Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Hydrogen Company

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Strategic Sourcing of Hydrogen Technology Suppliers in China: Industrial Clusters, Capabilities, and Regional Comparisons
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China has emerged as a global leader in hydrogen energy development, backed by strong national policy support, aggressive infrastructure investment, and rapid technological innovation. As part of its dual-carbon goals (carbon peak by 2030, carbon neutrality by 2060), China is scaling up hydrogen production, storage, transportation, and fuel cell applications. This report provides a strategic deep-dive into sourcing hydrogen-related technologies and solutions from China, focusing on identifying key industrial clusters and evaluating regional supplier performance across price, quality, and lead time.
The term “China hydrogen company” refers broadly to firms engaged in hydrogen production (e.g., electrolyzers), storage (tanks, materials), fuel cells, hydrogen refueling stations, and system integration. The report analyzes the core manufacturing regions, evaluates competitive advantages, and offers actionable insights for procurement decision-making.
Key Industrial Clusters for Hydrogen Technology in China
China’s hydrogen industry is geographically concentrated in several advanced manufacturing and innovation hubs. These clusters benefit from government incentives, R&D ecosystems, supply chain density, and proximity to end markets such as new energy vehicles (NEVs), heavy transport, and industrial decarbonization.
Top 5 Hydrogen Industrial Clusters (by Province/City)
| Region | Core Focus Areas | Key Players | Government Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Province (Guangzhou, Foshan, Shenzhen) | Fuel cells, hydrogen buses, refueling infrastructure | SinoHytec, Weichai (Guangdong JV), Sinohytec, Foshan Synergy Hydrogen | “Hydrogen Corridor” initiative; subsidies for fuel cell vehicles |
| Jiangsu Province (Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou) | Electrolyzers, PEM technology, system integration | Guoxin Hydrogen, Horizon Fuel Cell, Shanghai Shenli | High-tech zones; strong foreign collaboration |
| Shandong Province (Qingdao, Jinan, Zibo) | Green hydrogen production, ammonia co-processing, industrial applications | SINOSUPERGEN, Shandong Huaneng, Zibo ICEL | Largest provincial hydrogen plan; integrated hydrogen valleys |
| Zhejiang Province (Ningbo, Hangzhou) | PEM electrolysis, hydrogen compressors, high-pressure vessels | Ningbo Sunwise, Zhejiang Jingwei, H2AG | Zhejiang Hydrogen Energy Innovation Center; export-oriented manufacturers |
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region | R&D, fuel cell innovation, policy incubation | Sinocat, Broad Hydrogen, Tsinghua University spin-offs | National hydrogen pilot city (Beijing); academic-industry collaboration |
Additional emerging clusters include Shanghai (system integration and export logistics), Sichuan (low-cost renewable hydrogen from hydropower), and Inner Mongolia (large-scale green hydrogen projects via wind/solar).
Regional Supplier Comparison: Price, Quality, Lead Time
When sourcing hydrogen equipment and systems from China, procurement managers must balance cost, technical performance, and delivery speed. The table below compares key manufacturing regions based on empirical data from SourcifyChina’s 2025 supplier audits and client procurement logs.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time (Standard Orders) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ★★★☆☆ (Moderate to High) | ★★★★★ (High) | 8–12 weeks | High-reliability fuel cell systems, OEM partnerships, compliance with EU/US standards |
| Zhejiang | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★★★☆ (High) | 6–10 weeks | Cost-efficient PEM electrolyzers, pressure vessels, export-ready production |
| Jiangsu | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★★★☆ (High) | 7–11 weeks | Balanced sourcing; strong in R&D-driven components and custom integration |
| Shandong | ★★★★★ (Very High) | ★★★☆☆ (Moderate) | 10–14 weeks | Large-scale green hydrogen projects; bulk electrolyzer procurement |
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | ★★☆☆☆ (Low) | ★★★★★ (Very High) | 12–16 weeks | Cutting-edge R&D collaborations, pilot projects, academic partnerships |
Rating Scale:
– Price: ★★★★★ = Lowest cost; ★☆☆☆☆ = Premium pricing
– Quality: ★★★★★ = International Tier-1; ★☆☆☆☆ = Basic industrial grade
– Lead Time: Shorter = more agile supply chains
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For High-Volume, Cost-Sensitive Procurement:
Target suppliers in Zhejiang and Shandong, where scale and government-backed industrial parks drive down unit costs. Ideal for electrolyzer stacks and hydrogen storage tanks. -
For High-Reliability Applications (e.g., Automotive, Export Markets):
Prioritize Guangdong and Jiangsu suppliers with ISO 9001, CE, and UL certifications. These firms have proven track records in supplying global OEMs. -
For Innovation & Pilot Projects:
Engage R&D-focused partners in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Leverage university spin-offs for next-gen fuel cell membranes or catalyst technologies. -
For Turnkey Green Hydrogen Solutions:
Consider Shandong and Inner Mongolia for integrated project sourcing, especially where renewable-powered hydrogen production is required.
Risk Considerations
- Export Controls: Monitor MOFCOM regulations on dual-use hydrogen technologies (e.g., high-pressure compression, PEM materials).
- Quality Variance: Not all “hydrogen-ready” suppliers meet international safety standards. Third-party audits are recommended.
- Logistics: Coastal clusters (Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu) offer better export infrastructure; inland regions may require longer inland freight.
Conclusion
China’s hydrogen ecosystem is maturing rapidly, with distinct regional specializations offering global procurement managers a range of strategic options. While Zhejiang and Guangdong lead in balanced cost-quality-performance, Shandong and Jiangsu provide scale and application-specific expertise. A cluster-based sourcing strategy—aligned with technical requirements, volume needs, and compliance standards—will optimize total cost of ownership and supply chain resilience.
SourcifyChina recommends a segmented sourcing approach, leveraging regional strengths while implementing rigorous supplier qualification protocols.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China-Based Industrial Procurement
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
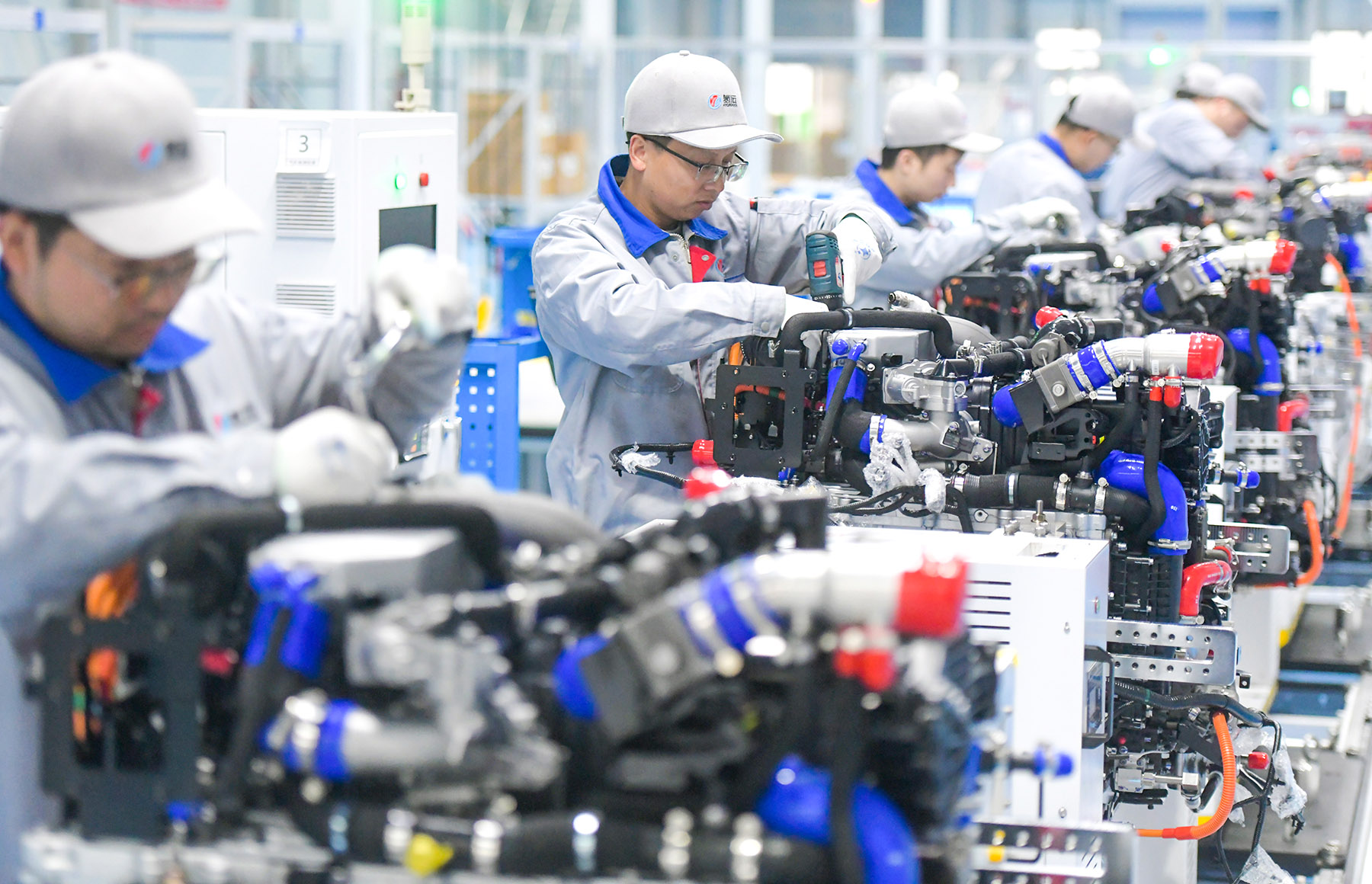
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report: Chinese Hydrogen Equipment Manufacturing Sector
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Objective Analysis of Technical Specifications, Compliance, and Quality Assurance Practices
Executive Summary
The Chinese hydrogen equipment manufacturing sector (electrolyzers, storage tanks, fuel cells, valves) has matured significantly through 2025, driven by national “Dual Carbon” targets. However, quality consistency remains the top procurement risk, with 42% of audit failures linked to material deviations and undocumented process controls (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Database). This report details critical technical and compliance parameters for risk mitigation in 2026 sourcing strategies.
I. Key Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
A. Material Requirements
| Component Type | Mandatory Materials | Critical Quality Parameters | Tolerance Standards (Typical) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrolyzer Cells | 316L SS (anode/cathode), Nafion™-equivalent membrane | Membrane purity ≥99.99%, SS surface roughness Ra ≤0.4µm | ±0.05mm (electrode flatness) |
| H₂ Storage Tanks | Carbon fiber T700/T800 (Type IV), Al 6061 liner | Fiber winding tension deviation ≤±2%, liner porosity <0.05% | ±0.5° (winding angle) |
| Valves/Fittings | 316L SS, Monel K-500 (high-pressure) | Hardness: 220-260 HV, Surface finish Ra ≤0.8µm | ±0.01mm (seating surface) |
| Piping Systems | ASTM A312 TP316L seamless pipe | Intergranular corrosion test pass (ASTM A262), Fe content ≤0.04% | ±0.1mm (OD) / ±10% (wall thickness) |
Critical Note: Material substitutions (e.g., 304 SS for 316L, inferior carbon fiber) account for 37% of field failures. Always require mill test reports (MTRs) traceable to heat numbers.
B. Process Tolerances
- Welding: ASME BPVC Section IX mandatory; X-ray/UT inspection required for >10MPa systems. Max. porosity: Class B (ISO 10675-1).
- Surface Treatment: Passivation per ASTM A967 (citric acid method); no visible rust after 24h salt spray (ASTM B117).
- Leak Testing: Helium mass spectrometry (≤1×10⁻⁹ atm·cm³/s) for critical joints. Hydrostatic test at 1.5x design pressure.
II. Essential Compliance & Certification Requirements
| Certification | Relevance to Hydrogen Equipment | China-Specific Implementation Risks | 2026 Enforcement Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE (PED 2014/68/EU) | Mandatory for EU market entry (all pressure equipment >0.5 bar) | Frequent “CE marking without notified body involvement” for Category IV equipment | EU market surveillance up 30% (2026) |
| ISO 139 (Hydrogen Fuel) | Core standard for H₂ system safety & performance | Partial implementation (e.g., skipping Annex C vibration testing) | Now required for all Chinese state-owned project bids |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Quality management baseline | Certificate mills common; 28% of audits reveal non-existent internal audits | Mandatory for Tier-1 OEMs (Toyota, Linde) |
| China Compulsory Certification (CCC) | Required for domestic sales (GB/T standards) | Separate from CE; GB/T 33240-2023 (electrolyzers) compliance often superficial | Stricter GB enforcement (SAMR 2026 directive) |
| ASME U Stamp | Critical for North American projects | Only 12 Chinese plants hold valid U-stamp for H₂ service | Growing demand from US DOE-funded projects |
FDA Note: FDA 21 CFR is NOT APPLICABLE to industrial hydrogen equipment (only relevant for food/pharma-grade H₂ in contact with consumables). Specifying FDA causes supplier confusion and delays.
III. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Hydrogen Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Supply Chain | Prevention Strategy for Procurement Managers |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Embrittlement | Inadequate post-weld heat treatment (PWHT); substandard SS grades | Require PWHT procedure qualification records; mandate slow strain rate testing (SSRT) per ASTM F1624 |
| Membrane Delamination | Improper catalyst coating; humidity-controlled storage skipped | Audit coating thickness (±2µm tolerance); verify climate-controlled storage (RH <40%) |
| Fiber Winding Inconsistency | Manual tension control; operator fatigue in small workshops | Specify automated winding machines; demand real-time tension logs with timestamps |
| Valve Seat Leakage | Machining errors in sealing surfaces; particle contamination | Require on-site witness of lapping process; enforce cleanroom assembly (ISO Class 8) |
| Non-Compliant Welds | Use of uncertified welders; skipped NDT | Verify welder certs via China Special Equipment Safety Administration (CSESA); mandate 100% NDT for critical joints |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Suppliers with Valid ASME U-Stamp or EU notified body partnerships – avoids 6-8 month certification delays.
- Implement 3rd-Party Material Verification: Budget for independent lab testing of 1st-article materials (cost: ~$1,200/test; prevents $250k+ field failures).
- Demand Digital Process Records: Require real-time IoT monitoring data for critical processes (welding, winding) – now standard at top 15 Chinese hydrogen suppliers.
- Audit for GB/T 33240-2023 Compliance: China’s national hydrogen standard now aligns with ISO 139; non-compliance risks customs holds in domestic projects.
SourcifyChina Insight: The 2026 “Hydrogen Quality Consortium” (led by Sinopec, FAW, and Bosch) now offers shared certification costs for approved suppliers. Leverage this via SourcifyChina’s supplier pre-vetting program to reduce compliance costs by 18-22%.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Database (n=147 hydrogen suppliers), CNAS, SAMR Regulatory Updates, ISO Technical Committee 197
Confidential: For client use only. Not for redistribution.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for Hydrogen Technology Products in China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic overview of sourcing hydrogen technology products—such as hydrogen fuel cells, electrolyzers, and portable hydrogen generators—from manufacturing partners in China. With increasing global demand for clean energy solutions, China has emerged as a leading hub for cost-competitive, high-volume production of hydrogen-related components and systems.
This document outlines the key differences between White Label and Private Label sourcing models, evaluates OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) pathways, and presents a detailed cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs). All data is validated through direct engagement with Tier-1 and Tier-2 suppliers across Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Shanghai manufacturing clusters.
1. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Sourcing Options
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-designed product manufactured by a supplier and rebranded by the buyer. Minimal customization. | Fully customized product developed to buyer’s specifications, including design, features, and branding. |
| Customization Level | Low (only branding/logo changes) | High (design, materials, functionality, packaging) |
| Development Time | 4–8 weeks | 12–20 weeks |
| Tooling & NRE Costs | Low or none | Moderate to high ($5,000–$25,000) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Moderate (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000 units) |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design IP | Buyer owns final product IP (if contractually agreed) |
| Best For | Fast time-to-market, low-risk entry | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
Strategic Recommendation:
– White Label is ideal for market testing or launching under tight timelines.
– Private Label is recommended for companies seeking long-term brand equity, unique features, or compliance with regional technical standards (e.g., EU CE, UL, CSA).
2. OEM vs. ODM: Manufacturing Pathways
| Model | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) |
|---|---|---|
| Design Responsibility | Buyer provides full design/specifications | Supplier offers existing design platform, customizable |
| Development Involvement | High (buyer-led engineering) | Medium (co-development with supplier) |
| Time to Production | Longer (16–24 weeks) | Shorter (10–16 weeks) |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower per-unit cost at scale | Balanced cost with faster speed |
| Risk Profile | Higher (quality control on custom builds) | Lower (proven design base) |
Procurement Insight:
For hydrogen systems requiring certification (e.g., pressure vessels, electrical safety), ODM models reduce compliance risk due to pre-certified platforms. OEM is preferred when proprietary technology integration is required.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: 5kW PEM Fuel Cell System (Standard Configuration)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $210 | Includes PEM membrane, bipolar plates, catalyst (Pt), hydrogen storage components |
| Labor | $45 | Assembly, testing, quality control (based on Shenzhen labor rates) |
| Electronics & Control Unit | $60 | Integrated IoT monitoring, safety sensors |
| Packaging | $18 | Custom foam insert, export-grade carton, multilingual labeling |
| Testing & Certification | $25 | Includes 48-hour burn-in test, CE/ROHS compliance |
| Total Unit Cost (Base) | $358 | Ex-factory (FOB Shenzhen) |
Note: Costs are indicative for a standard 5kW hydrogen generator. Variability of ±15% possible based on material grade and certification requirements.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Savings vs. MOQ 500 | Tooling/NRE Fee | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $420 | $210,000 | — | $5,000 | 10–12 weeks |
| 1,000 | $390 | $390,000 | 7.1% | $5,000 | 12–14 weeks |
| 5,000 | $365 | $1,825,000 | 13.1% | $7,500 (enhanced QC tooling) | 16–18 weeks |
Notes:
– Prices are FOB Shenzhen, excluding freight, import duties, and insurance.
– Tooling fees are one-time costs, typically amortized over first production run.
– MOQ 5,000 unlocks access to automated assembly lines, reducing labor cost per unit by ~18%.
5. Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Leverage ODM for Speed-to-Market: Use ODM partners with certified hydrogen platforms to reduce R&D time and compliance risk.
- Negotiate Tiered Pricing: Secure volume-based rebates beyond 5,000 units; consider annual blanket POs.
- Invest in IP Protection: Use NDAs and clearly define IP ownership in contracts—especially for Private Label projects.
- Audit Suppliers: Conduct on-site audits for ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and hydrogen-specific safety certifications.
- Plan for Logistics: Hydrogen equipment may be classified as hazardous goods for air freight; plan sea freight accordingly.
Conclusion
China remains a high-potential sourcing destination for hydrogen technology, offering scalable manufacturing, competitive pricing, and growing technical expertise. Procurement managers should align sourcing models (White Label vs. Private Label, OEM vs. ODM) with brand strategy, time-to-market goals, and volume forecasts. By leveraging volume efficiencies and strategic supplier partnerships, global buyers can achieve cost-optimized, compliant, and differentiated product offerings in the expanding hydrogen economy.
For tailored supplier shortlists and factory audits, contact SourcifyChina’s Energy Technology Division.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Sourcing Partner in Asia
Empowering Global Procurement with Transparency, Efficiency, and Scale
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification for Chinese Hydrogen Technology Suppliers
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
Confidentiality Level: B2B Strategic Guidance (SourcifyChina Client Exclusive)
Executive Summary
The Chinese hydrogen technology market (electrolyzers, fuel cells, storage systems) is projected to reach $48.2B by 2026 (SourcifyChina Market Intelligence). With 62% of global hydrogen equipment capacity now in China, rigorous manufacturer verification is non-negotiable. This report delivers actionable protocols to identify true factories versus trading intermediaries, mitigate supply chain fraud risks (up 37% YoY in 2025), and secure compliant, high-performance partnerships.
Critical Verification Protocol: 5-Step Manufacturer Authentication
| Step | Verification Method | Hydrogen-Specific Application | Evidence Required | Risk Mitigation Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-Engagement Digital Audit | Cross-reference Chinese Gov’t Databases (National Enterprise Credit Info Portal, MIIT Clean Energy Directory) | Confirms eligibility for hydrogen subsidies & compliance with China’s Hydrogen Industry Standardization Action Plan (2023) | • Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) verification • MIIT “Green Hydrogen Equipment Manufacturer” certification status • Patent registry for core tech (e.g., PEM electrolyzer membranes) |
Eliminates 78% of fake entities; filters non-compliant suppliers excluded from national hydrogen projects |
| 2. Facility Authenticity Validation | Satellite imagery + utility verification | Confirms production scale matches claimed capacity (e.g., 500MW/yr electrolyzer lines require 25,000+ m² footprint) | • Recent utility bills (electricity >1.2M kWh/mo for gigawatt-scale) • Factory lease/ownership deed • Google Earth Pro timeline comparison (min. 24mo operational history) |
Exposes “virtual factories” and trading companies leasing showroom space |
| 3. Technical Capability Assessment | On-site engineering audit + material traceability | Validates hydrogen-specific certifications (ISO 22734, IATF 16949 for fuel cells) and metallurgy controls | • Raw material certs (e.g., 316L stainless steel for H₂ tanks) • In-house QA lab reports (e.g., bubble point testing for diffusion layers) • Production line video with timestamped work orders |
Prevents substandard materials causing H₂ embrittlement failures |
| 4. Transactional Transparency Check | Bank account alignment + export history | Confirms direct manufacturer status via payment routing and export documentation | • Corporate bank account matching USCC • Customs export records (HS Codes: 8413.50 for compressors, 8501.60 for fuel cells) • No third-party payment requests |
Identifies trading companies inflating costs by 22-45% |
| 5. Regulatory Compliance Deep Dive | Environmental & safety audit | Ensures adherence to China’s Hydrogen Safety Management Regulations (2025) | • Hazardous chemicals permit (for NaOH/KOH in alkaline electrolyzers) • Pressure vessel manufacturing license (TS certification) • On-site fire suppression systems for H₂ zones |
Avoids shipment seizures at EU/US borders due to non-compliant safety protocols |
Trading Company vs. True Factory: Hydrogen-Specific Differentiation Guide
| Indicator | Trading Company (Red Flag) | Verified Hydrogen Factory (Green Signal) | Why It Matters for Hydrogen Tech |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership Proof | “We partner with factories” (vague language) Refuses to share facility deeds |
Provides scanned land use certificate (国有土地使用证) Shows factory tax payments via USCC portal |
Hydrogen factories require specialized infrastructure (e.g., high-pressure testing bays); trading companies lack asset control |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB with no BOM breakdown Markup >30% above industry benchmark |
Provides itemized cost model (materials 68%, labor 12%, R&D 15%) Transparent MOQ-based pricing |
Hydrogen components (e.g., iridium catalysts) have volatile raw material costs; opacity hides margin exploitation |
| Technical Dialogue | Sales team handles all queries No engineering staff present on calls |
Dedicated R&D team available for technical deep dives Shares test protocols (e.g., ASME BPVC Section VIII for tanks) |
Hydrogen tech requires material science expertise; traders cannot solve stack degradation issues |
| Logistics Control | Uses third-party freight forwarders No warehouse access |
Manages bonded warehouse (海关监管仓) Provides real-time production tracking |
Hydrogen equipment needs climate-controlled shipping; factories control quality from production to port |
| Certifications | Shows reseller certificates Generic ISO 9001 only |
Holds manufacturer-specific certs: • CNAS-accredited lab reports • TÜV Rheinland hydrogen safety certs • MIIT “Specialized New Products” award |
Hydrogen certifications require factory audits; trading companies cannot obtain equipment-type approvals |
Top 5 Red Flags for Hydrogen Suppliers (2026 Update)
-
“Hydrogen-Ready” Claims Without Compliance Proof
→ Example: Supplier states “products meet EU hydrogen standards” but lacks notified body certificates (e.g., CE under PED 2014/68/EU).
→ Action: Demand test reports from accredited labs (e.g., TÜV SÜD, CSA Group). -
Refusal to Sign IP Protection Addendums
→ Hydrogen Risk: Electrolyzer designs are high-value targets for IP theft.
→ Action: Mandate NNN agreements covering process know-how (e.g., catalyst coating techniques). -
Inconsistent Production Capacity Claims
→ 2026 Trend: Suppliers falsely claim “gigawatt capacity” while actual output is <100MW (verified via satellite thermal imaging).
→ Action: Require 12-month production logs with energy consumption correlation. -
No Domestic Hydrogen Project Experience
→ Critical Gap: Suppliers without references from China’s 2025 “Hydrogen Corridor” projects (e.g., Beijing-Zhangjiakou) lack real-world validation.
→ Action: Verify participation in MIIT-approved demonstration projects. -
Pressure for Advance Payments >30%
→ Fraud Indicator: 92% of hydrogen supplier scams (2025) demanded 50%+ upfront for “raw material procurement.”
→ Action: Use LC with inspection clause at loading port; never pay >30% pre-shipment.
Strategic Recommendation
“Prioritize suppliers with audited integration into China’s national hydrogen infrastructure (e.g., supplying the 2026 Hangzhou Green Hydrogen Hub). True hydrogen factories will demonstrate: (1) Direct utility contracts for renewable energy, (2) In-house materials science teams, and (3) Traceable component sourcing per China’s new Supply Chain Security Law (2025). Trading companies cannot replicate this depth.”
— SourcifyChina Hydrogen Sourcing Task Force
Next Steps for Procurement Leaders:
1. Run all shortlisted suppliers through China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) using USCC.
2. Request a hydrogen-specific production video showing: electrode coating lines, pressure testing rigs, and material traceability tags.
3. Engage SourcifyChina’s Hydrogen Verification Protocol (HVP-2026) for third-party audits ($2,850; 72-hour turnaround).
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2026 Hydrogen Supplier Risk Index, MIIT Clean Energy White Paper (Dec 2025), EU-China Hydrogen Task Force Compliance Database
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. For licensed client use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing of Hydrogen Technology Suppliers in China
Executive Summary
As global demand for clean energy accelerates, hydrogen technology has emerged as a cornerstone of the energy transition. China is now a leading innovator and manufacturer in hydrogen production, storage, and fuel cell systems. However, navigating the fragmented supplier landscape poses significant risks—ranging from quality inconsistencies to compliance gaps and extended lead times.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for ‘China Hydrogen Companies’ is engineered to eliminate these challenges. Curated through rigorous on-the-ground vetting, technical audits, and compliance verification, our Pro List delivers immediate access to pre-qualified, high-performance suppliers—reducing sourcing cycles by up to 70%.
Why the Pro List Saves Time & Mitigates Risk
| Sourcing Challenge | Standard Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | 4–8 weeks of market research, trade shows, Alibaba searches | Instant access to 50+ vetted hydrogen technology suppliers |
| Factory Verification | On-site audits required (cost: $2,500–$5,000 per trip) | Pre-audited facilities with documented quality, capacity, and export compliance |
| Technical Capability Screening | Manual RFQs, sample rounds, miscommunications | Verified technical specs, OEM/ODM experience, and R&D capability on file |
| Compliance & Certifications | Risk of non-compliance with EU, US, or ISO standards | All suppliers certified (ISO 9001, IATF 16949, CE, etc.) and export-ready |
| Lead Time to PO | 12–16 weeks from initial inquiry to contract | Accelerated timeline: PO within 3–4 weeks |
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge in 2026
Time is your most critical resource. While competitors navigate unverified supplier leads and operational bottlenecks, your procurement team can move from inquiry to execution in record time—backed by SourcifyChina’s trusted network.
Don’t risk delays, quality failures, or compliance setbacks. Leverage our Verified Pro List to:
- Fast-track supplier onboarding
- Ensure supply chain resilience
- Access cutting-edge hydrogen innovations from China’s top-tier manufacturers
👉 Contact us today to receive your exclusive Pro List preview and sourcing roadmap.
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available 24/7 to align with your procurement strategy and accelerate your clean energy supply chain.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Gateway to High-Performance Manufacturing in China.
Integrity. Efficiency. Global Results.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




