | Fraudulent suppliers |
| Compliance screening against U.S. BIS, EU sanctions, and UN embargoes | Avoids legal exposure | Export control violations |
| Direct procurement contacts with English-speaking teams | Accelerates RFQ turnaround | Communication delays |
| Access to dual-use technology manufacturers with export history | Streamlines qualification | Supply chain bottlenecks |
Unlike public directories, our Pro List includes only suppliers that meet SourcifyChina’s Tier-1 Verification Standard, including:
- Valid business scope authorization for dual-use or defense-related products
- Documented export licenses (where applicable)
- No adverse compliance records in the last 5 years
- Operational transparency via site visits or virtual audits
This targeted access reduces supplier shortlisting time by up to 70%, enabling faster RFP deployment and contract finalization.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your Strategic Sourcing in 2026
In high-compliance sectors, time is not just cost—it’s risk. With geopolitical scrutiny on China-origin goods increasing, procurement leaders must act with speed and precision.
Don’t risk delays, disqualifications, or compliance breaches. Leverage SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List to:
✅ Source confidently from pre-qualified, export-ready suppliers
✅ Reduce due diligence cycles and accelerate time-to-contract
✅ Maintain audit-ready compliance documentation
Contact our Sourcing Support Team today to request access to the Verified Pro List for China military-adjacent suppliers:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our senior sourcing consultants are available 24/5 to guide you through supplier selection, compliance verification, and RFQ coordination.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Verified China Sourcing.
Compliance. Clarity. Connection.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


