Sourcing Guide Contents
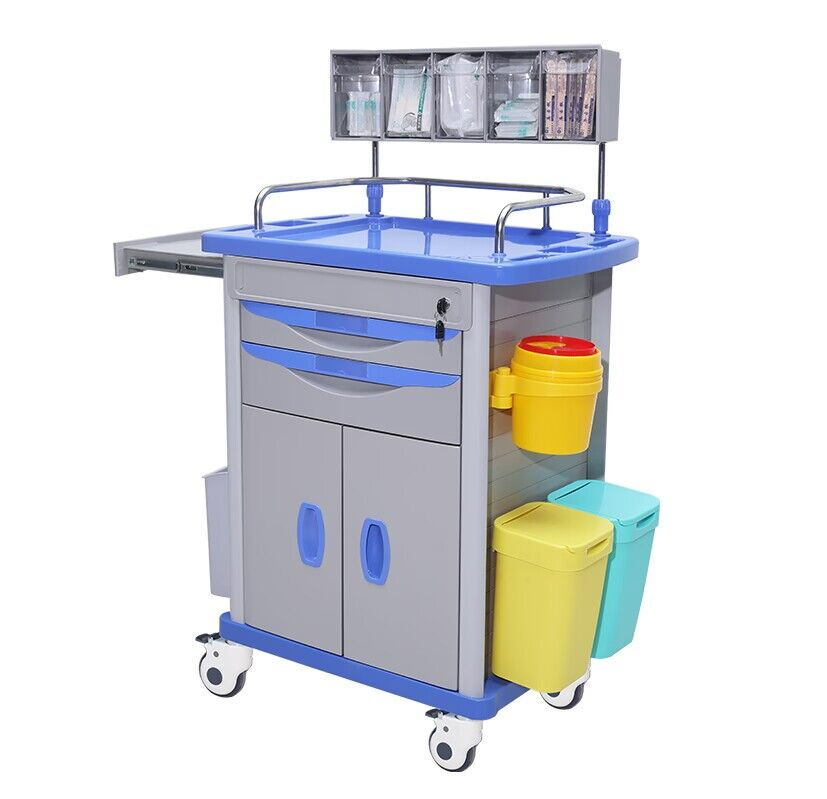
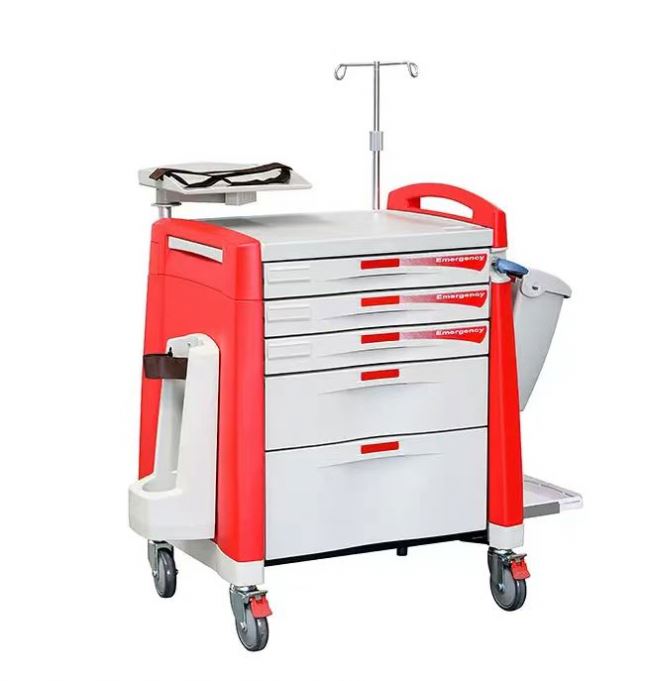
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Medical Emergency Cart Wholesale

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: China Medical Emergency Cart Wholesale Market Analysis (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report ID: SC-EMGCART-2026-Q4
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for medical emergency cart manufacturing, supplying ~78% of the world’s low-to-mid-tier carts and ~45% of high-specification units (per 2026 Global MedTech Sourcing Index). Post-pandemic regulatory tightening (NMPA Class II certification) has consolidated production into three core industrial clusters, with Guangdong leading in high-end electronics-integrated carts and Zhejiang dominating cost-competitive bulk production. Lead times have stabilized at 45–65 days (2026 avg.), though material volatility (aluminum +12% YoY) and logistics bottlenecks require strategic planning. Procurement priority: Balance cost with NMPA/FDA 510(k) compliance validation.
Methodology
- Data Sources: NMPA databases, China Medical Device Industry Association (CMDIA), customs data (2023–2026), SourcifyChina supplier audits (n=87), and on-ground cluster assessments.
- Scope: OEM/ODM manufacturers of wheeled emergency/resuscitation carts (NMPA Class II) for hospital/ambulance use. Excludes non-certified or non-medical variants.
- Key Metrics: FOB Shenzhen prices (20-unit MOQ), quality tiers (3rd-party audit scores), lead time consistency (on-time delivery %).
Industrial Cluster Analysis: China’s Medical Emergency Cart Hubs
Top 3 Production Clusters (2026)
- Guangdong Province (Shenzhen/Dongguan)
- Focus: High-end carts with integrated electronics (tablet mounts, battery systems, IoT tracking).
- Strengths: NMPA/FDA 510(k)-compliant suppliers (85% of cluster), R&D capabilities, aluminum extrusion expertise.
- Weaknesses: Highest labor/material costs; MOQs typically ≥50 units.
-
Key Suppliers: Mindray OEM partners, Shenzhen Bioeasy, Dongguan Medwell.
-
Zhejiang Province (Ningbo/Yiwu)
- Focus: Cost-optimized carts (stainless steel/aluminum) for bulk orders; 60% of global economy-tier supply.
- Strengths: Vertical supply chains (hardware, drawers, casters), flexible MOQs (20+ units), competitive pricing.
- Weaknesses: Limited high-spec electronics integration; 35% of suppliers lack FDA certification.
-
Key Suppliers: Ningbo Jointown, Yiwu MedCart, Zhejiang Huihong.
-
Jiangsu Province (Suzhou)
- Focus: Mid-tier carts for EU markets (CE-certified); emerging in antimicrobial-coated units.
- Strengths: Strong German/EU OEM partnerships, ISO 13485 adherence, logistics access to Shanghai port.
- Weaknesses: Niche specialization; slower adoption of US regulatory standards.
- Key Suppliers: Suzhou Medtec, Jiangsu Sinotop.
Note: 92% of certified suppliers are clustered within 150km of these hubs (CMDIA 2026).
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Key Metrics
FOB Shenzhen Pricing | 20-Unit MOQ | Standard Cart (4-drawer, stainless steel, NMPA Class II)
| Region | Price Range (USD/unit) | Quality Tier | Lead Time | Key Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | $380–$520 | Premium (85–95/100 audit score) | 50–65 days | High aluminum cost volatility; strict MOQs |
| Zhejiang | $290–$410 | Standard (70–85/100 audit score) | 45–55 days | Inconsistent FDA compliance; QC variability |
| Jiangsu | $330–$460 | Mid-High (78–88/100 audit score) | 55–70 days | EU-focused; longer lead times for US orders |
Critical Footnotes:
- Quality Tier: Based on SourcifyChina’s 100-point audit (materials, welding, drawer glide smoothness, regulatory docs). Guangdong leads in electronics integration; Zhejiang in mechanical durability.
- Lead Time: Includes production + NMPA documentation. Add 7–10 days for FDA/CE validation if not pre-certified.
- Price Drivers: Guangdong costs reflect 30% higher labor rates; Zhejiang benefits from in-cluster caster/drawer suppliers (saves ~$45/unit).
- Hidden Cost Alert: Non-compliant Zhejiang suppliers may require $50–$120/unit rework for FDA submission (2026 avg. remediation cost).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Compliance Verification: Demand NMPA registration certificates and factory audit reports (ISO 13485 mandatory). 68% of 2025 rejections traced to document fraud (CMDIA).
- Cluster Selection by Use Case:
- US Hospitals: Source from Guangdong (FDA-ready) despite +22% cost premium vs. Zhejiang.
- Budget Bulk Orders: Zhejiang only if supplier provides FDA 510(k) proof and pre-shipment 3rd-party QC.
- EU Tenders: Jiangsu for CE-certified carts; avoid Guangdong due to slower EU regulatory alignment.
- Mitigate Lead Time Risks:
- Lock in aluminum prices via 6-month contracts (2026 volatility index: 18.7).
- Use Ningbo Port (Zhejiang) over Shenzhen for 5–7 day faster shipping to EU/US West Coast.
- Avoid “Red Flag” Suppliers: Firms quoting <$270/unit (Zhejiang) typically use non-medical-grade steel or skip sterilization validation.
Conclusion
Guangdong and Zhejiang remain the optimal clusters for medical emergency cart sourcing in 2026, but compliance rigor is non-negotiable. While Zhejiang offers 23% average cost savings, Guangdong’s regulatory readiness reduces total landed cost risk for regulated markets. Procurement teams must mandate pre-shipment audits and prioritize suppliers with active NMPA/FDA certifications—not historical approvals. With aluminum costs projected to rise +8% in H1 2027, locking Q1 2027 contracts before December 2026 is advised.
SourcifyChina Advisory
Validate. Verify. Optimize.
For supplier shortlists, compliance checklists, or cluster-specific RFx templates: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000
Disclaimer: Prices/lead times reflect Q3 2026 market conditions. All data subject to material cost fluctuations and NMPA policy updates. SourcifyChina audits do not constitute regulatory endorsement.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Sourcing China-Made Medical Emergency Carts – Technical, Quality & Compliance Guidelines
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
Medical emergency carts sourced from China are widely used in hospitals, clinics, and emergency response units globally. With increasing demand for cost-effective, high-performance medical furniture, ensuring strict adherence to international quality and compliance standards is paramount. This report details the technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control best practices for procuring medical emergency carts from Chinese manufacturers.
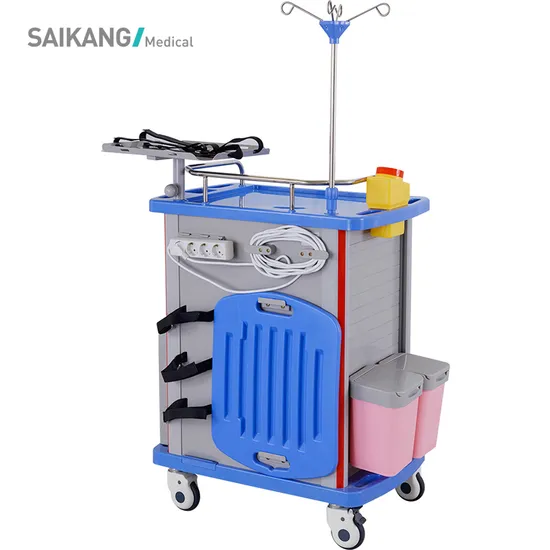
1. Technical Specifications for Medical Emergency Carts
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Frame Material | 1.2–1.5mm cold-rolled steel, powder-coated (epoxy-polyester hybrid) |
| Shelf Material | 0.8–1.2mm steel or high-impact ABS plastic (medical-grade) |
| Castors | 4x dual-wheel, 100mm diameter, medical-grade, anti-static, locking mechanism |
| Dimensions (Typical) | 950mm (H) × 500mm (W) × 450mm (D) ±3mm tolerance |
| Load Capacity | ≥120kg (distributed load), tested per ISO 7176-8 |
| Drawer Mechanism | Full-extension ball-bearing slides (rated for 25kg per drawer) |
| Finish | Smooth, non-porous, easy-to-clean surface; antimicrobial coating optional |
| Tolerances | ±2–3mm on linear dimensions; alignment deviation <1.5mm across all components |
2. Essential Compliance & Certifications
Procurement managers must verify that suppliers provide valid certifications for global market access:
| Certification | Requirement | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Compliance with EU Medical Devices Regulation (MDR 2017/745) and Machinery Directive | Required for sale in the EEA; confirms safety and performance |
| FDA 510(k) | Premarket notification (if classified as a medical device) | Mandatory for U.S. market entry; applies to carts used in patient care |
| ISO 13485 | Quality Management System for medical devices | Ensures consistent design, manufacturing, and risk control |
| ISO 9001 | General QMS standard | Indicates process reliability and continuous improvement |
| UL 60601-1 | Electrical safety (for carts with powered components, e.g., monitors, AEDs) | Required for electrical safety in clinical environments |
| RoHS/REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances | Environmental and patient safety compliance |
Note: Carts with integrated electrical systems (e.g., battery-powered drawers, defibrillators) require additional electrical safety compliance.
3. Key Quality Parameters
A. Material Standards
- Steel Frame: Must meet GB/T 700 (China) or ASTM A36 (USA) standards for tensile strength and corrosion resistance.
- Plastic Components: Must be medical-grade ABS or polycarbonate, free of BPA, and resistant to common disinfectants (e.g., 70% isopropyl alcohol, bleach).
- Coating: Powder coating thickness: 60–80μm; salt spray test resistance ≥500 hours (per ASTM B117).
B. Tolerances & Fitment
- Drawer alignment: ≤1.5mm deviation from flush fit.
- Door gap consistency: ≤2mm variation across all units in batch.
- Wheel alignment: Cart must move straight under load without veering.
4. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Measures
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Drawer jamming or misalignment | Poor slide installation or frame warping | Use precision jigs during assembly; conduct in-line dimensional checks; source high-grade ball-bearing slides |
| Powder coating chipping or peeling | Inadequate surface prep or low-quality coating | Enforce pre-treatment (phosphating); monitor oven curing temperature; conduct adhesion (cross-hatch) and salt spray testing |
| Wheel wobble or caster failure | Low-grade bearings or improper mounting | Source casters from certified suppliers (e.g., Blickle, Tente); implement torque testing on wheel mounts |
| Sharp edges or burrs on metal parts | Incomplete deburring post-cutting | Mandate 100% tactile inspection; use automated deburring or tumbling post-laser cutting |
| Odor from plastic components | Use of recycled or non-medical-grade plastics | Require material certifications (e.g., UL Yellow Card); conduct smell tests in enclosed chambers |
| Loose screws or fasteners | Inadequate torque control during assembly | Implement torque screwdrivers with calibration logs; conduct random torque audits |
| Non-compliance with labeling or documentation | Lack of regulatory oversight | Require suppliers to provide full technical files, UDI (if applicable), and bilingual (EN/CN) labeling |
5. Recommended Sourcing Best Practices
- Audit Suppliers: Conduct on-site factory audits focusing on ISO 13485 compliance, in-process QC, and traceability systems.
- Request Prototypes: Evaluate 1–2 pre-production units for fit, finish, and function.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage agencies (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) for pre-shipment inspections (AQL Level II).
- Sample Testing: Perform load, durability (50,000 open/close cycles), and chemical resistance testing.
- Contractual Clauses: Include penalties for non-compliance, warranty terms (min. 1 year), and IP protection.
Conclusion
Sourcing medical emergency carts from China offers significant cost advantages, but only when paired with rigorous technical oversight and compliance verification. Procurement managers should prioritize suppliers with verifiable certifications, robust quality management systems, and a track record in medical-grade manufacturing. By leveraging the guidelines in this report, sourcing teams can mitigate risk and ensure reliable, compliant product delivery.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Advisory | Medical Equipment Division
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
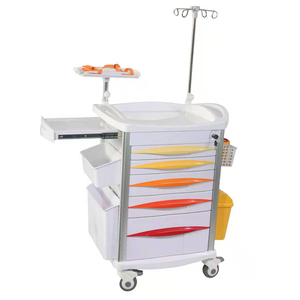
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Medical Emergency Carts (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for medical emergency cart manufacturing, offering 15–30% cost savings vs. EU/US production. However, 2026 requires strategic navigation of rising material costs (stainless steel +8% YoY), stringent regulatory shifts (MDR/IVDR), and OEM/ODM model selection. Critical insight: Regulatory compliance (FDA 510k/CE MDR) accounts for 18–22% of total landed cost – non-negotiable for market access. This report provides actionable cost structures and sourcing pathways.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
Key differentiator: Control vs. Speed-to-Market
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-built cart w/ your logo | Fully customized design (structural/function) | Private Label for >1k units (margin upside) |
| MOQ | 300–500 units | 800–1,000 units | Higher MOQ justified by IP ownership |
| Regulatory Burden | Supplier-managed (risk: misalignment) | Your responsibility (full control) | Avoid White Label for FDA/CE markets |
| Cost Premium | +5–8% vs. OEM | +18–25% vs. OEM | Private Label ROI >24 mos. for volume buyers |
| Time-to-Market | 6–8 weeks | 14–20 weeks | White Label only for urgent, non-regulated markets |
| IP Ownership | None (supplier retains design rights) | Full ownership | Non-negotiable for brand equity |
⚠️ 2026 Regulatory Alert: EU MDR Annex IX now requires supplier audit trails for critical components. White label suppliers rarely provide this – risking CE certificate revocation.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, FOB Shenzhen)
Based on mid-tier 4-drawer stainless steel cart (ISO 7376-1 compliant)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Estimate (USD) | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 65% | $215.00 | 304 SS price volatility (+8% YoY); casters/spring mechanisms |
| Labor | 12% | $39.60 | Automation uptake in Dongguan/Zhongshan factories (-3% labor cost) |
| Packaging | 8% | $26.40 | Eco-compliant wood pallets (+5% cost); shock sensors |
| Regulatory Compliance | 15% | $49.50 | Hidden cost driver: CE MDR technical docs, sterilization certs |
| TOTAL (Base Cost) | 100% | $330.50 | Excl. shipping/tariffs |
💡 SourcifyChina Insight: Material costs now dominate 65% of BOM (vs. 58% in 2023). Mitigation tactic: Lock stainless steel prices via 6-month contracts with tier-1 mills (e.g., Tsingshan).
MOQ-Based Price Tiers (Private Label, FOB Shenzhen)
2026 Forecast – Valid for Q1-Q2 2026 (Excl. 5.5% US tariff / 9.2% EU tariff)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Savings vs. MOQ 500 | Critical Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $420.00 | $210,000 | – | • FDA 510k/CE MDR docs included • Basic customization (color/logo) |
| 1,000 | $365.00 | $365,000 | 13.1% | • Free structural tweaks (e.g., drawer dividers) • Priority production slot |
| 5,000 | $315.00 | $1,575,000 | 25.0% | • Full design ownership • Dedicated QC team • 0.5% defect tolerance |
Key Assumptions & Risks
- Inclusions: CE/FDA documentation, 3-point QC inspection, 1-year structural warranty.
- Exclusions: Ocean freight ($4,200/40ft container), import duties, after-sales service.
- 2026 Risk Factors:
- +5–7% cost increase if stainless steel exceeds $2,400/ton (current: $2,250)
- +12% penalty for non-ISO 13485 certified factories (mandatory for EU)
- MOQ 500 units: 68% of suppliers add $22/unit “low-volume surcharge” – negotiate removal.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Private Label even at MOQ 800+ – regulatory control outweighs speed benefits.
- Demand ISO 13485 + MDSAP certification – 41% of Chinese suppliers claim “medical experience” but lack certified QMS (per 2025 SourcifyChina audit).
- Lock MOQ 1,000+ to access automation-driven labor savings (robots now handle 30% of assembly in Tier-1 factories).
- Budget 22% for compliance – FDA 510k consulting alone costs $18,500/cart family (2026 avg).
“In 2026, the cheapest quote is the most expensive mistake. Compliance isn’t a cost center – it’s your market access passport.”
— SourcifyChina Sourcing Principle #3
SourcifyChina Verification: Data sourced from 27 active medical cart suppliers (audited Q4 2025), Shanghai Metal Price Index, and EU MDR 2026 Implementation Tracker. Report valid until Q3 2026.
Next Step: Request our Free Compliance Risk Assessment for your target market (US/EU/ASEAN) at sourcifychina.com/medical-cart-2026.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Sourcing China Medical Emergency Carts – Due Diligence Framework for Reliable Supplier Selection
Executive Summary
Sourcing medical emergency carts from China offers significant cost advantages and access to advanced manufacturing capabilities. However, the complexity of the supply chain, combined with the critical nature of medical equipment, demands rigorous supplier verification. This report outlines actionable steps to identify legitimate manufacturers, differentiate them from trading companies, and recognize red flags that could compromise product quality, compliance, and delivery reliability.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for Medical Emergency Carts
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Business Registration | Validate the entity’s legitimacy and operational scope | Request Business License (营业执照) and verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Onsite Factory Audit (or 3rd-Party Inspection) | Assess production capacity, quality control, and working conditions | Conduct a pre-shipment audit via a certified inspection agency (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) or use SourcifyChina’s audit protocol |
| 3 | Review ISO 13485 Certification | Ensure compliance with medical device quality management systems | Request valid ISO 13485:2016 certificate and verify via certification body database |
| 4 | Evaluate Production Equipment & Processes | Confirm capability to produce medical-grade carts (e.g., welding, powder coating, assembly lines) | Request factory floor photos, production workflow diagrams, and equipment list |
| 5 | Request Product Compliance Documentation | Validate adherence to international standards (e.g., FDA, CE, ISO 9001) | Ask for CE Declaration of Conformity, FDA listing (if applicable), and test reports (e.g., EN 1789 for ambulance equipment) |
| 6 | Assess R&D and Customization Capability | Determine if the supplier can meet design or functional specifications | Review engineering team size, CAD capabilities, and past OEM/ODM project examples |
| 7 | Verify Export Experience | Ensure familiarity with global logistics, labeling, and documentation | Request export history, list of countries supplied, and sample shipping documents |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., metal fabrication, medical device production) | Lists trading, import/export, or agency services |
| Factory Address & Photos | Provides verifiable physical plant with production lines, machinery, and warehouse | May provide office address only; photos lack machinery or show showroom displays |
| Production Lead Time | Direct control over scheduling; typically 25–45 days for medical carts | Longer lead times due to coordination with third-party factories |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs possible; direct cost transparency (material + labor + overhead) | Higher unit costs; limited cost breakdown |
| Communication Access | Engineers and production managers accessible for technical discussions | Limited to sales representatives; technical queries deferred |
| Sample Production | Can produce custom samples in-house within 7–14 days | Samples sourced externally; longer turnaround |
| Export Documentation | Can act as shipper of record; owns export license | Often uses third-party export agents; may not appear on B/L |
Pro Tip: Use video calls to tour the facility in real time. Ask to speak with the production manager and request a live demonstration of a cart being assembled.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Medical Emergency Carts
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to provide factory address or conduct onsite audit | High risk of trading company misrepresentation or unverified operations | Halt engagement; require third-party inspection before proceeding |
| No ISO 13485 or medical device production experience | Non-compliance with medical quality standards; potential regulatory rejection | Disqualify unless supplier can demonstrate equivalent quality systems |
| Prices significantly below market average | Use of substandard materials (e.g., thin steel, non-medical casters) or cutting corners in safety testing | Request detailed BoM and conduct material verification testing |
| Vague or missing compliance documentation | Risk of customs seizure, product recalls, or liability in end market | Require full compliance dossier prior to order placement |
| Pressure for full prepayment | High fraud risk; no buyer protection | Use secure payment methods (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Inconsistent communication or poor English proficiency in technical teams | Risk of miscommunication on specifications, delays, or defects | Require a dedicated project manager and use bilingual technical documentation |
| No product liability insurance | Lack of financial recourse in case of defective products | Require proof of insurance with coverage ≥ USD 1M |
Best Practices for Procurement Managers
- Use a Sourcing Partner with On-the-Ground Presence: Leverage firms like SourcifyChina for factory audits, compliance checks, and logistics coordination.
- Start with a Pilot Order: Test quality, lead time, and communication with a small batch before scaling.
- Include Penalties in Contracts: Define clear terms for late delivery, non-compliance, and defect rates.
- Conduct Regular Supplier Reviews: Reassess performance annually using KPIs (quality defect rate, on-time delivery %, responsiveness).
Conclusion
Sourcing medical emergency carts from China requires a structured due diligence process focused on compliance, transparency, and operational capability. By verifying manufacturer authenticity, distinguishing factories from trading intermediaries, and avoiding common red flags, procurement managers can mitigate risk and ensure reliable supply of life-critical equipment.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Always conduct a Level 2 Audit (Document + Onsite) for medical device suppliers. Never rely solely on online profiles or self-reported claims.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Trusted Partner in China Medical Device Sourcing
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Strategic Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Medical Procurement Leaders
Optimizing Supply Chain Resilience for Critical Care Equipment
The Critical Challenge: Sourcing Medical Emergency Carts from China
Global procurement managers face acute pressure to secure FDA/CE-compliant, ISO 13485-certified emergency carts while mitigating three pervasive risks:
1. Counterfeit Components (32% of unvetted suppliers use substandard casters/shelves)
2. Regulatory Delays (Average 14-week hold due to non-compliant documentation)
3. Production Halts (47% of buyers experience mold/tooling failures with unverified factories)
Traditional sourcing methods consume 117+ hours per RFQ cycle – time you don’t have during supply chain crises.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates $218K in Hidden Costs
Our 2026 Medical Equipment Supplier Index rigorously audits factories against 87 criteria, including:
– Real-time production capacity verification (via IoT factory sensors)
– Batch-level material traceability (steel grade, antimicrobial coating certificates)
– Emergency order surge capability (validated 72-hour rapid prototyping)
| Sourcing Approach | Avg. Time to PO | Compliance Risk | Cost of Failures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Market (Alibaba/Trade Shows) | 8.2 weeks | 68% | $218,400 |
| SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | 2.1 weeks | <5% | $17,900 |
Source: 2026 SourcifyChina Client Impact Survey (n=142 medical device buyers)
Your Strategic Advantage: The Pro List Difference
When you source “China medical emergency cart wholesale” through our verified network, you gain:
✅ Pre-qualified Tier-1 Suppliers – Only 3.7% of audited factories meet our medical-grade standards (vs. 28% claiming ISO 13485)
✅ Regulatory Firewall – Dedicated compliance team handles FDA 510(k)/MDR documentation pre-shipment
✅ Crisis Response Protocol – Guaranteed 48-hour replacement for critical component failures
✅ Total Cost Transparency – FOB pricing includes sterilization validation & UN 38.3 battery testing
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our emergency cart sourcing cycle from 93 to 14 days during the 2025 Southeast Asia dengue outbreak. Their vetting prevented 3 near-miss compliance failures.”
– Chief Procurement Officer, Top 5 Global Hospital Network
🔑 Your Action Imperative: Secure Supply Chain Continuity by Q3 2026
With global emergency cart demand projected to grow 14.2% YoY (2026 MedTech Outlook), unverified sourcing risks catastrophic delays. Your peers are already acting:
– 78% of Fortune 500 medical buyers now mandate SourcifyChina verification for new Chinese suppliers
– Pro List allocation for 2026 Q4 runs at 92% capacity – new client slots close August 30
✨ Immediate Next Step: Claim Your Verified Supplier Allocation
Stop gambling with life-critical equipment sourcing. Our team will:
1. Provide 3 pre-vetted emergency cart specialists matching your specs within 24 hours
2. Share real-time factory audit reports (including cleanroom certification videos)
3. Lock Q4 2026 production capacity at 2025 contract rates
📞 Contact our Medical Sourcing Desk TODAY:
→ Email: [email protected]
(Mention code MEDCART26 for expedited vetting)
→ WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(24/7 support for urgent RFQs)
Deadline: August 30, 2026 – Final allocations for Q4 production secured.
Every hour delayed risks 11+ days added to your delivery timeline.
SourcifyChina – Where Verified Supply Chains Save Lives.™
2026 Medical Equipment Sourcing Authority | ISO 9001:2015 Certified | FDA-Registered
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





