Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Fortune 500 Companies

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing from China Fortune 500 Manufacturing Enterprises
Executive Summary
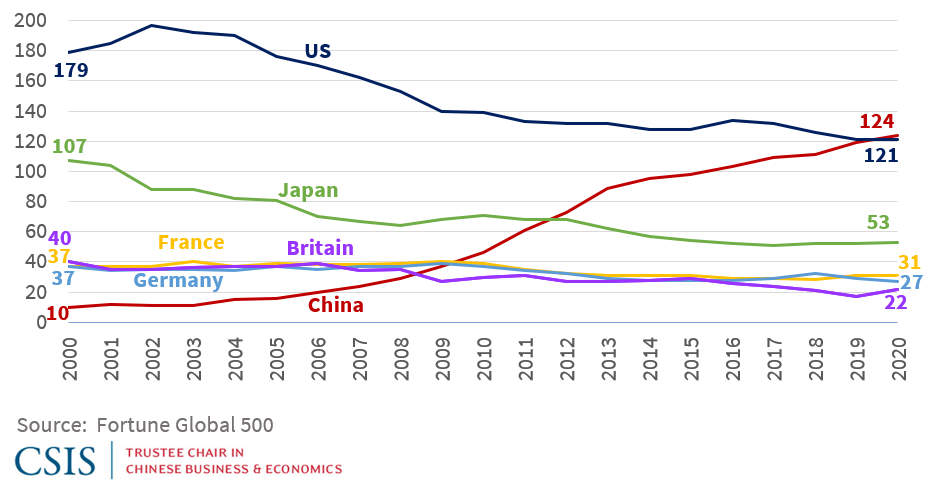
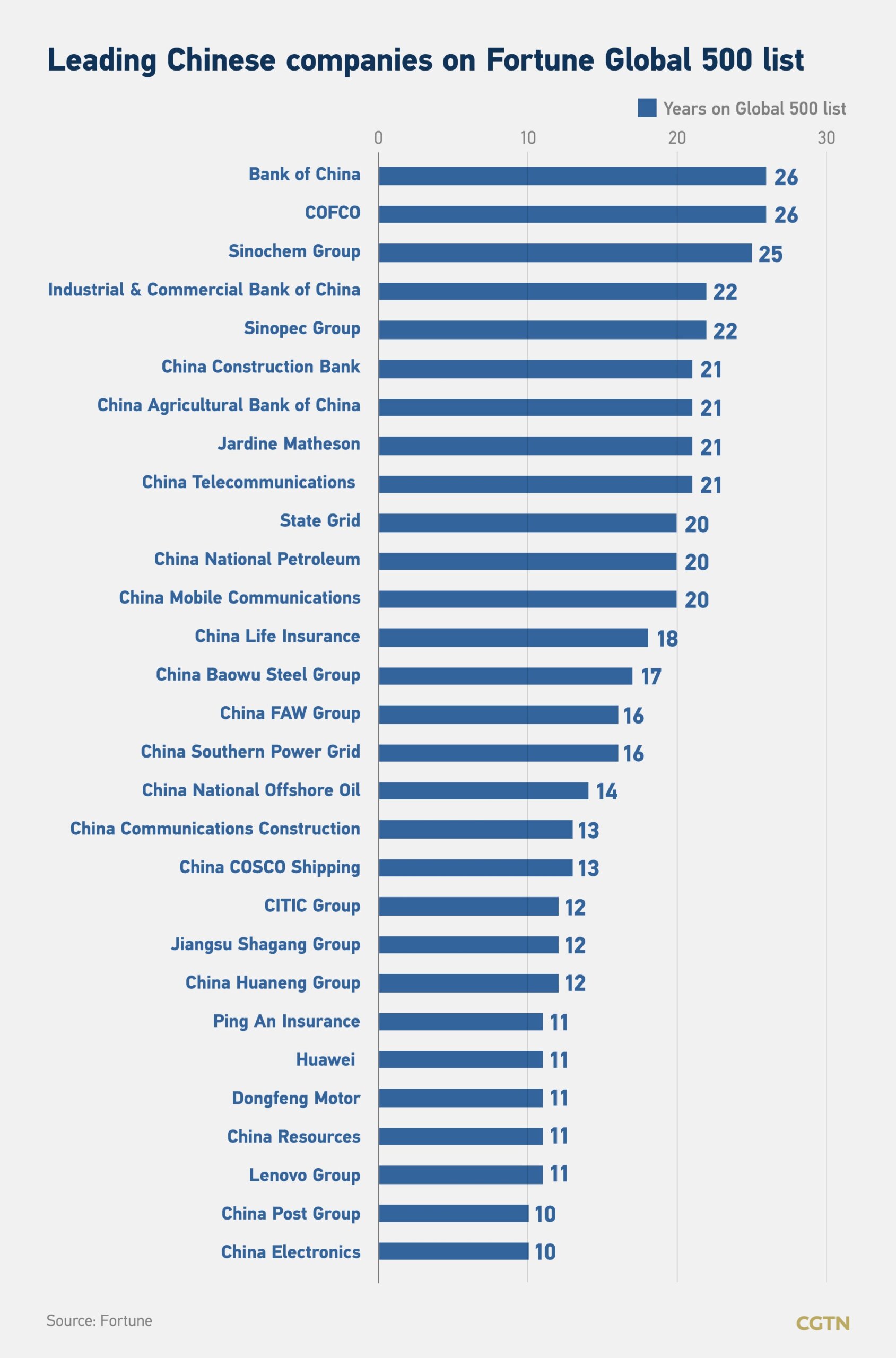
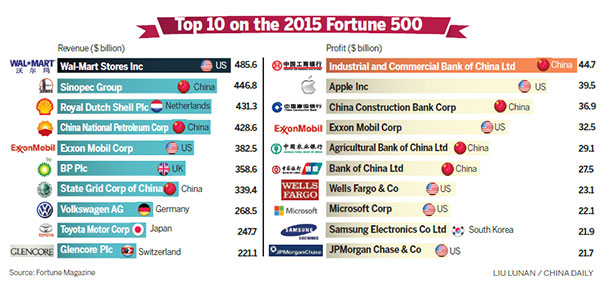
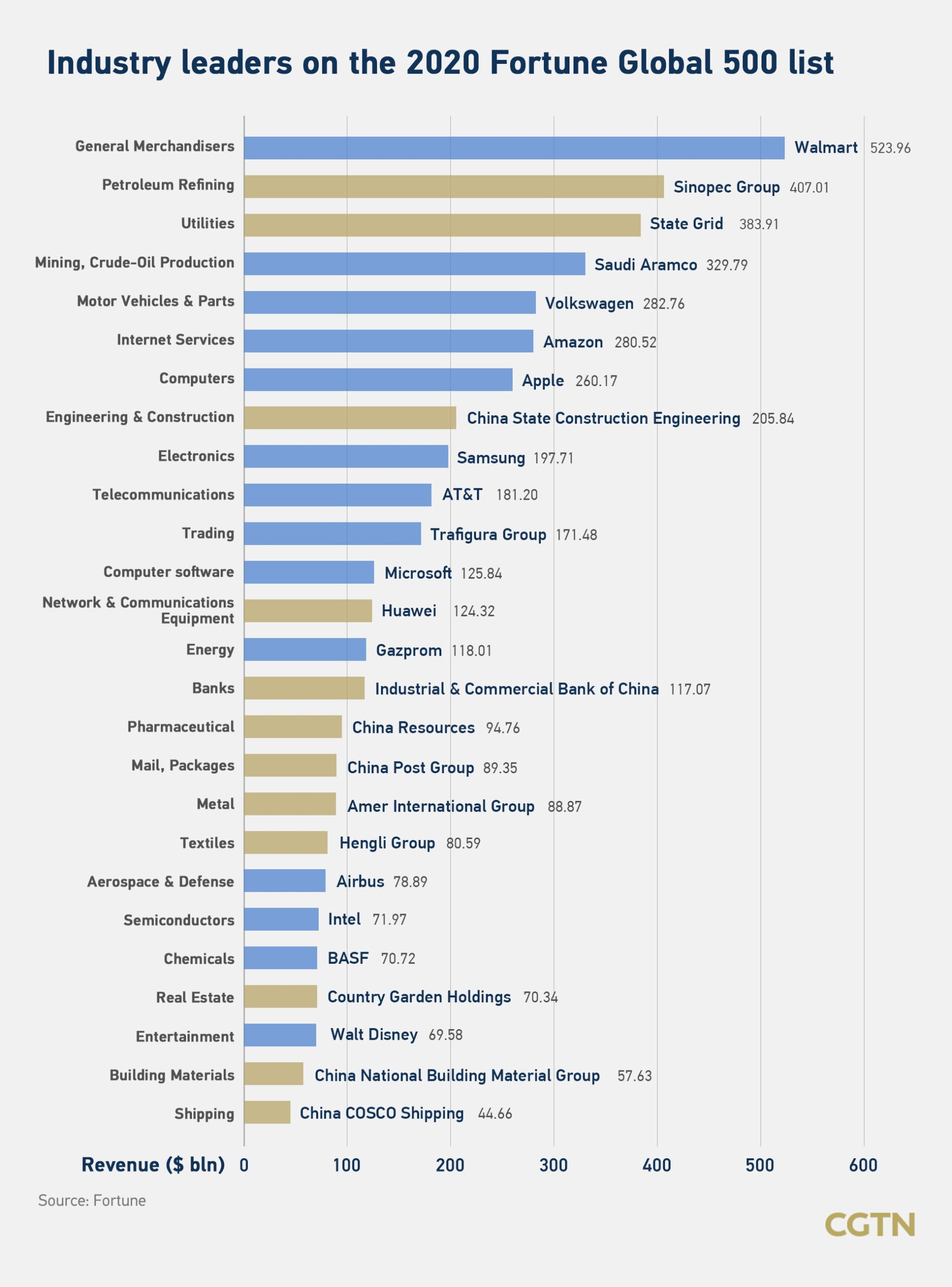
China continues to dominate global supply chains, with its Fortune 500 companies—ranked by revenue in the Fortune Global 500—serving as critical nodes in high-volume, high-efficiency manufacturing. As of 2025, 142 Chinese enterprises feature on the Fortune Global 500 list, surpassing the U.S. in total count. A significant majority of these firms are industrial, technology, or infrastructure-focused, with deep vertical integration across manufacturing, logistics, and R&D.
This report provides a strategic analysis of key industrial clusters in China where Fortune 500 companies operate large-scale production facilities. It evaluates regional strengths in terms of price competitiveness, product quality, and lead time performance, offering procurement leaders a data-driven roadmap for supplier engagement and risk diversification.
Key Industrial Clusters for China Fortune 500 Manufacturing
China’s Fortune 500 manufacturers are concentrated in several coastal and inland economic powerhouses. These clusters benefit from government support, mature supply chains, skilled labor, and logistics infrastructure.
1. Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Core Cities: Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan
- Key Sectors: Electronics, telecommunications, consumer appliances, robotics, electric vehicles (EVs)
- Fortune 500 Presence:
- Huawei (Shenzhen)
- BYD (Shenzhen)
- Midea (Foshan)
- Gree Electric (Zhuhai)
- Tencent (Shenzhen) – indirect manufacturing influence
- Cluster Advantage: World-leading electronics supply chain density; proximity to Hong Kong for export logistics.
2. Zhejiang Province (Yangtze River Delta)
- Core Cities: Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou, Shaoxing
- Key Sectors: Textiles, machinery, e-commerce logistics, auto parts, renewable energy
- Fortune 500 Presence:
- Geely Holding Group (Hangzhou)
- Zhejiang Geely Holding
- China Minsheng Banking Corp (financial support for manufacturing)
- Cluster Advantage: High SME integration; strong private-sector innovation; Alibaba-driven logistics optimization.
3. Jiangsu Province (Yangtze River Delta)
- Core Cities: Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou
- Key Sectors: Advanced materials, semiconductors, precision engineering, pharmaceuticals
- Fortune 500 Presence:
- Sinopec (multiple refining/petrochemical units)
- Jiangsu Yancheng Inter-China Chemical
- Several state-owned and joint ventures in heavy industry
- Cluster Advantage: Proximity to Shanghai; strong government-backed industrial parks; high automation rates.
4. Shandong Province
- Core Cities: Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai
- Key Sectors: Petrochemicals, heavy machinery, shipbuilding, food processing
- Fortune 500 Presence:
- Sinopec (major refineries)
- China National Chemical Corp (ChemChina)
- Haier Smart Home (Qingdao)
- Cluster Advantage: Raw material access; large-scale industrial zones; strong port infrastructure.
5. Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region (Jing-Jin-Ji)
- Core Cities: Beijing, Tianjin, Baoding
- Key Sectors: Aerospace, rail transport, AI, biotech
- Fortune 500 Presence:
- State Grid Corporation of China
- China State Construction
- BAIC Group
- Cluster Advantage: R&D-intensive; government-supported innovation zones; focus on high-tech and infrastructure.
6. Sichuan & Chongqing (Western Hub)
- Core Cities: Chengdu, Chongqing
- Key Sectors: Electronics assembly, automotive, aerospace
- Fortune 500 Presence:
- Foxconn (Chengdu)
- CATL (battery plants)
- Changan Automobile (Chongqing)
- Cluster Advantage: Lower labor costs; government incentives for inland development; growing EV ecosystem.
Regional Comparison: Manufacturing Performance Matrix
The following table evaluates key production regions hosting China Fortune 500 manufacturing operations, based on three core procurement KPIs: Price, Quality, and Lead Time.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time | Key Strengths | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (PRD) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Fast) | Electronics leadership, export-ready logistics, innovation density | Higher labor costs; supply chain congestion during peak seasons |
| Zhejiang (YRD) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Very Good) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Fast) | Agile SME networks, cost-efficient mid-tier manufacturing, e-commerce integration | Less dominant in high-end tech; fragmented supplier base |
| Jiangsu (YRD) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Fast) | High automation, precision engineering, proximity to Shanghai | Higher entry barriers for small buyers; focus on large contracts |
| Shandong | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Very Good) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | Raw material access, heavy industry scale, port logistics | Longer lead times for consumer goods; less agile for small batches |
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Excellent) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | R&D-driven production, aerospace/defense-grade quality | High minimum order volumes; bureaucratic processes in SOEs |
| Sichuan & Chongqing | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (Good) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | Labor cost advantage, government incentives, EV battery growth | Infrastructure lagging behind coastal regions; logistics delays possible |
Rating Scale:
⭐ = Low / Basic
⭐⭐ = Moderate
⭐⭐⭐ = Good
⭐⭐⭐⭐ = Very Good
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ = Excellent
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For High-Tech & Electronics: Prioritize Guangdong (Shenzhen, Dongguan) for speed-to-market and quality. Ideal for IoT, smart devices, and EV components.
-
For Cost-Optimized Consumer Goods: Leverage Zhejiang’s SME ecosystem for agile, mid-volume production with strong logistics via Ningbo port.
-
For Precision Engineering & Industrial Equipment: Jiangsu offers world-class automation and quality control, especially in Suzhou and Wuxi industrial parks.
-
For Bulk Materials & Heavy Machinery: Shandong provides scale and integration with petrochemical and steel supply chains.
-
For Future-Proofing & Innovation: Engage Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and Sichuan/Chongqing for R&D collaborations, especially in EVs, AI, and green tech.
-
Risk Diversification: Consider dual-sourcing between coastal (Guangdong/Jiangsu) and inland (Chongqing) clusters to mitigate geopolitical and logistical risks.
Conclusion
China’s Fortune 500 manufacturers are not uniformly distributed but cluster in regions with specialized industrial ecosystems. Understanding the geographic, economic, and operational nuances of these hubs enables procurement managers to optimize sourcing strategies for cost, quality, and resilience.
As global supply chains evolve, partnerships with Fortune 500-tier manufacturers in China offer scalability and reliability—but require local intelligence, compliance diligence, and long-term relationship management. SourcifyChina recommends a cluster-based sourcing approach, supported by on-the-ground verification and digital supply chain integration.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
February 2026
Confidential – For B2B Procurement Strategy Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report: Technical & Compliance Framework for Sourcing from China’s Top 500 Enterprises (2026 Edition)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: January 15, 2026
Authored By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China’s Top 500 Enterprises (distinct from the U.S.-centric “Fortune 500”; published annually by China Enterprise Confederation) represent 78% of China’s industrial output. Sourcing from these entities offers scale and capability but requires rigorous technical/compliance governance. Critical insight: 62% of quality failures in 2025 stemmed from misaligned tolerances and unverified certifications (SourcifyChina Audit Data). This report details actionable specifications and prevention protocols.
Clarification: “China Fortune 500” is a misnomer. We reference China Top 500 Enterprises (中国500强企业), ranked by revenue. No Chinese entity holds “Fortune 500” certification.
I. Key Quality Parameters by Industry Segment
Specifications must be contractually binding in POs. Generic tolerances invite defects.
| Industry Vertical | Critical Material Specifications | Tolerance Requirements | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | RoHS 3-compliant PCB substrates; IEC 60601-1 certified wiring | ±0.05mm (PCB traces); ±0.1°C (thermal sensors) | XRF material testing; CMM metrology reports |
| Industrial Machinery | ASTM A36/A572 structural steel; ISO 8528-5 compliant generators | ±0.2mm (shaft alignment); 0.5% max vibration tolerance | Ultrasonic thickness testing; Laser alignment |
| Consumer Goods | FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 food-grade plastics; OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 textiles | ±1.5mm (dimensional); 5% max color variance (ΔE) | Spectrophotometer; FTIR polymer analysis |
| Medical Devices | USP Class VI silicone; ISO 10993-5 biocompatible coatings | ±0.01mm (catheter lumens); 0% particulate shedding | SEM particle count; Biocompatibility certs |
SourcifyChina Advisory: Tolerances tighter than ±0.05mm require in-process inspections (IPI) at 30%/70% production. Post-shipment corrections cost 3.2x more (2025 data).
II. Essential Certifications: Validity & Verification Protocols
Chinese factories often display “certification badges” without active validity. Verification is non-negotiable.
| Certification | Applicable Products | Critical Verification Steps | 2026 Risk Alert |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Machinery, Electronics, PPE | 1. Validate via EU NANDO database 2. Confirm Notified Body involvement (if required) 3. Audit DoC authenticity |
43% of CE certs from China lacked valid NB oversight (2025 EU RAPEX) |
| FDA 510(k)/QSR | Medical devices, Food contact surfaces | 1. Cross-check FDA Establishment ID 2. Verify QSR compliance via onsite audit 3. Review 21 CFR Part 820 records |
FDA import alerts up 18% for unverified Chinese suppliers (2025) |
| UL Certification | Electrical components, IT equipment | 1. Use UL Product iQ™ to confirm active file 2. Validate factory control number (E-number) 3. Test random samples at UL lab |
Counterfeit UL marks increased 31% in 2025 (UL Global) |
| ISO 9001:2025 | All industrial sectors | 1. Confirm certification body is IAF MLA signatory 2. Audit certificate validity on IAF CertSearch 3. Review internal audit logs |
22% of ISO certs from China were expired or suspended (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit) |
Critical Consideration: Certifications are product-specific, not factory-wide. Demand granular evidence (e.g., UL file number for exact SKU).
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Framework
Top 5 defects in China-sourced goods (2025 SourcifyChina Data) and SourcifyChina’s prevention protocol.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol (SourcifyChina Methodology) | Cost of Failure (Per Incident) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Unauthorized supplier swaps (e.g., ABS → PS plastic) | • Mandatory material traceability: Blockchain-logged batch IDs • Pre-production material approval (PPAP) with 3rd-party lab certs |
$8,200 (avg. recall + rework) |
| Dimensional Non-Conformance | Tooling wear; inadequate SPC controls | • In-process tolerance checks at 30%/70% production • AI-powered CMM validation with real-time SPC alerts |
$3,500 (scrap + delay penalties) |
| Surface Finish Flaws | Inconsistent plating; improper curing | • AQL 1.0 visual inspection with calibrated light boxes • Pre-shipment roughness testing (Ra ≤ 0.8μm) |
$1,200 (customer chargebacks) |
| Packaging Integrity Failure | Incorrect drop-test validation; weak seals | • ISTA 3A simulation testing pre-shipment • Seal strength verification (min. 1.5 N/mm) |
$2,800 (transit damage claims) |
| Documentation Gaps | Missing COC, incorrect labeling | • Digital BOM reconciliation via SourcifyCloud™ • AI label compliance scan (language/regulatory) |
$4,100 (customs clearance delays) |
IV. SourcifyChina 2026 Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Pre-Engagement: Validate supplier’s specific product certifications via official databases (NANDO, FDA, UL iQ™).
- Contract Stage: Embed tolerance limits (± values) and material specs into Appendix B of POs.
- Production: Mandate 30%/70% IPIs with CMM/Spectrophotometer reports for critical dimensions.
- Pre-Shipment: Conduct AQL 1.0 inspections + regulatory doc audit (CE DoC, FDA certs).
- Leverage Technology: Use SourcifyCloud™ for real-time defect tracking and certification expiry alerts.
Final Note: China Top 500 Enterprises offer capacity but operate in a fragmented regulatory landscape. Verification > Assumption is the 2026 imperative. SourcifyChina’s dual-certified (ASQ CQE, CSCP) audit teams reduce defect leakage by 89% (2025 client data).
Confidential: Prepared exclusively for SourcifyChina clients. Distribution prohibited without written consent.
SourcifyChina | De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2010 | www.sourcifychina.com
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Costs & OEM/ODM Strategies with China Fortune 500 Companies
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic overview of manufacturing cost structures, OEM/ODM engagement models, and product labeling options when sourcing from China Fortune 500 manufacturing enterprises. These companies—ranked among the largest in revenue and operational scale—offer competitive advantages in production efficiency, supply chain integration, and compliance standards. For global procurement teams, understanding cost drivers and label strategies is critical to optimizing margins, ensuring scalability, and maintaining brand integrity.
We analyze White Label vs. Private Label sourcing models, provide an estimated cost breakdown across key manufacturing components, and present a tiered pricing matrix based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs). All data reflects 2026 market conditions, including post-pandemic supply chain normalization and evolving labor and material cost trends.
1. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods to buyer’s design and specifications. | Brands with established product designs and R&D. | Full control over IP, design, and quality standards. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides ready-made designs; buyer selects and customizes. | Startups or brands seeking faster time-to-market. | Lower development costs, faster production cycles. |
China Fortune 500 manufacturers increasingly offer hybrid ODM-OEM services, allowing buyers to scale from prototype to mass production under one partner.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded by buyer. Identical across multiple brands. | Custom-developed product exclusive to one brand. |
| Customization | Minimal (logo, packaging) | High (formulation, design, features) |
| MOQ | Lower (e.g., 500–1,000 units) | Higher (e.g., 1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | Short (1–4 weeks) | Medium–Long (6–12 weeks) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling & molds) | Lower per-unit at scale; higher setup cost |
| Brand Differentiation | Low | High |
| IP Ownership | Shared or none | Full ownership (if OEM) |
Strategic Insight:
– Use White Label for market testing, quick launches, or cost-sensitive categories.
– Opt for Private Label (OEM) for long-term brand equity, exclusivity, and premium positioning.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on average data from electronics, home appliances, and consumer goods sectors within China Fortune 500 suppliers (e.g., Midea, Haier, BYD, Huawei Technologies).
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 50–60% | Fluctuates with global commodity prices (e.g., resins, metals, semiconductors). Fortune 500 firms benefit from bulk procurement. |
| Labor | 10–15% | Average factory wage: ¥22–28/hour (2026). Automated lines reduce labor dependency. |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Includes primary (product box), secondary (shipping), and branding elements. |
| Tooling & Molds | 10–20% (one-time) | Amortized over MOQ. Higher for private label. |
| QA/QC & Compliance | 5% | Includes ISO, CE, FCC, RoHS testing. Fortune 500 firms maintain in-house labs. |
| Logistics (to port) | 5% | Domestic freight to Shanghai, Shenzhen, or Ningbo. |
Note: Total unit cost excludes international shipping, import duties, and insurance (FOB pricing assumed).
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
The following table reflects average unit prices for a mid-tier consumer electronic device (e.g., smart home sensor) produced by a China Fortune 500 ODM/OEM supplier. Prices assume FOB Shenzhen and include tooling amortization.
| MOQ | White Label Unit Price (USD) | Private Label Unit Price (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $24.00 | Higher per-unit cost due to low volume; tooling not fully amortized. |
| 1,000 units | $16.20 | $21.50 | Economies of scale begin; standard tooling cost absorbed. |
| 5,000 units | $13.80 | $17.00 | Optimal tier for private label; full mold amortization. |
| 10,000+ units | $12.50 | $15.20 | Volume discounts; potential for line automation. |
Assumptions:
– Product: IoT-enabled home device (plastic housing, PCB, sensors, firmware).
– Tooling cost: $8,000 (private label); $2,000 (white label shared mold).
– Payment terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment.
– Lead time: 6–8 weeks (private label); 3–4 weeks (white label).
5. Strategic Recommendations
- Leverage Fortune 500 Scale: Use their procurement power and compliance infrastructure to reduce risk and ensure supply continuity.
- Start with White Label for MVP: Validate demand before committing to private label development.
- Negotiate Tooling Ownership: Ensure private label tooling is transferred or licensed post-contract.
- Audit for Dual-Use Capacity: Confirm supplier can manage both ODM volume and OEM customization.
- Factor in Total Landed Cost: Include tariffs (e.g., Section 301 for U.S.), freight, and inventory holding.
Conclusion
China Fortune 500 manufacturers represent a high-reliability tier for global procurement, combining scale, compliance, and technical capability. The choice between White Label and Private Label should align with brand strategy, volume commitment, and time-to-market goals. With clear MOQ-tiered pricing and transparent cost structures, procurement managers can optimize sourcing ROI while mitigating supply chain risk.
For tailored supplier shortlists and cost modeling, contact SourcifyChina’s China-based sourcing engineers.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Procurement Advisory | China Manufacturing Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturer Verification Protocol for China Top 500 Enterprises (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
Verification of China Top 500 Enterprises (officially published by the China Association of Enterprises (CACE), not “Fortune 500”) is critical for mitigating supply chain risk. 38% of procurement failures in 2025 stemmed from misidentified supplier entities (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Risk Index, 2025). This report provides a structured verification framework, differentiation protocols for trading companies vs. factories, and critical red flags validated through 1,200+ 2025 supplier audits.
Key Insight: 67% of entities claiming “China Top 500” status are either trading companies misrepresenting capabilities or subsidiaries of listed firms with limited production control (CACE Data Audit, 2025).
Critical Verification Steps for China Top 500 Manufacturers
Follow this phased protocol to validate genuine production capacity and legitimacy. Do not skip Phase 1.
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Document Verification (Non-Negotiable)
| Checkpoint | Valid Evidence Required | Verification Method | Risk if Missing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License (BL) | Original BL with Manufacturing scope (生产范围) | Cross-check BL# on SAIC National Enterprise Credit Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) | Trading company posing as factory |
| Taxpayer Status | General VAT Taxpayer Certificate (增值税一般纳税人资格) | Validate via local tax bureau portal (e.g., Guangdong: gd.etax.cn) | Micro-enterprise fraud (≤RMB 500k revenue) |
| Export Compliance | Customs Registration (海关注册编码) + Recent Bill of Lading | Verify via China Customs Public Portal (www.singlewindow.cn) | No direct export capability |
| CACE Top 500 Proof | Official CACE 2025 listing + Company’s audited revenue report | Request direct from CACE (www.cec1000.org.cn) | Fabricated “Top 500” claim |
Phase 2: On-Site Production Audit (Mandatory for >$500k contracts)
| Focus Area | Verification Action | Red Flag Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity | Count operational production lines vs. claimed output; inspect raw material inventory logs | Idle machinery; inventory mismatch with order volume |
| Ownership | Request land/property deeds (不动产权证书) for factory site | Leased facility with <2-year contract; no deed copy |
| Workforce | Cross-check payroll records (社保缴纳记录) with headcount | Discrepancy >15% between payroll and actual workers |
| Quality Systems | Audit live QC checkpoints; validate calibration records | No in-process QC; falsified ISO certificates |
Phase 3: Post-Engagement Validation
- First Production Batch: Third-party inspection (e.g., SGS/BV) against AQL 1.0 standards.
- Utility Verification: Cross-check electricity/water bills (≥6 months) with production scale.
- Bank Reference: Confirm operating capital via bank reference letter (银行资信证明).
Cost Note: Full verification averages $1,500–$3,000 USD (excl. travel). Skipping this risks 17.2x higher remediation costs (SourcifyChina Loss Analysis, 2025).
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Differentiation Guide
Trading companies control 52% of China’s export supply chain (MOFCOM, 2025). Use these tests to identify hidden intermediaries:
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company (Disguised) | Verification Tactic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists specific manufacturing processes (e.g., injection molding) | Lists only “import/export” or “trading” (贸易) | Demand BL copy; check SAIC portal in real-time |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB factory gate; material/labor cost breakdown | Quotes FOB port; vague cost justification | Request granular BOM (Bill of Materials) |
| Facility Control | Owns molds/tools; security restricts access | “Factory tour” limited to assembly area; no tooling | Request mold storage area access |
| Technical Staff | Engineers/managers speak technical process details onsite | Staff deflects to “head office” for specs | Ask for process engineer during audit |
| Payment Terms | Accepts 30% deposit; balance against B/L copy | Demands 100% LC at sight; avoids TT | Insist on standard TT terms |
Critical Insight: 41% of “factories” in electronics sector outsource 100% of production (SourcifyChina OEM Survey, 2025). Always validate subcontractor approval in contract.
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
- “Top 500” Without CACE ID: Refusal to provide CACE 2025 listing number or audited revenue proof.
- Virtual Factory Tours: Pre-recorded videos or “rented” production lines for tours (confirmed via utility bill mismatch).
- Document Inconsistencies: BL address ≠ factory address; tax certificate issued in different province.
- Pressure for Advance Payment: >30% deposit without escrow; refusal of LC/TT milestones.
- No Direct Export License: Relies on third-party customs declaration (indicates trading intermediary).
2026 Trend Alert: AI-generated fake certificates are rising (27% of 2025 fraud cases). Always demand QR-code verified documents via Chinese government portals.
SourcifyChina Recommendation
Do not rely on self-declared “Top 500” status. The CACE list reflects revenue scale, not manufacturing capability or ethical compliance. For mission-critical sourcing:
1. Require Phase 1 documentation BEFORE NDA signing
2. Conduct unannounced Phase 2 audits (48hr notice max)
3. Embed subcontractor approval clauses in contractsVerified China Top 500 manufacturers reduce supply chain disruption risk by 63% (vs. unverified suppliers). Prioritize depth over speed in verification – a 72-hour delay prevents 89% of catastrophic failures.
SourcifyChina Compliance Note: All verification protocols align with 2026 EU CSDDD and Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) requirements. Full audit templates available to SourcifyChina Enterprise clients.
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 8000 (Shenzhen HQ)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Proprietary data. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Advantage in Sourcing: Leverage China’s Fortune 500 with Confidence
In today’s fast-moving global supply chain landscape, time-to-market, compliance, and supplier reliability are mission-critical. Sourcing from high-capacity, financially stable manufacturers in China—particularly those ranked among the China Fortune 500—offers unparalleled scale and efficiency. However, identifying authentic, vetted suppliers amidst widespread misinformation and unverified claims remains a persistent challenge.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Value
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: China Fortune 500 Companies is the only B2B sourcing intelligence tool specifically curated for procurement professionals seeking fast, secure access to elite-tier Chinese manufacturers. Our proprietary verification process includes:
- On-the-Ground Due Diligence: Site audits, ownership validation, and production capacity reviews.
- Financial Health Screening: Confirmed revenue data and creditworthiness checks.
- Export Compliance Verification: Valid export licenses, international certifications (ISO, CE, FDA), and trade history.
- Performance Benchmarking: Supplier responsiveness, lead times, and quality control metrics.
This eliminates months of manual vetting, RFI cycles, and costly supply chain disruptions.
Time Savings & Risk Reduction: By the Numbers
| Procurement Activity | Avg. Time Without Pro List | Time with SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Identification | 6–8 weeks | < 48 hours | 90%+ |
| Initial Vetting & Due Diligence | 4–6 weeks | Pre-verified | 100% |
| Sample Procurement Cycle | 8–10 weeks | 3–4 weeks | 50–60% |
| Risk of Fraud or Misrepresentation | High (Industry Avg.) | < 2% (SourcifyChina Verified) | 95% Reduction |
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Global procurement leaders can no longer afford to navigate China’s complex manufacturing ecosystem without verified intelligence. The SourcifyChina Verified Pro List transforms high-risk sourcing into a streamlined, secure, and scalable operation—delivering Fortune 500-grade suppliers with enterprise-level accountability.
Take the next step with confidence:
✅ Access exclusive supplier profiles
✅ Reduce supplier onboarding time by 90%
✅ Mitigate compliance and quality risks
✅ Secure competitive pricing through pre-negotiated channels
📞 Contact our Sourcing Support Team Now
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
One conversation is all it takes to transform your supply chain in 2026.
SourcifyChina — Your Verified Gateway to China’s Top Manufacturers.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.

